Activity 3: Bones of the Pelvic Girdle
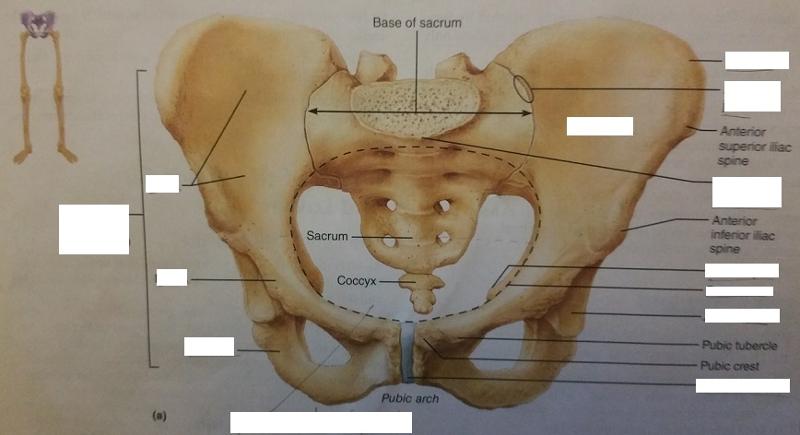
The pelvic girdle is formed by what 3 bones?
2 hip bones and the sacrum.
The pelvis is formed by what 4 bones?
2 hip bones, sacrum, and coccyx
The bones of the shoulder girdle is light, what are the bones of the pelvic girdle like in regards to weight and size?
Heavy and massive
The bones of the pelvic girdle attach securely to which skeleton?
The axial skeleton
The sockets (or acetabulum) of the heads of the femurs are heavily reinforced by what?
Ligaments
The sockets of the heads of the femurs are reinforced by ligaments, and what do they provide in regards to attachment?
Stable, strong limb attachment
Is the ability to bear weight more important at the shoulder girdle or the pelvic girdle?
Pelvic girdle
The combined weight of the upper body rests on which type of girdle?
Pelvic girdle
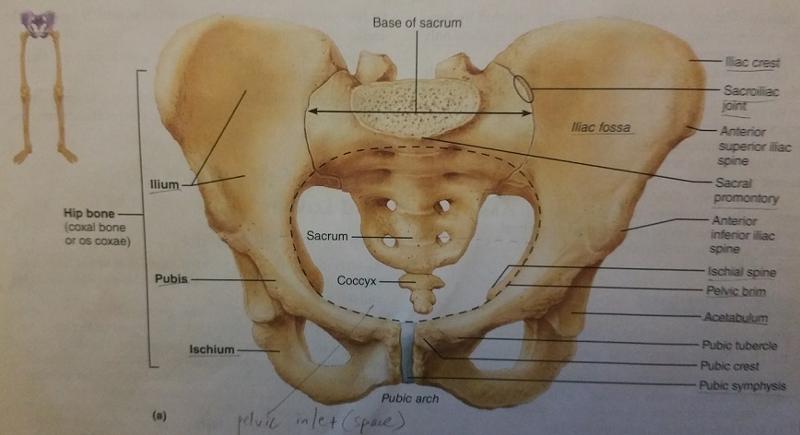
Each hip bone is the fusion of what 3 bones?
1. ilium
2. ischium
3. pubis
The ilium, ischium, and pubis fuse at which socket?
Acetabulum
The acetabulum receives the head of which bone?
The femur
The rami of the pubis and ischium form a bar of bone enclosing what opening of the pelvic girdle?
Obturator foramen
The oburator foramen allows which type of vessels to pass?
Blood vessels
Each hip bone articulates posteriorly with what feature of the pelvic girdle?
Sacrum
The two hip bones join at which feature of the pelvic girdle?
Pubic symphysis
Which joint is a common site of lower back problems?
Sacroiliac joint
Why is the sacroiliac joint such a common site of lower back problems?
Because it has to bear a lot of pressure.
The female pelvis reflects differences for what process of life?
Childbearing
What 4 characteristics of the female pelvis differentiates it from the male's?
1. Wider
2. Shallower
3. Lighter
4. Rounder
A female pelvis supports a growing ____ and must be large enough to allow what to pass through the birth canal?
A female pelvis supports a growing fetus and is large enough to allow an infant's head to pass through the birth canal.
