Econ 202 Final
Economics of the long run is
classical economics
Economics of the short run is
keynesian economics
In the long run
the economy operates at full employment
If GDP is above potential output, the economy is in a
boom, prices and wages wil increase
If the unemployment rate is above the natural rate, then GDP (output) is
below potential output
If the unemployment rate is below the natural rate, we would expect
GDP above potential output, and rising wages and prices
A wage-price spiral occurs when
rising wages cause higher prices, which in turn causes higher wages
If the economy has been experiencing 3% annual inflation and output is less than full employment, prices will generally rise at
a rate less than 3%, because unemployment causes wages to fall.
The keynesian (short run) aggregate supply curve is horizontal (flat) because
short run prices are fixed but output may shift
The classical (long run) aggregate supply curve is vertical because
long run prices are flexible but output is equal to potential
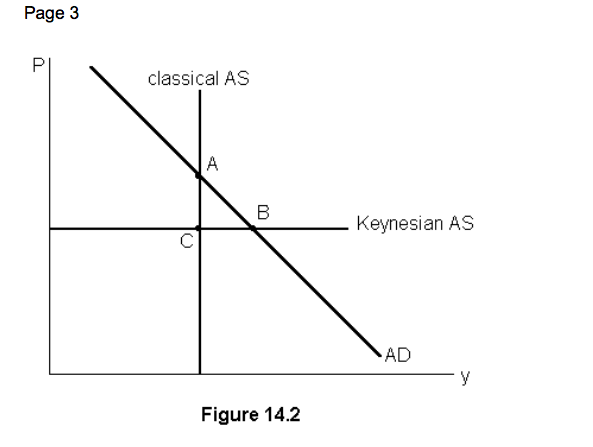
Long run equilibrium occurs at
A
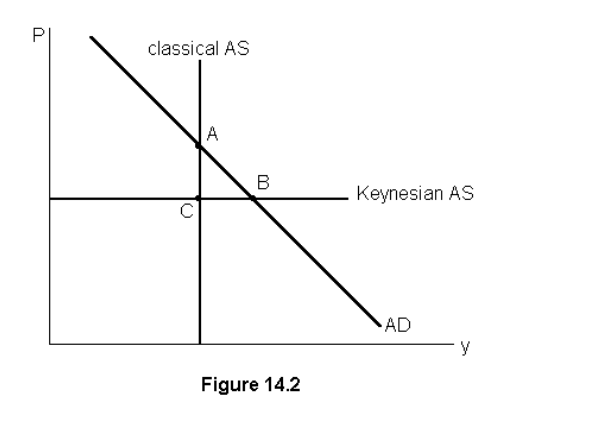
The short run equilibrium occurs at
B
Output is likely to rise and prices to fall if the economy is at point
C
An increase in wages is represented by a movement from points
C to B, higher wages means higher price and less output
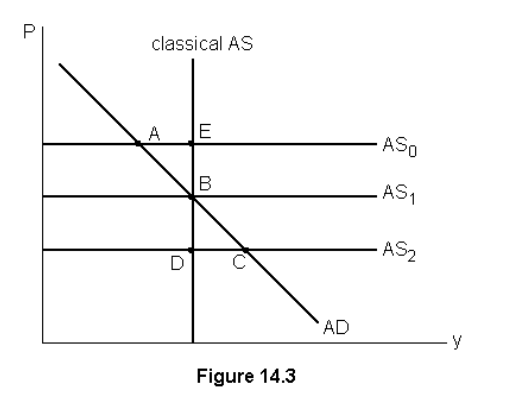
Change from short run to long run equilibrium is shown by movements from
A to B
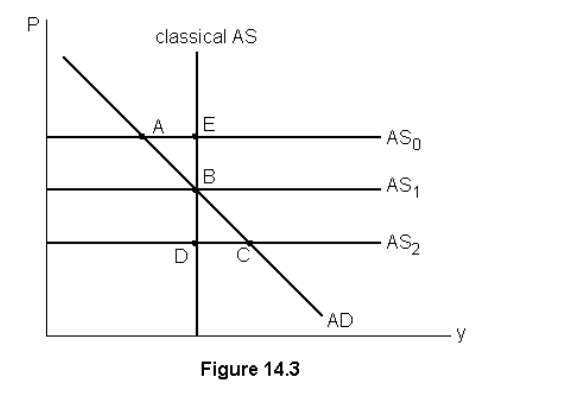
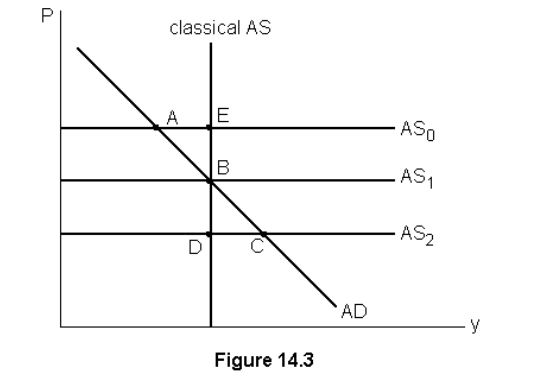
If GDP is above potential output then we expect
increasing wages cause my an upward shift in the short run aggregate supply curve
If the unemployment rate is less than the natural rate then
none of the listed answers, If unemployment is below the natural rate output must be above potential output. So we would expect to see increasing wages, keynesian supply shift up and a decrease in output.
