Vertebrate Histology Exam 1
Histology
Purpose of course in histology is to understand the microanatomy of cells, tissues, and organs and to correlate structure with function.
Histological Sections
- Thin, flat slices of fixed and stained tissues or organs mounted on glass slides
- Tissues and organs composed of cellular, fibrous, and tubular structures
- Cells: variety of shapes and sizes, may be layered
- Fibrous: solid structures found in connective, nervous, and muscle tissues; “fibers”
- Tubular: hollow, represent blood vessels, ducts, or glands
Histological Sections
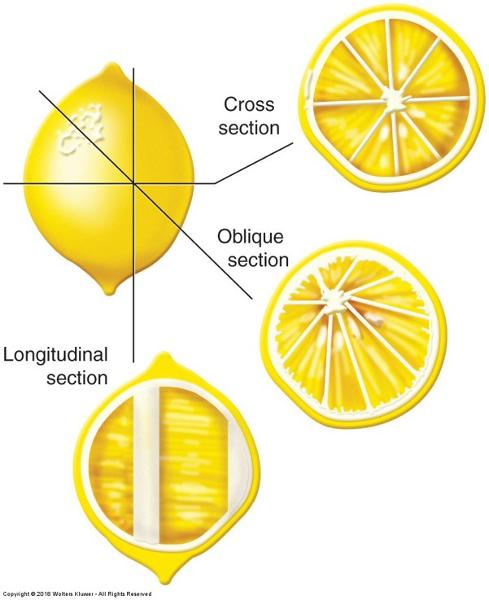
Transverse/cross section
- Perpendicular to the longitudinal axis
Longitudinal/ sagittal section
- Parallel to the longitudinal axis
- We have to interpret a 2-dimensional image into a 3-dimensional structure. The way a section passes through a tissue can drastically alter its appearance.
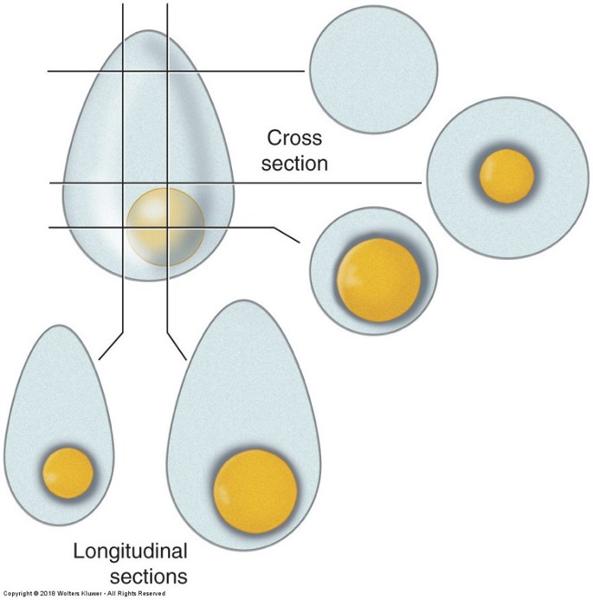
Planes of section of a round object:
why a nucleus may not always be visible & object size misjudged
Planes of section of a tube:
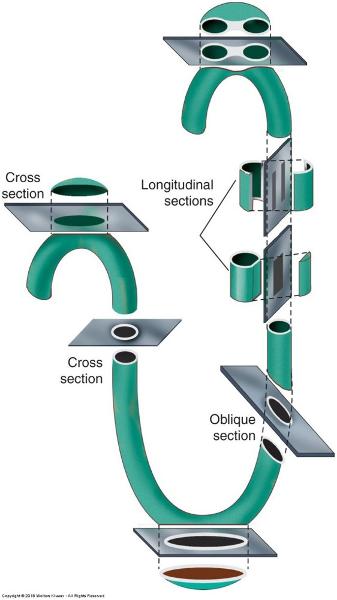
# of tubes, # cell layers of wall can be misjudged
Convoluted tubules of testis in different planes of section:
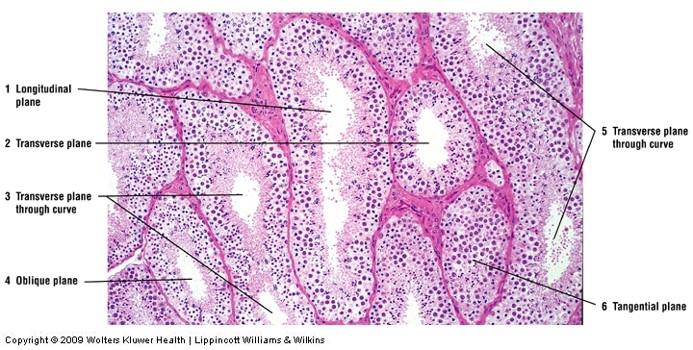
some are round and some are oblique
Tissue preparation
- Fixation to preserve structure: chemical or mixture of chemicals that permanently preserves the tissue structure (e.g. formaldehyde, alcohols, organic solvents)
- Terminates cell metabolism
- Prevents enzymatic degradation of tissue and cells by autolysis
- Kill pathogenic microorganisms
- Hardens tissue via cross-linking or denaturing proteins
Tissue preparation
- Dehydration & Clearing: increasing concentrations of ethanol typically followed by xylene
- Makes tissue transparent
- Allows embedding medium to penetrate the tissue more easily
Tissue preparation
- Embedding specimen in paraffin (wax) or plastic polymer for sectioning (or tissue may be frozen for immediate medical diagnosis)
- Allows for thin sections to be made while keeping tissue structures intact
Tissue preparation
- Sectioning of embedded specimen & mounting onto glass slides
- 5-15 μm thickness (paraffin)
- 0.1 µm or less (plastic polymer
Tissue preparation
- Staining
- Paraffin must be dissolved if used—dyes are hydrophilic
- Visualize cell structures by using dyes that bind to specific properties of biomolecules found in cells, tissues, and organs
- Basic (cationic) stains stain basophilic structures, e.g. nucleic acids
- Acidic (anionic) stains stain acidophilic structures, e.g. cytoplasmic proteins
- Most common: hematoxylin and eosin (H & E)—what we’ll see most often in our book and in lab
H & E stain: most commonly used stain in histology
- Hematoxylin (basic stain)
- Nuclei stain blue to purple
- Eosin (acidic stain)
- Cytoplasm stains pink or red
- Collagen fibers stain pink
- Muscles stain pink
Masson’s Trichrome stain: highlights connective tissue
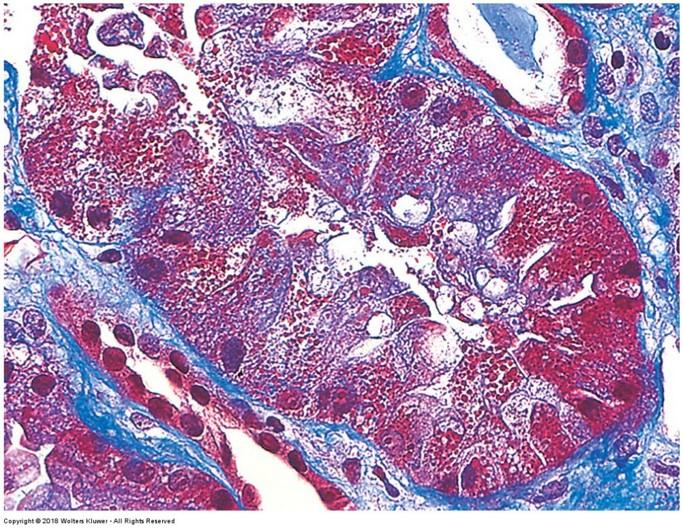
- Nuclei stain black or blue black
- Muscles stain red
- Collagen and mucus stain green or blue
- Cytoplasm of most cells stains pink
Periodic Acid-Schiff Reaction (PAS): highlights secretions, basement membranes, and microvilli
- Glycogen stains deep red or magenta
- Goblet cells in intestines and respiratory epithelia stains magenta red
- Basement membranes and brush borders (microvilli) in kidney tubules stain pink
Elastic Tissue stain: highlights elastic fibers
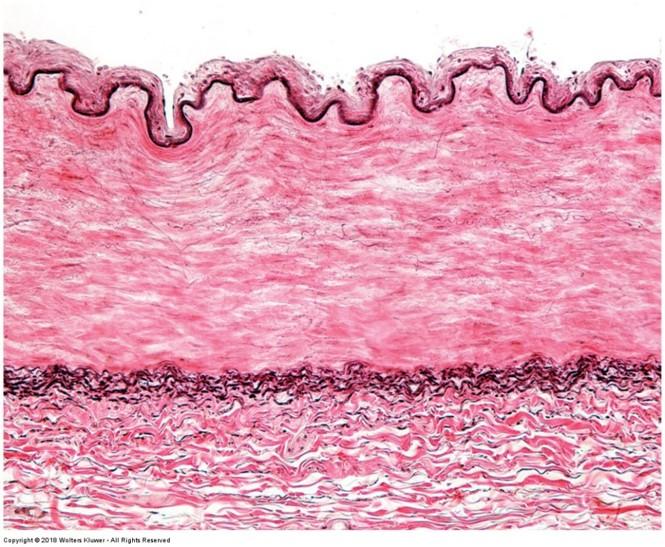
- Elastic fibers stain jet black or brown
- Nuclei stain gray
- Remaining structures stain pink
Mallory-Azan stain: highlights connective tissue
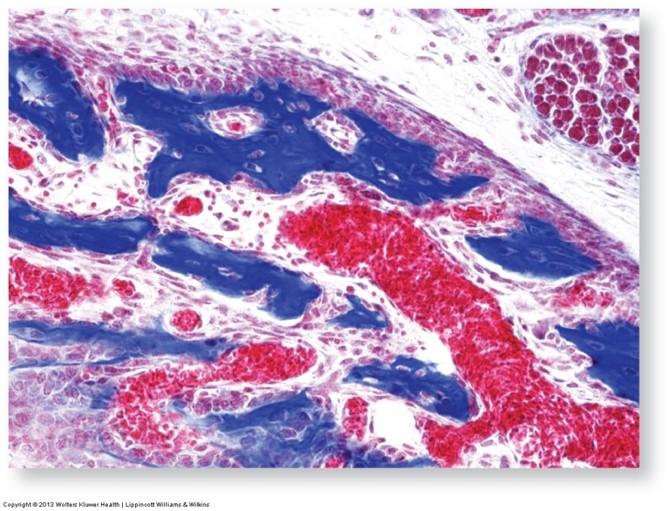
- Fibrous connective tissue, mucus, and hyaline cartilage stain deep blue
- Erythrocytes stain red-orange
- Cytoplasm of liver and kidneys stains pink
- Nuclei stain red
Wright/Giesma stain: highlights blood cells
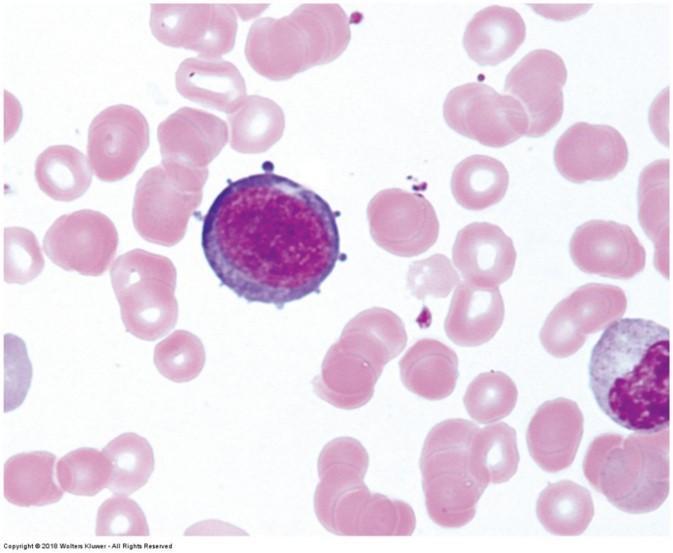
- Erythrocyte cytoplasm stains pink
- Lymphocyte nuclei stain dark purple-blue with pale blue cytoplasm
- Monocyte cytoplasm stains pale blue and nucleus stains medium blue
- Neutrophil nuclei stain dark blue
Wright/Giesma stain: highlights blood cells
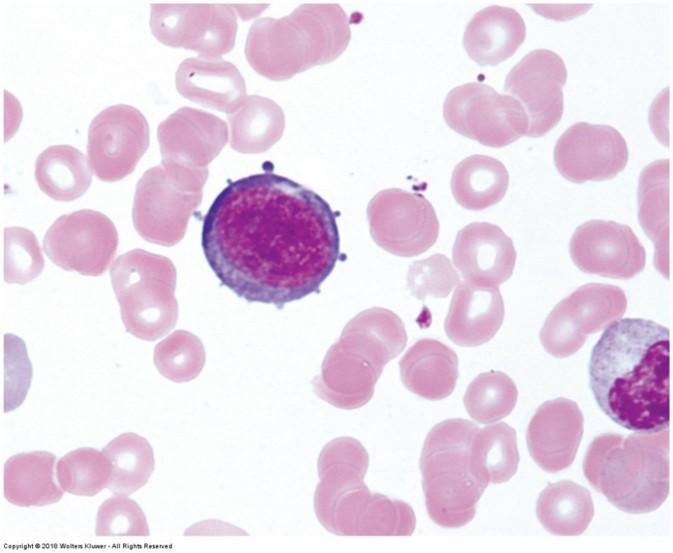
- Eosinophil nuclei stain dark blue and granules stain bright pink
- Basophil nuclei stain dark blue or purple, cytoplasm stains pale blue, and granules stain deep purple
- Platelets stain light blue
Cajal’s (or Bielschowsky’s) and Del Rio Hortega’s Methods (silver and gold stains): highlights nervous tissue
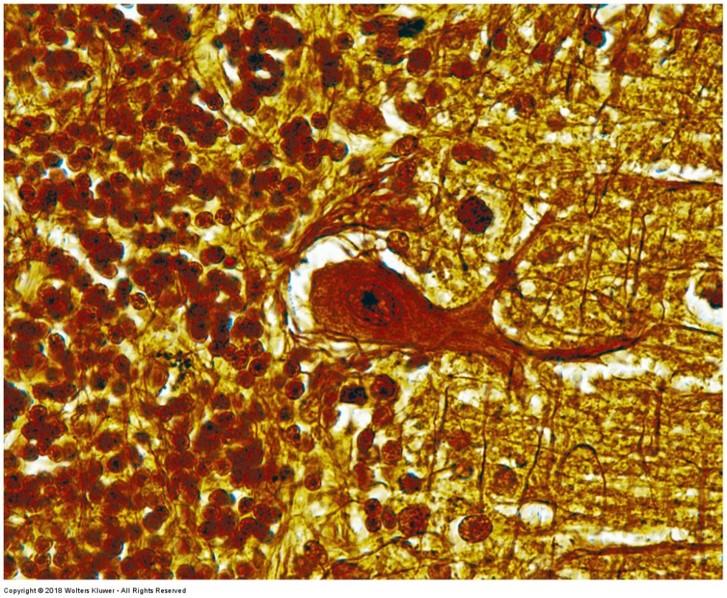
- Myelinated and unmyelinated fibers and neurofibrils stain blue-black, brown, or gold
- General background nearly colorless
- Astrocytes stain black
Osmic Acid (osmium tetroxide) stain: highlights lipids
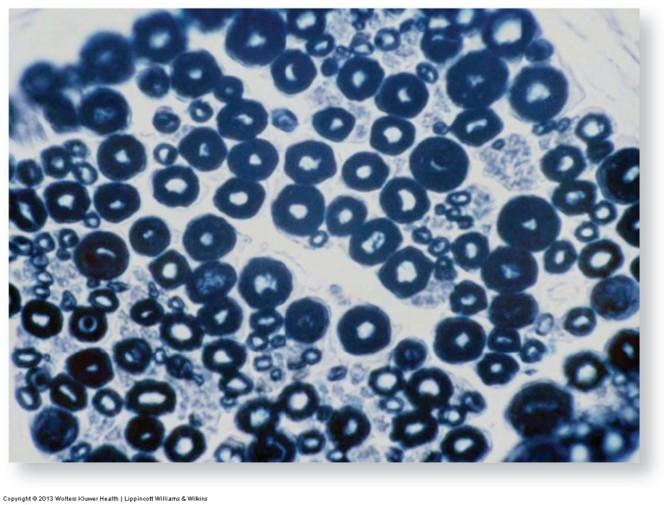
- Lipids generally stain black
- Including lipids in myelin sheath of nerves
Iron Hematoxylin & Alcian Blue Stain: highlights connective tissue, mucus, & muscle and cell membrane structures
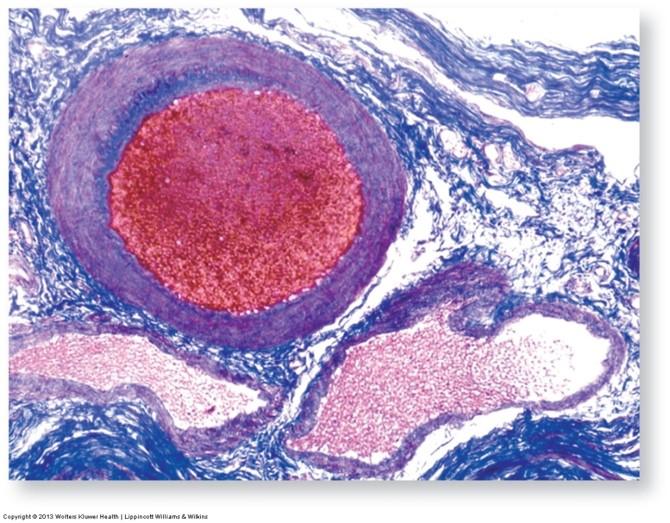
- Cell membranes, muscle striations, & intercalated discs stain black
- Connective tissue fibers & mucus stain dark blue
- Smooth muscles stain light pink
- Nuclei stain dark pink
- Cytoplasm stains light pink
Iron Hematoxylin & Alcian Blue Stain: highlights connective tissue, mucus, & muscle and cell membrane structures
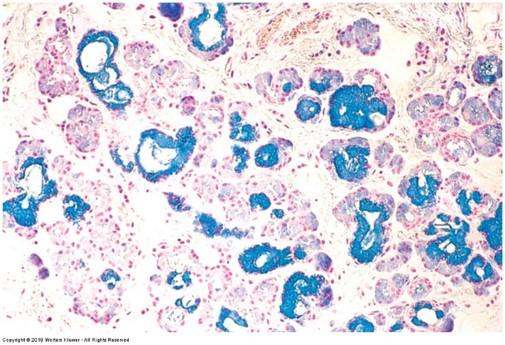
- Cell membranes, muscle striations, & intercalated discs stain black
