A & P Test Chapter 3
Functions of the plasma membrane include all of the following except
thermal insulation.
The plasma membrane is composed of
a bilayer of phospholipids.
The plasma membrane includes
- A) integral proteins.
- B) glycolipids.
- C) phospholipids.
- D) cholesterol.
All of the answers are correct
Identify the role of cholesterol in the plasma membrane.
affects membrane permeability
The organelles and the watery component of the cell together is called
cytoplasm
The watery component of the cytoplasm is called
cytosol
Which of the following descriptors regarding cytoplasm is false?
- A) extracellular fluid contains more protein
- B) the material that fills a cell
- C) variable consistency
- D) includes cytoskeleton
- E) includes cytosol
extracellular fluid contains more protein
Most of the ATP required to power cellular operations is produced in the
mitochondria
Synthesis of lipids and glycogen takes place at the
smooth ER.
Which of the following statements concerning mitochondria is false?
- A) The cristae increase the inner surface area of the organelle.
- B) The matrix contains metabolic enzymes involved in ATP synthesis.
- C) Respiratory enzymes are attached to the surface of the cristae.
- D) The mitochondria require carbon dioxide and produce oxygen in the process of energy transformation.
- E) The mitochondria produce most of a cell's ATP.
The mitochondria require carbon dioxide and produce oxygen in the process of energy transformation.
Some cells contain large numbers of mitochondria while others have relatively few or none. This suggests that
cells with large numbers of mitochondria have a high energy demand.
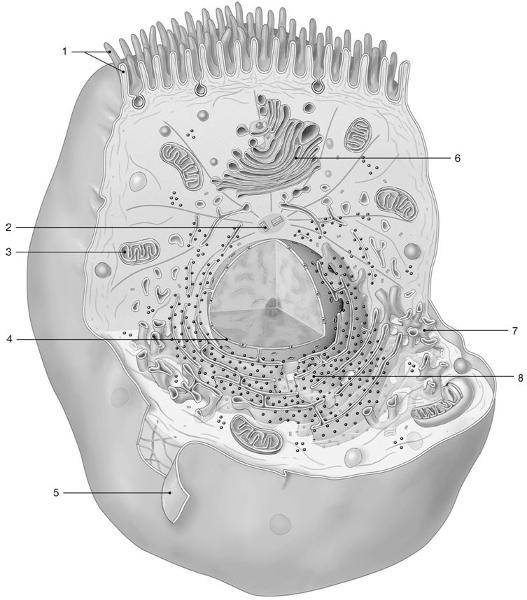
Synthesis of carbohydrates and lipids occurs in the structure labeled
7
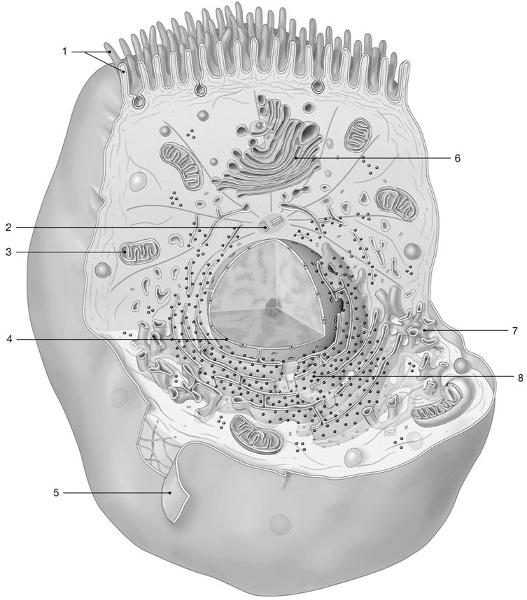
Which structure produces ATP for the cell?
3
Most of a cell's DNA is located in its
nucleus
The control center for cellular operations is the
nucleus
As each codon arrives at the active site of a ribosome, it attracts another molecule containing the anticodon. This molecule is called
tRNA
The process of protein formation directed by mRNA is called
translation
The process of forming mRNA is called
transcription
The mRNA sequence that is complementary to the sequence ATC on DNA is
UAG
The anticodon for the triplet UCA is
AGU
The unit of DNA that specifies a certain amino acid is called a ________, the same unit of mRNA is called a ________, which, during protein synthesis, is matched by the ________ of tRNA.
triplet; codon; anticodon
The duplication of DNA is called ________, the copying of DNA to mRNA is called ________, and the reading of the mRNA by the cell to make a protein is called ________.
replication; transcription; translation
What would the complimentary DNA template strand be to produce the mRNA sequence of
ACA - GTT
A DNA nucleotide is composed of
one nitrogen base, deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate group.
The movement of oxygen from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration is an example of
diffusion
A solution that contains a lower osmotic pressure than the cytoplasm of a cell is called
hypotonic
Which of the following best describes osmosis?
diffusion of water from a greater to a lesser water concentration across a selectively permeable membrane
A blood cell undergoes crenation when it is placed in a(n) ________ solution.
hypertonic
Hemolysis may occur when a blood cell is placed into a(n) ________ solution.
hypotonic
The process by which molecules such as glucose are moved into cells along their concentration gradient with the help of membrane-bound carrier proteins is called
facilitated diffusion.
Facilitated diffusion differs from ordinary diffusion in that
the rate of molecular movement is limited by the number of available carrier molecules.
A process that requires cellular energy to move a substance against its concentration gradient is called
active transport.
The intake of materials from the extracellular fluid using vesicles is called
endocytosis
Two types of vesicular transport include
endocytosis and exocytosis.
The principal cations in our body fluids are ________ and ________.
sodium; potassium
In order to maintain cellular homeostasis, an exchange pump ejects ________ ions from the cell and imports ________ ions.
sodium; potassium
Endocytosis is a
method for transporting substances into the cell.
A defense cell engulfing a bacterium illustrates
phagocytosis
Which of the following statements about a cell's resting membrane potential is incorrect?
Inside slightly more positive than outside.
A cell duplicates its chromosomes during the ________ phase.
S
Mitosis is to somatic cells as meiosis is to ________ cells.
reproductive
During mitosis, two daughter cells form, each of which has
the same number of chromosomes as the original cell.
If a cell has 18 chromosomes and undergoes mitosis how many chromosomes would each daughter cell have?
18
The genetically programmed death of cells is called
apoptosis
Cancer cells
may exhibit metastasis.
The cytoplasm contains the fluid cytosol and the suspended
organelles
The nucleus is surrounded by the
nuclear envelope.
A molecule of ________ contains all the codons needed to produce a particular polypeptide.
mRNA
During the synthesis of proteins, amino acids are assembled in the proper sequence because each tRNA molecule that brings them to the ribosome has a(n) ________ that binds to a complementary codon in the mRNA.
anticodon
A point mutation involves a change in
a single nucleotide.
The membrane potential in an undisturbed cell is called its
resting membrane potential.
Nuclear division of somatic cells is known as
mitosis
The process of duplicating chromosomes prior to cell division is called
replication.
A malignant neoplasm is often called a(n)
cancer
Differentiate between transcription and translation.
In transcription, RNA polymerase uses the nucleotide sequence on DNA to construct a complementary strand of mRNA. In translation, ribosomes use information carried by the mRNA strand and tRNA to synthesize the corresponding polypeptide.
Define osmosis
Osmosis is the transfer of water across a semipermeable membrane due to a difference in concentration of impermeable solute.
What role does the sodium-potassium exchange pump play in stabilizing the resting membrane potential?
By ejecting sodium ions from the cytosol and absorbing potassium ions from the extracellular fluid, the sodium-potassium pump maintains the K concentration gradient that leads to a negative resting membrane potential.