GSU Nerves of the Lower Limb
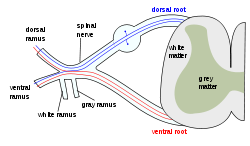
What forms a spinal nerve?
a dorsal root and a ventral root
What type of fibers does a dorsal root contain?
afferent/sensory fibers
What type of fibers does a ventral root contain?
efferent/motor fibers
We have 31 pairs of spinal nerves. How man of each type?
8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, a coccygeal
A spinal nerve bifurcates into a _______ and a ________
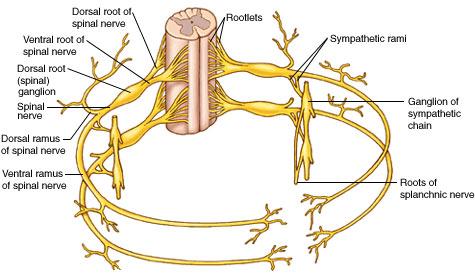
dorsal ramus and ventral ramus
classified by impulse direction, a dorsal ramus or ventral ramus is which type of nerve?
mixed nerve
which ventral rami do NOT form plexuses?
T1-T12
Which vertebrae join to form the lumbar plexus?
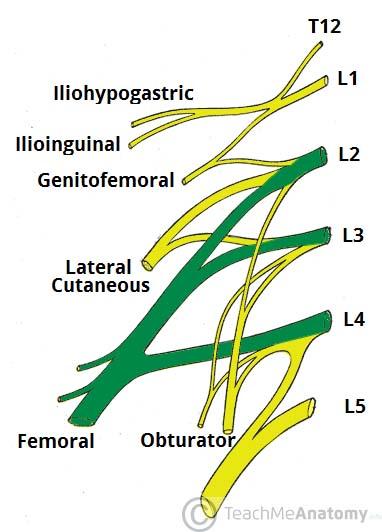
T12-L4
Which vertabrae join to form the sacral plexus?
L4-S4
Which two important nerves come from the lumbar plexus?
femoral and obturator
The femoral nerve is formed from ventral rami of spinal cord levels ___________
L2-L4
The obturator nerve is formed from ventral rami of spinal cord levels ___________
L2-L4
What is the path of the femoral nerve?
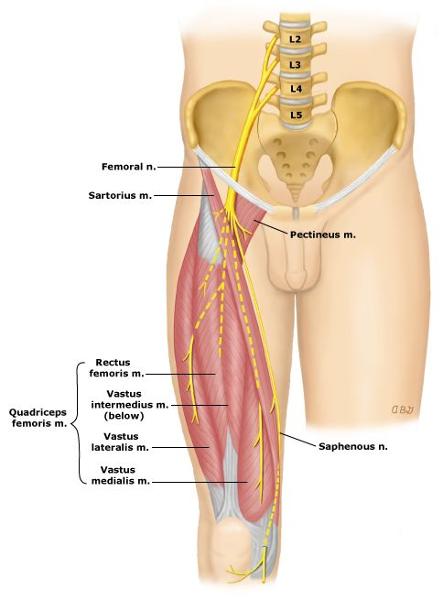
located superficial to iliacus
runs deep to inguinal ligament to enter anterior thigh
most lateral content of the femoral triangle
Which muscles are innervated by the femoral nerve?
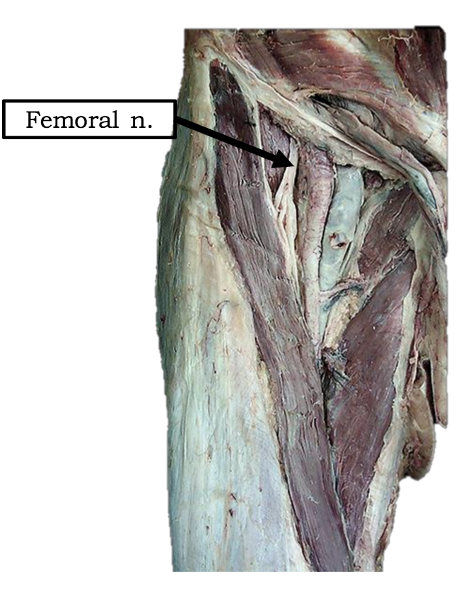
all muscles of anterior thigh: sartorius, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius
the iliacus
and half of pectinius
What is the path of the obturator nerve?
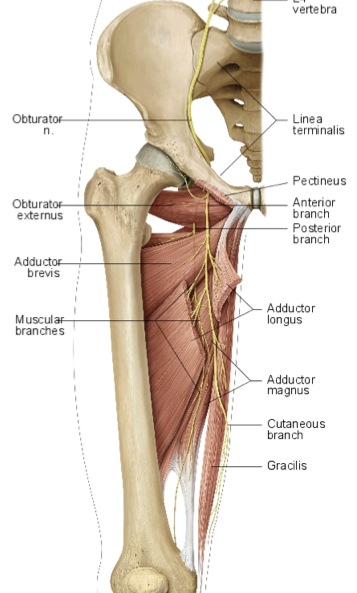
runs medial to psoas major in pelvis
enters medial thigh through obturator foramen
splits into deep and superficial branches at adductor brevis
Which muscles are innervated by the obturator nerve?
anterior and posterior branches?