- Connective tissue fibers & mucus stain dark blue
- Smooth muscles stain light pink
- Nuclei stain dark pink
- Cytoplasm stains light pink
Microscopy
- Magnifies an image and allows visualization of greater detail
- Simple = 1 lens
- Compound = multiple lenses
- Resolving power (resolution): ability of lens or optical system to produce separate images of closely positioned objects
- Can you tell the difference between 2 adjacent objects (2-point discrimination)?—depends on power of microscope and distance between objects
Microscopy
- Resolution dependent on:
- Optical system
- Wavelength of light source
- Specimen thickness
- Quality of fixation
- Staining intensity
Microscopy
Eye Versus Instrument Resolution
Distance between resolvable points
Human eye: 0.2 mm
Bright-field microscope: 0.2 µm
SEM: 2.5 nm
TEM Theoretical Tissue Section: 0.05 nm
1.0 nm
Atomic force microscopy: 50 pm
Microscopy:
series of lenses that focus and magnify a beam of light or electrons
Microscopy
- Bright-field microscope: what we use in laboratory (see more in-depth description in Lab #1 Exercise Handout)
- Light source: illuminates specimen
- Condenser lens: focuses light onto specimen
- Stage: where specimen is placed
- Objective lens: gathers light passing through specimen
- Ocular lens: where image is examined
Visualize
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Cell membrane
- Organelles are stain dependent—not typically seen with H & E
Microscopy
- Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM): beam of electrons to produce an image
- Uses thinner sections: ~100nm
- Light areas are where electrons pass through specimen
- Dark areas are where electrons are absorbed or scattered
- Scanning electron microscopy: electron beam passes across specimen surface (topography of cells or tissues)
The Cell
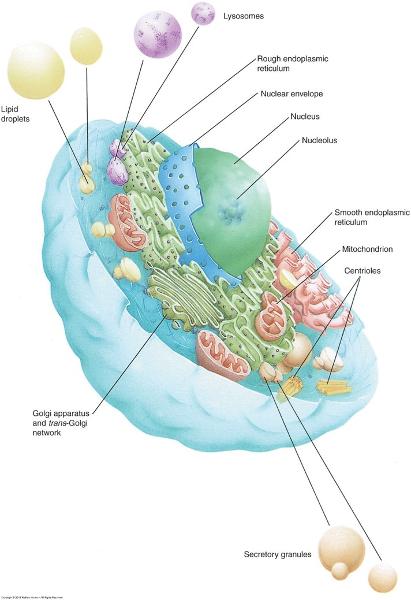
- Living organisms contain multiple cell types to maintain homeostasis
- Common structural features in all cells (organelles)—see also Graphic 1-2
- Quantity, distribution, and appearance of organelles will differ with type of cell and cell’s function
Mammalian cells
- Cytoplasm: dense, fluid-like medium
- Cell (plasma) membrane: barrier between internal and external environments
- Organelles and intracellular elements: suspended in cytoplasm, each has a unique special function
- Nucleus: control center
- Mature red blood cells DO NOT have one
- Microtubules: cytoskeleton
- Microfilaments: cytoskeleton
- Membrane-bound secretory granules and organelles
- Ingested material
Organelles: Membrane-bound
Membrane-bound
- Nucleus (typically only organelle visible with light microscopy)
- Mitochondria
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): Smooth & Rough
- Golgi apparatus
- Endosomes
- Lysosomes
- Nucleus
- the centrally located compartment of eukaryotic cells that is bounded by a double membrane and contains the chromosomes
- enclosed by the nuclear envelope, composed of an inner and an outer nuclear membrane with an intervening perinuclear cistern. The outer nuclear membrane is studded with ribosomes and is continuous, in places, with the RER.
- the central and most important part of an object, movement, or group, forming the basis for its activity and growth.
- Mitochondria
- energy-generating organelles that contain the enzymes of the citric acid cycle, the respiratory chain, and oxidative phosphorylation
- composed of an outer and an inner membrane with an intervening compartment between them known as the intermembrane space. The inner membrane is folded to form flat (or tubular in steroid-manufacturing cells) shelf-like structures known as cristae and enloses a viscous fluid-filled space known as the matrix space
- function in the generation of ATP, utilizing a chemiosmotic coupling mechanism that employs a specific sequence of enzyme complexes and proton translocator systems (electron transport chain and the ATP synthase-containing elementary particles) embeded in their cristae
- generate heat in brown fat instead of producing ATP
- Also assist in the synthesis of certain lipids and proteins; they possess the enzymes of the TCA cycle, circular DNA molecules, and matrix granules in their matrix space
- increase in number by undergoing binary fission
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): Smooth & Rough
- SER: functions in the synthesis of cholesterols and lipids well as in the detoxification of certain drugs and toxins (such as barbiturates and alcohol). Additionally, in skeletal muscle cells, this organelle is specialized to sequester and release calcium ions and thus regulate muscle contraction and relaxation
- RER: whose cytoplasmic surface possesses receptor molecules for ribosomes and signal recognition particles (known as ribophorins and docking proteins, respectively), is continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The RER functions in the synthesis and modification of proteins that are packaged, as well as in the synthesis of membrane lipids and proteins.
- Golgi apparatus
- a system of concentrically folded membranes found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells; functions in secretion from the cell by exocytosis
- the Golgi apparatus is composed of a specifically oriented cluster of vesicles, tubules, and flattened membrane-bounded cisternae
- Endosomes
- are intermediate compartments within the cell, utilized in the destruction of endocytosed, phagocytosed, or autophagocytosed materials as well as in the formation of lysosomes
