Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Identifying Accessory Eye Structures
The adult human eye measures about how much in diameter?
2.5 cm (1 inch)
What fraction of the eye's anterior surface is observable?
1/6th
The remaining 5/6th of the eye that is not observable is enclosed and protected by what 2 features?
1. A cushion of fat
2. The walls of the bony orbit
What are the 5 accessory structures of the eye?
1. Eyebrows
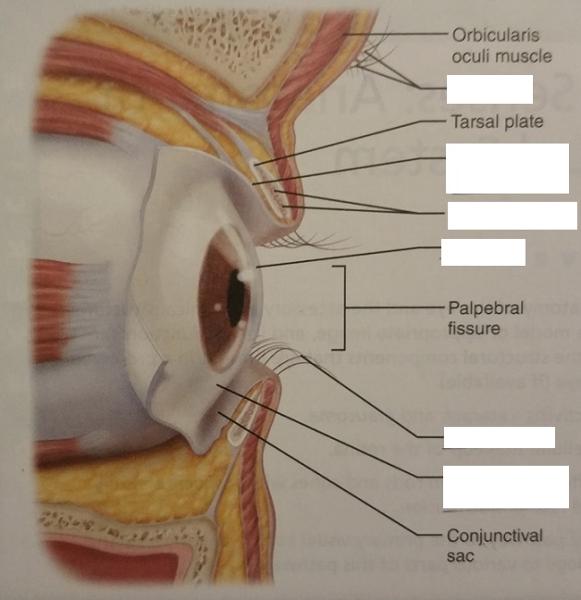
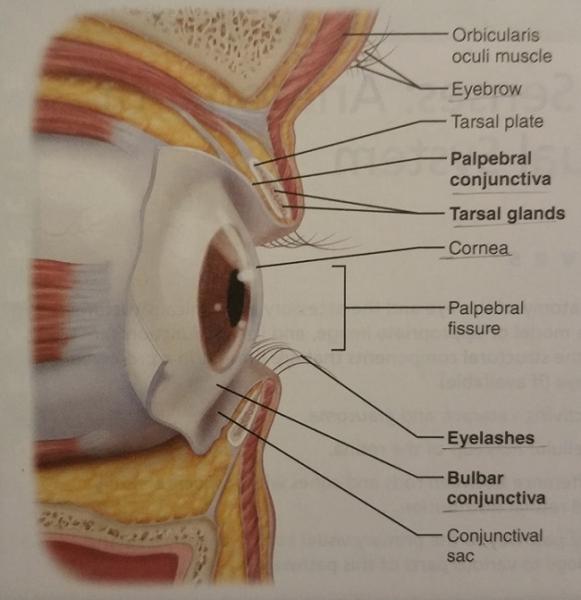
2. Eyelids
3. Conjunctivae
4. Lacrimal apparatus
5. Extrinsic eye muscles
What is the anterior white of the eye called?
Bulbar conjunctiva
The eyebrows are located where?
On the supraorbital margins
What are the 2 functions of the eyebrows?
1. Shade the eyes
2. Prevent sweat from entering the eyes
What are the 2 functions of the eyelids?
1. Protect the eyes
2. Spread lacrimal fluid (tears) with blinking
An eyelid is also called what?
Palpebral conjunctiva
The tarsal glands are modified from what type of glands?
Modified sebaceous glands
1. What is the function of the tarsal glands?
2. Where can the tarsal glands be found?
1. Secrete an oily secretion to lubricate the surface of the eye.
2. Embedded in the tarsal plate of the eyelid.
1. Ciliary glands are what 2 types of glands?
2. Where may ciliary glands be found?
1. They are...
- Sebaceous glands
- Modified sweat glands
2. Found between the eyelash follicles
What is the function of the ciliary glands?
Secrete an oily secretion that lubricates the eye surface and the eyelashes
An infection of the ciliary gland is called what?
Sty
What is the conjunctivae?
A clear mucous membrane
The conjunctivae lines what 2 features?
1. Eyelids (palpebral conjunctivae)
2. Bulbar conjunctiva (anterior white of the eye)
What is the function of the conjunctivae?
Secrete mucus to lubricate the eye
Inflammation of the conjunctivae results in what disease?
