Festival 5 (Digestive and Metabolism)
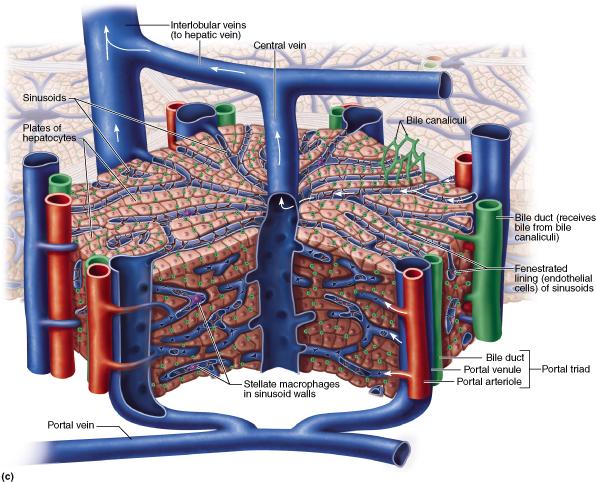
Which vessel delivers nutrient-rich blood to the liver from the digestive tract?
hepatic vein
hepatic portal vein
inferior vena
cava
central vein
Hepatic portal vein
The sheets of peritoneal membrane that hold the digestive tract in place are called ________.
mucosal lining
serosal lining
lamina propria
mesenteries
Mesenteries
Which of the following is not a phase of gastric secretion?
gastric
cephalic
intestinal
enterogastric
Enterogastric
Saliva does NOT __________.
clean the mouth
aid in the chemical digestion of
proteins
contain carbohydrate-dissolving enzymes
dissolve
food chemicals so that they can be tasted
aid in the chemical digestion of proteins
The __________ guards the entry of food into the stomach.
diaphragm
pyloric sphincter
ileocecal valve
cardiac sphincter
cardiac sphincter

What structural modification of the small intestine slows the movement of chyme through the lumen?
microvilli
circular folds
lacteals
villi
Circular folds
The mechanical and chemical receptors that control digestive activity are located ________.
in the walls of the tract organs
in the pons and medulla
in the glandular tissue that lines the organ lumen
in the oral cavity
in the walls of the tract organs
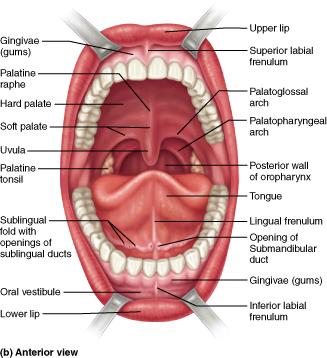
What muscle forms the labia of the mouth?
zygomaticus
orbicularis oris
orbicularis oculi
buccinator
Orbicularis oris
Most digestion and absorption of nutrients occur in the __________.
large intestine
liver
stomach
small intestine
Small intestine
The __________ is the serous membrane that lines the abdominal body wall.
mesentery
omenta
visceral peritoneum
parietal peritoneum
Parietal peritoneum
The absorptive effectiveness of the small intestine is enhanced by increasing the surface area of the mucosal lining. Which of the following accomplish this task?
plicae circulares, villi, and microvilli
the rugae and
haustra
the vast array of digestive enzymes
Brunner's
glands and Peyer Patches
plicae circulares, villi, and microvilli
Chemical digestion reduces large complex molecules to simpler compounds by the process of ________.
fermentation
anabolism
mastication
catabolism
Catabolism
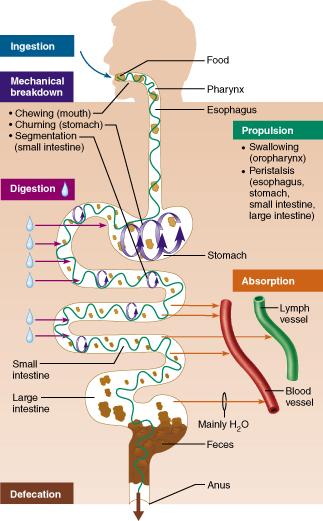
How would you classify chewing food?