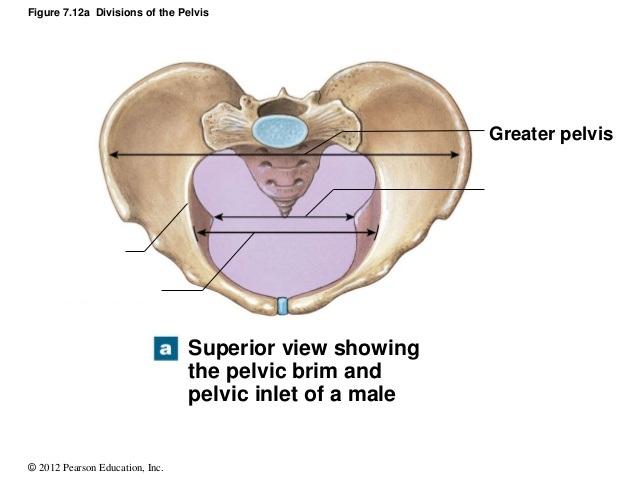
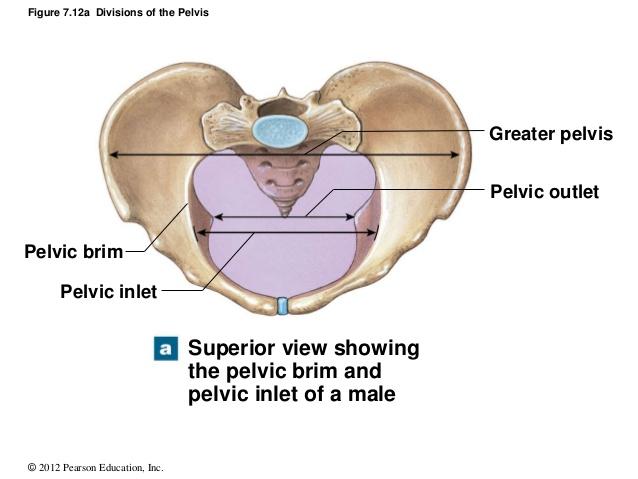
The pelvic brim is a continuous oval ridge of bone that runs along what 5 features of the pelvic girdle?
(Overlook)
1. Public symphysis
2. Pubic crests
3. Arcuate lines
4. Sacral alae
5. Sacral promontory
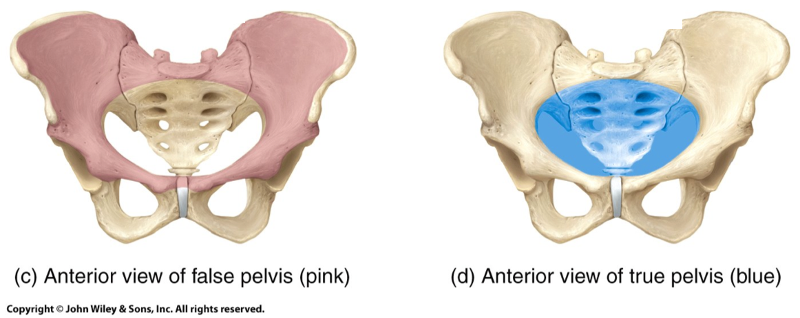
The false pelvis is superior to what feature of the pelvic girdle?
Pelvic brim
The false pelvis is bounded by what 2 features of the pelvic girdle and what type of vertebrae and how so directionally?
1. Alae of the ilia laterally
2. Sacral promontory posteriorly
3. Lumbar vertebrae posteriorly
The false pelvis supports what part of the abdomen?
Abdominal viscera
Does the false pelvis restrict childbirth? Yes or no?
No.
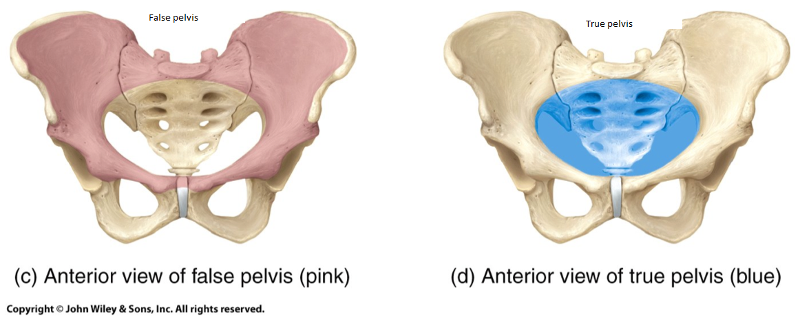
The true pelvis is inferior to what feature of the pelvic girdle?
Pelvic brim
The true pelvis is almost entirely surrounded by what tissue?
Bone
The posterior boundary of the true pelvis is formed by what feature of the pelvic girdle?
Sacrum
What 3 bones of the pelvic girdle define the limits of the true pelvis and how directionally in 2 ways?
1. Ilia
2. Ischia
3. Pubic bones
All define the limits laterally and anteriorly.
What is the pelvic inlet of the pelvic girdle?
The opening traced by the pelvic brim.
Directionally, the widest margin of the pelvic inlet is from ____ to ____ ?
Left to right
The pelvic outlet makes up which feature of the pelvic girdle and how so directionally?
Inferior margin of the true pelvis.
The pelvic outlet is bounded anteriorly by which feature of the pelvic girdle?
