The Digestive System
Which of following processes is the function of the smooth muscle layer of the digestive system?
- Ingestion
- Secretion
- Mixing and propulsion
- Absorption
- None of the above
C
Which of following processes is the primary function of the mouth?
- Ingestion
- Secretion
- Mixing and propulsion
- Absorption
- None of the above
A
Which of following processes is the primary function of the villi of the small intestine?
- Ingestion
- Secretion
- Mixing and propulsion
- Absorption
- None of the above
D
Which of the following accessory organs produces a fluid to soften food?
- Teeth
- Salivary glands
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Pharynx
B
Which of the following accessory organs produces a fluid that functions to emulsify dietary fats?
- Teeth
- Salivary glands
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Pharynx
C
Which of the following accessory organs stores bile?
- Teeth
- Salivary glands
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Pharynx
D
The capability of the GI tract to move material along its length is called
1. Motility
2. Propulsion
3. Digestion
4. Defecation
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 4 only
- Both 1 and 2
E
This layer of the GI tract is composed of areolar connective tissue containing blood and lymph vessels.
- Mucosa
- Lamina propria
- MALT
- Musclaris
- Epithelium
B
This layer of the GI tract is composed of areolar connective tissue that binds the mucosa to the muscularis.
- Submucosa
- Lamina propria
- Epithelium
- Serosa
- None of the above
A
This layer functions by secreting a lubricating fluid.
- Serosa
- Submucosa
- Muscularis
- Mucosa
- MALT
A
These are composed of prominent lymphatic nodules that function in the immune response.
- Mucosa
- Lamina propria
- MALT
- Submucosa
- Serosa
C
This plexus is located between the longitudinal and circular smooth muscle layers of the muscularis.
- ENS
- Myenteric plexus
- Submucosal plexus
- Digestive plexus
- Absorption plexus
B
Why do emotions such as anger or fear slow digestion?
- Because they stimulate the parasympathetic nerves supplying the GI tract
- Because they stimulate the somatic nerves that supply the GI tract
- Because they stimulate the sympathetic nerves that supply the GI tract
- They do not affect digestion
- Because all emotions are controlled by the Vagus nerve
C
This portion of the peritoneum drapes over the transverse colon and coils of the small intestine.
- Greater omentum
- Falciform ligament
- Lesser omentum
- Mesentery
- Mesocolon
A
This portion of the peritoneum attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and diaphragm.
- Greater omentum
- Falciform ligament
- Lesser omentum
- Mesentery
- Mesocolon
B
This portion of the peritoneum is largely responsible for carrying blood and lymph vessels to the intestines.
- Greater omentum
- Falciform ligament
- Lesser omentum
- Mesentery
- Mesocolon
E
The hard palate
1. Is the anterior portion of the roof of the mouth
2. Is formed by the maxillae and palatine bones
3. Is covered by a mucous membrane
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- Both 1 and 2
- All of the above
E
Lateral to the base of the uvula in the mouth, this muscular fold runs posteriorly down the lateral sides of the soft palate to the pharynx.
- Uvula
- Palatoglossal arch