Economists who believe that adjustments to long run equilibrium happen quickly suggest that the government
avoid stabilization policies and rely on natural stabilization
GDP for an economy is below potential output, if adjustment to the long run equilibrium happens slowly the government is likely to persue a policy of
increasing government spending to increase aggregate demand
A decrease in the price level causes
a decrease in demand for money
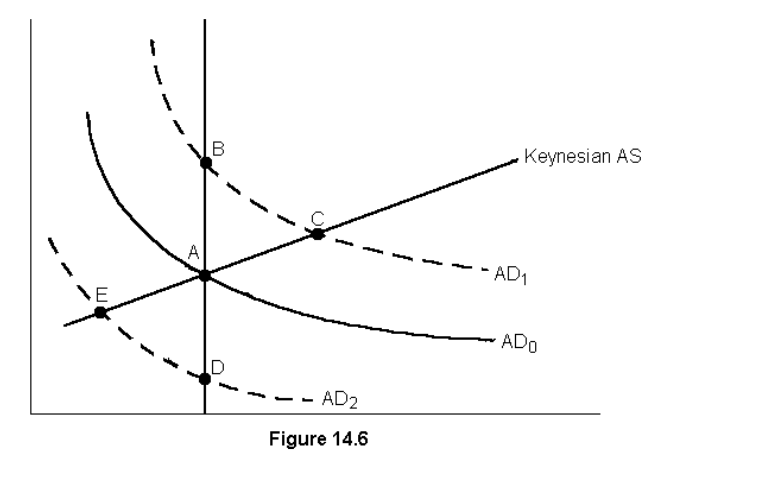
the economy is in equilibrium at point A but as the supply of money increases in the long run the economy moves to point
B
Unemployment is above natural rate
prices, money demand, and interest rates fall but total demand rises
the Federal reserve can use monetary policy to
change output in the short run, but not the long run
In the long run and increase in the money supply
has no effect on real interest rates, investment or output
Investment is "crowded out" by an increase in government spending because
increase in government spending causes output and prices to rise, which also causes interest rates to rise
Compared to other countries inflation in the US has been
generally less severe
If workers confuse real and nominal magnitudes, they are experiencing
money illusion
Suppose the inflation rate is 4% this year. If nominal wages increase by 4% then real wages will
no change
Suppose inflation is 8% this year, if nominal wages increase by 6% then real wages will
decrease by 2%
If nominal wages increase by 7% while real wages increase by 3%, the inflation rate must be :
4%
The real rate of interest is defined as the :
nominal interest rate - expected inflation rate
S
uppose you have $100 to invest for a year and the
nominal interest rate
is 5%. If the inflation rate for the year is 3%, your
real investment will be
$2 (2% x $100)
Suppose you have $100 to invest for a year and the
nominal interest rate
is 7%. If the inflation rate is 3% , your nominal gain
will be
$7, problem gives you nominal rate of 7%
In the long run, increases in the growth rate of the money supply will __________ nominal rates of interest and __________ real rates of interest.
increase, not affect
Money is neutral in the long run. Thus, no long-run effect on real interest rates, but increases in the growth rate of money lead to higher inflation and expected inflation, which implies higher nominal interest rates in the long run.