- possess proton pumps in their membranes, which pump H+ into the endosome, thus acidifying the interior of this compartment
- are intermediate stages in the formation of lysosomes
- Lysosomes
- a membrane enclosed organelle originating from the golgi apparatus and containing hydrolytic enzymes
- a formed by the utilization of late endosomes as an intermediary compartment
- both lysosomal membranes and lysosomal enzymes are packaged in the TGN
- they are delivered in seperate clathrin-coated vesicles to late endosomes, forming endolysosomes, which then mature to become lysosomes
- Peroxisomes
- peroxisomes are membrane-bounded organelles housing oxidative enzymes such as urate oxidase, D-amino acid oxidase, and catalase
- these organelles function in the formation of free radicals (superoxides), which destroy various substances
- they protect the cell by degrading hydrogen peroxide by catalase
- they also function in detoxification of certain toxins and in elongation of some fatty acids during lipid synthesis
Organelles: Not membrane-bound
Not membrane-bound
- Ribosomes
- Basal bodies
- Centrioles
- Centrosomes
- Cytoplasmic inclusions
- Ribosomes
- small, bipartite nonmembranous organelles that exist as individual particles that do not coalesce with each other until protein synthesis begins
- the 2 subunits are of unequal size and constitution. The large subunit is 60s, and the small subunit is 40s in size
- each subunit is composed of proteins and r-RNA, and together, they function as an interactive "workbench" that not only provides a surface upon which protein synthesis occurs but also acts as a catalyst that facilitates the synthesis of proteins
- Basal bodies
- each cilium arises from a structure known as the basal body that resembles a centriole in that it is composed of 9 microtubule triplets
- an organelle that forms the base of a flagellum or cilium
- Centrioles
- A centriole is a small set of microtubules arranged in a specific way. There are nine groups of microtubules. When two centrioles are found next to each other, they are usually at right angles. The centrioles are found in pairs and move towards the poles (opposite ends) of the nucleus when it is time for cell division
- a paired organelle that helps organize the microtubules in animal and protist ells during nuclear division
- Centrosomes
- are associated with the nuclear membrane during the prophase stage of the cell cycle. In mitosis the nuclear membrane breaks down and the centrosome nucleated microtubules can interact with the chromosomes to build the mitotic spindle
- the major microtubule organizing center of an animal cell
- Cytoplasmic inclusions
- lipids, glycogen, secretory granules, and pigments, are also consistent constitutes of the cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
- Network of protein filaments and tubules that extend throughout cytoplasm
- Structural framework of cell
3 filament types
- Microfilaments/actin (forms core of microvilli)
- Intermediate filaments
- Microtubules (forms mitotic spindles, cilia, and flagella)
Ciliated vs. nonciliated epithelium
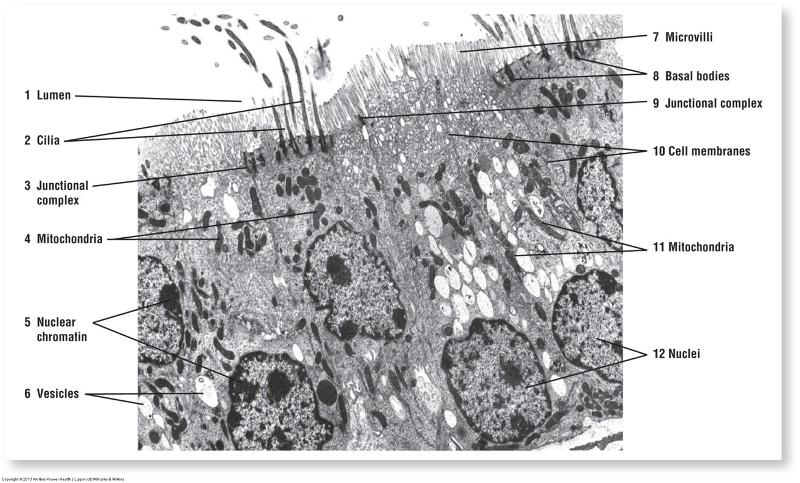
Cell Components & Sizes
Cell Components
Cell Components
Special features of certain cells
Apical vs. basal modifications of epithelial cells
- Cilia
- Microvilli
- Basal infoldings
Apical: Cilia and microvilli
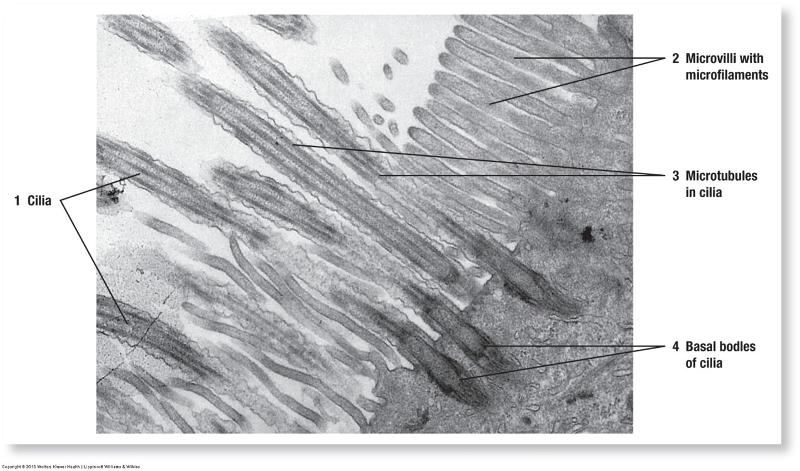
Basal: Basal Infoldings
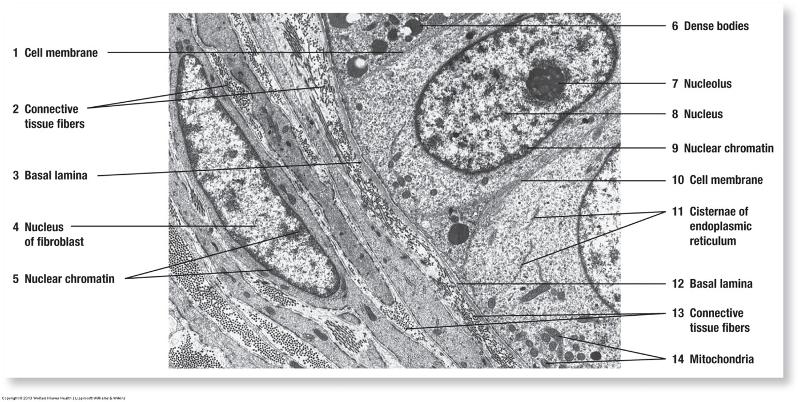
Basal: Basal Infoldings of ion-transporting cells

Basal: Basal Infoldings ion-transporting cells
Special features of certain cells
- Junctional complexes: hold cells together into tissues (barrier and cell-to-cell communication)—used by epithelial and connective tissues
- Lateral and basal surfaces of cells
- Zonula occludens (tight junctions)
- Zonula adherens
- Desmosomes
- Hemidesmosomes
- Gap junctions
Lateral: Junctional Complexes
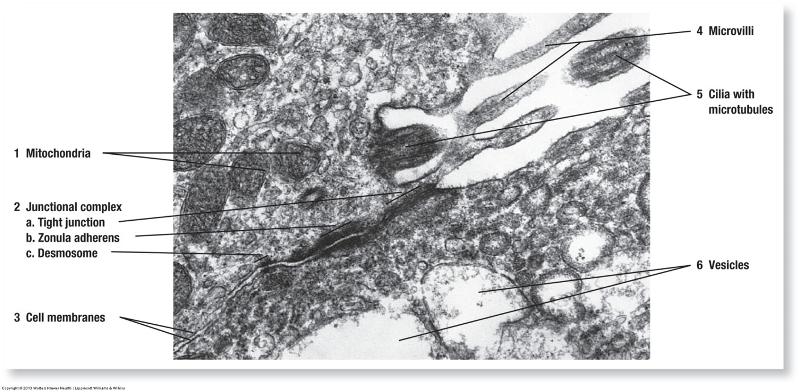
Describing Normal Cells
- Cell Shapes
- Features of the cytoplasm
- Features of the nucleus
Cell Shape
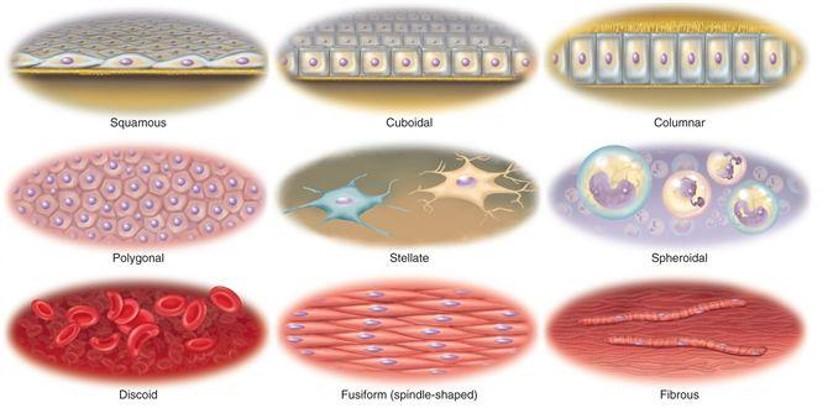
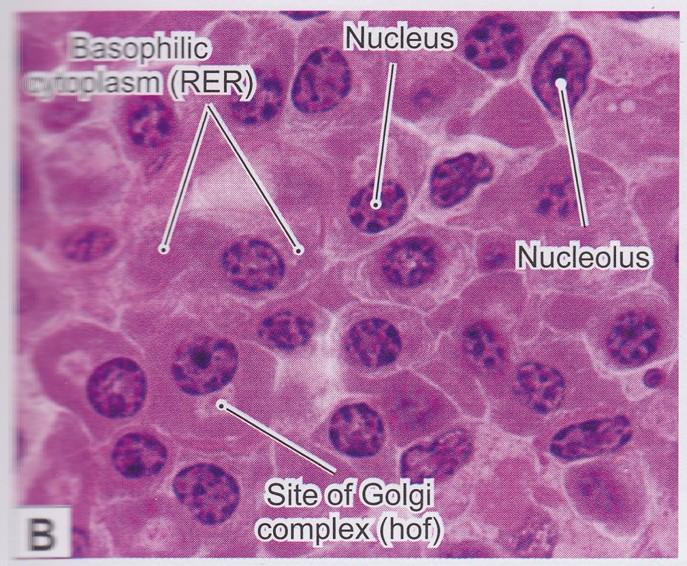
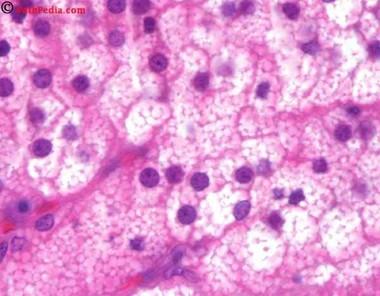
Basophilic vs. Acidophilc Cytoplasm
- Basophilia is often seen in cells with increased rER for protein synthesis.
- Acidophilia is often seen in cells with increased mitochondria
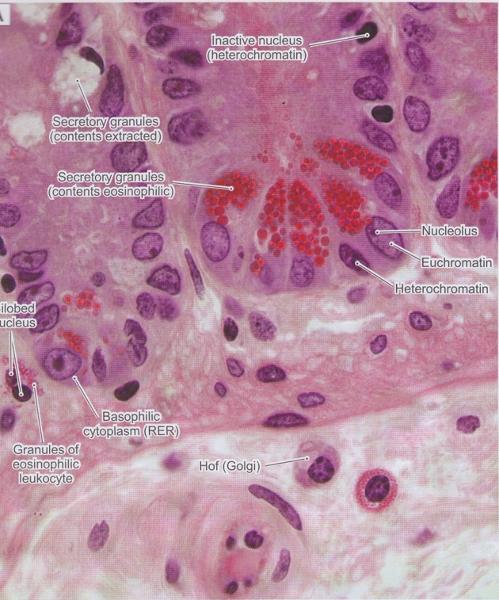
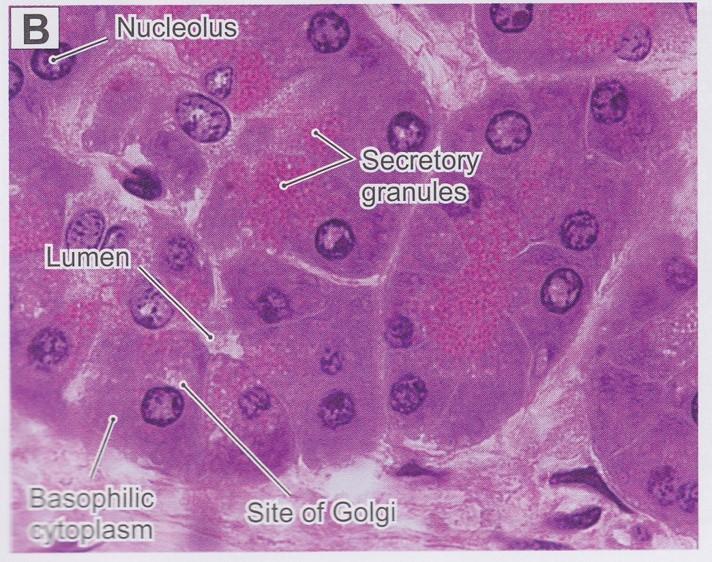
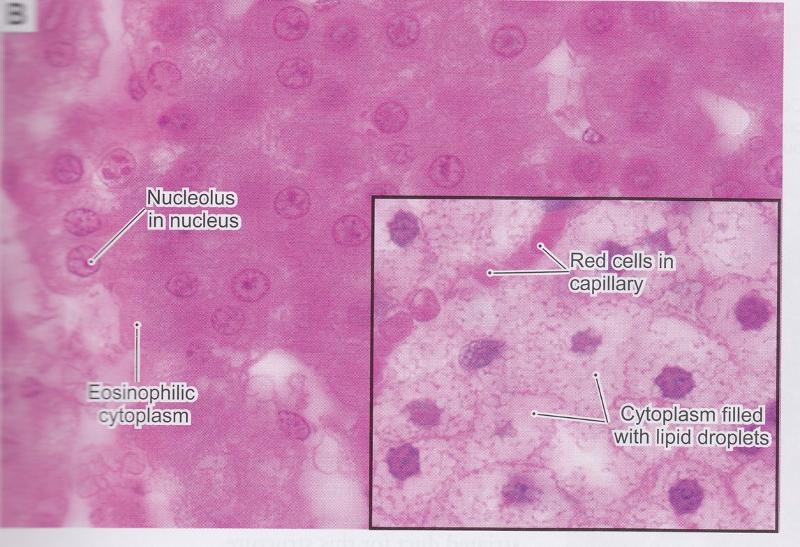
Granules & Lipid Droplets in Cytoplasm
- Secretory granules with H & E
- Normal cytoplasm with H & E
- Lipid droplets with H & E
- Secretory granules with H & E
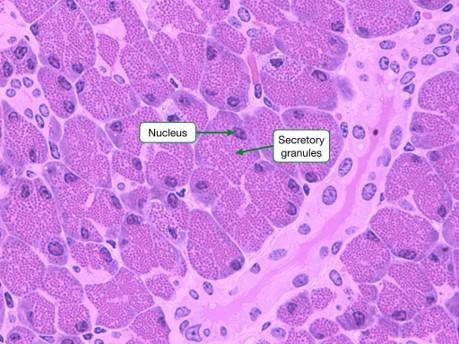
- Normal cytoplasm with H & E
- Lipid droplets with H & E
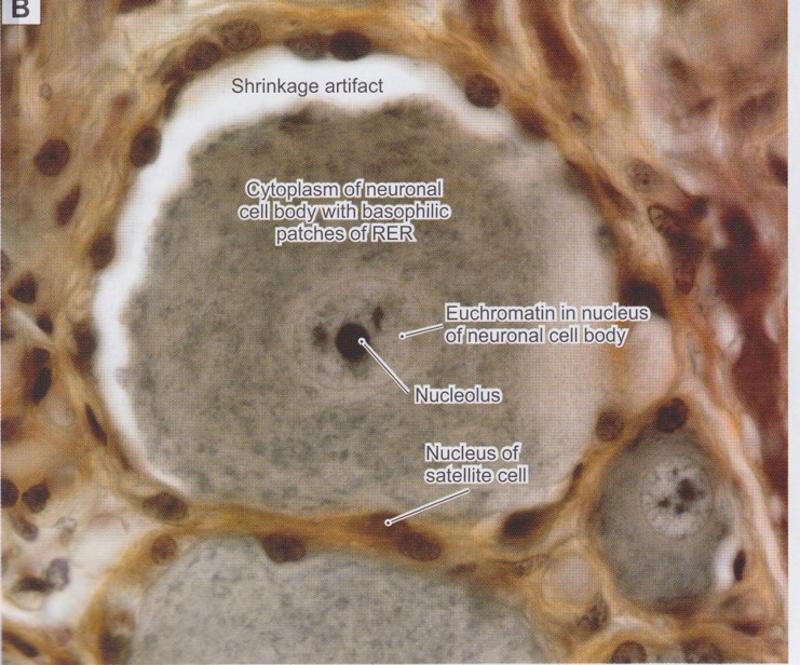
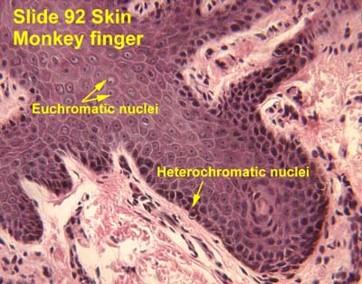
Euchromatic vs. Heterochromatic Nuclei
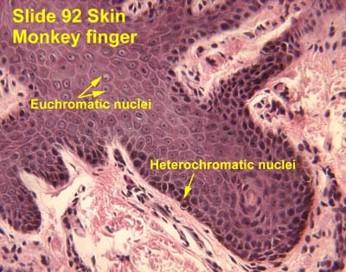
Euchromatic nuclei
- Lightly staining chromosomes in the nucleus
- Genes are accessible for transcription
Heterochromatic nuclei
- Darkly staining chromosomes in the nucleus
- Genes are NOT being transcribed
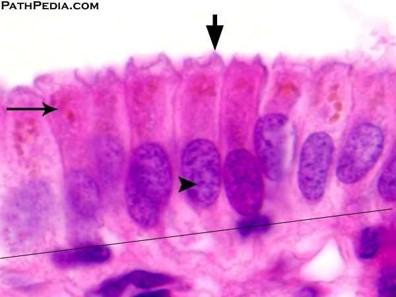
Nucleoli
- Nucleoli indicate active protein synthesis so they appear prominently in euchromatic nuclei
Simple vs. Segmented Nuclei
Simple nuclei are a single structure, usually round/oval or indented.
Simple vs. Segmented Nuclei
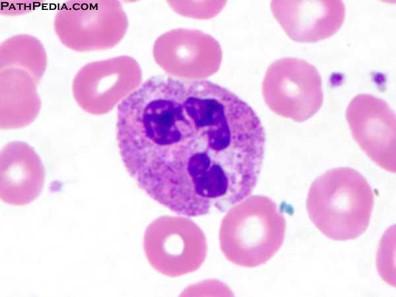
Segmented nuclei are often seen in white blood cells and are 2+ lobes connected together.