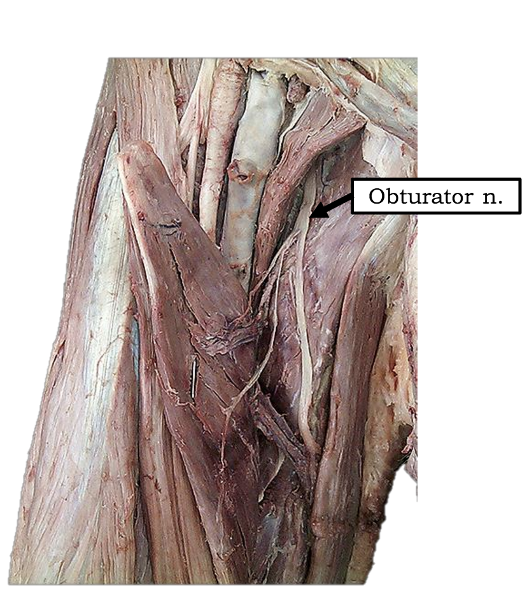
all medial thigh muscles: gracilis, pectinius, adductor longus, adductor brevis, and adductor magnus (adductor part)
posterior branch is adductor magnus
anterior branch is to all other muscles
MAKE A FLOW CHART OF THE IMPORTANT NERVES COMING OFF SACRAL AND LUMBAR PLEXUS
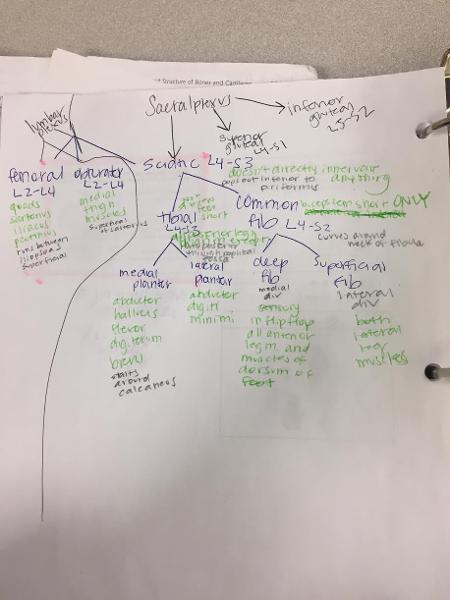
From which vertabrae does the superior gluteal nerve originate?
L4-S1
What is the pathway of the superior gluteal nerve?
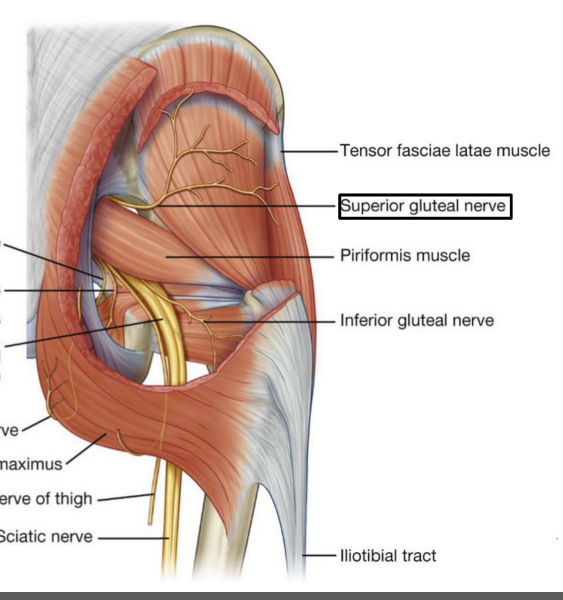
exits pelvis through greater sciatic foramen. in the gluteal region it is located superior to the piriformis muscle and runs between gluteus medius and gluteus minimus
Which muscles does the superior gluteal nerve innervate?
gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and the tensor fasciae latae muscle
From which spinal cord levels does the inferior gluteal nerve form?
L5.S2
What is the pathway of the inferior gluteal nerve through the body?
