A&P Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
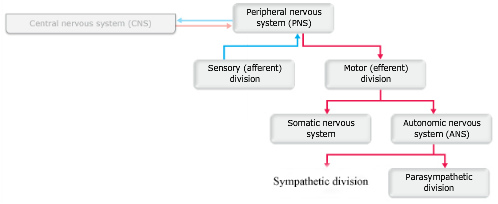
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
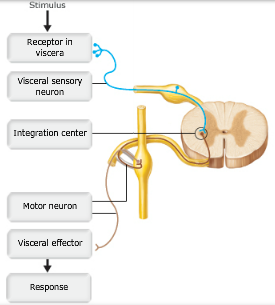
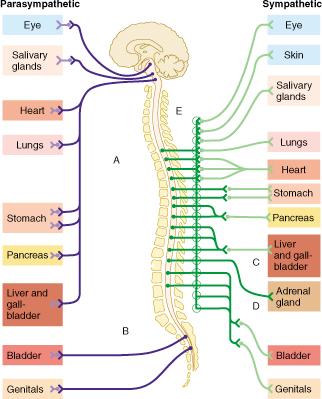
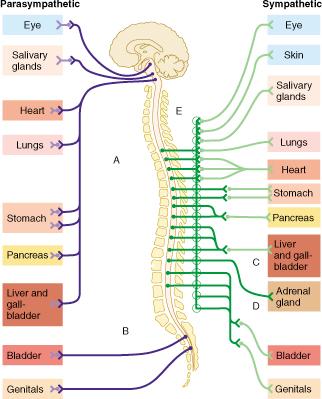
Outflow of the sympathetic division occurs from which regions of the CNS?
thoracic and lumbar
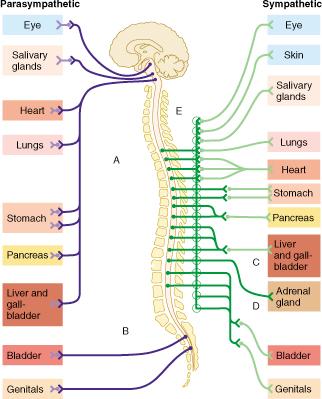
Which organ receives major input from the sympathetic, but not parasympathetic, division?
skin
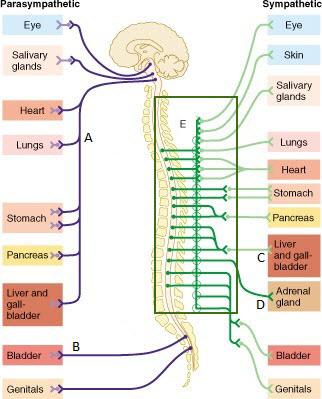
The group of fibers indicated by E represents which of the following?
white rami communicantes
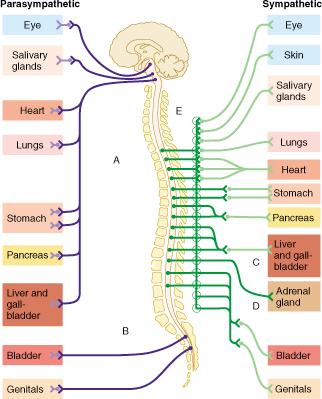
Which of the following statements is true of the group of fibers indicated by the letter D?
D indicates fibers which bypass collateral ganglia and terminate within the adrenal gland.
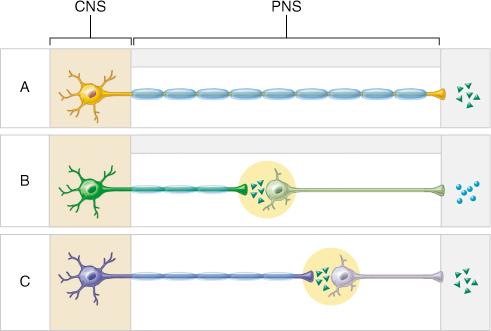
Neurons that control the voluntary movement of the arm would be associated with which pathway?