Describing Abnormal Cells & Tissues
- Presence of inflammation
- Markers of cell death—apoptotic or necrotic
- Changes in cell size, shape, or number
- Presence of abnormal lipids, water, or pigments
Acute vs. Chronic Inflammation
- Both involve an influx of immune cells into a tissue that normally are not there
- Acute: active, infection with abundance of neutrophils (abscess is a collection of neutrophils)
- Chronic: infectious process lasting weeks to months involving lymphocytes, plasma cells, mast cells, & eosinophils
Ulcer
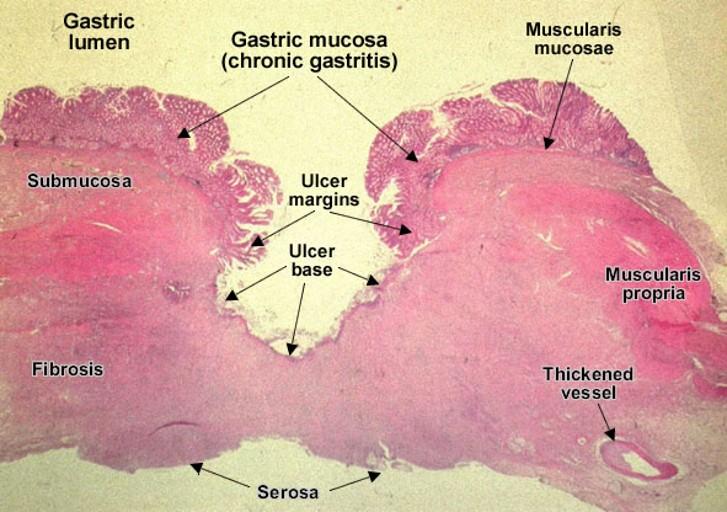
- Ulcers are a break in the epithelial tissue lining of an organ creating a crater-shaped lesion
- Causes:
- Infection
- Chemical exposure
- Prolonged pressure
- Compromised blood vessels
Apoptosis vs. Necrosis
- Apoptosis is programmed cell death initiated within nucleus & mitochondria of cell—nuclear fragmentation without inflammation.
- Necrosis is an irreversible cell death caused by cell injury—cells rupture & leak into extracellular space causing inflammation.
Types of Necrosis
- Caseous necrosis
- Coagulative necrosis
- Fat necrosis
- Liquefactive necrosis
- Caseous necrosis
- Obliteration of tissue structure (holes) & presence of neutrophils caused by infections
- Coagulative necrosis
- Cells appear to be intact, but nuclei are absent seen in heart attacks & kidney injury.
- Fat necrosis
- Seen only in adipose tissue, where adipocyte death from trauma or enzymatic digestion releases lipids into extracellular space and accumulates in macrophages.
- Liquefactive necrosis
- Bacterial infections or injury in the central nervous system.
Pyknosis
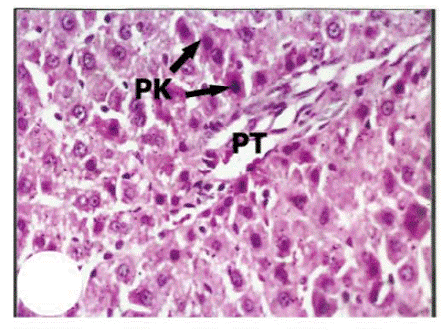
- Seen with apoptosis and necrosis
- Morphological change occurring in the nucleus of an irreversibly damaged cell.
- Condensation of chromatin & increased basophilia within the nucleus
Hyperplasia vs. Hypertrophy
- Hyperplasia is an increase in cell number.
- Hypertrophy is an increase in cell size.
Atrophy
- Atrophy is a decrease in cell size (opposite of hypertrophy).
- Causes: denervation; decreased use, blood supply, or nutrients; pressure
Steatosis (fatty change) vs. Hydropic change
- Steatosis is an abnormal collection of lipid often seen in liver cells.
- Hydropic change is a reversible cell injury hallmarked by cell swelling due to ion-pump function.
Amyloid accumulation
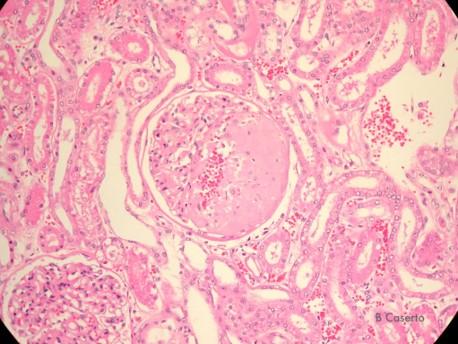
Amyloid is an abnormal protein that accumulates in many diseases
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Lymphocyte cancers
- Chronic inflammation
Accumulation often disrupts function of the cells leading to their death
Anthracosis vs. Melanin accumulation
- Antrhacosis is an exogenous carbon pigment found in macrophages following exposure to smoking or air pollution.
- Melanin is a pigment produced by skin cells and may accumulate in macrophages during chronic skin inflammation.
Epithelium & Glands
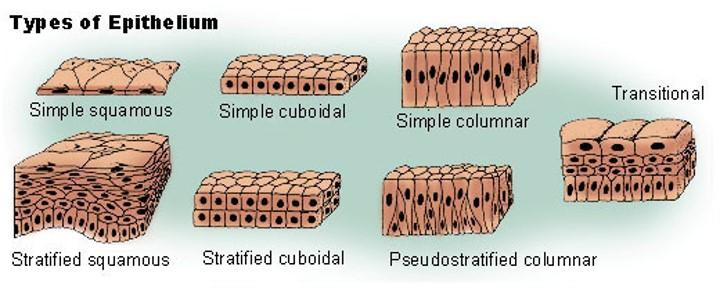
4 basic tissue types
- Connective tissue
- Muscle tissue
- Nervous tissue
- Epithelial tissue (focus of this chapter)
Epithelial tissue (epithelium; epithelia)
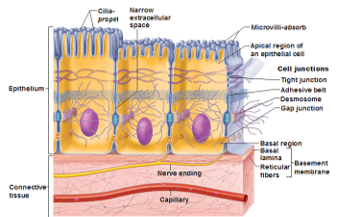
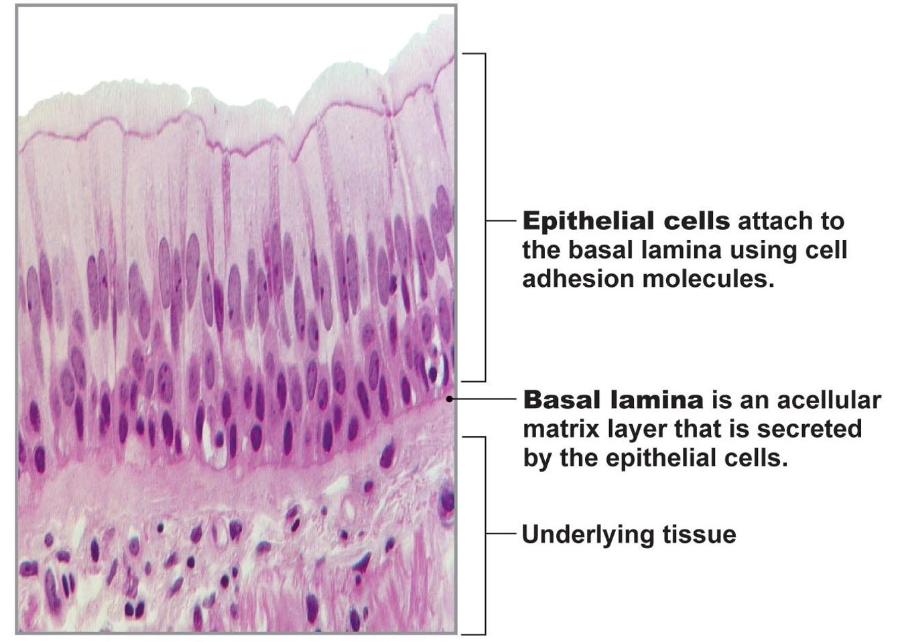
- Consists of sheets of cells resting on basement membrane
- Cells contact each other via cell junctions
- Covers external body surfaces
- Lines internal body cavities and ducts
Epithelial tissue (epithelium; epithelia)
- Forms glands, organs, and specialized receptor cells (smell, taste, hearing, vision)
- Nonvascular
- O2, nutrients, and metabolites diffuse from blood vessels in underlying loose connective tissue
- Classification based on morphological characteristics (cell shape and layers)
- Structure varies with function of tissue
Epithelial tissue (epithelium; epithelia)
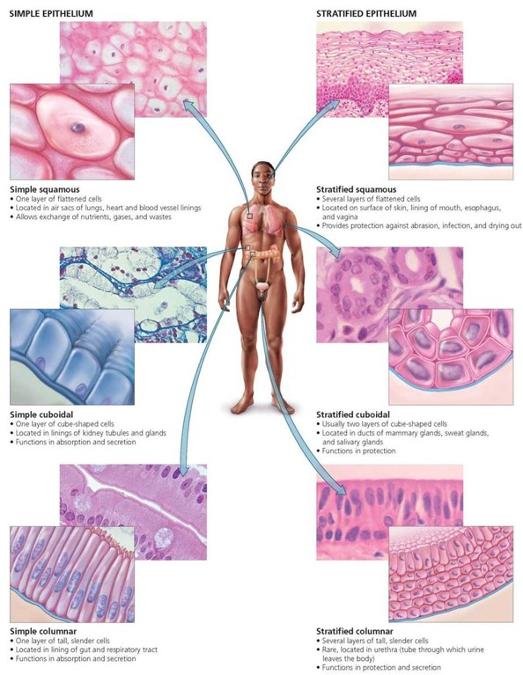
- Cells are close together and present at a free surface:
- Exterior of body
- Outer surface of many internal organs
- Lining of body cavities, tubes, and ducts
- Open to exterior: Mouth, nose, respiratory tract
- Enclosed in body: Pleural, pericardial, and peritoneal cavities & tubes of cardiovascular system
Classification of Epithelia
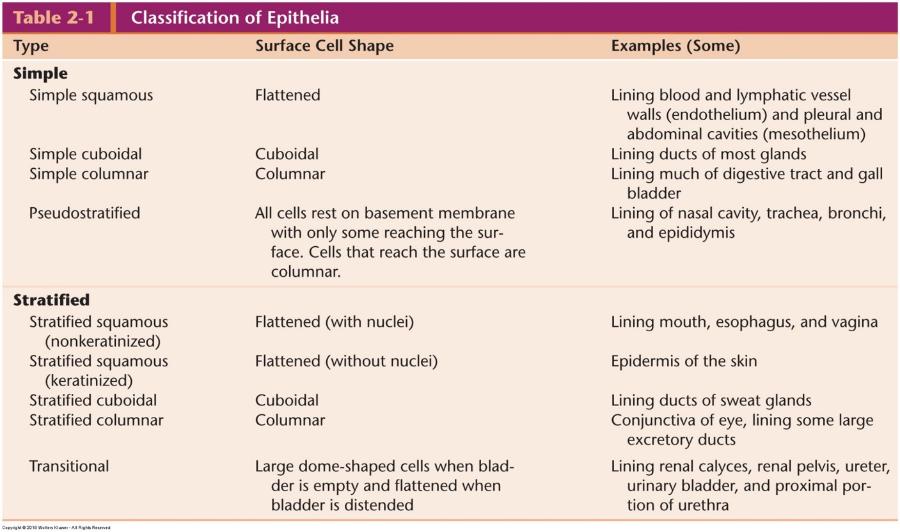
Epithelial tissue in different organs
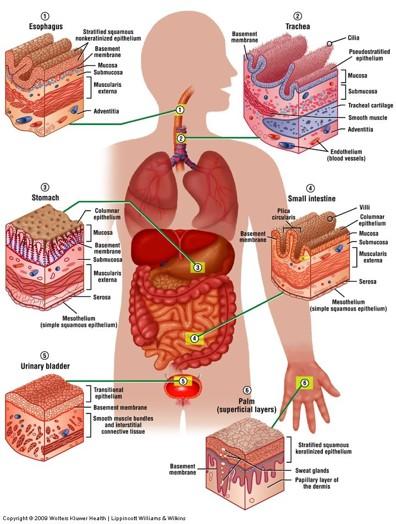
Epithelial tissue (epithelium; epithelia)
- Single or multiple layers
- Cells joined by specialized cell junctions -->barrier (main function) between free surface and adjacent loose connective tissue
- Minimal intercellular space
- Other functions: regulate material exchange and produce and secrete chemicals
Epithelial tissue can be classified based on structure or function.
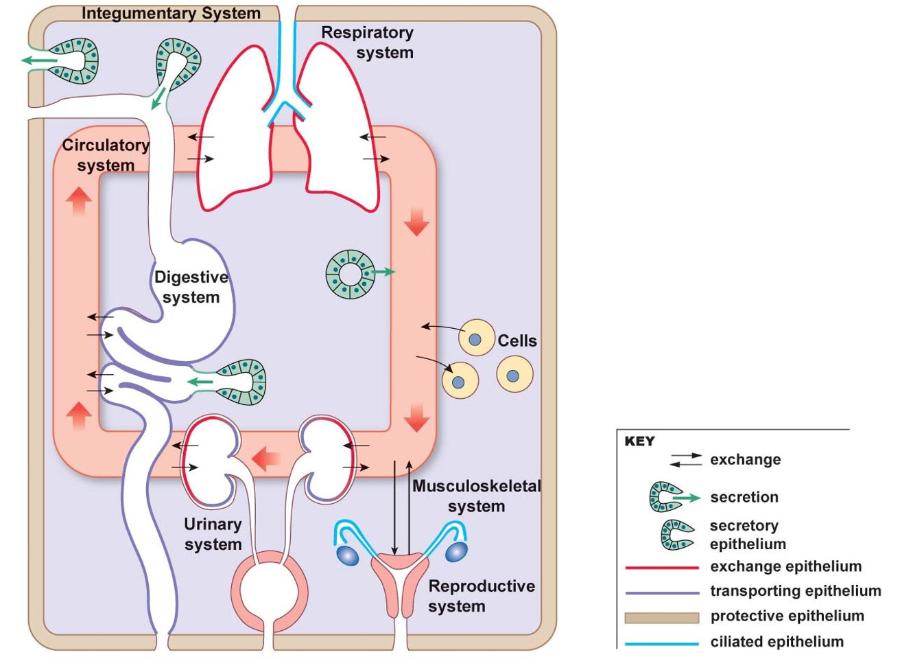
We will identify epithelial tissue based on structure for this course.