- Palatopharyngeal arch
- Parotid glands
- Sublingual glands
C
In the mouth, the tooth sockets are lined with
- Gingivae
- Cementum
- Periodontal ligament
- Pulp
- Root
C
Deciduous molars are replaced by
- Bicuspids
- Molars
- Incisors
- Canines
- Wisdom teeth
A
Which of the following contains skeletal muscle?
- Muscularis
- Mucosa
- Serosa
- Submucosa
A
How many stages of deglutition are there?
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 8
B
This structure of the stomach allows greater distension for food storage.
- Cardia
- Fundus
- Pylorus
- Rugae
- Sphincter
D
Which of the following secrete hydochloric acid?
- Mucous cells
- Parietal cells
- Chief cells
- Serosa cells
- Chyme cells
B
This cell secretes the hormone that promotes production of hydrochloric acid.
- Neck cell
- Chief cell
- G cell
- Chyme cell
- Parietal cell
C
How long can food stay in the fundus before being mixed with gastric juices?
- 10 minutes
- 20 minutes
- 30 minutes
- 45 minutes
- 1 hour
E
This major duct carries a fluid rich in bicarbonate ions.
- Pancreatic duct
- Hepatopancreatic duct
- Cystic duct
- Bile duct
- Hepatic duct
A
Which of the following pancreatic enzymes digests lipids?
- Trypsin
- Elastase
- Lipase
- Pepsin
- All of the above
C
This is the heaviest gland of the body.
- Heart
- Liver
- Pancreas
- Large intestine
- Thyroid
B
This is found on the liver and is a remnant of the umbilical cord in a fetus.
- Coronary ligament
- Falciform ligament
- Round ligament
- Kupffer ligament
- Bile ductules
C
This is the principle bile pigment.
- Stercobilin
- Bilirubin
- Biliverdin
- Both A and B
- All of the above
B
Which of the following is NOT a function of the liver?
- Conversion of carbohydrates
- Protein metabolism
- Storage of bilirubin
- Phagocytosis
- Storage of vitamins
C
Which of the following small intestine cells secrete lysozyme?
- Goblet cells
- Absorptive cells
- Mucosa cells
- Paneth cells
- S cells
D
Brunner's glands
- Secrete an acidic mucus
- Secrete an alkaline juice
- Secrete an alkaline mucus
- Secrete an acidic juice
C
Which of the following enzymes acts to produce monoglycerides as products?
- Lipase
- Amylase
- Trypsin
- Phosphatase
- Ligase
A
Which of the following pancreatic enzymes acts to on glycogen and starches?
- Chymotrypsin
- Amylase
- Trypsin
- Phosphatase
- Nucleosidase
B
Which of the following pancreatic enzymes acts on peptide bonds?
- Chymotrypsin
- Amylase
- Pepsin
- Phosphatase
- Nucleosidase
A
This hormone functions to counteract the effect of gastric acid in the small intestine.
- Pepsin
- Secretin
- Gastrin
- Cholecystokinin
- Amylase
B
This hormone is stimulated by high levels of dietary fat in the small intestine.
- Pepsin
- Secretin
- Gastrin
- Cholecystokinin
- Amylase
D
This digestive aid, produced by the stomach, begins digestion by denaturing proteins.
- Bicarbonate ion
- mucus
- Bile
- Hydrochloric acid
- Water
D
This structure regulates the flow of material into the colon.
- Ileocecal sphincter
- Pyloric sphincter
- Appendix
- Sigmoid colon
- Anal canal
A
Which of the following is NOT the primary function of the large intestine?
- Mechanical digestion
- Chemical digestion
- Absorption
- Feces formation
- Regulation of blood glucose
E
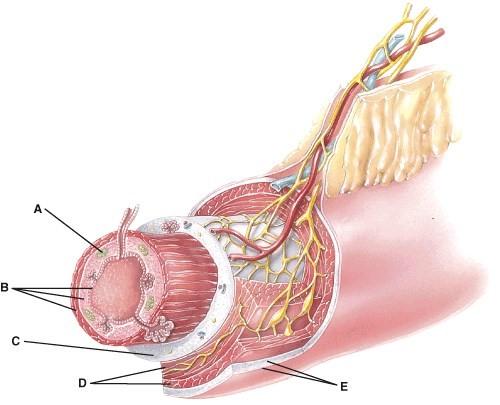
What is line A pointing to?
- Lumen
- MALT
- Mucosa
- Submucosa
- Muscularis
B