Conjunctivitis (aka pinkeye)
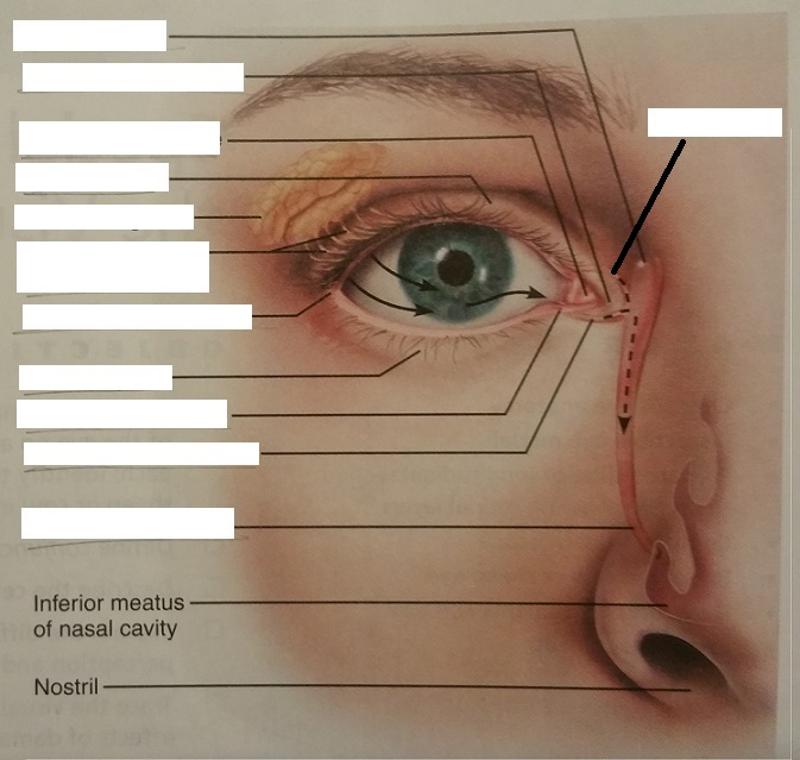
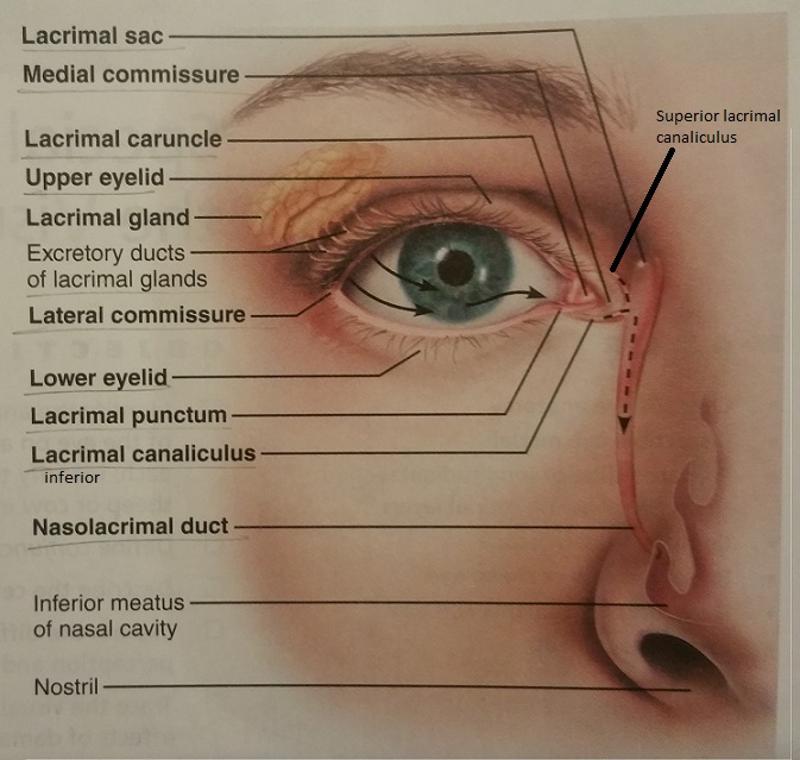
What are medial and lateral commissures?
Junctions where the eyelids meet medially and laterally
1. What is the function of the medial and lateral commissures?
2. Which commissure contains the lacrimal caruncle?
1. Form the corners of the eyes.
2. Medial commissure
The lacrimal caruncle contains what 2 types of glands?
1. Sebaceous glands
2. Sweat glands
What is the function of the lacrimal caruncle?
Secretes an oily secretion for lubrication of the eye.
The lacrimal apparatus includes what 2 structures of the eye?
1. Lacrimal glands
2. Excretory ducts of lacrimal glands
What is the function of the lacrimal apparatus?
Protects the eye by keeping it moist.
What is the function of the excretory ducts of lacrimal glands?
Allow lacrimal fluid to enter the surface of the eye.
What action spreads the lacrimal fluid?
Blinking
Describe the lacrimal gland's location in 2 ways in regard to the orbit of the eye.
1. Located in the superior aspect of the eye orbit
2. Located in the lateral aspect of the eye orbit
What is the function of the lacrimal gland?
Secretes lacrimal fluid
Lacrimal fluid contains what 3 products?
1. Mucus
2. Antibodies
3. Lysozyme
What are the lacrimal puncta and where may they be found?
