Activity 2: Studying the Microscopic Anatomy of a Lymph node, the Spleen, and a Tonsil
The lymph node is enclosed in what?
A fibrous capsule
From the fibrous capsule of the lymph node, what extends inwards to divide the node into several compartments?
Trabeculae
The trabeculae is composed of what tissue type?
Connective tissue
The cortex contains what type of center?
Germinal center
The germinal centers contain what rapidly-dividing group of cells?
B lymphocytes/cells
The rest of the cortical cells (cortex cells) are primarily what group of cells?
T cells
The remaining T lymphocytes/cells in the cortical or cortex cells do what in regard to circulation?
Circulate continuously from the blood into the nodes, and then from exiting the nodes in the lymphatic stream
Lymphocytes are arranged in a cordlike fashion in what portion of the lymph nodes?
Medulla portion
Most medullary cells are what type of cells?
Macrophages
Macrophages are important for what 2 functions?
1. Phagocytosis
2. Antigen-presentation to the T cells
Lymph enters the lymph nodes through what vessels?
Afferent vessels
Lymph circulates through what in the lymph nodes?
Lymph sinuses
Lymph leaves the lymph nodes through what vessels located at which structure of the nodes?
Leaves through efferent vessels at the hilum
What is the benefit of having fewer efferent vessels than afferent vessels?
The lymph stagnates within the node
Why is it beneficial to have lymph stagnate within the nodes? (Hint: 2 reasons)
1. Allows time to generate an immune response
2. Allows macrophages to remove debris from the lymph before it reenters the blood vascular system
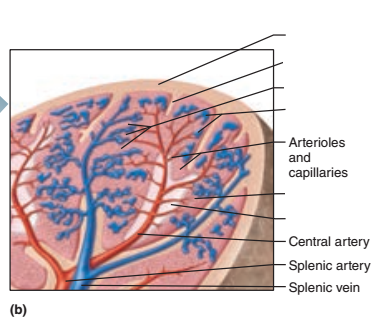
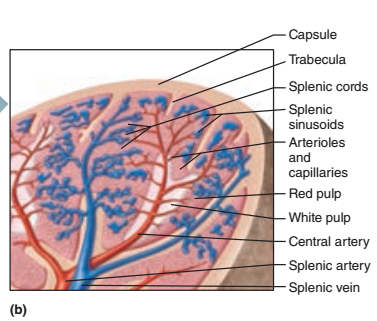
In the spleen, the white pulp are areas of what cells suspended in what fibers?
Areas of lymphocytes suspended in reticular fibers
The white pulp is clustered around what vessels?
Central arteries
The red pulp of the spleen has what 3 components? (Hint: sinusoids, tissue, cell type)
1. Splenic sinusoids
2. Reticular tissue
3. Macrophages
The macrophages in the red pulp are called what?
Splenic cords
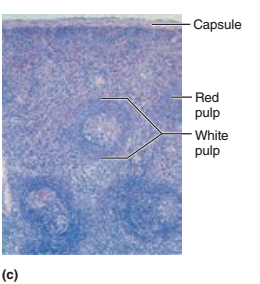
Which pulp is responsible for the immune functions of the spleen?
White pulp
Why is the white pulp responsible for the immune functions of the spleen?
It contains primarily lymphocytes
Macrophages in the red pulp remove what 5 substances?
1. Worn-out RBCs
2. Debris
3. Bacteria
4. Viruses
5. Toxins
In tonsils, what contains the germinal centers?
Lymphoid follicles
The lymphoid follicles and germinal centers are surrounded by what cell type?
Lymphocytes
What is the function of the tonsilar crypts of the tonsils?
Trap bacteria and other foreign material.
How are bacteria in the tonsils destroyed eventually?
Eventually, they work their way into the lymphoid tissue and are destroyed.
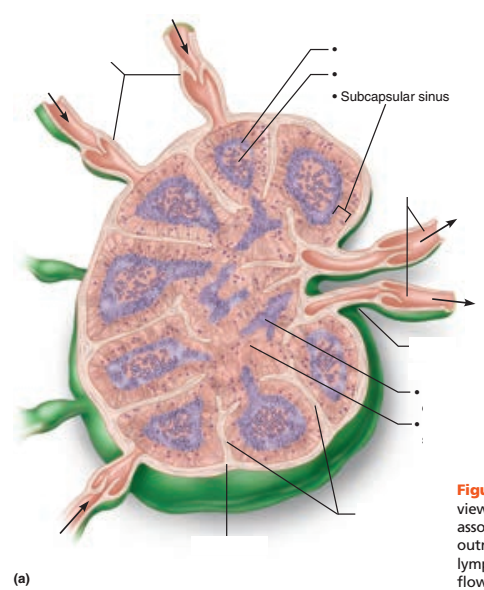
Identify the blanks.