What layer is composed of areolar connective tissue and epithelium?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
E

Which layer contains the lamina propria?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
B
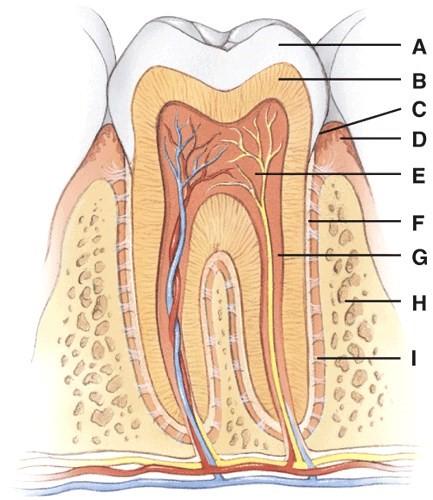
This consists of calcified connective tissue.
- A
- B
- E
- F
- G
B

What is line F pointing to?
- Pulp cavity
- Cementum
- Root canal
- Alveolar bone
- Gingival sulcus
B

This has an opening called the apical foramen.
- A
- F
- G
- H
- I
C
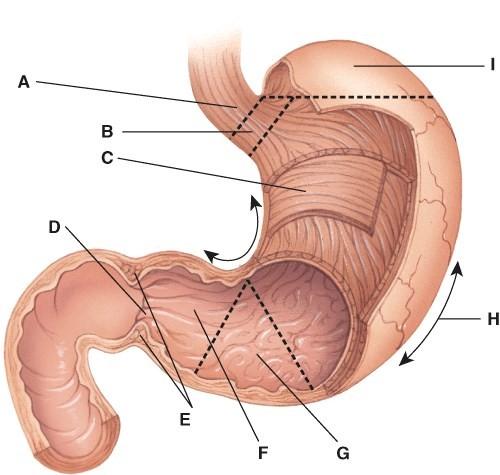
This is the portion of the stomach that connects to the duodenum.
- A
- E
- D
- B
C

What does line G point to?
- Pylorus
- Pyloric sphincter
- Ruggae
- Pyloric antrum
- Greater curvature
D

This is the area where pyloric stenosis occurs.
- E
- F
- G
- B
- I
A

What is line I pointing to?
- Greater curvature
- Lesser curvature
- Body
- Fundus
- Cardia
D
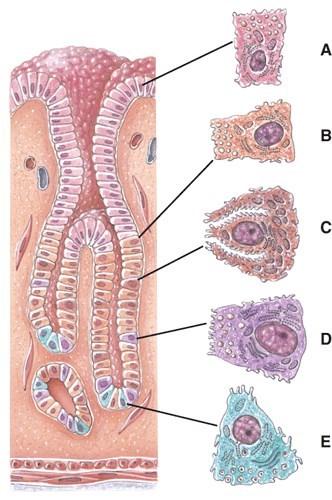
Which of the following cells secrete mucus?
- B
- C
- D
- E
A

Which of the following cells secretes intrinsic factor?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
C

Which of the following cells secretes gastrin?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
E

Which of the following cells secretes pepsinogen?
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
D
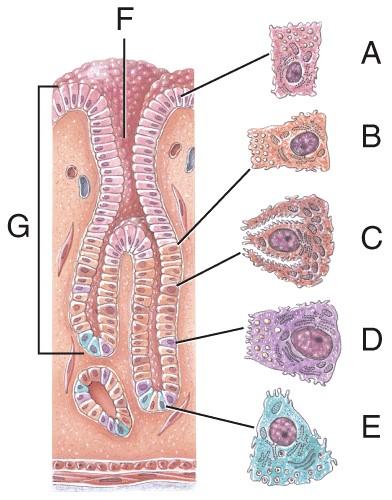
Name the structure labeled F
- Parietal cell
- Gastric glands
- Gastric pit
- Chief cell
- Simple columnar epithelium
C

Name the structure labeled G
- Parietal cell
- Gastric glands
- Gastric pit
- Chief cell
- Simple columnar epithelium
B

Name the structure labeled C
- Parietal cell
- Gastric glands
- Gastric pit
- Chief cell
- Simple columnar epithelium
A

Name the structure labeled D
- Parietal cell
- Gastric glands
- Gastric pit
- Chief cell
- Simple columnar epithelium
D
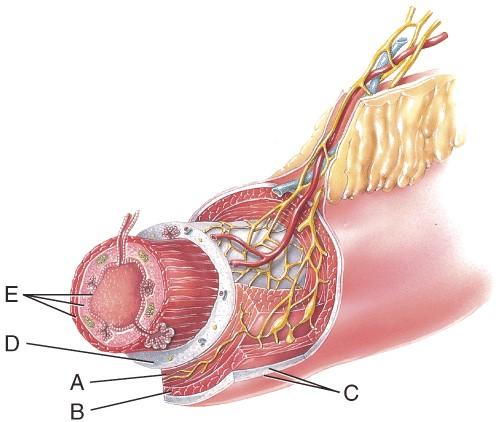
Name the layer labeled A
- Submucosa
- Serosa
- Longitudinal muscle
- Mucosa
- Circular muscle
E