2 tiny openings on the medial margin of each eyelid.
What is the function of the lacrimal puncta?
Allow lacrimal fluid to drain into the superior and inferior lacrimal canaliculi
What are the lacrimal canaliculi?
Two canals (superior and inferior) that are located on the eyelids
What is the function of the lacrimal canaliculi?
Drain lacrimal fluid into the lacrimal sac
Where is the lacrimal sac located?
In the medial orbital wall
What is the function of the lacrimal sac?
Allow lacrimal fluid to drain into the nasolacrimal duct
What is the nasolacrimal duct and what cavity does it empty into?
It is a single tube that empties into the nasal cavity
What is the function of the nasolacrimal duct?
Allows lacrimal fluid to flow into the nasal cavity
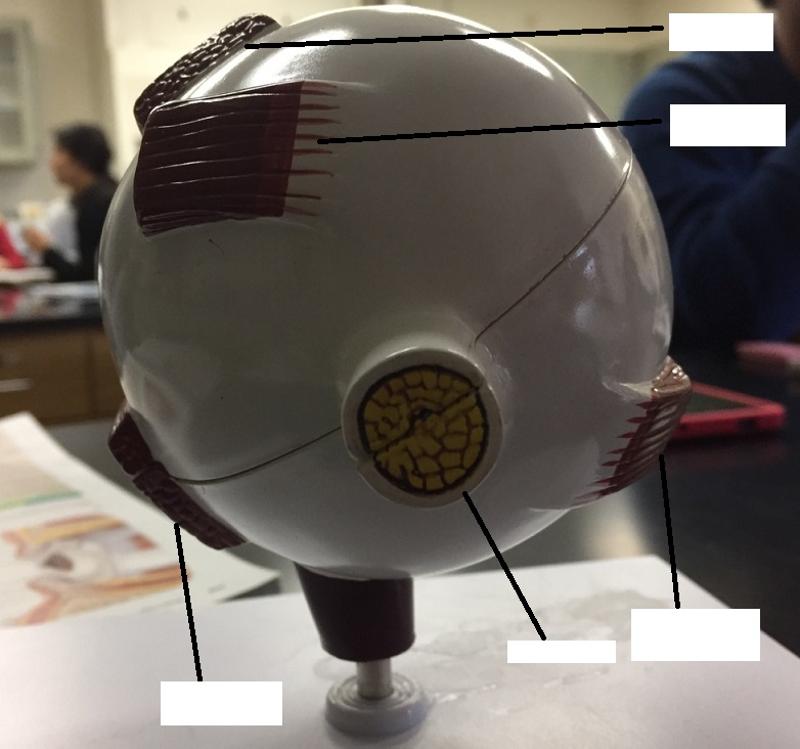
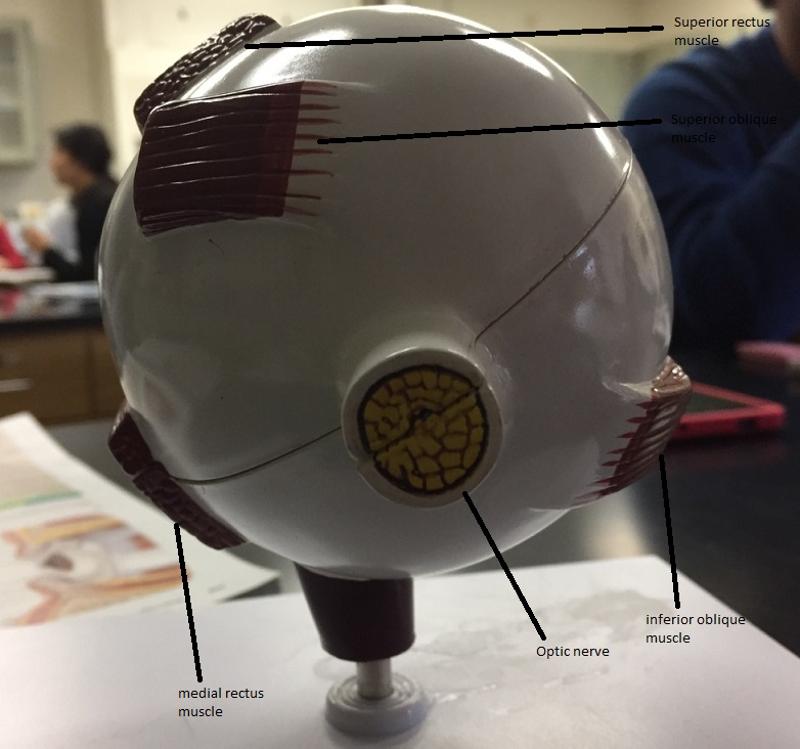
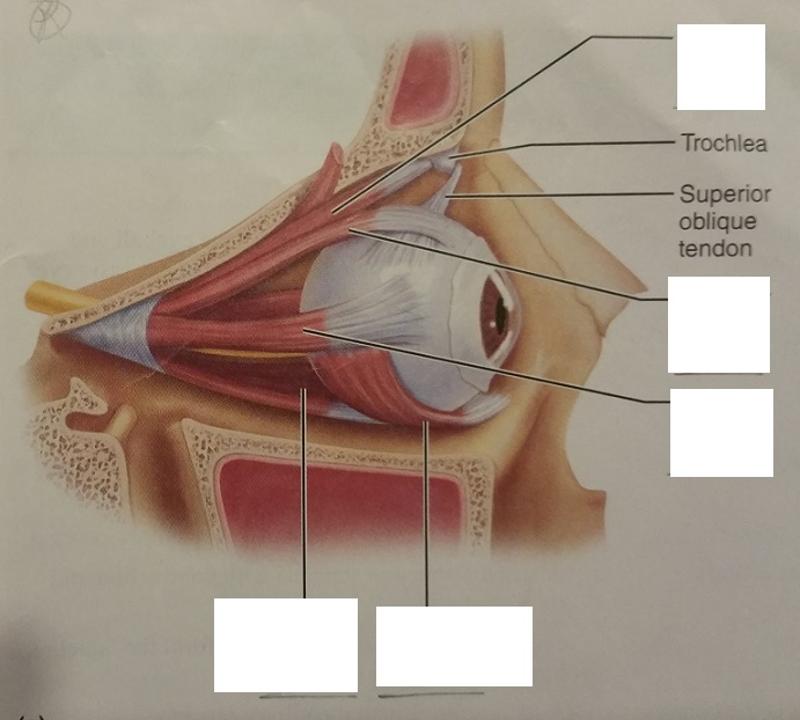
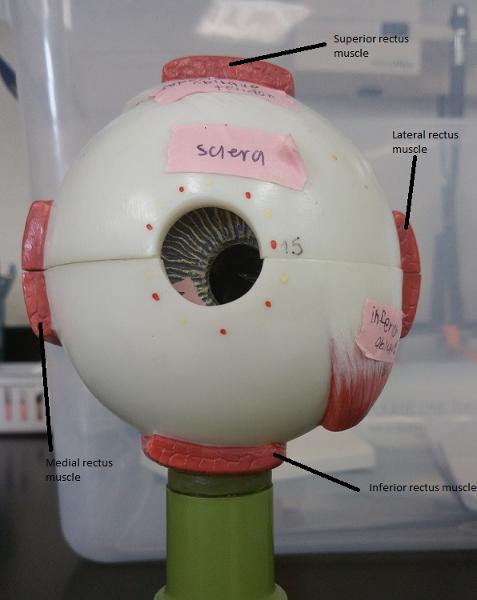
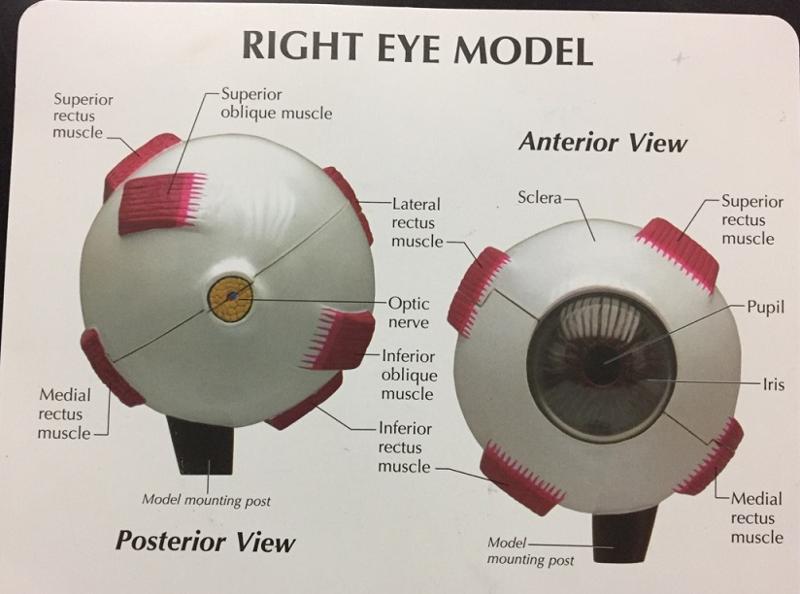
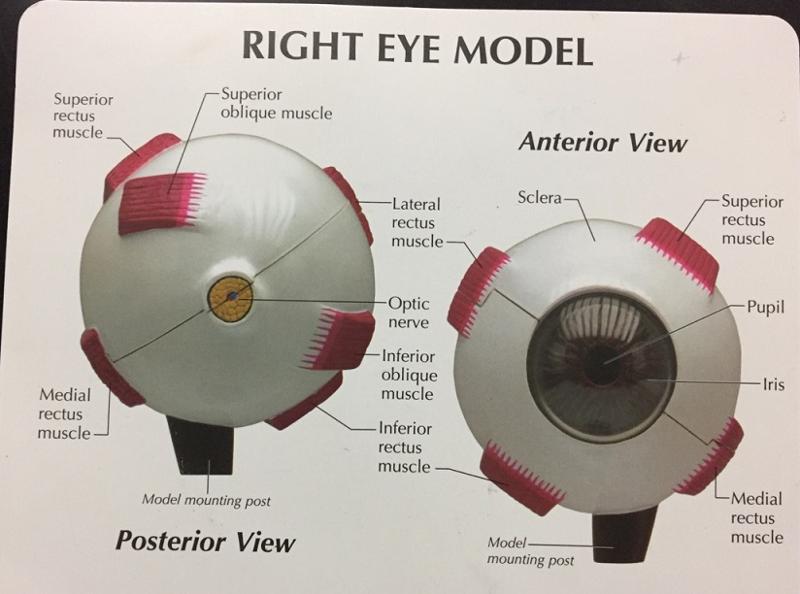
1. How many extrinsic eye muscles are there?
2. What are the extrinsic eye muscles then?
1. 6
2. The extrinsic eye muscles are...
- 4 recti muscles
