A&P Chapter 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
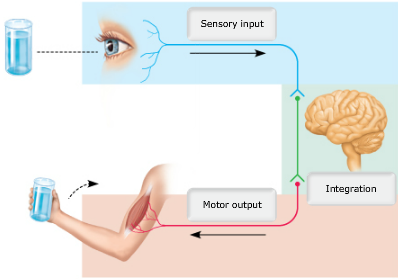
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
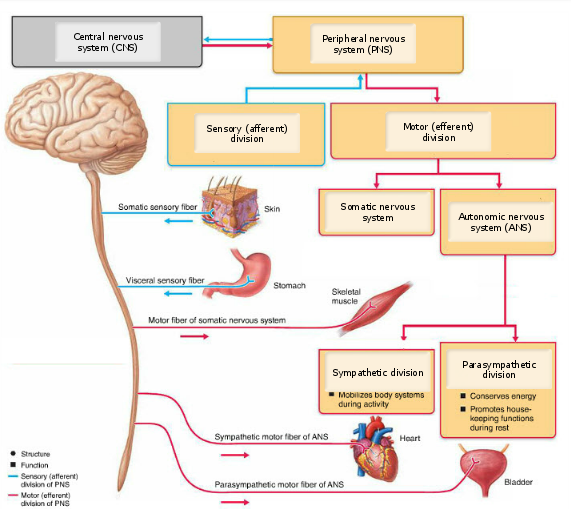
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
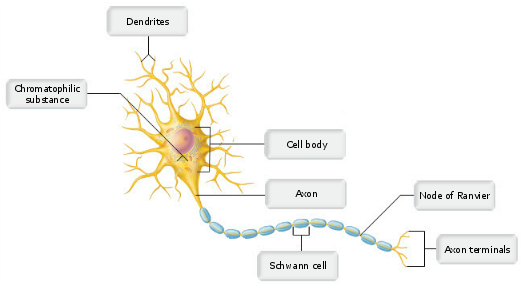
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
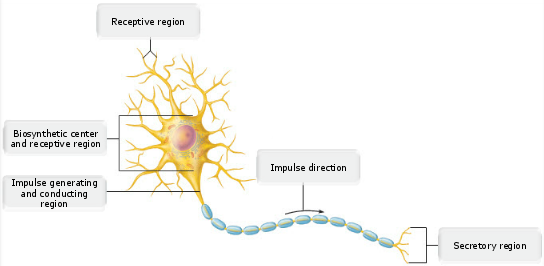
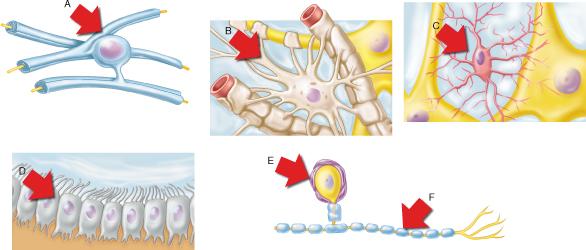
What structural classification describes the neuron associated with the neuroglia shown by E and F?
unipolar
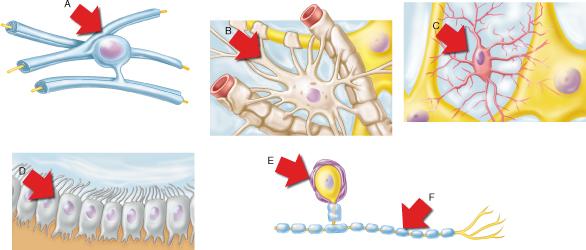
Destruction of which of the neuroglial cell types leads to the disease multiple sclerosis (MS)?
A
Which lettered region in the figure is referred to as the soma?
B
Where do most action potentials originate?
Initial segment
What opens first in response to a threshold stimulus?
Voltage-gated Na+ channels
What characterizes depolarization, the first phase of the action potential?
The membrane potential changes from a negative value to a positive value.
What characterizes repolarization, the second phase of the action potential?
Once the membrane depolarizes to a peak value of +30 mV, it repolarizes to its negative resting value of -70 mV.
What event triggers the generation of an action potential?
The membrane potential must depolarize from the resting voltage of -70 mV to a threshold value of -55 mV.
What is the first change to occur in response to a threshold stimulus?
Voltage-gated Na+ channels change shape, and their activation gates open.
What type of conduction takes place in unmyelinated axons?
Continuous conduction
An action potential is self-regenerating because __________.
depolarizing currents established by the influx of Na+ flow down the axon and trigger an action potential at the next segment
Why does regeneration of the action potential occur in one direction, rather than in two directions?
The inactivation gates of voltage-gated Na+ channels close in the node, or segment, that has just fired an action potential.