A only
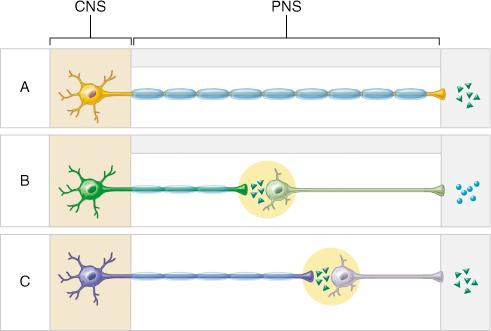
The circular structures shown within both pathways B and C represent which of the following?
ganglia
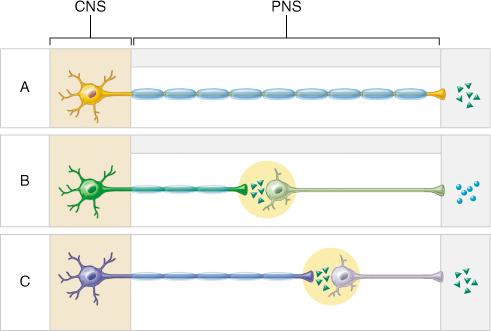
Which of the following is the site of the release of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine?
terminus of a sympathetic postganglionic neuron
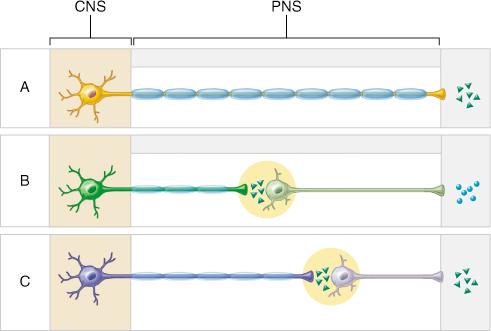
Which of the following statements is true?
The effects of neurotransmitters released from either sympathetic or parasympathetic postganglionic neurons may be stimulatory or inhibitory.
Which of the following is a way in which the somatic and autonomic nervous systems are similar?
Both systems elicit the same target organ responses to their
neurotransmitters.
Both systems have ganglia in their motor
pathways.
Both systems share common efferent pathways.
Both systems share common effectors.
None of the above.
Which of the following is not a result of parasympathetic stimulation?
dilation of the pupils
Because the ANS is a visceral motor system, afferent pathways are of no importance and actually are rarely found.
False
The ANS contains both sensory and motor neurons..
False
Which component of the ANS is characterized by ganglia located in or near effector organs?
parasympathetic division
Oculomotor nerves are responsible for which of the following functions?
focusing the eyes on close objects
Parasympathetic ganglia are also called __________ because of their location.
terminal ganglia
The secretions of the adrenal medulla act to supplement the effects of ________.
sympathetic stimulation
The parasympathetic ganglion that serves the eye is the ________.
ciliary ganglion
Sympathetic nerves may leave the spinal cord at which vertebra?
first thoracic
Which of the following is NOT an autonomic nervous system (ANS) effector?
skeletal muscle
Conduction through the autonomic efferent chain is faster than conduction in the somatic motor system.
False
The ANS stimulates smooth muscles, skeletal muscles and glands, whereas the somatic nervous system innervates skeletal muscles only.
False
Which of these effectors is not directly controlled by the autonomic nervous system?
skeletal muscle
Preparing the body for the "fight-or-flight" response is the role of the ________.
sympathetic nervous system
Which of the following is responsible for the overall integration of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
hypothalamus
All visceral organs receive dual innervation from both the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the ANS.
False
Norepinephrine-releasing fibers are called cholinergic fibers.
False
For which of the following activities is the parasympathetic nervous system generally responsible?
resting and digesting
Thermoregulatory responses to increased heat are mediated by the sympathetic nervous division.
True
Through direct neural stimulation, the sympathetic division promotes many metabolic effects via hormone release.
True
The two types of receptors that bind acetylcholine are __________ and __________ receptors.
nicotinic; muscarinic
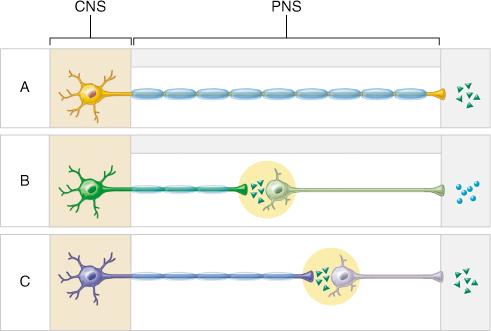
Which pathways comprise the autonomic nervous system?
