Mastering Chemistry End of Chapter 6
Based on the structure of the periodic table, which becomes occupied first, the 6 s orbital or the 5d orbitals?
6s
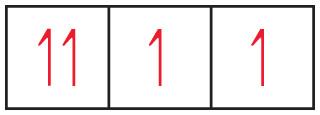
As drawn, the drawing is incorrect. Why?
In the left-most box, the two electrons cannot have the same spin. The Pauli principle states that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers. Since the first three quantum numbers describe an orbital, the fourth quantum number must have different values for two electrons in the same orbital; their "spins" must be opposite.
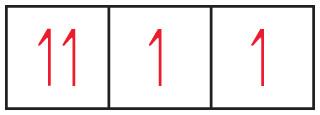
How would you correct the drawing without changing the number of electrons?
Flip one of the arrows in the left-most box, so that one points up and the other down.
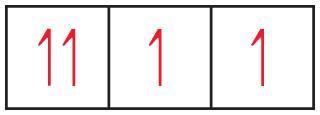
To which group in the periodic table does the element belong?
Group 6A. The drawing shows three boxes or orbitals at the same energy, so it must represent p orbitals. Since some of these p orbitals are partially filled, they must be the valence orbitals of the element. Elements with four valence electrons in their p orbitals belong to group 6A.
Which is a statement of Hund's rule?
Energy is a minimum when the number of same-spin electrons is maximized.
No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
The dual nature of matter places a fundamental limitation on how precisely we can know both the location and momentum of an object at a given instant.
Mathematical functions called wave functions are used to describe electrons in an atom.
Energy is a minimum when the number of same-spin electrons is maximized.
Which element has the same electron configuration as the nitride ion?
15P
10Ne
4Be
16S
10Ne
State where in the periodic table these elements appear: elements with the valence-shell electron configuration ns2 np5
7A
State where in the periodic table these elements appear: elements that have three unpaired p electrons
5A
State where in the periodic table these elements appear: an element whose valence electrons are 4s2 4p1
Ga
State where in the periodic table these elements appear: the d-block elements
Groups 1-2
Groups 3-12
Groups 3-8
Lanthanides
Actinides
Groups 3-12
What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy each of the following subshells?
3p
6 electrons
What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy each of the following subshells?
5d
10 electrons
What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy each of the following subshells?
2s
2 electrons
What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy each of the following subshells?
4f
14 electrons
What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that can have the following quantum numbers?
n=2, ms=-1/2
4 electrons
What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that can have the following quantum numbers?
n=5, l=3
14 electrons
What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that can have the following quantum numbers?
n=4, l=3, ml=-3
2 electrons
What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that can have the following quantum numbers?
n=4, l=0, ml=0
2 electrons
For each element, count the number of core electrons, valence electrons, and unpaired electrons in the ground state.
Carbon
2, 4, 2 electrons
For each element, count the number of core electrons, valence electrons, and unpaired electrons in the ground state.
Phosphorus
10, 5, 3 electrons
For each element, count the number of core electrons, valence electrons, and unpaired electrons in the ground state.
Neon
2, 8, 0 electrons
Identify the specific element that corresponds to each of the following electron configurations.
1s2 2s2
Be
Identify the specific element that corresponds to each of the following electron configurations.
1s2 2s2 2p4
O
Identify the specific element that corresponds to each of the following electron configurations.
[Ar] 4s1 3d5
Cr
Identify the specific element that corresponds to each of the following electron configurations.
[Kr] 5s2 4d10 5p4
Te
The following electron configurations represent excited states. Identify the element, and write its ground-state condensed electron configuration.
ls2 2s2 3p2 4p1
N
Write N ground-state condensed electron configuration.
[He]2s^22p^3
The following electron configurations represent excited states. Identify the element, and write its ground-state condensed electron configuration.
[Ar] 3d10 4s1 4p4 5s1
Se
Write Se ground-state condensed electron configuration.
[Ar]4s^23d^104p^4
The following electron configurations represent excited states. Identify the element, and write its ground-state condensed electron configuration.
[Kr] 4d6 5s2 5p1
Rh
Write Rh ground-state condensed electron configuration.
[Kr]5s^14d^8