Basic organization of epithelial tissue
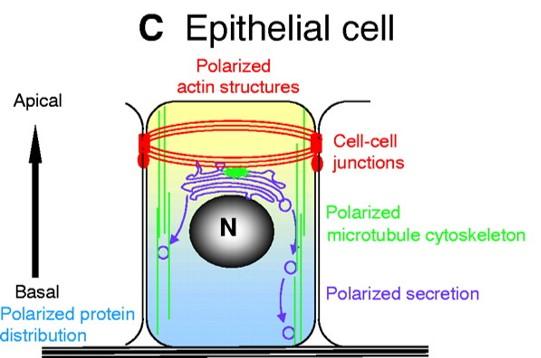
Epithelial cells have polarity
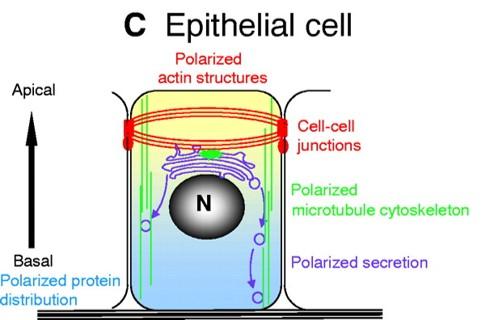
- Apical domain (free surface): motility, absorption, and secretion
- Lateral domain (sides of cell): communication & anchor to adjacent cells
- Basal domain (attaches to basement membrane): anchor to underlying loose connective tissue
- Each domain has different membrane composition (lipid and proteins)
Apical surface modifications
Motility
- Cilia (uterine tubes, uterus, and tubes of respiratory system)
Absorption
- Microvilli (small intestine and kidney)
- Stereocilia: long, nonmotile, branched microvilli (epididymis, vas deferens, and hair cells of inner ear)
Classification of epithelium
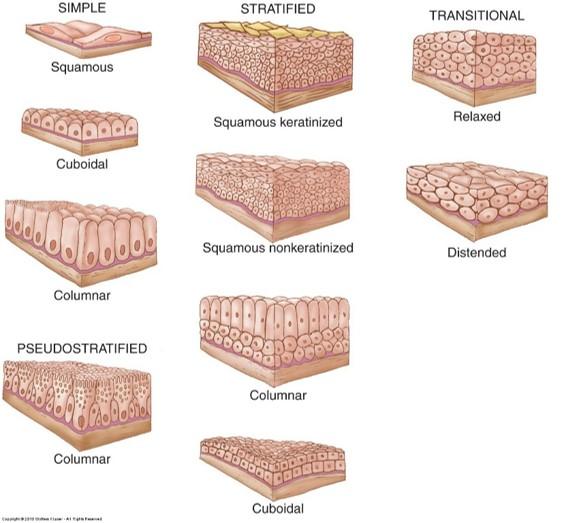
Based on shape of cells and number of cell layers
Shape of surface cells
- Squamous (flattened; width > height)
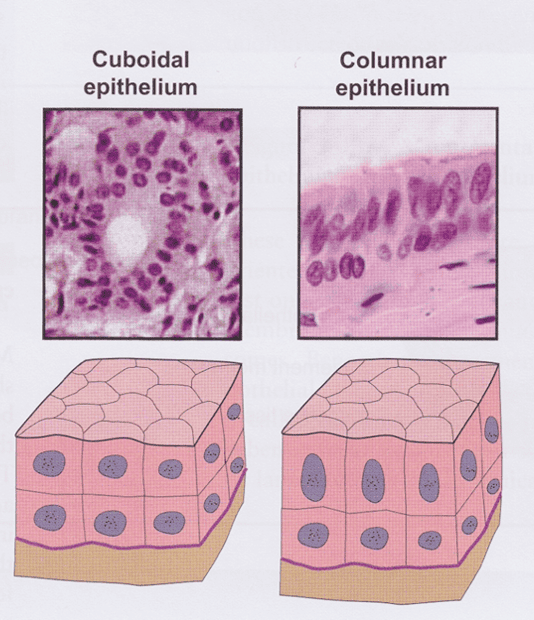
- Cuboidal (round; width = height)
- Columnar (height > width)
Cell layers
- Simple (single layer)
- Stratified (multiple layers)
- Pseudostratified (single layer of cells but not all cells reach free surface)—appear as multiple layers
Classification of epithelium: simple
Classification of epithelium: stratified
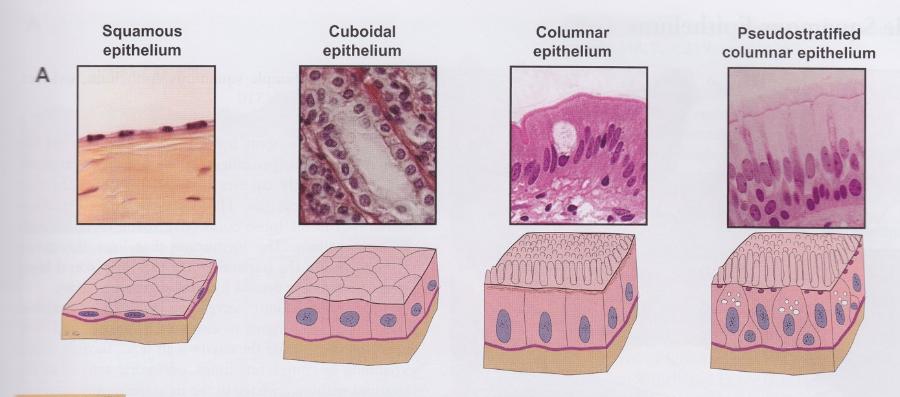
Simple squamous epithelium
- One layer of flattened cells
- Mesothelium: covers external surfaces of digestive organs
- Endothelium: covers lumina of heart chambers, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
Simple squamous epithelium: mesothelium surface view

Flat cells tightly adhered to one another.
Simple squamous epithelium: transverse section
Flat cells with purple nuclei and pink cytoplasm.
Simple cuboidal epithelium
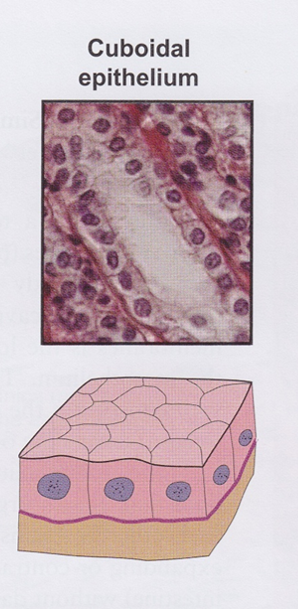
Lines small excretory ducts in different organs
- Provides sturdiness and protection
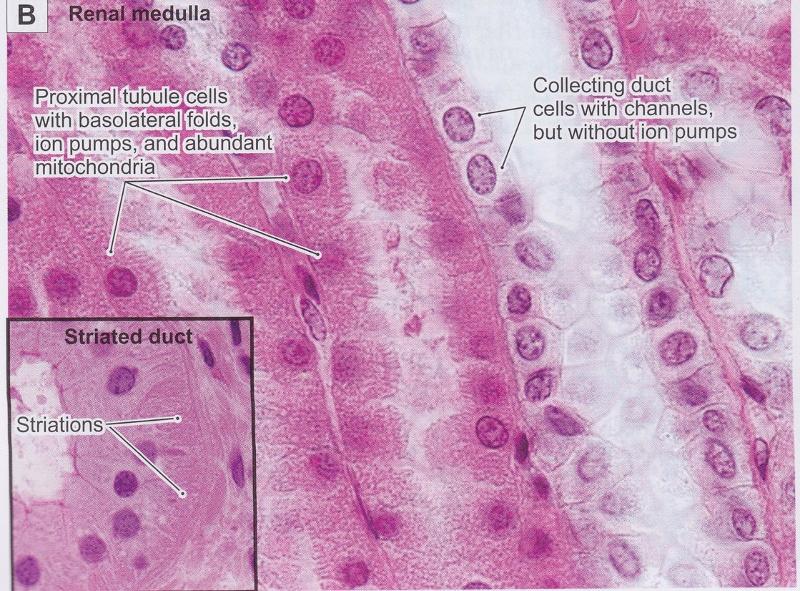
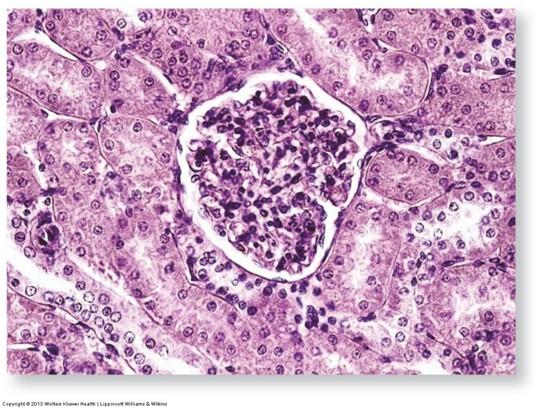
Line proximal tubules of kidneys (apical surface has a brush border of microvilli)
- Transport and absorption of filtered substances
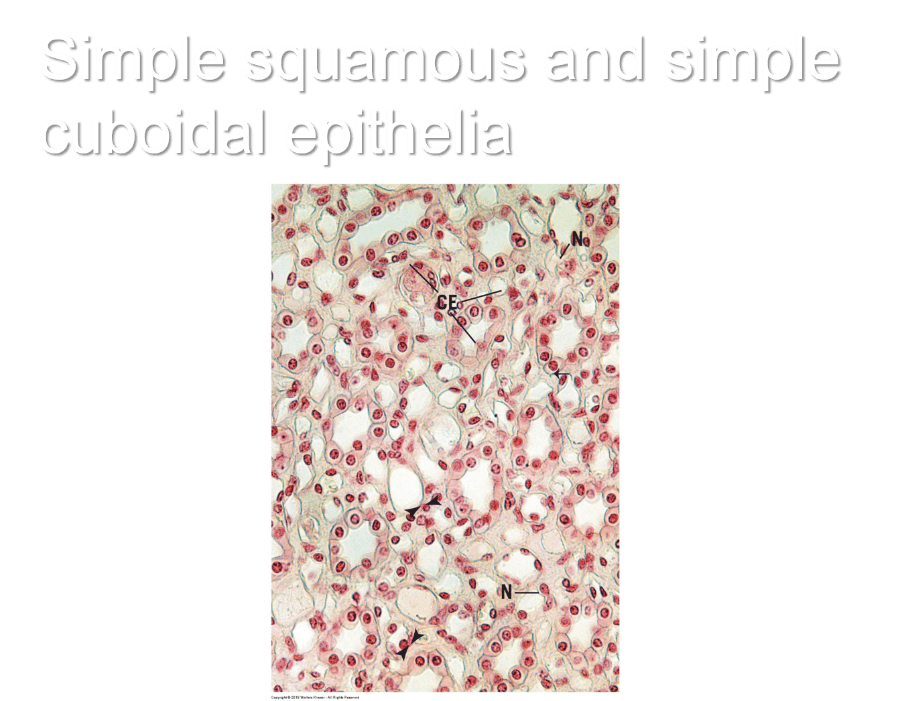
Simple squamous and simple cuboidal epithelia
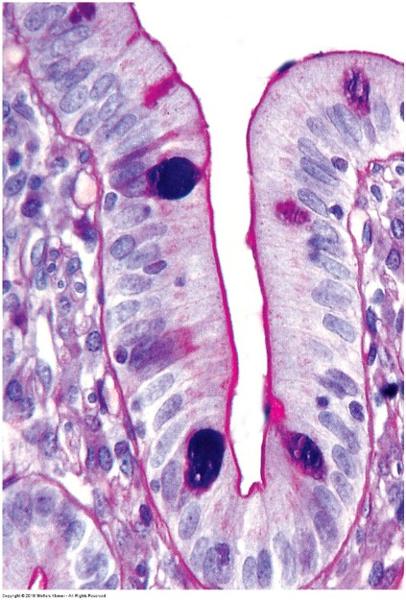
Simple columnar epithelium
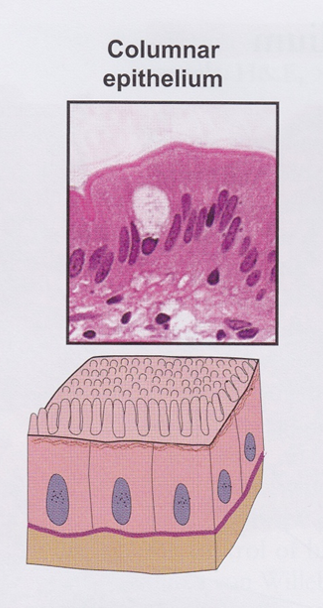
Covers digestive organs (stomach, small and large intestines, and gall bladder)
- Produce and secrete mucus
Microvilli on cells in small intestine
- Absorption of nutrients