ingestion
digestion
mechanical breakdown
propulsion
Mechanical breakdown
Chyme is created in the ________.
esophagus
mouth
stomach
small intestine
Stomach
The innermost tissue layer of the alimentary canal is the __________.
serosa
mucosa
muscularis
submucosa
Mucosa
In a patient suffering from a gastric ulcer caused by Helicobacter pylori, the cells most likely to have been damaged first are the ______.
enteroendocrine cells
parietal cells
chief cells
mucous cells
Mucous cells
True or False:
When swallowing, the epiglottis prevents food from entering the larynx.
True
True or False:
All the chemical and mechanical phases of digestion from the mouth through the small intestine are directed toward changing food into forms that can pass through the epithelial cells lining the mucosa into the underlying blood and lymphatic vessels.
True
Which teeth are best suited for cutting or nipping off pieces of food in the permanent dentition?
canines
premolars (bicuspids)
molars
incisors
Incisors
The major means of propelling food through the digestive tract is __________.
swallowing
peristalsis
segmentation
churning
Peristalsis
From the esophagus to the anal canal, the walls of every organ of the alimentary canal are made up of the same four basic layers. Arrange them in order from the lumen.
serosa, mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis externa
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa
submucosa, serosa, muscularis externa, and mucosa
muscularis externa, serosa, mucosa, and submucosa
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa
Which hormone causes an increased output of enzyme-rich pancreatic juice and stimulates gallbladder contraction to release bile?
secretin
cholecystokinin
gastric inhibitor peptide
gastrin
Cholecystokinin
The chemical and mechanical processes of food breakdown are called ________.
ingestion
absorption
digestion
secretion
Digestion
True or False:
The peritoneum is the most extensive serous membrane in the body.
True
Which of the following is not a factor that helps create the stomach mucosal barrier?
replacing of damaged epithelial mucosa cells
production of intrinsic factor
thick coating of bicarbonate-rich mucus
tight junctions of epithelial mucosa cells
production of intrinsic factor
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of the stomach?
The stomach produces a double-layered coat of alkaline mucus.
The stomach has three layers of muscle in the muscularis tunic.
The stomach mucosa is folded into rugae.
The stomach releases enzymes to digest carbohydrates.
The stomach releases enzymes to digest carbohydrates.
If an incision has to be made in the small intestine to remove an obstruction, the first layer of tissue to be cut is the ________.
mucosa
submucosa
muscularis externa
serosa
Serosa
There are three phases of gastric secretion. The cephalic phase occurs ________.
at the end of a large meal, and the juices secreted are powerful and remain in the GI tract for a long period of time
when the meal is excessively high in acids and neutralization is required
immediately after food enters the stomach, preparing the small intestine for the influx of a variety of nutrients
before food enters the stomach and is triggered by aroma, sight, or thought
before food enters the stomach and is triggered by aroma, sight, or thought
Pepsinogen, a digestive enzyme, is secreted by the ________.
goblet cells of the small intestine
parietal cells of the
duodenum
Brunner's glands
chief cells of the stomach
Chief cells of the stomach
What role of the stomach is essential to life?
production of intrinsic factor
production of chyme
production of VIP
production of hydrochloric acid
Production of intrinsic factor
Which vitamin requires intrinsic factor in order to be absorbed?