- 2 oblique muscles
What is the function of the lateral rectus eye muscle?
Moves eye laterally
What is the function of the medial rectus eye muscle?
Moves eye medially
What are the 2 functions of the superior rectus eye muscle?
1. Elevates eye
2. Turns it medially
What are the 2 functions of the inferior rectus eye muscle?
1. Depresses eye
2. Turns it medially
What are the 2 functions of the inferior oblique eye muscle?
1. Elevates eye
2. Turns it laterally
What are the 2 functions of the superior oblique eye muscle?
1. Depresses eye
2. Turns it laterally
Ask an individual to look to the left and follow his/her eyes. What extrinsic eye muscles are responsible for this action?
Right eye:
Left eye:
Right eye: medial, superior, and inferior rectus eye muscles
Left eye: lateral rectus, inferior and superior oblique eye muscles
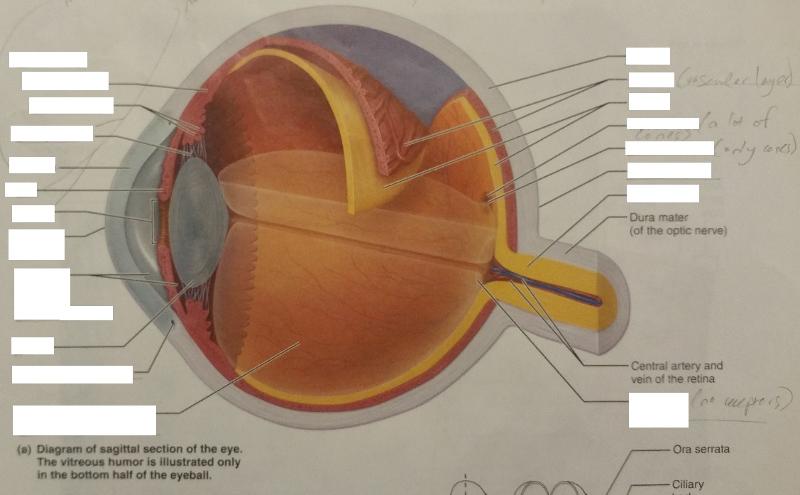
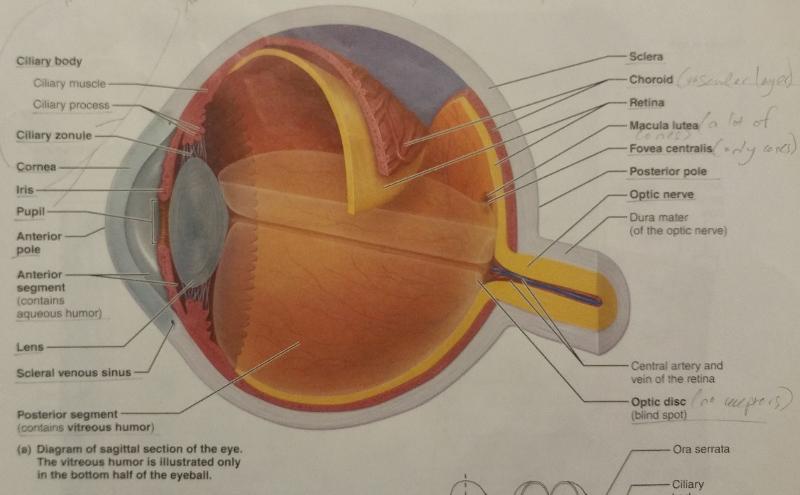
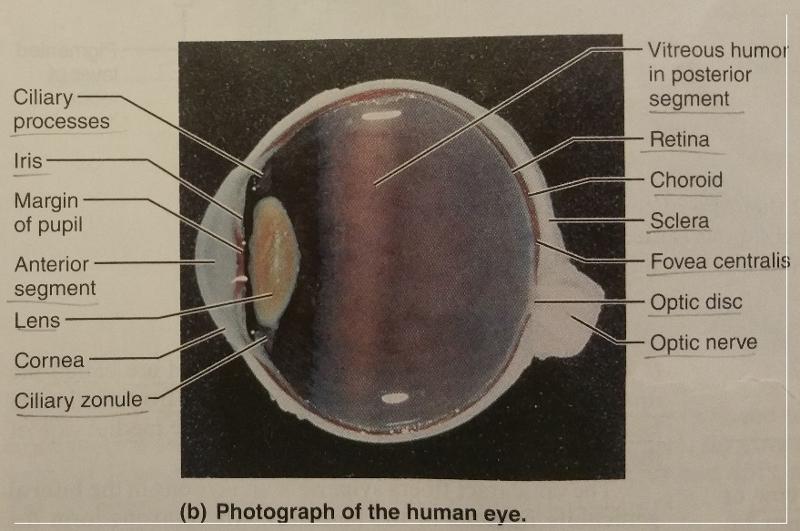
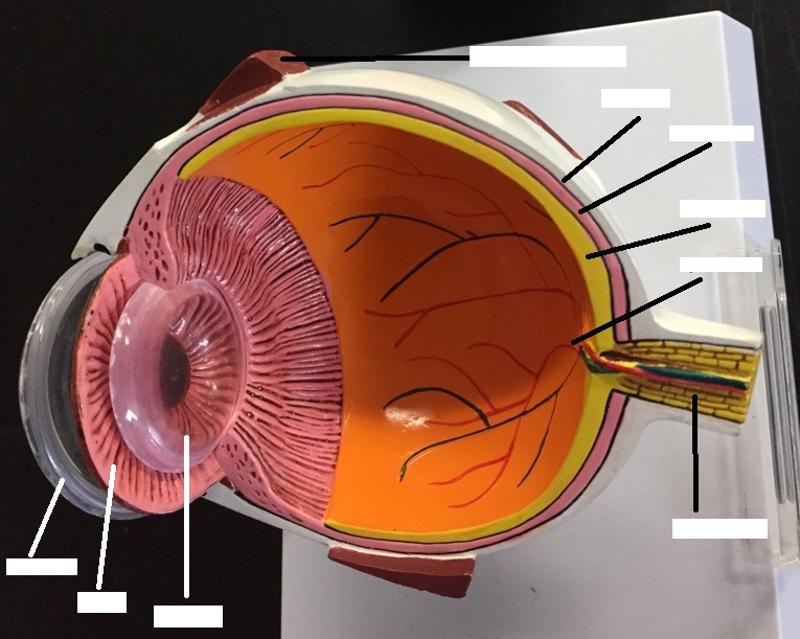
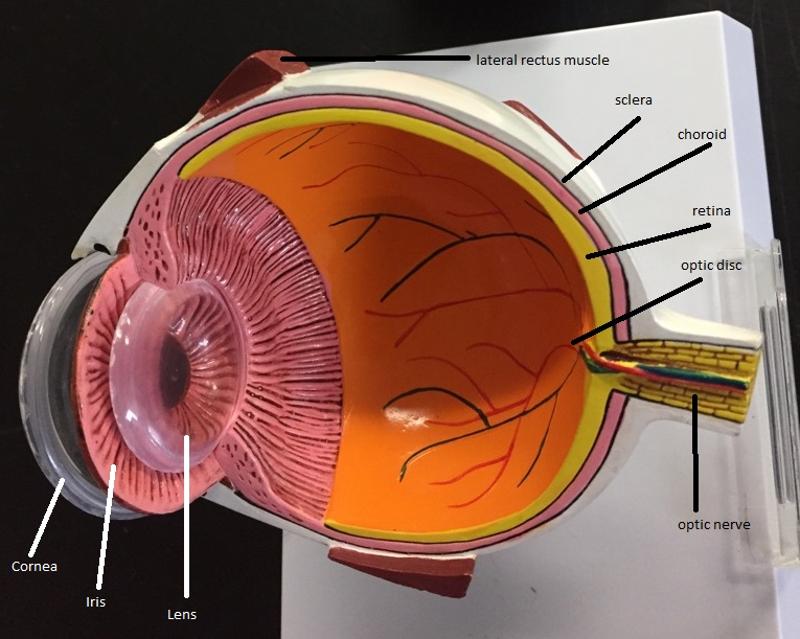
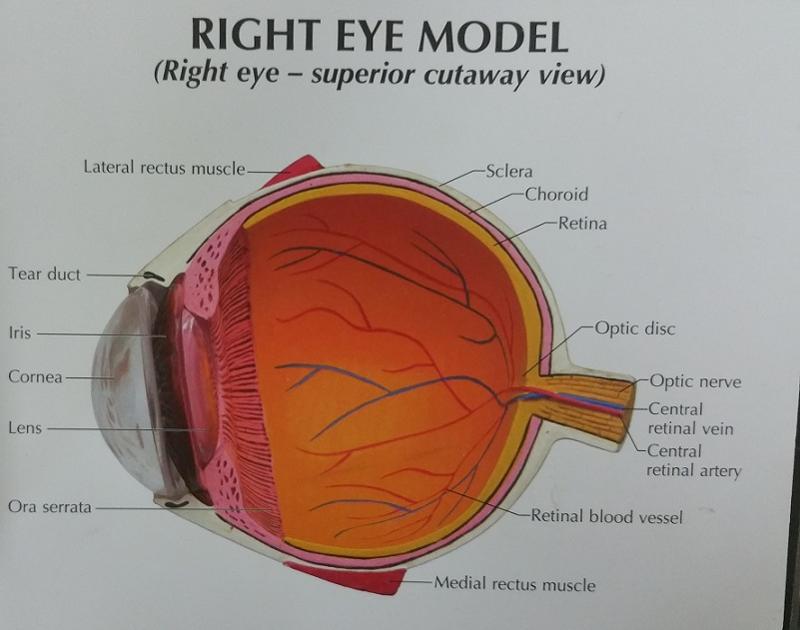
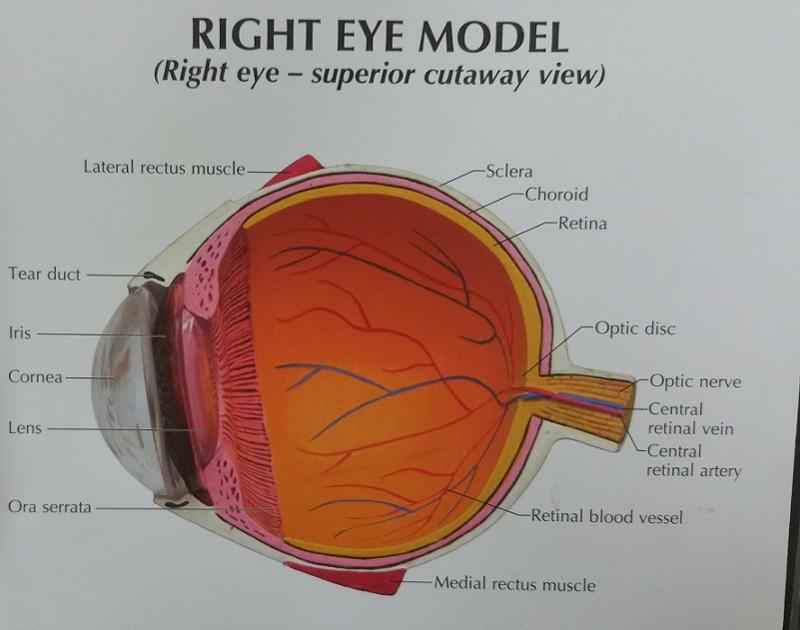