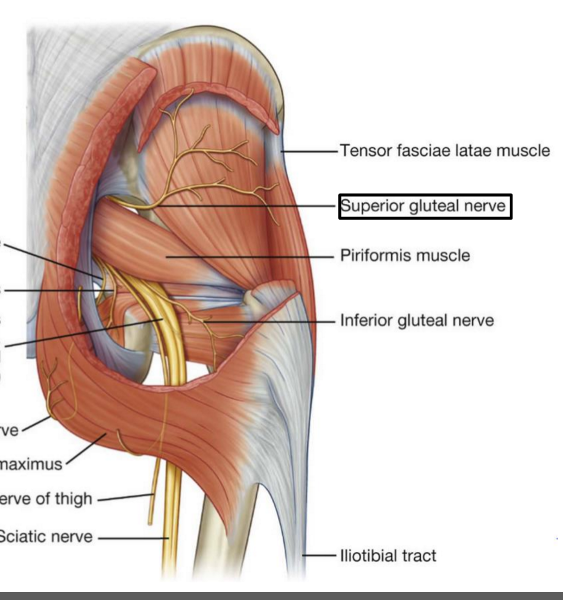
exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen, is located inferior to the piriformis muscle in the gluteal region. runs just deep to gluteus maximus
What does the inferior gluteal nerve innervate?
gluteus maximus only
The sciatic nerve is formed from ventral rami from spinal cord levels ________-
L4 - S3
What is the path of the sciatic nerve?
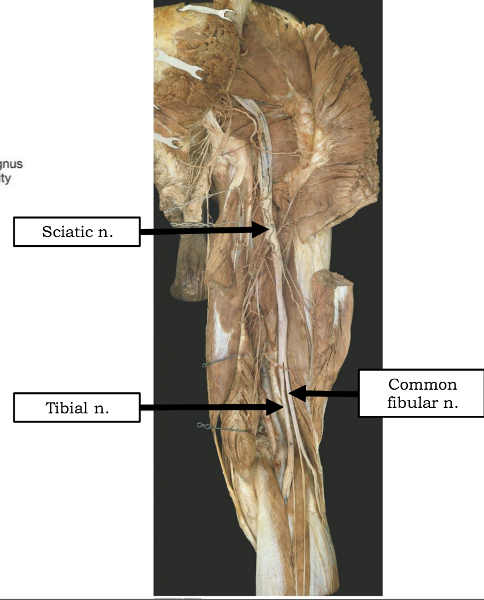
exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen. IN the posterior gluteal region, located inferior to piriformis m
Into which two nerves does the sciatic nerve bifurcate?
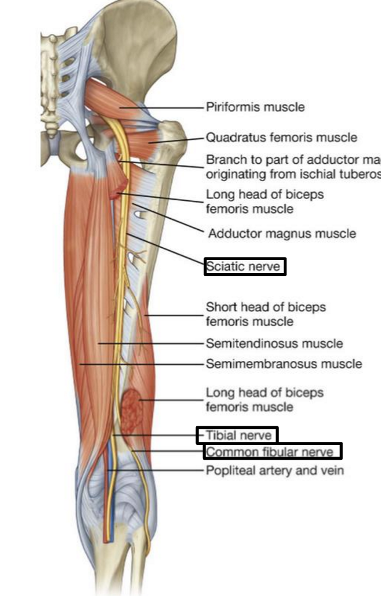
tibial and common fibular
The tibial nerve is fromed form ventral rami from spinal cord levels _______
L4-S3
The tibial nerve is the (medial/lateral) division of the sciatic nerve
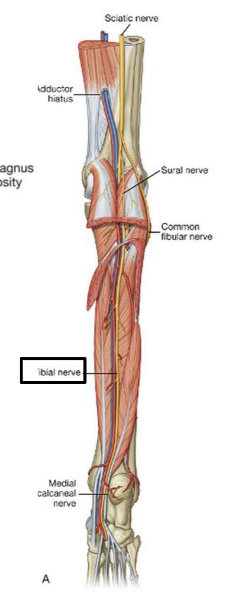
medial
What is the pathway of the tibial nerve?
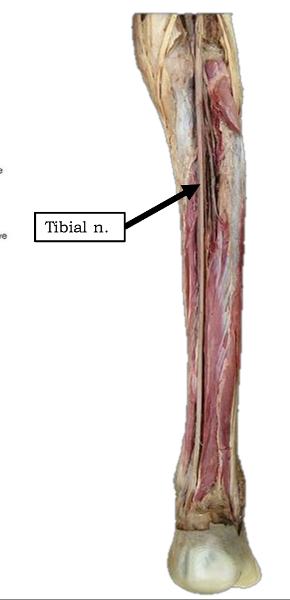
runs through popliteal fossa
runs with tom dick AN harry though medial malleoulus
bifurcates into medial and lateral plantar nerves
Which muscles are innervated by tibial nerve?
all posterior thigh muscles except short head of biceps femoris (long head, semitendinosis, semimembranosis)
^^technically tibial division of sciatic n
ALL posterior leg muscles (gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris. popliteus, tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus)
Into which nerves does tibial nerve bifurcate?
medial and lateral plantar nerve
Which muscles are innervated by the medial plantar nerve?