In female reproductive tract, cells have cilia
- Transport oocytes and sperm
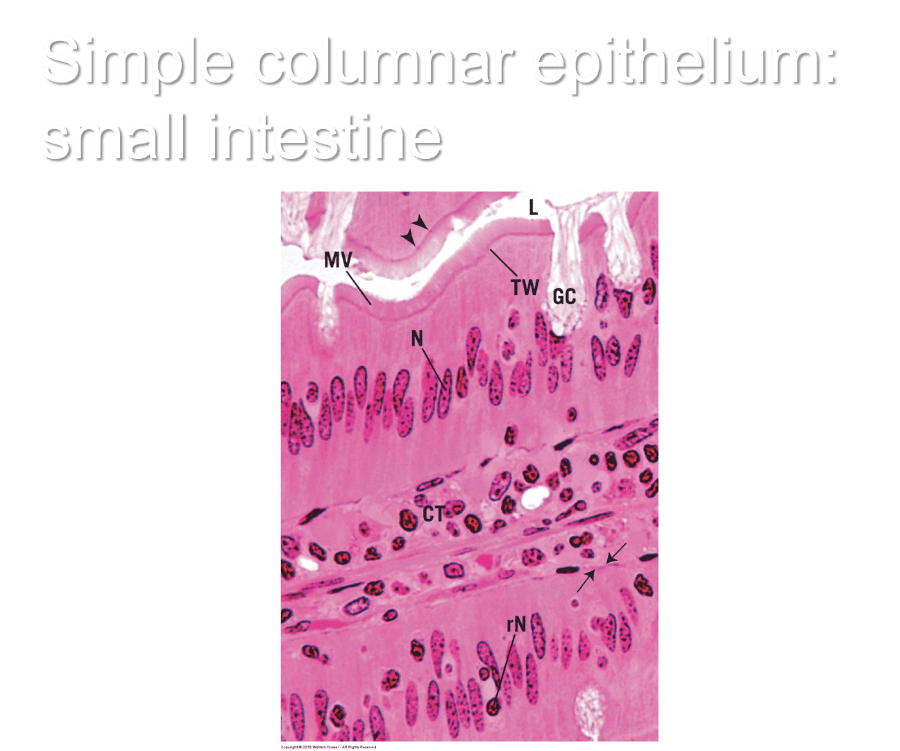
Simple columnar epithelium: small intestine
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
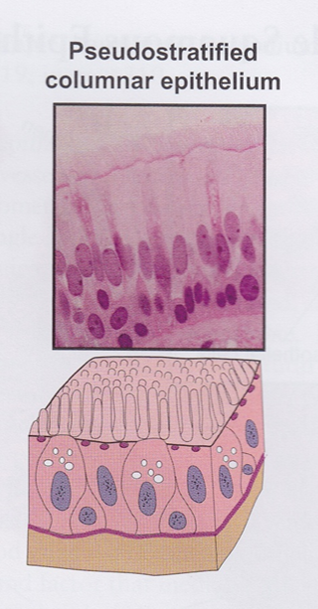
- Lines respiratory passages, epididymis, and vas deferens
- Respiratory passages: motile cilia present
- Goblet cells produce mucus that is transported by cilia to oral cavity (protection)
- Male reproductive tract: nonmotile stereocilia present
- Absorb fluid
- Not all cells reach free surface, but ALL cells rest on basement membrane
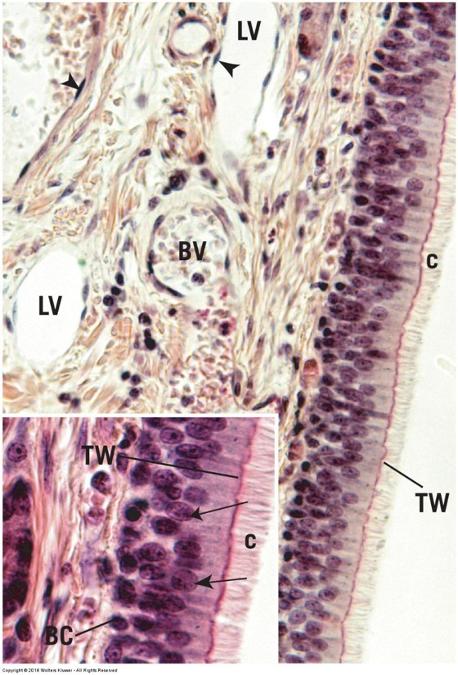
Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
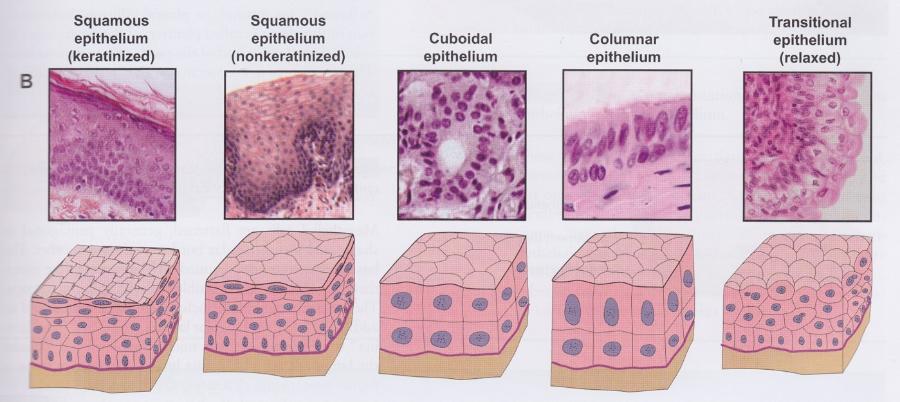
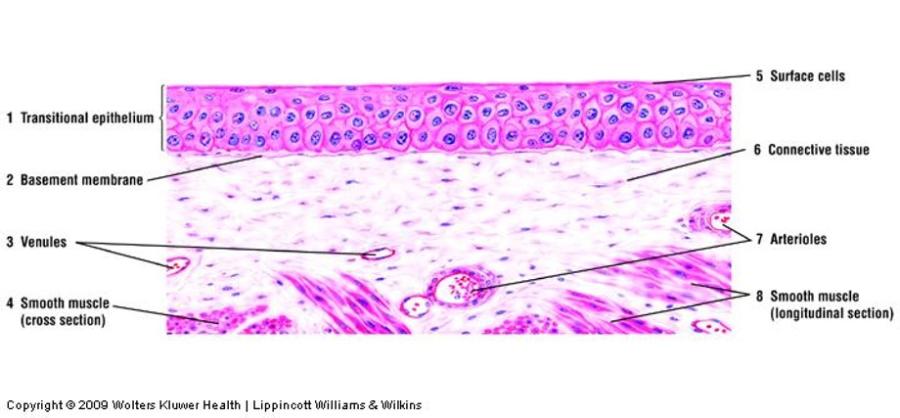
Transitional epithelium
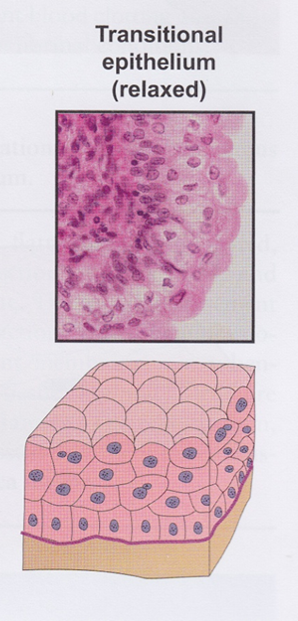
- Multiple cell layers
- Changes shape
- Relaxed state: stratified cuboidal with dome-shaped surface cells
- Stretched state: stratified squamous with squamous-shaped surface cells
- Lines calyxes, pelvis, ureter, and bladder of urinary system
- Also called urothelium
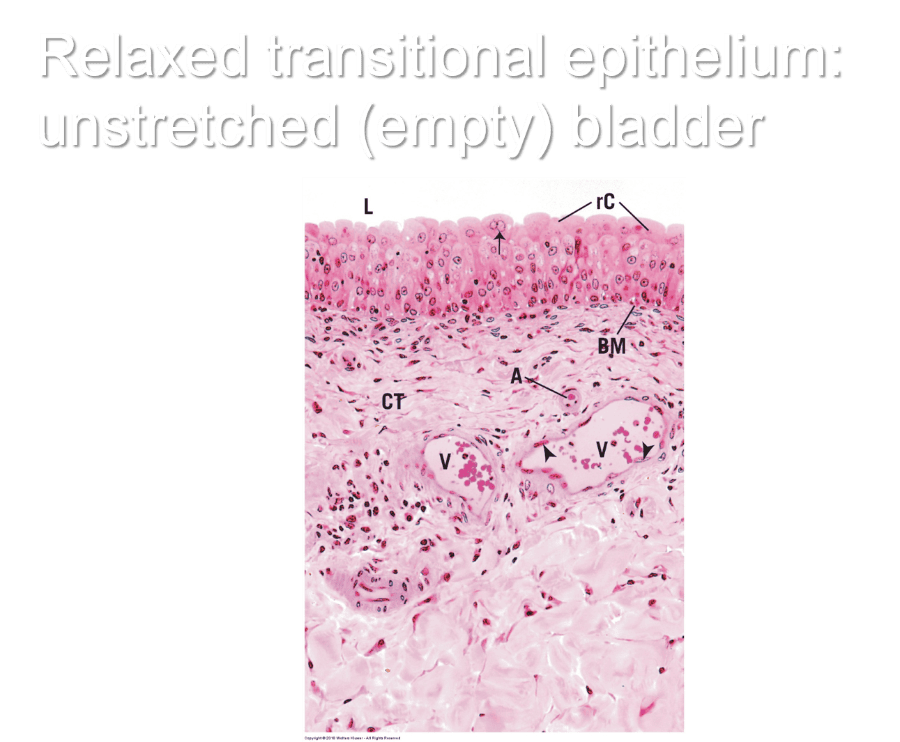
Relaxed transitional epithelium: unstretched (empty) bladder
Stretched transitional epithelium: stretched (full) bladder
Stratified squamous epithelium
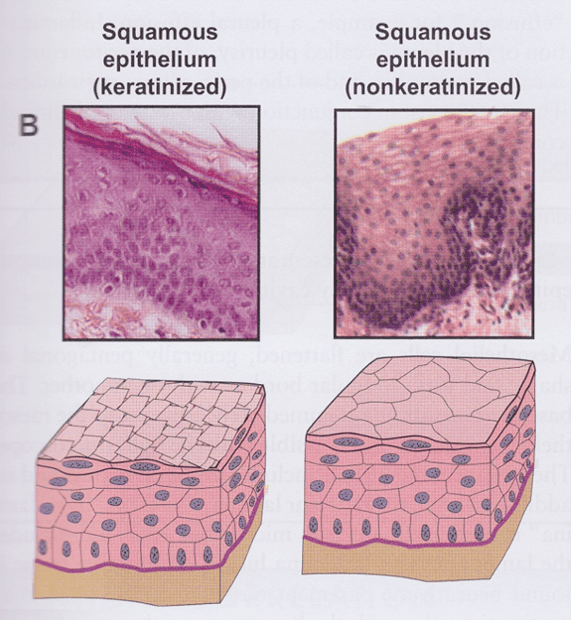
- Multiple cell layers
- Basal cells are cuboidal or columnar
- Migrate to free surface and become squamous in shape
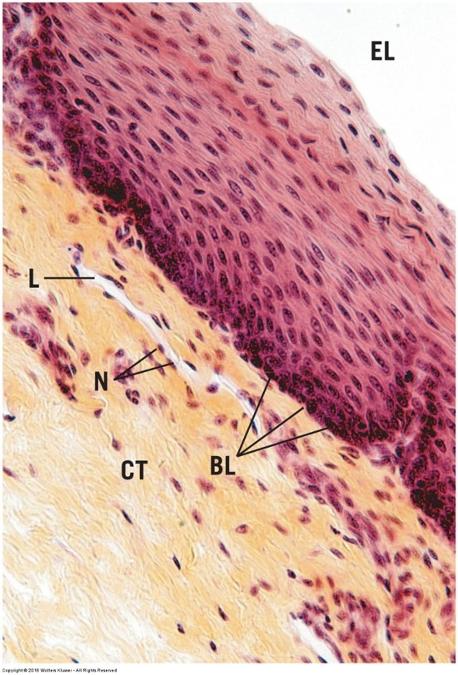
- Nonkeratinized: living surface cells (protects from wear and tear)
- Line moist cavities (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, vagina, and anal canal)
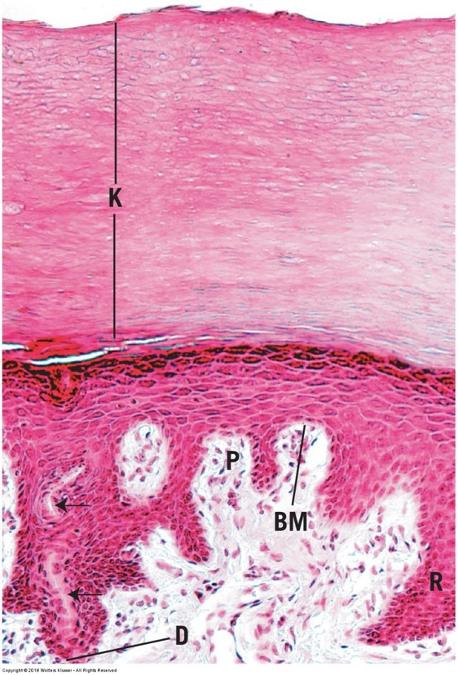
- Keratinized: nonliving surface cells filled with keratin protein (protects from abrasion, desiccation, and bacterial invasion)
- Line external surfaces of body
- Layers called strata
Stratified squamous nonkeratinized: living surface cells
Stratified squamous keratinized: nonliving surface cells
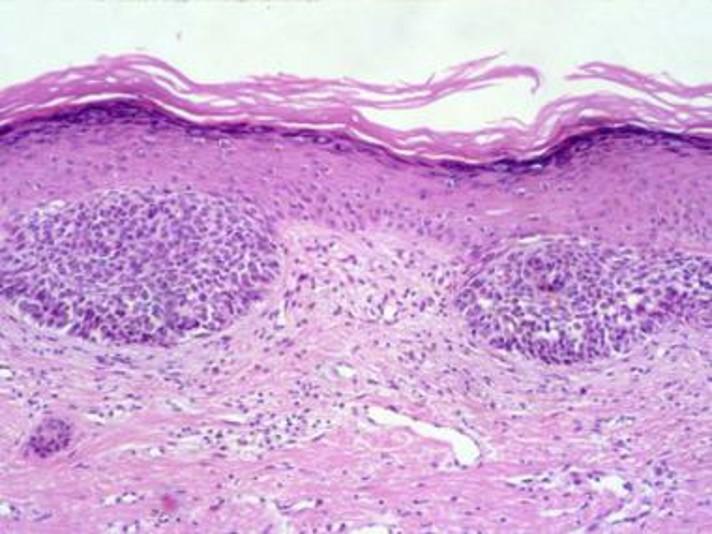
Stratified squamous: Basal cell carcinoma
Stratified cuboidal (or columnar) epithelium
- Two layers of cells
- Surface cells cuboidal or columnar
- Line larger excretory ducts of pancreas, salivary glands, and sweat glands
- Withstands wear and tear
Stratified cuboidal epithelium: excretory duct of salivary gland
Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium: note appearance of more than two rows of nuclei & cilia!