What are the 2 fibrous layers or external layers of the eye?
1. Sclera
2. Cornea
The sclera is made out of what type of tissue?
connective tissue
The sclera forms what part of the eye?
"white of the eye"
What are the 2 functions of the sclera?
1. Maintain the shape of the eyeball
2. Provides attachment point for extrinsic eye muscles
The cornea is a modified structure of what layer of the eye?
Sclera
What is the function of the cornea?
The major light bending (refracting) medium of the eye
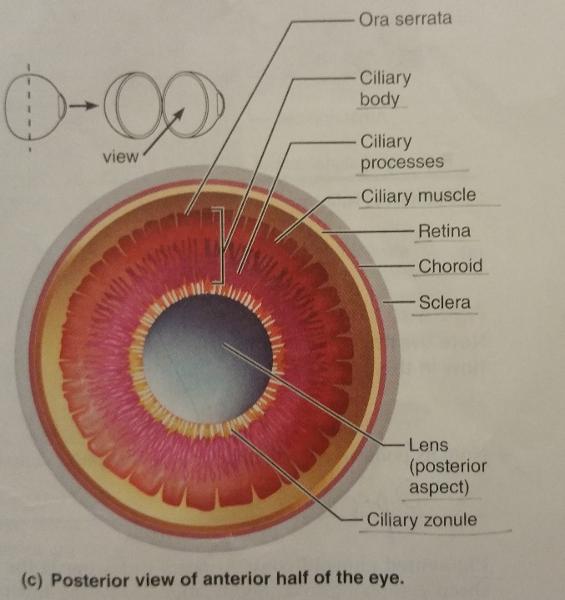
What are the 7 vascular layers or middle layers of the eye?