What is the function of the myelin sheath?
The myelin sheath increases the speed of action potential conduction from the initial segment to the axon terminals.
What changes occur to voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels at the peak of depolarization?
Inactivation gates of voltage-gated Na+ channels close, while activation gates of voltage-gated K+ channels open.
In which type of axon will velocity of action potential conduction be the fastest?
Myelinated axons with the largest diameter
Ions are unequally distributed across the plasma membrane of all cells. This ion distribution creates an electrical potential difference across the membrane. What is the name given to this potential difference?
Resting membrane potential (RMP)
Sodium and potassium ions can diffuse across the plasma membranes of all cells because of the presence of what type of channel?
Leak channels
On average, the resting membrane potential is -70 mV. What does the sign and magnitude of this value tell you?
The inside surface of the plasma membrane is much more negatively charged than the outside surface.
The plasma membrane is much more permeable to K+ than to Na+. Why?
There are many more K+ leak channels than Na+ leak channels in the plasma membrane.
The resting membrane potential depends on two factors that influence the magnitude and direction of Na+ and K+ diffusion across the plasma membrane. Identify these two factors.
The presence of concentration gradients and leak channels
What prevents the Na+ and K+ gradients from dissipating?
Na+-K+ ATPase
Which of the following describes the nervous system integrative function?
analyzes sensory information, stores information, makes decisions
Which of the following types of glial cells monitors the health of neurons, and can transform into a special type of macrophage to protect endangered neurons?
microglia
Which of the following are bundles of neurofilaments that are important in maintaining the shape and integrity of neurons?
neurofibrils
Which of the following is true of axons?
A neuron can have only one axon, but the axon may have occasional branches along its length.
Which of the following is NOT a functional classification of neurons?
multipolar
Which of the following is NOT true of association neurons?
Most association neurons are confined within the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Neurons are also called nerve cells.
True
Unmyelinated fibers conduct impulses faster than myelinated fibers.
False
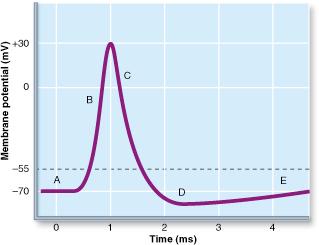
At which point of the illustrated action potential are the most gated Na+ channels open?
B
In myelinated axons the voltage-regulated sodium channels are concentrated at the nodes of Ranvier.
True
Collections of nerve cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system are called ________.
ganglia
What does the central nervous system use to determine the strength of a stimulus?
frequency of action potentials
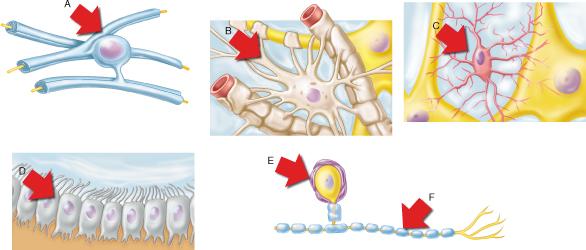
Which of the neuroglial cell types shown form myelin sheaths within the CNS?
A
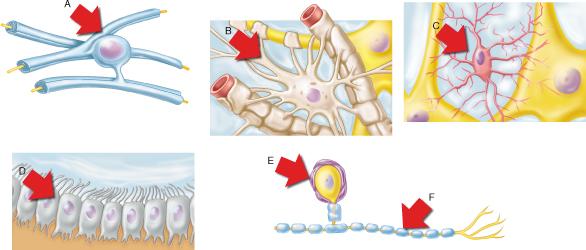
Which of the neuroglial cell types shown is the most abundant in the CNS?
B
Saltatory conduction is made possible by ________.
the myelin sheath
Large-diameter nerve fibers conduct impulses much faster than small-diameter fibers.
True
The part of a neuron that conducts impulses away from its cell body is called a(n) ________.
axon
Schwann cells are functionally similar to ________.
oligodendrocytes
Bipolar neurons are commonly ________.
found in the retina of the eye
If bacteria invaded the CNS tissue, microglia would migrate to the area to engulf and destroy them.
True
Myelination of the nerve fibers in the central nervous system is the job of the oligodendrocyte.
True
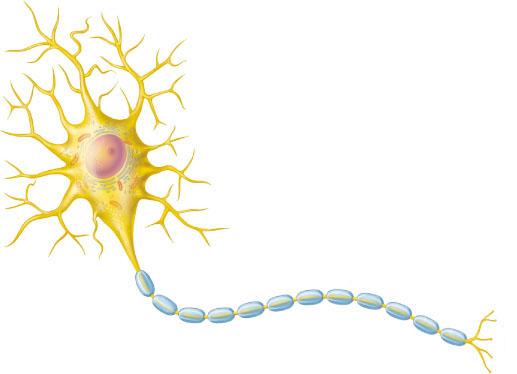
What structural classification describes this neuron?
multipolar
What part of the nervous system performs information processing and integration?
central nervous system
Which of the following types of neurons carry impulses away from the central nervous system (CNS)?
motor
Efferent nerve fibers may be described as motor nerve fibers.