K
B12
A
C
B12
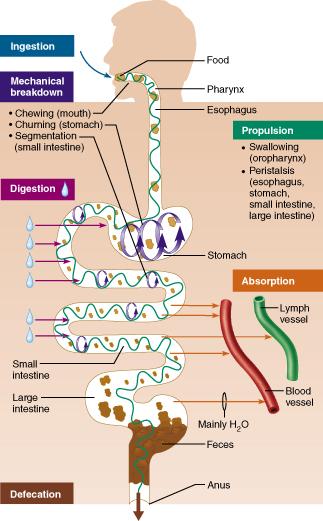
Which major process involves the elimination of indigestible substances from the body via the anus?
mechanical breakdown
defecation
ingestion
absorption
Defecation
What is the major digestive function of the pancreas?
production of digestive enzymes
production of glucagon
production of insulin
production of bicarbonate ions
Production of digestive enzymes
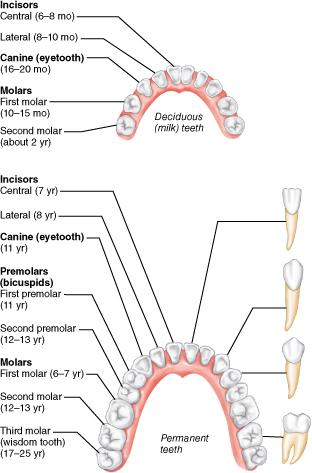
How are wisdom teeth (third molars) classified?
milk teeth
incisors
primary teeth
permanent teeth
Permanent teeth
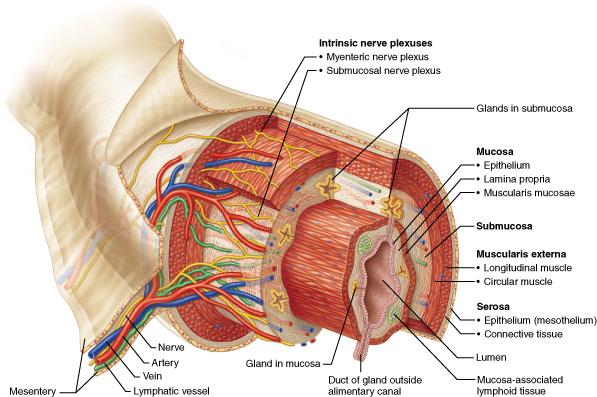
Which layer of the alimentary canal contains the nerve supply of the enteric neurons that regulate digestive system activity?
submucosa
muscularis externa
mucosa
serosa
Submucosa
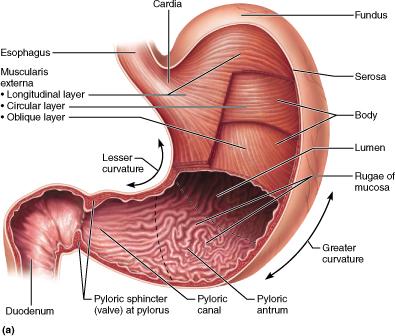
The mucosa collapses inward when the stomach is empty, forming large folds known as __________.
cardia
fundus
rugae
pylorus
rugae
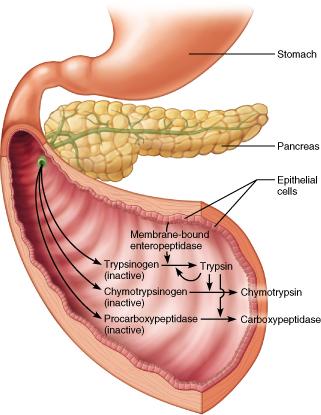
What is a major function of pancreatic juice?
emulsifying fats by breaking them into smaller pieces
neutralizing chyme entering the small intestine from the stomach
acidifying the contents of the small intestine
acidifying the contents of the stomach
neutralizing chyme entering the small intestine from the stomach
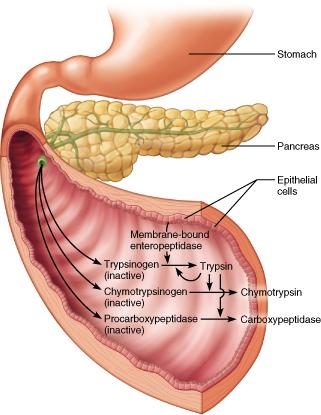
Which chemical activates the transformation of trypsinogen to trypsin?
chymotrypsin
amylase
enteropeptidase
carboxypeptidase
Enteropeptidase
True or False:
When swallowing, the epiglottis prevents food from entering the larynx.