1. Choroid
2. Ciliary body
3. Ciliary muscle
4. Ciliary process
5. Ciliary zonule
6. Iris
7. Pupil
The choroid is rich in what type of vessels, and how is it colored?
blood vessels and is pigmented darkly
What are the 2 functions of the choroid?
1. The blood vessels nourish the other layers of the eye
2. The melanin helps to absorb excess light
The ciliary body is a modification of what layer of the eye and encircles which eye feature?
A modification of the choroid and encircles the lens
The ciliary body contains what 2 ciliary features of the eyes?
1. Ciliary muscle
2. Ciliary process
The ciliary muscle is what type of muscle?
Smooth muscle
What is the function of the ciliary muscle?
Alters the shape of the lens with contraction and relaxation
The ciliary process is made up of folds of which muscle?
Made up of radiating folds of the ciliary muscle.
What is the function of the ciliary process?
Capillaries of the ciliary process form the aqueous humor
Aqueous humor is formed from the filtration of what?
Plasma
The ciliary zonule is made up of what, extends from what eye feature, and surrounds what part of the eye?
Made up of protein fibers, extends from the ciliary process around the lens
What is the function of the ciliary zonule?
Attaches the lens to the ciliary process
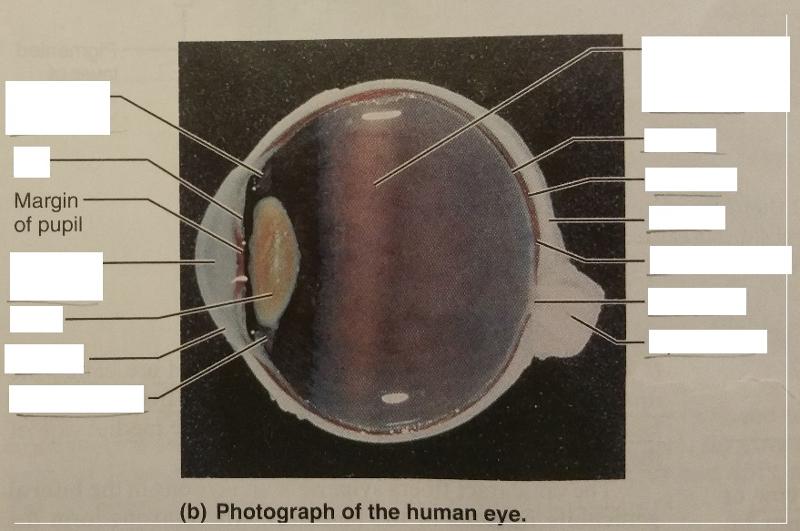
Is the iris pigmented?
Yes
The iris consists of what 2 groups of muscles?
1. Sphincter pupillae
2. Dilator pupillae
The sphincter and dilater pupillae muscles in the iris are what type of muscle?
Smooth muscle
What is the function of the iris?
Controls the amount of light entering the eye by changing the size of the pupil diameter.
Which muscle contracts to constrict the pupil?
Sphincter pupillae
Which muscle contract to dilate the pupil?
Dilator pupillae
What is the pupil in regard to the iris?
The opening of the iris.
What is the function of the pupil?
Allows light to enter.
What are the 2 inner layers or retina layers?
1. Pigmented layer of the retina
2. Neural layer of the retina
What is the thicker, outer layer of the retina?
The pigmented layer of the retina
The outer, pigmented layer of the retina is composed of how many layers of what type of pigment cells?
A single layer of melanocytes (pigment cells)
What are the 2 functions of the outer, pigmented layer of the retina?
1. Absorbs light
2. Prevent it from scattering in the eye
Pigment cells like melanocytes also have 2 functions. What are they?
1. Cleaning up cell debris.
2. Store vitamin A for photoreceptor renewal.
What is the thinner, inner layer of the retina?
The neural layer of the retina
The thinner, inner layer of the retina is composed of what 3 main types of neurons?
1. Photoreceptor cells (rods and cones)
2. Bipolar cells/neurons
3. Ganglion cells/neurons
What is the function of the inner, neural layer of the retina?
The photoreceptor cells (rods and/or cones) in the aforementioned layer respond to light and convert the light energy into action potentials that travel to the primary visual cortex of the brain.