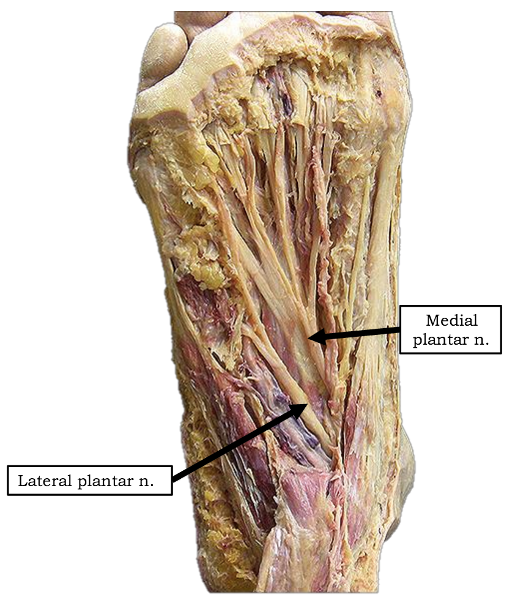
abductor hallucis and flexor digitorum brevis
1 medial lumbrical
flexor hallucis brevis
Which muscles are innervated by lateral plantar nerve in the first layer of dorsal surface?
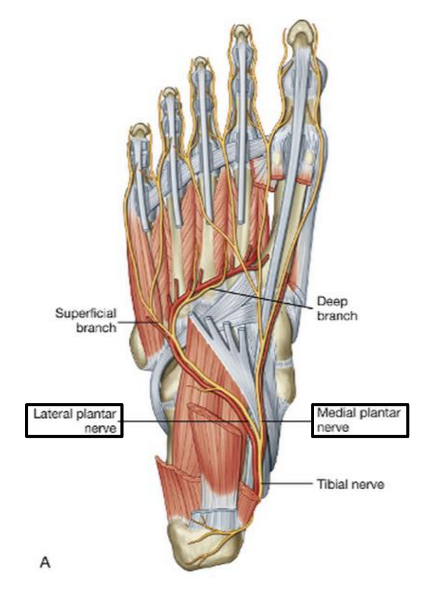
abductor digiti minimi
The common fibular nerve is formed from ventral rami from spinal cord levels _______
L4 - S2
The common fibular nerve is the (lateral/medial) division of the sciatic nerve
lateral
Describe the pathway of the common fibular nerve
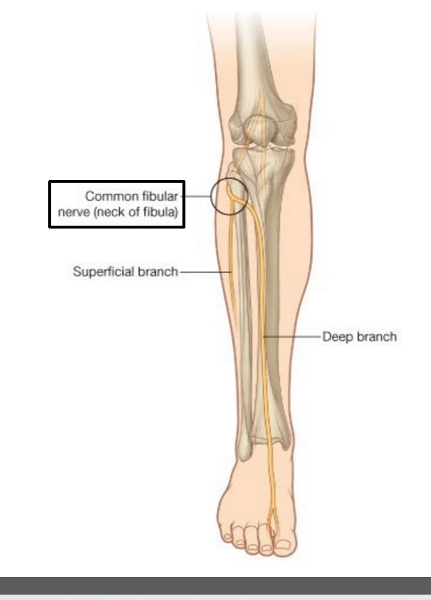
wraps around the neck of the fibula
bifurcates into deep and superficial fibular nerves
What muscle does the common fibular division of sciatic nerve innervate?
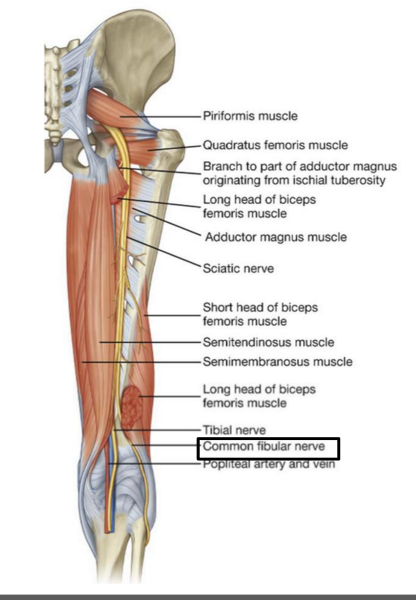
ONLY biceps femoris short head
To which nerve might there be damage if a patient is suffering from foot drop?
common fibular nerve
What would be the consequences if the common fibular nerve was completely severed?
Patient would be unable to evert foot
numbness on dorsum of foot
unable to doriflex or extend digits of foot
The superficial fibular nerve is the (lateral/medial) branch of the ________
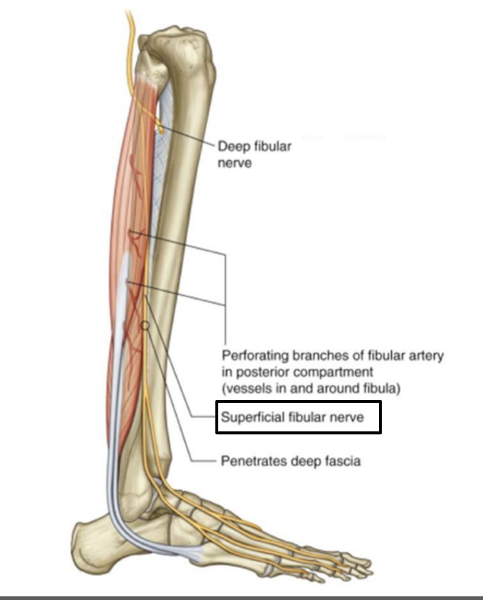
lateral; common fibular nerve
which muscles does the superficial fibular nerve innervate?