Name the layer labeled B
- Submucosa
- Serosa
- Longitudinal muscle
- Mucosa
- Circular muscle
C

Name the layer labeled C
- Submucosa
- Serosa
- Longitudinal muscle
- Mucosa
- Circular muscle
B

Name the layer labeled E
- Submucosa
- Serosa
- Longitudinal muscle
- Mucosa
- Circular muscle
D

Name the layer labeled D
- Submucosa
- Serosa
- Longitudinal muscle
- Mucosa
- Circular muscle
A
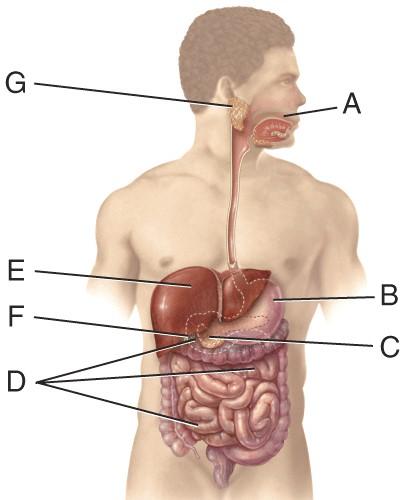
The enzyme produced in the organ labeled C which digests DNA is called:
- Deoxyribonuclease
- Ribonuclease
- Salivary amylase
- Pepsin
- Sucrase
A

The enzyme produced in the organ labeled C which digests RNA is called:
- Sucrase
- Deoxyribonuclease
- Salivary amylase
- Ribonuclease
- Pepsin
D

The enzyme, produced in the organ labeled C, that produces fatty acids and monoglycerides during digestion is called:
- Sucrase
- Pancreatic lipase
- Salivary amylase
- Trypsin
- Elastase
B

The enzyme, produced in the organ labeled D, that produces both glucose and fructose as products is called:
- lactase
- pancreatic lipase
- sucrase
- pepsin
- nucleases
C

The enzyme, produced in the organ labeled D, that produces both glucose and galactose as products is called:
- lactase
- pancreatic lipase
- sucrase
- pepsin
- nucleases
A

An enzyme, produced in the organ labeled D, that produces only glucose as a product is called:
- maltase
- pancreatic lipase
- sucrase
- pepsin
- nucleases
A

An enzyme, produced in the organ labeled D, that produces only glucose as a product is called:
- pancreatic lipase
- sucrase
- lactase
- α-dextrinase
- chymotrypsin
D

The enzyme, active in the organ labeled D, that has starches as a substrate is:
- Trypsin
- Salivary amylase
- Ribonuclease
- α-dextrinasee
- Pancreatic amylase
E

Which enzyme, active in organ D, has nucleotides as a substrate?
- ribonuclease
- salivary amylase
- phosphatases
- α-dextrinase
- Pancreatic amylase
C

Which enzyme, active in organ D, has nucleotides as a substrate?
- nucleases
- Salivary amylase
- α-dextrinase
- nucleosidases
- pancreatic amylase
D

Which of the following disorders result in an enlargement of the organ labeled G?
- peritonitis
- heartburn
- mumps
- vomiting
- pancreatitis
C

Name the disorder caused by a lack of proper enzymatic action in the organ labeled D resulting in diarrhea, gas and bloating after consumption of dairy products
- peritonitis
- heartburn
- gallstones
- lactose intolerance
- pancreatitis
D

Which of the following disorders involving the organ labeled F can result from cholesterol crystallization?
- peritonitis
- heartburn
- mumps
- gallstones
- pancreatitis
D

Which of the following disorders involving the organ labeled C can result from alcohol abuse?
- heartburn
- mumps
- pancreatitis
- peritonitis
- vomiting
C

Which of the following disorders involving the organ labeled E can result from viruses, drugs and chemicals such as alcohol?
- heartburn
- mumps
- pancreatitis
- hepatitis
- vomiting
D

Which of the following disorders can occur in the organ labeled B?
- Appendicitis
- mumps
- pancreatitis
- hepatitis
- peptic ulcers
E