B and C
Which of the following is responsible for the overall integration of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
hypothalamus
What differentiates an autonomic reflex from a somatic reflex?
a two-neuron motor pathway
Beta-blockers ________.
decrease heart rate and blood pressure
Which autonomic neurons release norepinephrine as a neurotransmitter?
sympathetic postganglionic neurons
The sympathetic division is also called the "thoracolumbar division" of the autonomic nervous system.
True
Cardiovascular effects of the sympathetic division include all except ________.
dilation of the blood vessels serving the skin and digestive viscera
The two divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) normally have a(n) __________ relationship.
antagonistic
Because many of the same cardiac cells are innervated by both parasympathetic and sympathetic fibers, the influence of the two divisions on the heart is synergistic.
False
The autonomic nervous system may cause activation or inhibition, depending on the division that is active and the target that is affected.
True
The craniosacral division is another name for the parasympathetic division.
True
Autonomic reflex centers occur in the spinal cord, medulla, and midbrain.
True
Which of the following does not describe the ANS?
a system of motor neurons that innervates all muscle cells
The sympathetic division is also called the "thoracolumbar division" of the autonomic nervous system.
True
Because many of the same cardiac cells are innervated by both parasympathetic and sympathetic fibers, the influence of the two divisions on the heart is synergistic.
False
Emotions influence autonomic reactions primarily through integration in the ________.
hypothalamus
Which of the following is NOT an autonomic nervous system (ANS) effector?
skeletal muscle
Which autonomic neurons release norepinephrine as a neurotransmitter?
sympathetic postganglionic neurons
The "resting and digesting" division of the autonomic nervous system is the ________.
parasympathetic division
Thermoregulatory responses to increased heat are mediated by the sympathetic nervous division.
True
All visceral organs receive dual innervation from both the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the ANS.
False
Cardiovascular effects of the sympathetic division include all except ________.
dilation of the blood vessels serving the skin and digestive viscera
Which division of the nervous system has short preganglionic neurons?
sympathetic
Acetylcholine is the substance released by the axonal endings of the somatic efferent fibers and by the parasympathetic nerve fiber endings.
True
Which of the following is NOT associated with the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
emergency action
Conduction through the autonomic efferent chain is faster than conduction in the somatic motor system.
False
The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the ANS have the same effect on most body organ systems.
False
Norepinephrine-releasing fibers are called cholinergic fibers.
False
The ANS stimulates smooth muscles, skeletal muscles and glands, whereas the somatic nervous system innervates skeletal muscles only.
False
For which of the following activities is the parasympathetic nervous system generally responsible?
resting and digesting
Autonomic reflex centers occur in the spinal cord, medulla, and midbrain.
True
Preparing the body for the "fight-or-flight" response is the role of the ________.
sympathetic nervous system
Which of the following is responsible for the overall integration of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
hypothalamus
Which of these effectors is not directly controlled by the autonomic nervous system?
skeletal muscle
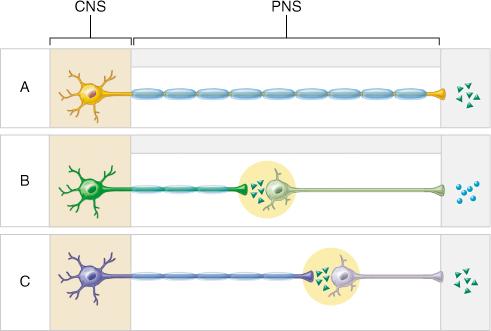
Which pathways comprise the autonomic nervous system?
B and C
What is the effect of norepinephrine on the heart?
an increase in heart rate
Which of the following does not describe the ANS?
a system of motor neurons that innervates all muscle cells
Through direct neural stimulation, the sympathetic division promotes many metabolic effects via hormone release.
True