Pubic arch
The pelvic outlet is bounded laterally by which feature of the pelvic girdle?
Ischia
The pelvic outlet is bounded posteriorly by what 2 features of the pelvis?
1. Sacrum
2. Coccyx
What feature of the pelvis and what feature of the pelvic girdle can dramatically narrow the outlet and why?
1. Sharply angled coccyx
2. Sharp ischial spines
Because they protrude into the outlet opening.
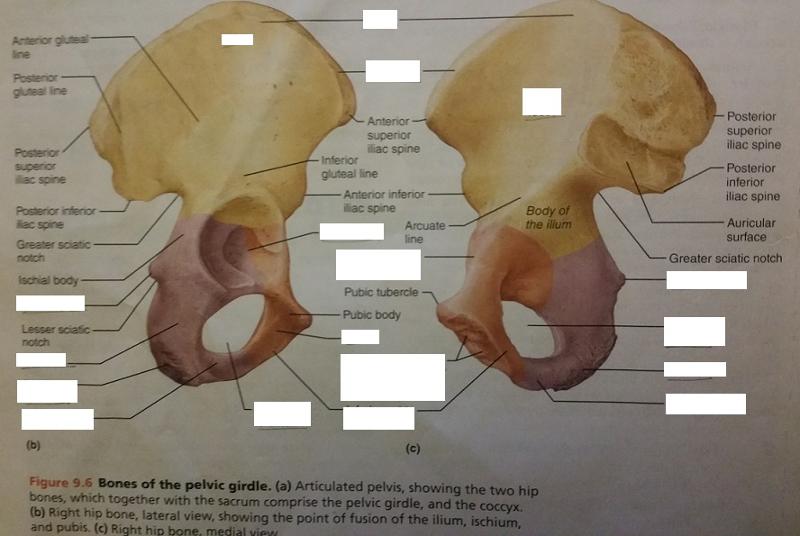
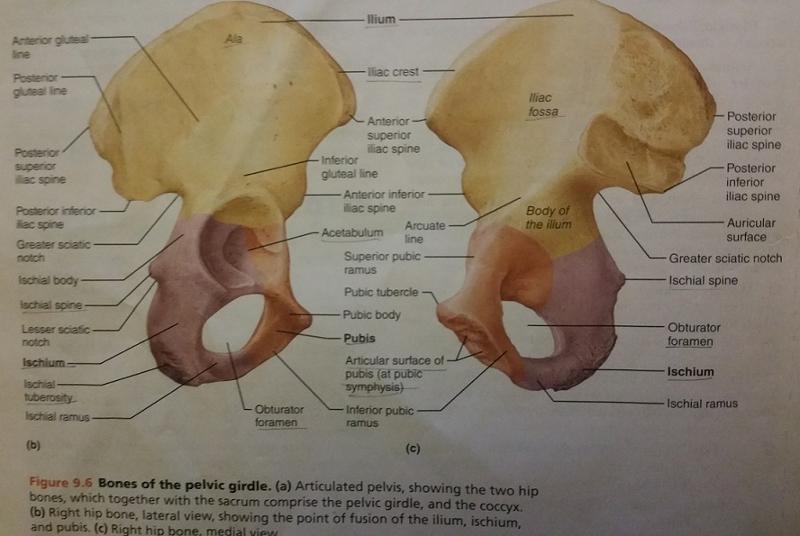
Describe the iliac crest in regard to the pelvic girdle?
Thick superior margin of bone
The iliac crest is a feature of which bone of the 3 bones that make up the hip bone?
Ilium
Describe the iliac fossa of the pelvic girdle in regard to the iliac crest?
Shallow depression in the iliac crest.
The iliac fossa is a feature of which bone of the 3 bones that make up the hip bone?
Ilium
The iliac fossa of the pelvic girdle forms what surface of the ilium?
Internal surface of the ilium
The ischial tuberosity is a feature of which bone of the 3 bones that make up the hip bone?
Ischium
Describe the shape of the ischial tuberosity in the pelvic girdle?
Rough projection
The ischial tuberosity functions in which way to help a human sitting position?
Receives the weight of the body during sitting
How is the ischial spine located directionally in regard to the ischial tuberosity?
Superiorly
The ischial spine projects medially into which cavity?
Pelvic cavity
The ischial ramus is part of which bone?
Ischium
The ischium articulates with which bone of the 3 bones that makes up the hip bone?
Pubis
The superior and inferior pubic ramus are parts of which bone of the 3 bones that make up the hip bone?
Pubis
Describe the superior pubic ramus in regard to the pubis bone.
Superior extension of the body of the pubis.
Describe the inferior pubic ramus in regard to the pubis bone.
Inferior extension of the body of the pubis.
The inferior pubic ramus articulates which bone of the 3 bones that make up the hip bone?
Ischium