both lateral leg muscles (fibularis longus and fibularis brevis)
The deep fibular nerve is the (medial/lateral) division of the _________-
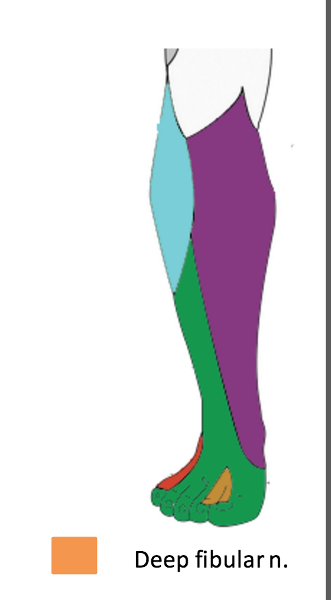
medial; common fibular nerve
What is the path of the deep fibular nerve?
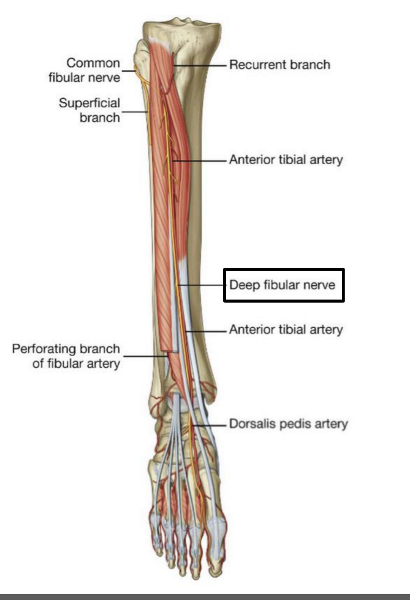
travels between tibialis anterior and extensor hallucis longus
continues onto the dorsum of the foot for sensory innervation in the flip flop area
What is the pathway of the superficial fibular nerve?
runs between fibularis longus and fibularis brevis
continues onto the dorsum of the foot
Which muscles does the deep fibular nerve innervate?
innervates all anterior leg muscles (extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, tibialis anterior, and fibularis tertius) and both muscles of the dorsum of the foot (extensor digitorum brevis, extensor hallucis brevis)
Which nerve does not arise directly or indirectly from the sacral plexus? Superior gluteal n. Sciatic n. Obturator n. Tibial n. Deep fibular n.
Obturator n
What nerve passes deep to the inguinal ligament to innervate the muscles of the anterior thigh? Obturator n. Sciatic n. Femoral n. Inferior gluteal n. Tibial n.
femoral n
Which nerve is found within the popliteal fossa? Tibial n. Popliteal n. Obturator n. Deep fibular n. Femoral n.
tibial n
Ventral rami from T12 and L1-L4 form the __________ plexus.
lumbar
sacral
cervical
thoracic
brachial
lumbar
Which group of muscles below is supplied by the obturator nerve?
The major adductors of the thigh.
The major lateral rotators of the thigh.
The major flexors of the thigh.
The major extensors of the thigh.
The major abductors of the thigh.
major adductors of the thigh
The nerve that wraps around the neck of the fibula is the _______
common fibular
If a patient cannot dorsiflex, which nerve may not be functioning?
deep fibular
Which plexus is involved with the contraction of LEG muscles?
sacral
This nerve innervates three muscles that have a common origination point on the ischial tuberosity. Which nerve is being described?
tibial division of sciatic n
Which of the following nerves is critical for leg extension? Femoral n. Obturator n. Tibial n. Common fibular n. Medial plantar n.