True
Which of the following does not occur in the mitochondria?
glycolysis
Krebs cycle
formation of malic acid from
fumaric acid
electron transport
Glycolysis
Which of the following food groups are considered good sources of complete proteins?
corn, cottonseed oil, soy oil, and wheat germ
eggs, milk, yogurt, meat, and fish
egg yolk, fish roe, and grains
lima beans, kidney beans, nuts, and cereals
Eggs, milk, yogurt, meat, and fish
__________ is the key hormone regulator of the absorptive state.
Glucagon
Cortisol
Insulin
Parathyroid hormone
Insulin
True or False:
The body is able to form glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors.
True
Which of the following nutrients yield the highest amount of energy per gram when metabolized?
fats
proteins
foods and beverages high in caffeine
vitamins and minerals
Fats
True or False:
The primary function of carbohydrates is energy production within cells.
True
When proteins undergo deamination, the waste substance found in the urine is mostly________.
acetyl CoA
urea
ammonia
ketone bodies
Urea
Glycolysis occurs in the __________ of cells and is an __________ process.
mitochondria; aerobic
cytosol; anaerobic
cytosol;
aerobic
mitochondria; anaerobic
Cytosol; anaerobic
True or False:
The preferred energy fuel for the brain is fat.
False
True or False:
Cellular respiration is an anabolic process.
False
Oxidative deamination takes place in the ________.
brain
muscles
blood
liver
Liver
True or False:
It would not be healthy to eliminate all fats from your diet because they serve a useful purpose in maintaining the body.
True
Which of the following mechanisms produces the most ATP during cellular respiration?
oxidative phosphorylation
lactic acid production
oxidation reactions
substrate-level phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation
As the body progresses from the absorptive to the postabsorptive state, only the ________ continues to burn glucose while every other organ in the body mostly switches to fatty acids.
spleen
brain
pancreas
liver
Brain
Which term describes the breakdown of stored fats into glycerol and fatty acids?
lipolysis
beta oxidation
lipogenesis
ketogenesis
Lipolysis
Which nutrient molecule is the pivotal fuel molecule in the oxidative pathways?
glucose
cholesterol
fat
protein
Glucose
Which of the following is NOT a pathway in the oxidation of glucose?
Krebs cycle
gluconeogenesis
electron transport chain and
oxidative phosphorylation
glycolysis
Gluconeogenesis
__________ are considered "bad" cholesterol; high blood levels are believed to increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
HDLs
LDLs
Chylomicrons
VLDLs
LDLs
True or False :
There are no complete proteins. All animal products should be eaten with plant material to make a complete protein.
False
Which of the following is a water-soluble vitamin?
vitamin A
vitamin B
vitamin K
vitamin D
Vitamin B
The term metabolism is best defined as ________.
the number of calories it takes to keep from shivering on a cold day
the length of time it takes to digest and absorb fats
the sum of biochemical reactions involved in building and breaking down molecules
a measure of carbohydrate utilization, typically involving measurement of calories
the sum of biochemical reactions involved in building and breaking down molecules
Which nutrients function as coenzymes and are needed in only small amounts?
electrolytes
vitamins
carbohydrates
minerals
Vitamins
What is the primary function of cellular respiration - its end-purpose?
to oxidize glucose
to metabolize nutrients
to produce
proteins
to generate ATP
To generate ATP
Which of the following would decrease body temperature?
shivering
eating a large meal
enhanced thyroxine
release
dilation of cutaneous blood vessels
Dilation of cutaneous blood vessels
True or False:
The increased use of noncarbohydrate molecules for energy to conserve glucose is called glucose sparing.
True