In the short run, increases in the growth rate of the
money supply will
__________ nominal rates of interest and __________
real rates of
interest.
decrease, decrease
In the short run, increases in the money supply will
decrease both nominal and real interest rates
(recall the graph of money supply and money demand,
with money supply shifting to the right), as money
has no effect on prices in the short run.
The expectations Phillips curve describes the relationship between inflation and unemployment :
when expectations of inflation are taken into account
Assume that last year's inflation rate is the same as the expectation of inflation for the next year. According to the expectations Phillips curve, if the inflation rate decreases, the unemployment rate :
increases
Suppose the economy has been at full employment for the
past two years
with a 5% inflation rate. If the Federal Reserve
unexpectedly increases
the rate of money growth to 7%, the following
sequence of events occurs
:
real interest rates fall, investment spending increases, GDP increases, unemployment falls and prices rise
In the short run, the higher money growth (unanticipated) causes real interest rates to fall, which increases investment and GDP and decreases unemployment. In the longer run, the higher money growth will also cause prices then to rise (and begin reversing the previous effects).
Suppose the economy has been at full employment for the
past two years
with a 4% inflation rate. If the Federal Reserve
unexpectedly increases
the rate of money growth to 6%, the following
sequence of events occurs
:
real interest rates fall, investment spending increases, GDP increases, unemployment falls and prices rise
To finance a budget deficit, the government can :
increase borrowing from the public and print new money
A nation that cannot borrow money but creates a large
budget deficit is
likely to experience
:
hyperinflation
Monetarists :
emphasize the role of money in the economy
Suppose workers negotiate for a 5% nominal wage increase and expect a 4% inflation rate. If the actual inflation rate is 7%, then workers :
are worse off and firms are better off
Workers are clearly worse off because inflation is higher than what they expected when they negotiated their nominal wage increases, so in real terms they have less purchasing power.
As the result of unanticipated inflation, workers are better off while firms are worse off if the actual inflation rate :
is less than the expected inflation rate
As the result of unanticipated inflation, borrowers are better off while lenders are worse off if the actual inflation rate :
exceeds the expected inflation rate
Borrowers are better off if actual inflation exceeds expected inflation because they are later repaying the borrowed funds in money than has less purchasing power,
Suppose that the expected inflation rate is 5.5% and the actual inflation rate is 3%. Then borrowers :
are worse off and lenders are better off
A deficit is defined as :
Government expenditures are defined as :
Transfer payments include :
The government debt is defined as :
If government spending is $100 billion while government revenue is $120 billion, the government is said to have a :
If government spending is $500 billion while government revenue is $475 billion, the government is said to have a :
Suppose the government's initial debt is $70 billion.
If for the next
three years the government runs deficits of $10, $25,
and $40 billion,
the government's total debt at the end of the three
years will be
:
Suppose the government's initial debt is $150 billion
and that during th
e next two years the government runs deficits of $30
and $10 billion. If
during the third year the government has a $15 billion
surplus, the
government's additional debt at the end of the three
years will be
:
If there was a federal budget surplus it would make it possible to :
Which of the following equations is correct?
The government borrows money to cover budget deficits by :
The government finances budget deficits by :
Excessive creation of new money to finance a government
budget deficit
can lead to
:
If the Federal Reserve purchases newly issued government debt :
Which of the following is a burden of the national debt?
Which of the following illustrates a burden of the national debt?
Government debt lowers the amount of capital in the
economy because the
debt
:
"Servicing the debt" refers to :
Which of the following is a burden the government places on future generations?
Social Security and Medicare represent promises made to :
Automatic stabilizers are changes in taxes and transfer
payments that
occur
:
Changes in taxes and transfer payments that dampen
economic fluctuations
are known as
:
During recessions, unemployment __________ while the
budget deficit as a
percentage of GDP __________
A constitutional balanced budget amendment would :
Arguments for the balanced budget amendment include which of the following?
Which of the following is an argument for the balanced budget amendment?
To reduce inflation usually requires that actual unemployment :