True
The period after an initial stimulus when a neuron is not sensitive to another stimulus is the ________.
absolute refractory period
Which of the following is NOT a type of circuit?
pre-discharge circuits
Which part of the neuron is responsible for generating a nerve impulse?
axon
What are ciliated CNS neuroglia that play an active role in moving the cerebrospinal fluid called?
ependymal cells
Which of the following is NOT one of the basic functions of the nervous system?
regulation of neurogenesis
The oligodendrocytes can myelinate several axons.
True
Immediately after an action potential has peaked, which cellular gates open?
potassium
What type of stimulus is required for an action potential to be generated?
a threshold level depolarization
Which of the following is not a function of the autonomic nervous system?
innervation of skeletal muscle
A neuron that has as its primary function the job of connecting other neurons is called a(n) ________.
association neuron
Which of the following is a factor that determines the rate of impulse propagation, or conduction velocity, along an axon?
degree of myelination of the axon
Neurons in the CNS are organized into functional groups.
True
Which of the following peripheral nervous system (PNS) neuroglia form the myelin sheaths around larger nerve fibers in the PNS?
Schwann cells
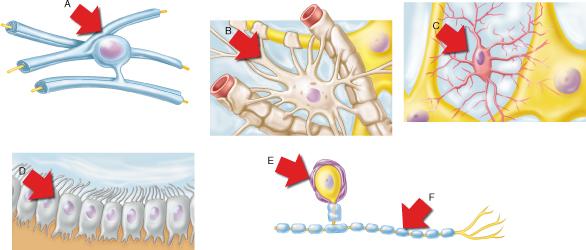
Which of the neuroglial cell types shown is the most abundant in the CNS?
B
Neuroglia that control the chemical environment around neurons by buffering ions such as potassium and recapturing and recycling neurotransmitters are ________.
astrocytes
Which of the following is NOT one of the basic functions of the nervous system?
regulation of neurogenesis
What are ciliated CNS neuroglia that play an active role in moving the cerebrospinal fluid called?
ependymal cells
Which part of the neuron is responsible for generating a nerve impulse?
axon
Efferent nerve fibers may be described as motor nerve fibers.
True
The action potential is caused by permeability changes in the plasma membrane.
True
What does the central nervous system use to determine the strength of a stimulus?
frequency of action potentials
Which of the choices below describes the ANS?
motor fibers that conduct nerve impulses from the CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
Which of the following is not characteristic of neurons?
They are mitotic.
Large-diameter nerve fibers conduct impulses much faster than small-diameter fibers.
True
Bipolar neurons are commonly ________.
found in the retina of the eye
Which ion channel opens in response to a change in membrane potential and participates in the generation and conduction of action potentials?
voltage-gated channel
Which of the following is NOT a type of circuit?
pre-discharge circuits
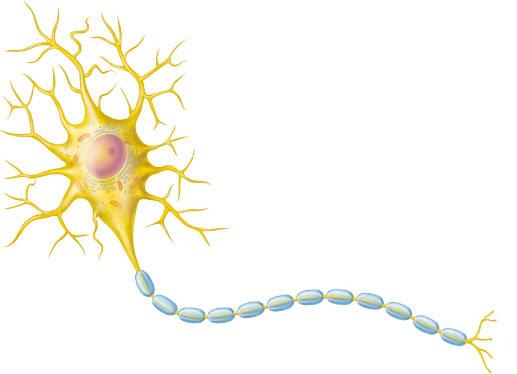
What structural classification describes this neuron?
multipolar
A neuron that has as its primary function the job of connecting other neurons is called a(n) ________.
association neuron
Immediately after an action potential has peaked, which cellular gates open?
potassium
Which of the following circuit types is involved in the control of rhythmic activities such as the sleep-wake cycle, breathing, and certain motor activities (such as arm swinging when walking)?
reverberating circuits
Collections of nerve cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system are called ________.
ganglia
The __________ is due to the difference in K+ and Na+ concentrations on either side of the plasma membrane, and the difference in permeability of the membrane to these ions.
resting membrane potential
During depolarization, the inside of the neuron's membrane becomes less negative.
True
The all-or-none phenomenon as applied to nerve conduction states that the whole nerve cell must be stimulated for conduction to take place.
False