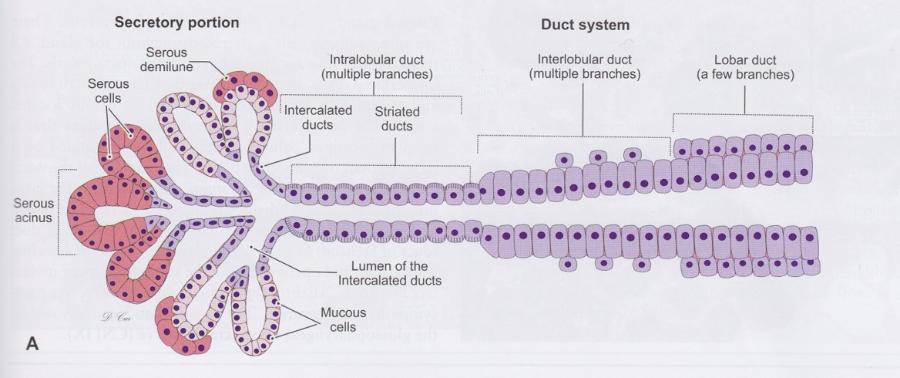
Glandular tissue
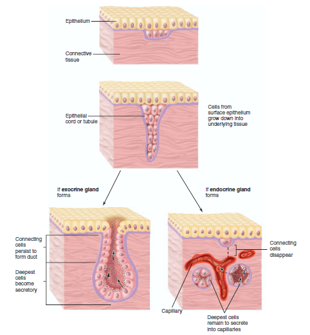
Exocrine glands: secrete products onto surface directly or through ducts
- Secretion may be modified in the ducts
Endocrine glands: lack ducts; secrete into connective tissue--> bloodstream --> target cells; secretions are called hormones
Exocrine Gland Characteristics
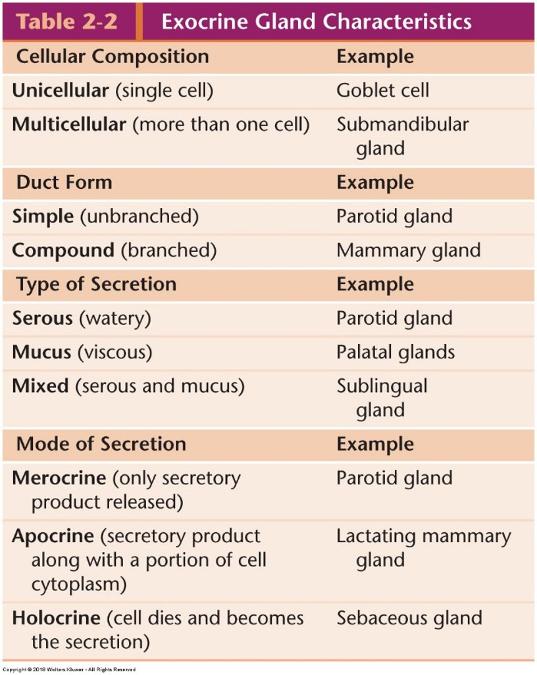
Types of glands
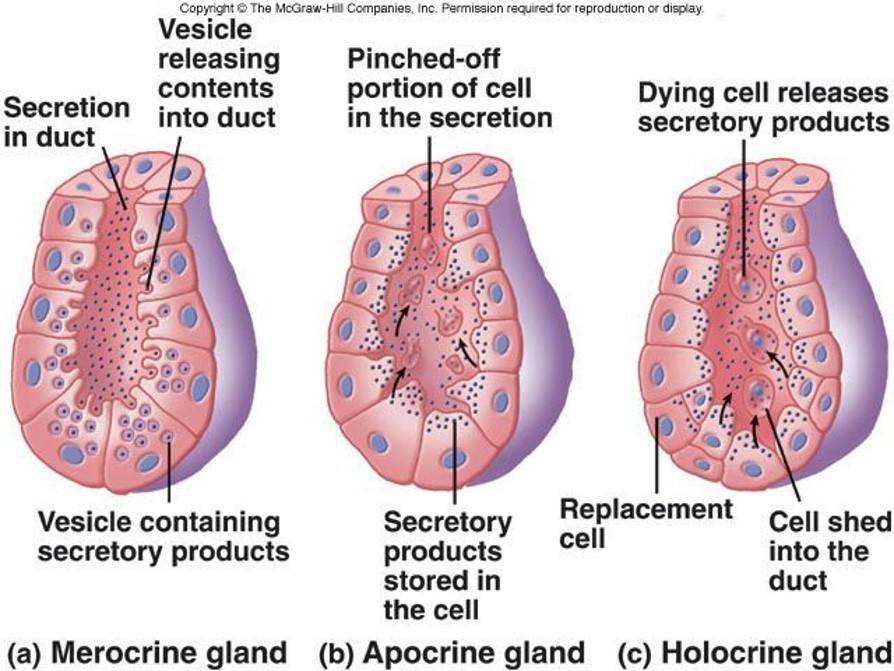
Types of secretions
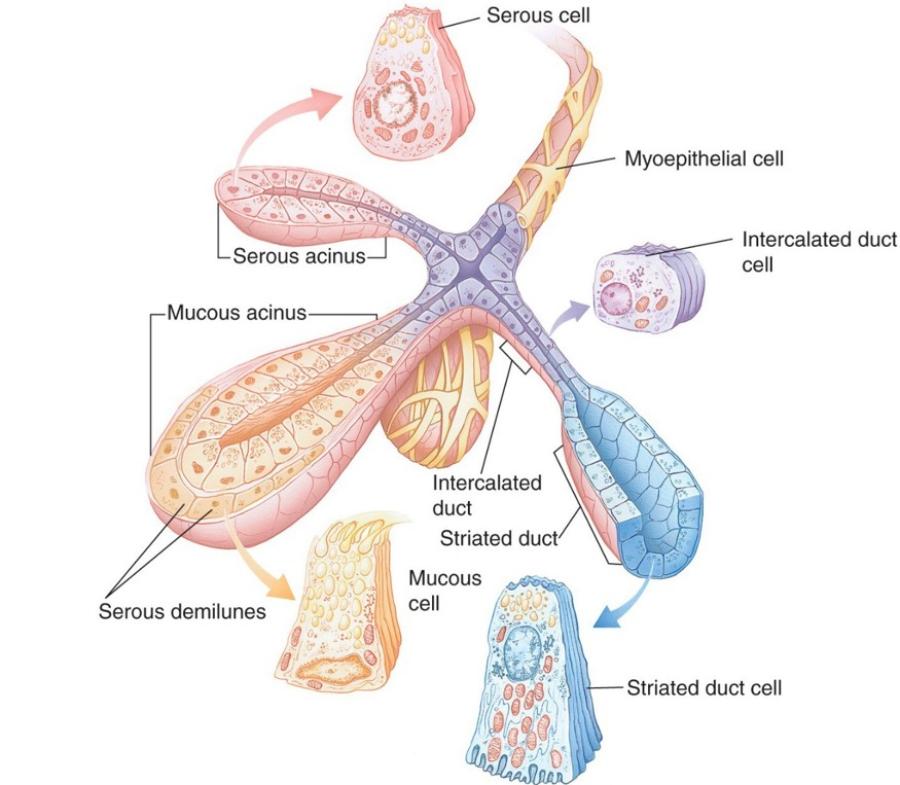
Types of secretions
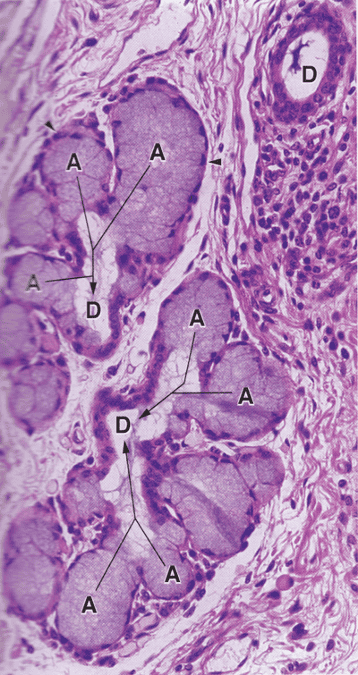
Mucus: viscous secretion that lubricates or protects inner lining of organs; cells appear white or pale purple with H & E
- Goblet cells
- Sublingual salivary glands
- Surface cells of stomach
Types of secretions
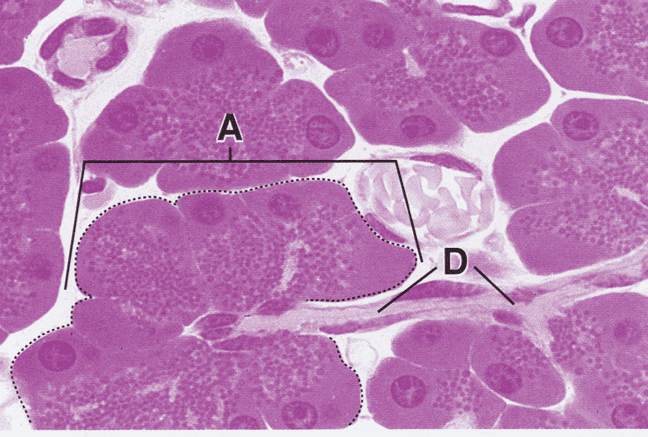
Serous: watery secretion often rich with enzymes; stain intensely with eosin (pink/red)
- Acini of parotid glands
- Acini of pancreas
Types of secretions
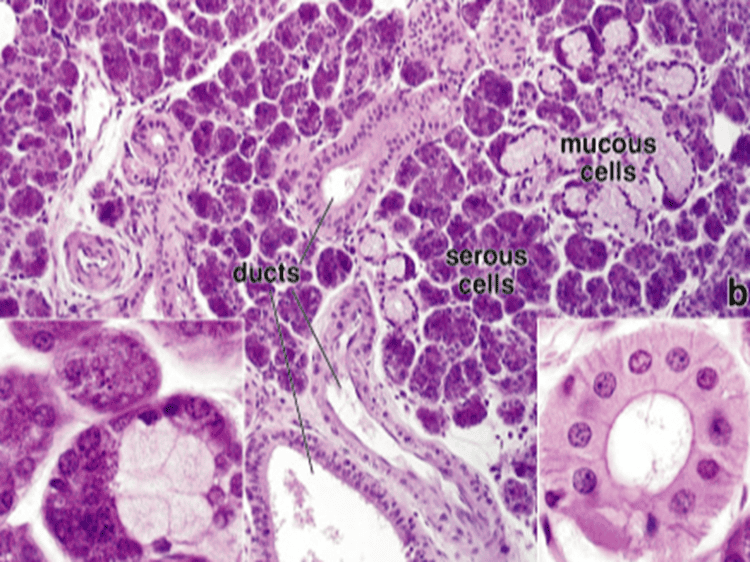
Mixed: mucus and serous secretory cells
- Acini of submandibular glands
Exocrine ducts: epithelia
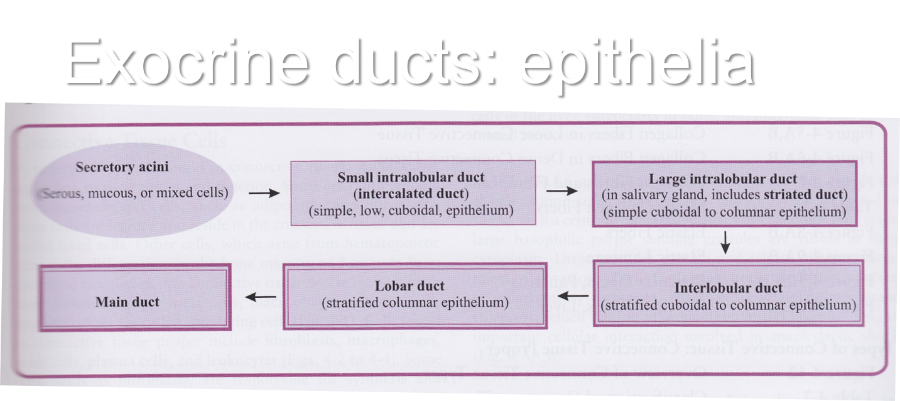
Classifying exocrine glands
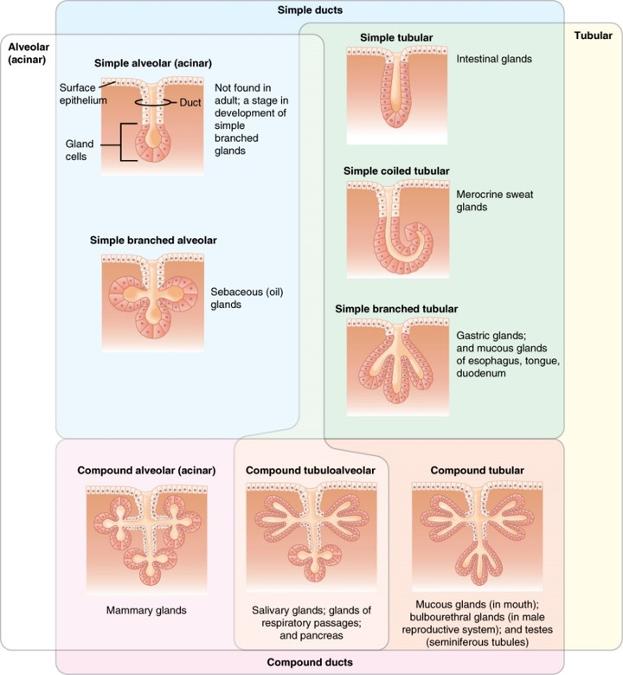
Single cell vs. sheet of cells
Acinus vs. ducts
- Describes where secretions are released vs. transported
Simple vs. compound
- Describes complexity of duct branching
Alveolar (acinar) vs. tubular
- Describes shape of duct ends where secretory acini are located
Unicellular exocrine glands
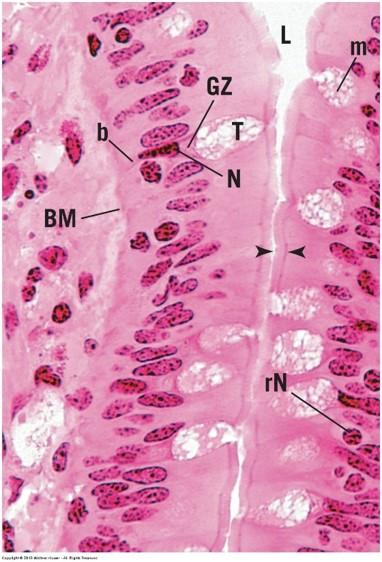
- Single cells distributed among nonsecretory cells