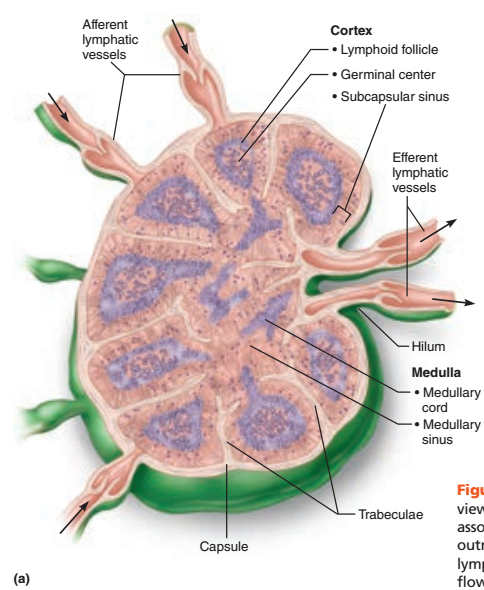
Identify the blanks.
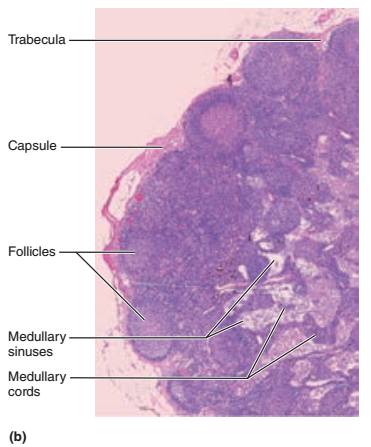
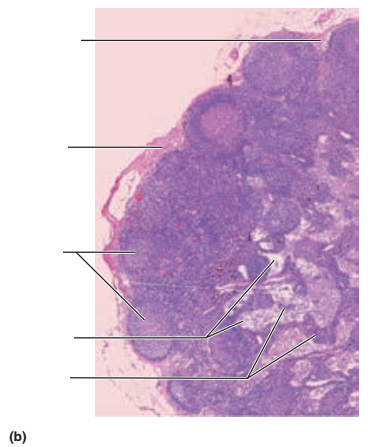
Identify the blanks.
Identify the blanks.
Identify the blanks.