femoral n
origin and course of superior cluneal nerve
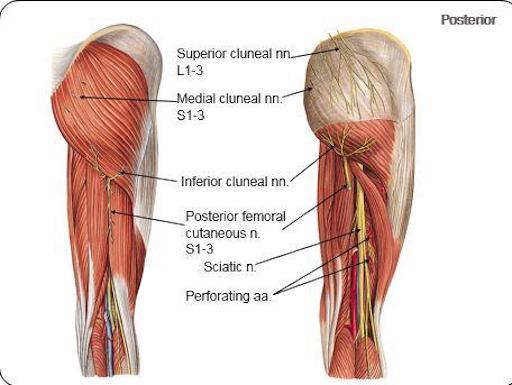
posterior rami of L1-L3 nerves
crosses iliac crest
origin course and distribution of saphenous nerve
spinal cord level
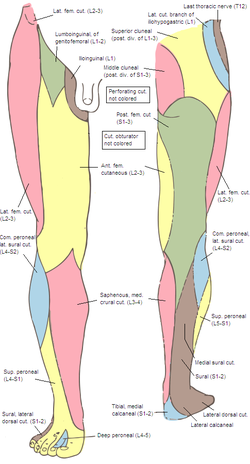
O femoral nerve
C descends with femoral vessels through femoral triangle and adductor canal then descends with great saphenous vein
D supplies skin on medial side of leg and foot
L3-L4
name the clunial nerves and their distribution
spinal cord levels
superior (posterior rami of L1-L3), inferior (S2-S3) and middle clunial nerves (posterior rami of (S1-S3)
supplies the skin of the gluteal region as far as greater trochanter
origin and course of middle clunial nerve
posterior rami of S1-S3 nerves
exits through posterior sacral foramina and enters gluteal region
origin and course of inferior clunial nerve
posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh
curves around inferior border of gluteus maximus
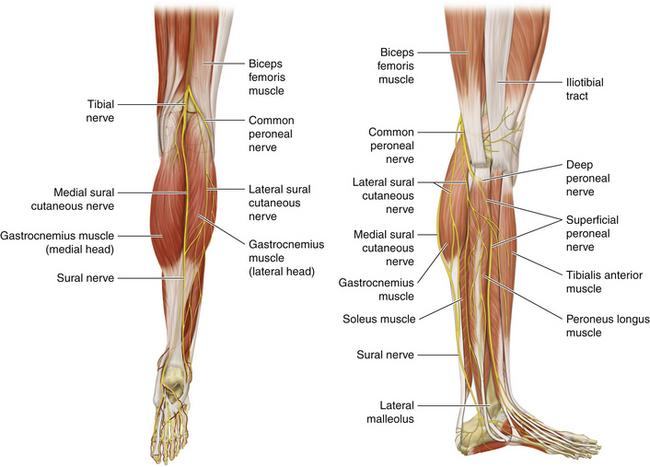
origin course and distribution of sural nerve
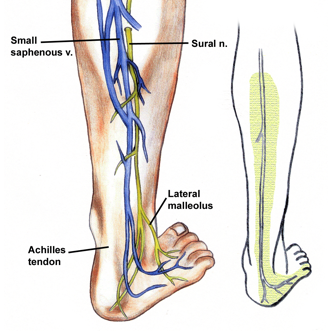
O formed by the union of the cutaneous banches from the tibial and common fibular nerves
C descends between heads of gastroc; becomes superficial at middle of leg; descends with small saphenous vein; passes inferior to lateral malleoulus to lateral side of foot
origin course and distribution of lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
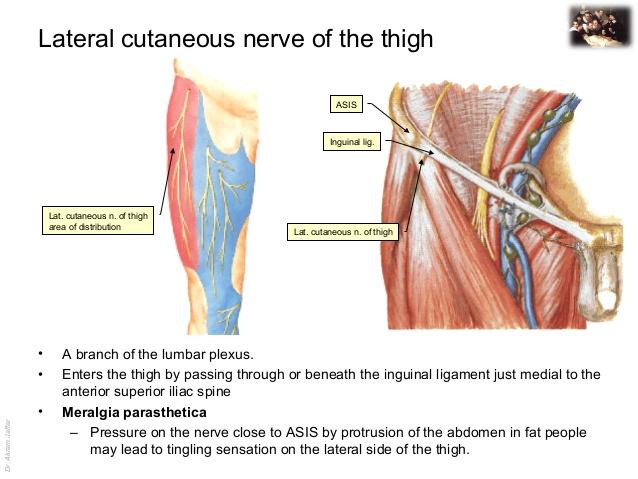
O L2-L3
C emerges from the lateral border of the psoas major, crosses the iliacus muscle obliquely toward ASIS. Under the inguinal ligament, over sartorius muscle into the thigh, where it divides into an anterior and a posterior branch.
D lateral skin of thigh
origin course and distribution of posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh

O S1-S3
C From pelvis below piriformis, beneath gluteus maxius and back of thigh, bakc of knee and dives into deep fasica and runs with small saph to middle of back of leg. gives off inferior clunial n.