- Goblet cells (mucus secretion)
Multicellular exocrine glands
- More than 1 cell
- Subclassified based on arrangement of secretory cells (parenchyma) and branching of duct elements
- Simplest is sheet of secretory cells at surface
- Multicellular exocrine glands
Sebaceous gland
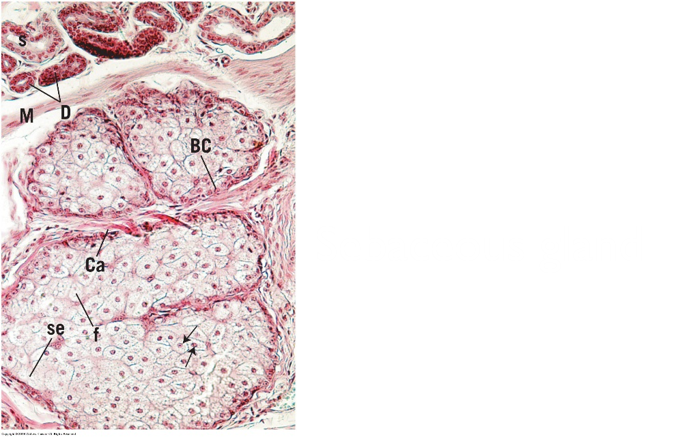
- Multicellular exocrine glands
Mucus-secreting cells
lining the stomach
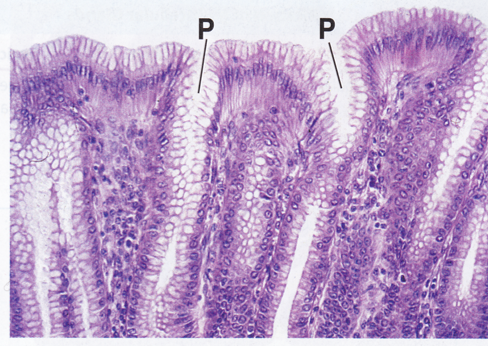
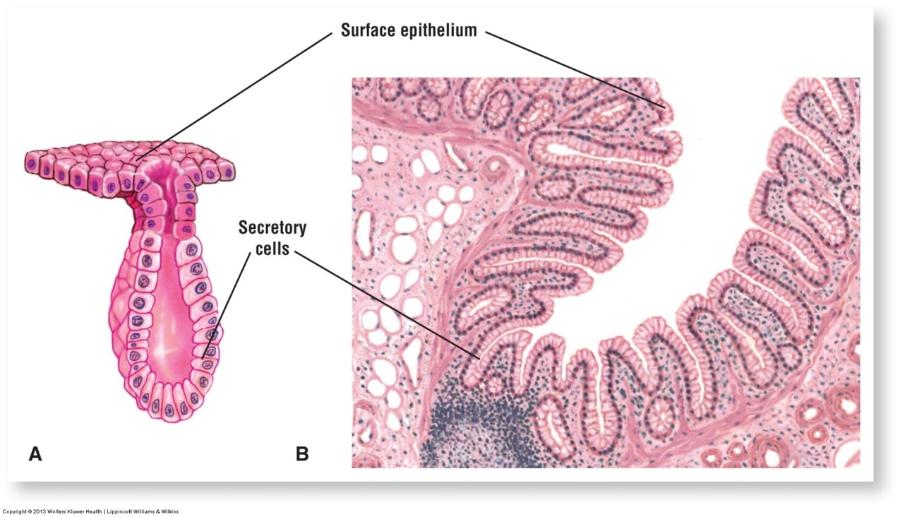
Simple tubular exocrine gland: large intestinal glands
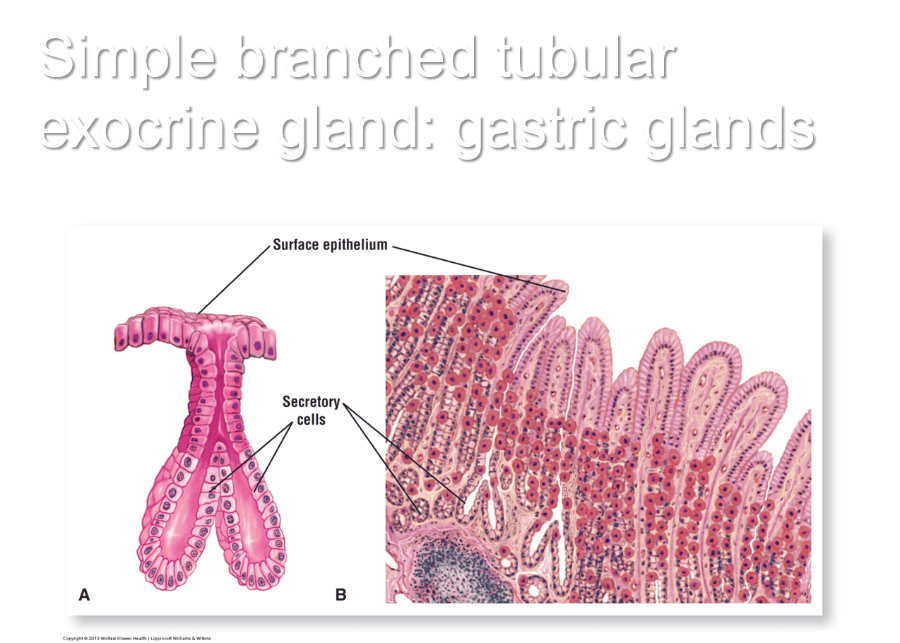
Simple branched tubular exocrine gland: gastric glands
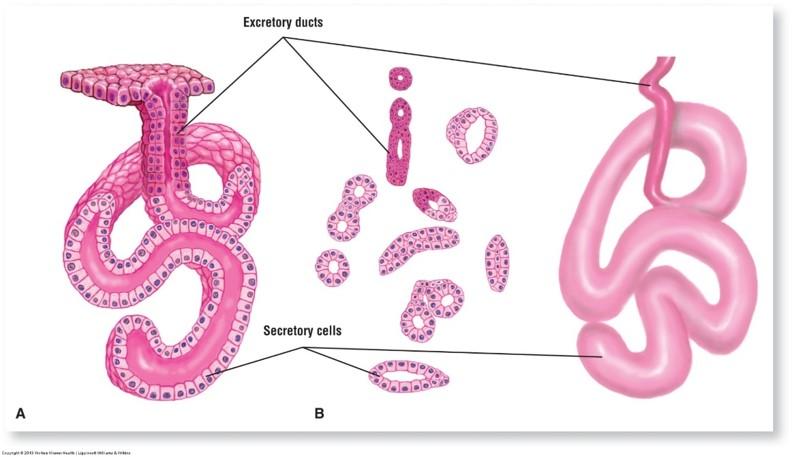
Simple coiled tubular exocrine gland: sweat glands
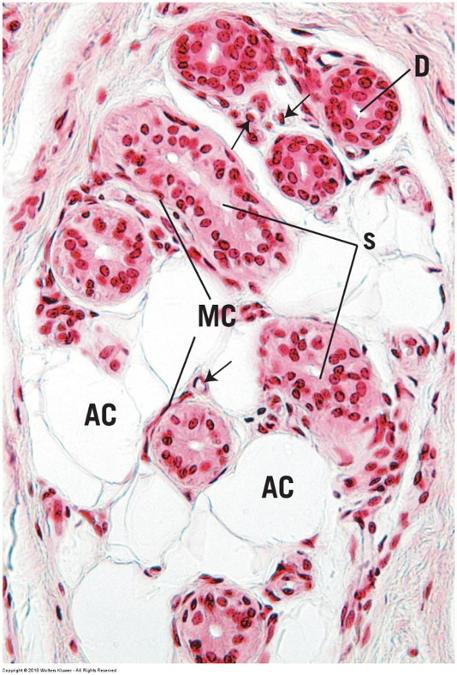
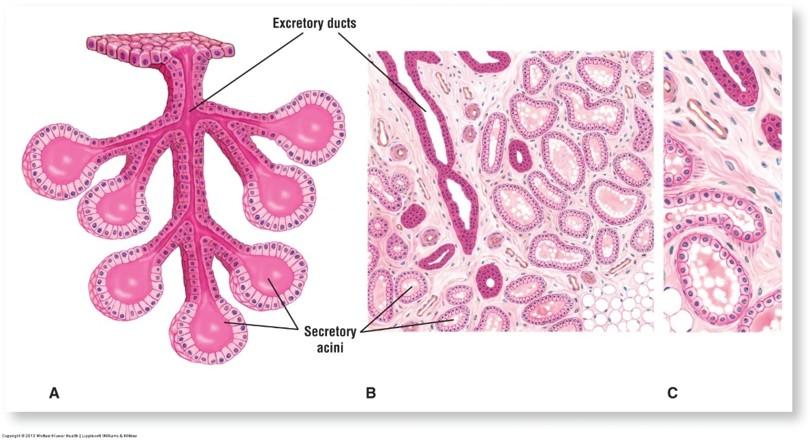
Compound acinar exocrine gland: mammary glands
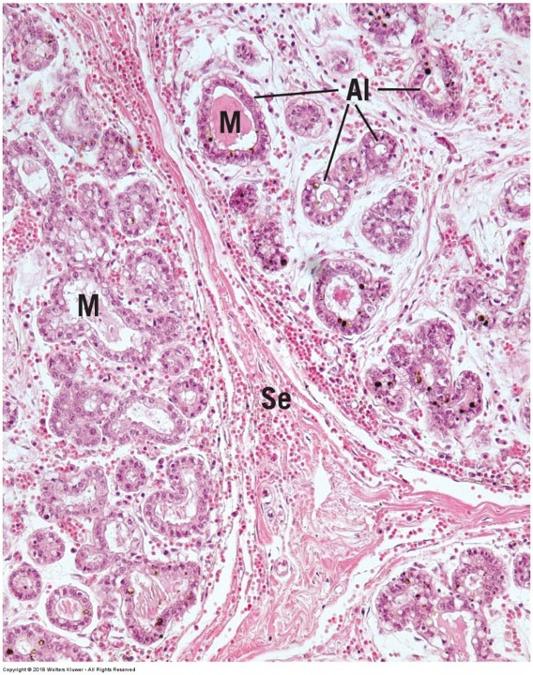
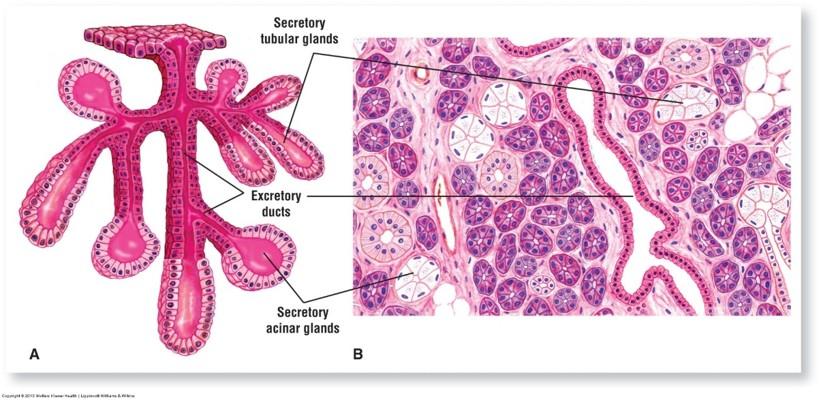
Compound tubuloacinar gland: submandibular salivary gland
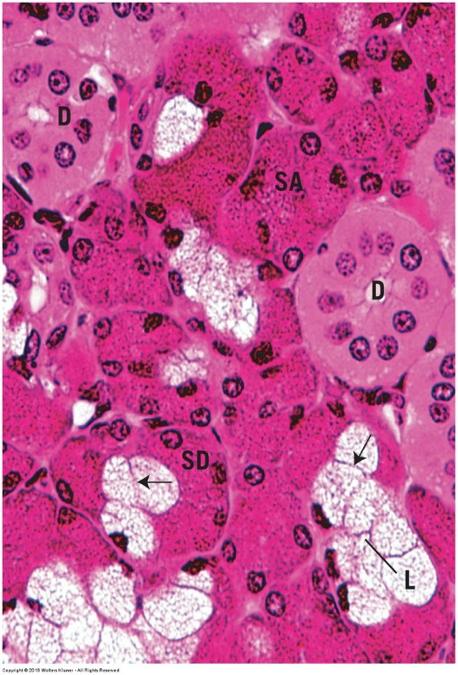
Endocrine glands
- No ducts
- Glands surrounded by capillary networks
- Individual cells found in digestive organs
- Endocrine tissue found in mixed glands that also have exocrine components
- Pancreas and reproductive organs
- Endocrine organs (typical hormone secreting glands)
- Pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, and adrenal glands
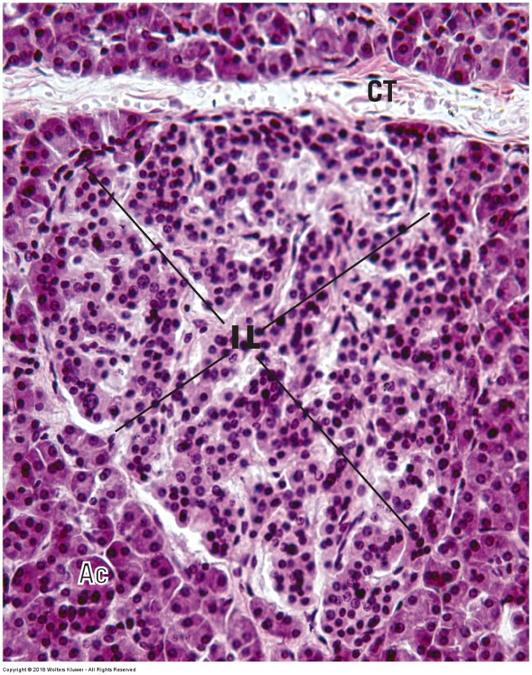
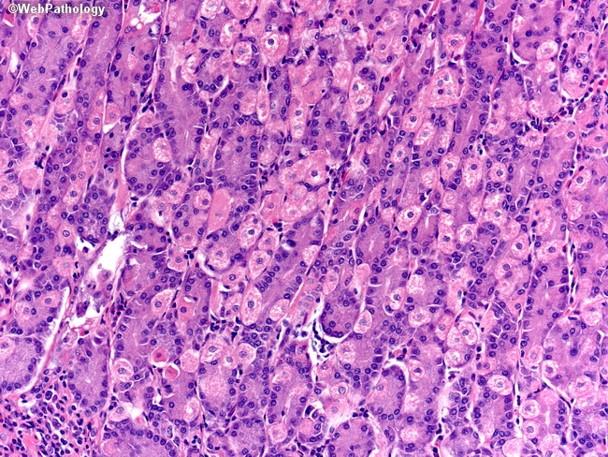
Mixed endocrine/exocrine gland: Pancreas
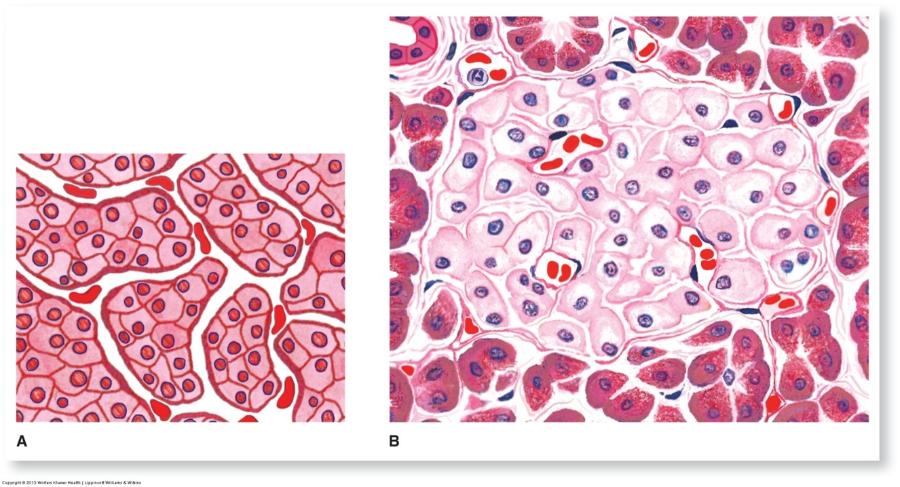
Mixed endocrine/exocrine gland: Pancreas