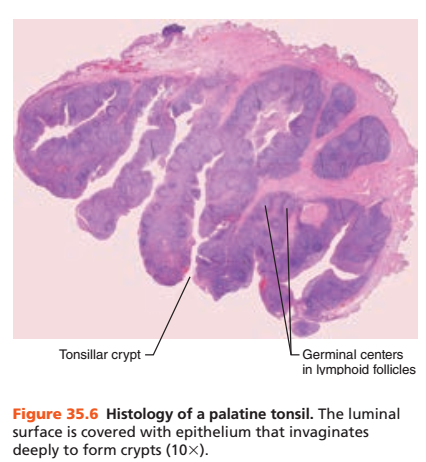
1. Identify the blanks.
2. What lymphoid organ is this slide?
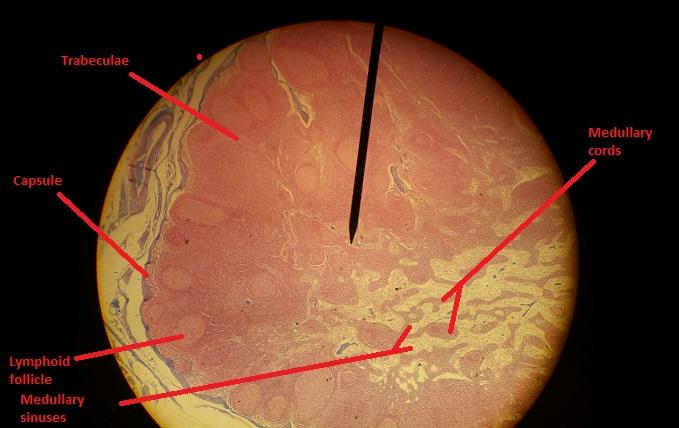
2. Lymph node
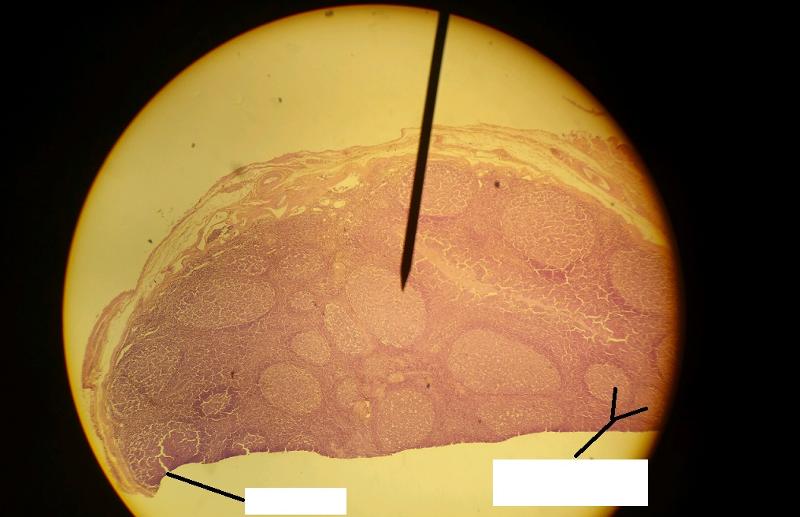
1. Identify the blanks.
2. What lymphoid organ is this slide?
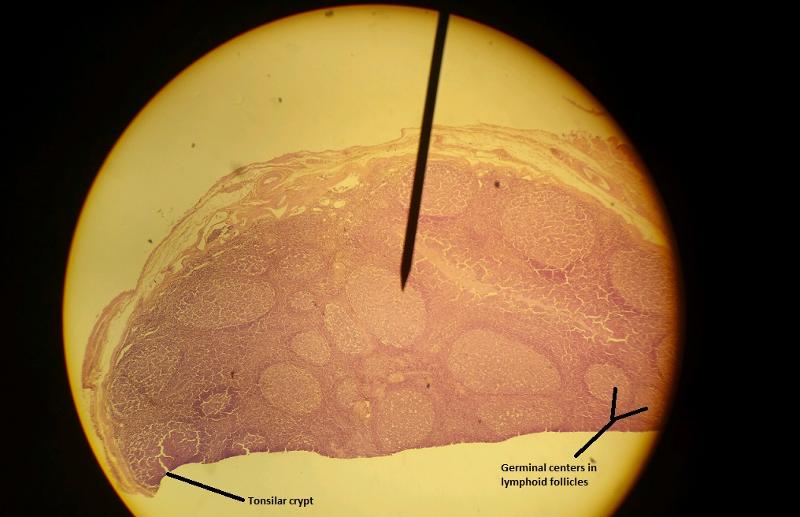
2.Tonsil
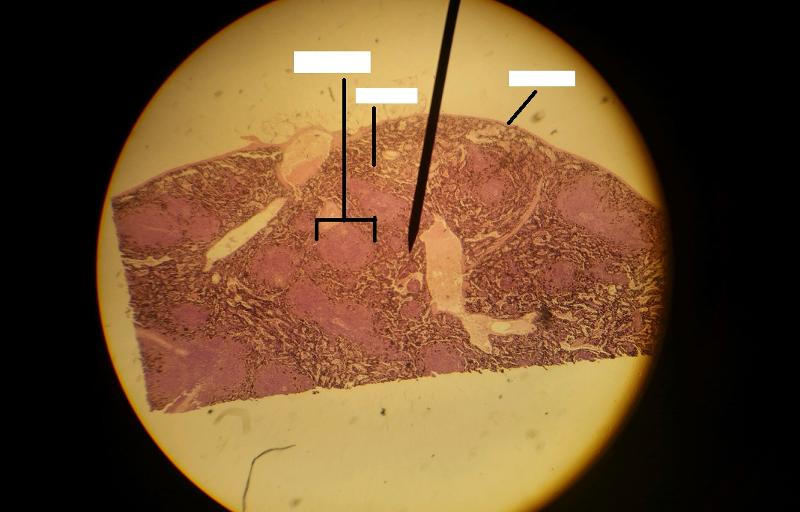
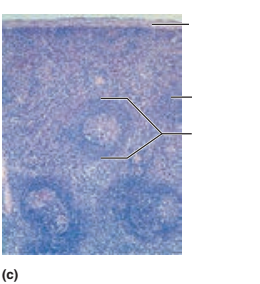
1. Identify the blanks.
2. What lymphoid organ is this slide?
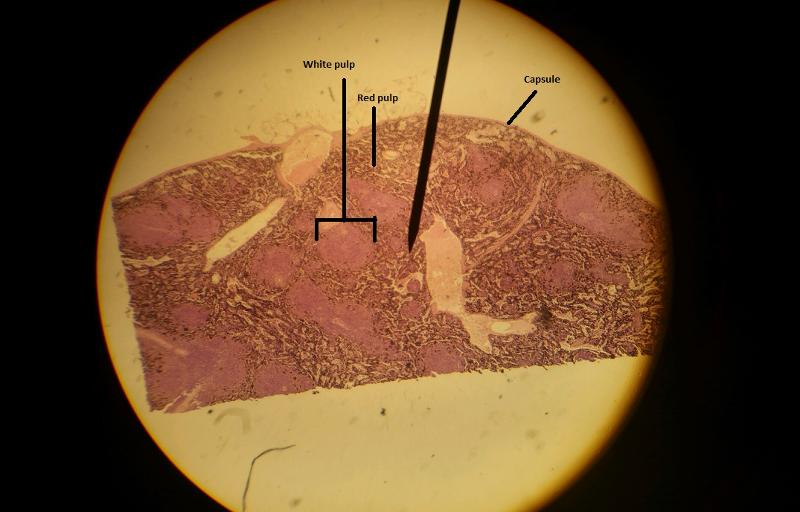
2. Spleen