D posterior surface of thigh and leg, skin of perineum
origin course and distribution of superior gluteal nerve
O sacral plexus L4-S1
C leaves pelvis through greater sciatic foramen superior to piriformis; runs between gluteus medius and minimus
D gluteus medius, minimis, and TFL
origin course and distirbution of inferior gluteal nerve
O L5-S2
C eaves pelvis through greater sciatic foramen inferior to prififormis; divides into several branches
D gluteus maximus
origin course and distribution of sciatic nerve
O L4-S3
C leaves pelvis through greater sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis; enters gluteal region; descends deep to biceps femoris; bifurcates into tibial and common fibular nerves at apex of popliteal fossa
D no muscles
origin course and distribution of nerve to obturator internus
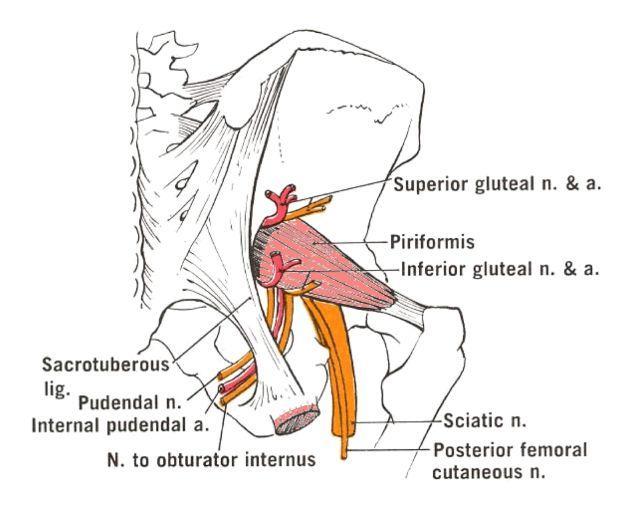
O sacral plexus L5-S2
C enters gluteal region through greater sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis, descends posterior to ischial spine, enters lesser sciatic foramen; passes to obturator internus
D superior gemellus and obturator internus
origin course and distribution of obturator n
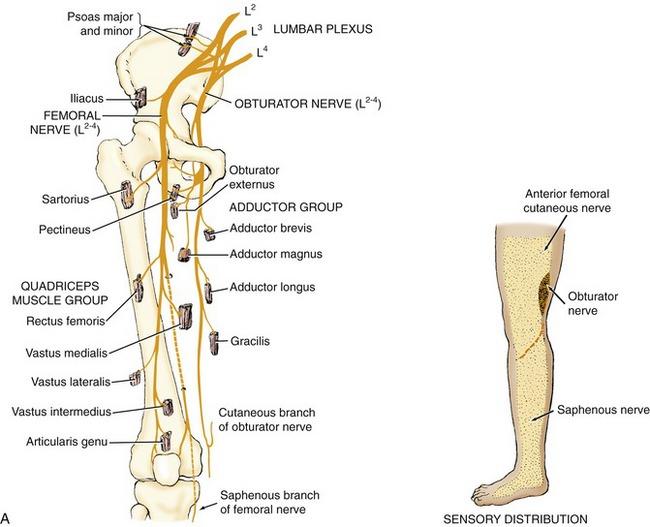
O L2-L4
C descends along medial border of psoas and enters thigh through obturator foramen through with obturator artery and vein. divides into anterior and posterior branches that straddle adductor brevis.
D medial muscles of thigh except hamstring part of adductor magnus
origin and distribution of anterior branch of obturator nerve
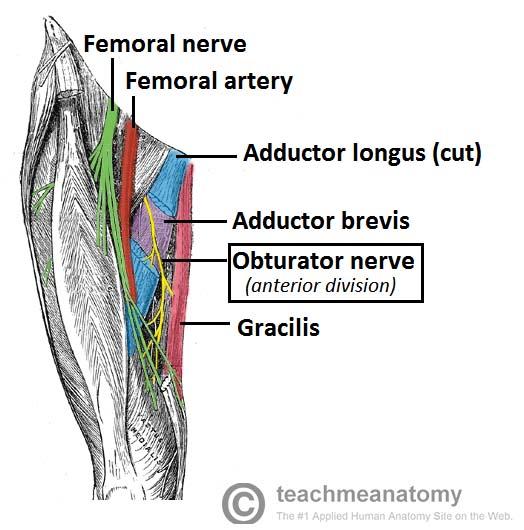
O obturator n
D adductor longus, brevis, gracilis and pectineus
origin and distribution of posterior branch of obturator nerve

O obturator n
D obturator externus and adductor magnus (adductor part)
origin and distribution of femoral nerve
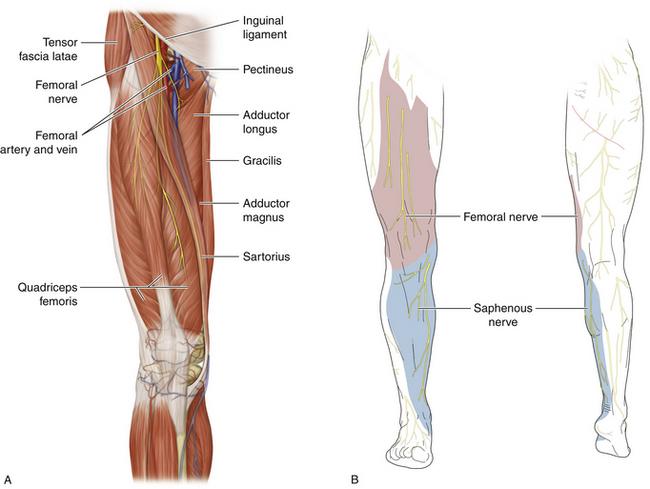
O L2-L4
D iliacus, flexors of the hip and extensors of the knee
origin and distribution of tibial nerve
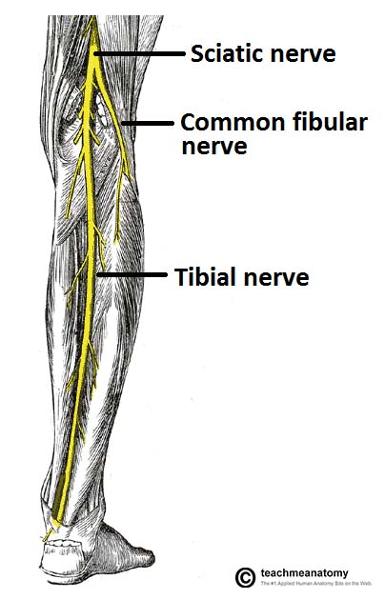
O sciatic nerve
C forms as sciatic nerve bifurcates at apex of popliteal fossa; descends through popliteal fossa; runs inferior to tibialis posterior with posterior tibial vessels; terminates beneath flexor retinaculum by dividing into medial and lateral plantar nerves
D supplies plantar flexor muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg and knee joint
origin and distribution of lateral plantar nerve
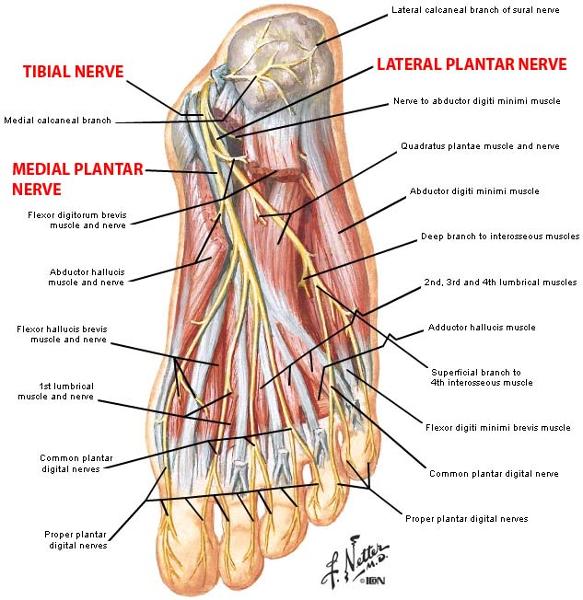
O tibial nerve beneath flexor retinaculum
D abductor digiti minimi muscle (foot), flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle (foot), quadratus plantae, 3 lateral lumbricals of the foot, adductor hallucis muscle, plantar interossei muscles, dorsal interossei muscles
origin and distribution of medial plantar nerve
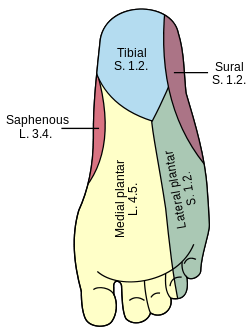
O tibial nerve beneath flexor retinaculum
D abductor hallucis, the flexor digitorum brevis, the flexor hallucis brevis, and the first lumbrical
branches of lateral plantar nerve
deep branch
superficial branch
branches of medial plantar n
common plantar digital nerves --> proper plantar digital nerves
O C D of common fibular nerve
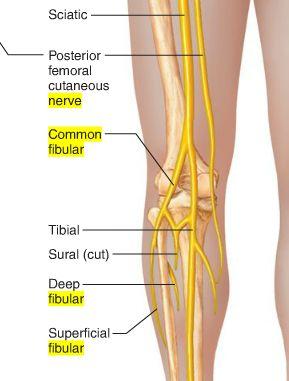
O sciatic nerve
C forms as sciatic nerve bifurcates at apex of popliteal fossa. follows medial border of biceps femoris with its tendon. passes over posterior aspect of head of fibula then winds around neck of fibula deep into fibularis longus where it divides into deep and superficial fibular nerves
D knee joint via articular branch and lateral aspect of posterior leg via sural cutaneous nerve
(common fibular branch of sciatic nerve innervates short head of biceps femoris)
OCD of superficial fibular nerve
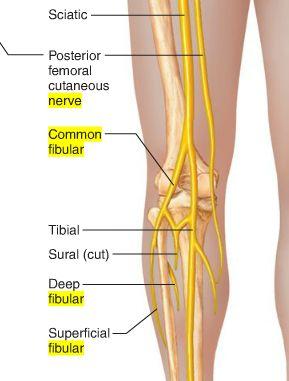
O common fibular nerve
C arises between fibularis longus and neck of fibula. descends into lateral compartment of leg; pierces deep fascia at distal third of leg to become subcutaneous
D fibularis longus and brevis. medial dorsal cutaneous n, intermediate dorsal cutaneous n
OCD of deep fibular nerve
O common fibular nerve
C arises between fibularis longus and neck of fibula; passes through extensor digitorum longus and descends on interosseous membrane. crosses distal end of tibia and enters dorsum of foot.
D tibialis anterior, extensors digitorum brevis and longus, extensor hallucis brevis and longus, and fibularis tertius. lateral cutaneous of big toes, medial cutaneous of second toe.