REVIEW Q&A chapter 4
Makes up the pleura and pericardium.
Serous membrane
- Lines blood vessels and the heart.
- The epithelial membrane that lines the closed ventral cavities of the body.
Endothelium
Derived from mesenchyme
Tendon
- Found lining the digestive and respiratory tracts.
- The epithelial membrane that lines body cavities open to the exterior membrane
Mucous membrane
Consists of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
Cutaneous
SKELETAL MUSCLE
Weak regenerative ability
Has a surface to which nothing is
attached
Skin epidermis
Tendons and ligaments
Moderate regenerative ability
Moves food through the GI tract
Tendon
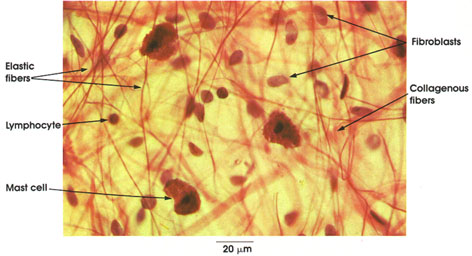
Areolar connective tissue

Regenerates extremely well
Moderate regenerative ability
Smooth muscle.
- Moves blood through the body
- Virtually no functional regenerative ability
Cardiac muscle
Explain why an infection may occur in a tissue injury.
The skin is the largest organ in the body and protects underlying tissues from injury by preventing the passage of microorganisms. The skin and the mucous membranes are considered the body's first line of defense.
A 6-year-old child fell off his bike and scraped his knee. Describe the first stage of wound healing.
The first stage is the inflammatory stage, characterized by injured cells releasing inflammatory chemicals, which causes increased permeability and allows white blood cells and clotting proteins to seep into the injured area. This protects the body from bacteria and loss of blood.
Explain why an open wound would need a bed of granulation tissue for wound healing to occur.
Epithelium cannot grow across a defect without a blood supply from underlying connective tissue. Granulation tissue contains capillaries that grow in from nearby areas and first lay down the needed capillary bed.
Aunt Jessie woke up one morning with excruciating pain in her chest. She had trouble breathing for several weeks. Following a visit to the doctor, she was told she had pleurisy. What is this condition and what did it affect?
Pleurisy is an inflammation of the pleura, the serosal membranes covering the lungs and lining the thoracic wall. Pain is caused by the irritation and friction as the lungs rub against the walls of the cavity.
What distinguishes cancer cells from the cells of benign neoplasms?
metastasis and invasiveness

Without macrophages, wound healing is delayed. Why?

Macrophages are large, irregularly shaped cells that act as key defenders that avidly phagocytize a broad variety of foreign materials, ranging from foreign molecules to entire bacteria to dust particles. This "big eater" also disposes of dead tissue cells, which helps to clean out the wound, allowing for granulation tissue to form.
The salivary glands are a good example of a(n) ________ exocrine gland.
compound tubuloalveolar
Explain what is meant by epithelial tissue being avascular but innervated.
Epithelial tissue contains no blood vessels but is supplied by nerve fibers.
Which of the following is not a step in tissue repair?
A)Restoration of blood supply
B)Inflammation
C)Formation of new stem cells
D)Regeneration and fibrosis.
Answer: C
John, a 72-year-old grandfather, had been smoking heavily for 24 years and had a persistent cough. A biopsy of his lung tissue revealed considerable amounts of carbon particles. How could this happen considering the natural cleaning mechanism of the respiratory system?
The sweeping action of the ciliated epithelium is essential in order to propel inhaled dust and other debris out of the respiratory tract. Anything that inhibits this mechanism would allow foreign substances to remain in the tract, which may cause damage. Chemicals such as nicotine may inhibit the action of the cilia, allowing carbon particles found in smoke to reach the lungs.

A 45-year-old woman is admitted to the hospital for surgical removal of a tumor on her thyroid gland. The surgeon informs her that she will have only a very thin scar. How could this be possible?

By making a sharp incision which minimizes the number of injured cells and wound defects once reapproximated, the amount of granulation (scar-forming) tissue will be minimal. As the scar tissue beneath matures and contracts, very little new epithelium needs to bridge the gap. The final result may be only a fine white line.
Kidney tubules are composed of ________ epithelium.
simple cuboidal
In adult humans, most cancers are carcinomas or adenocarcinomas. These include cancers of the skin, lung, colon, breast, and prostate. Which of the four basic tissue types is involved? Why do you think this is so?
Epithelium gives rise to most cancers. This is probably because epithelial cells divide more, leading to more opportunity for damage to growth control mechanisms, and because epithelia are more often in contact with environmental insults such as ultraviolet radiation and carcinogens.
What are the primary germ layers during embryonic development and what do they ultimately produce?
The ectoderm produces the skin and nervous system. The mesoderm produces muscles and connective tissue. The endoderm produces the inner epithelial surface of all internal organ tubes opening to the outside and many endocrine glands.
How is blood unique among connective tissues?
Blood does not give mechanical support, its matrix is fluid, the cells are loose, the fibers are soluble, it carries nutrients, waste products, and other substances, and it attaches to several gases.
Since mature adipocytes rarely divide, how can adults gain weight?
Adipocytes contain a fat-filled vacuole that can fill or empty, causing the cell to gain or lose volume.
How can one tell the difference between stratified squamous epithelium and transitional epithelium?
The most reliable distinctions are two. Compared to stratified squamous epithelium, transitional epithelium has fewer layers (6 or less) and has more rounded surface cells when it is bunched up with more apparent layers and more likely to be mistaken for stratified squamous..
The uppermost layer of skin is composed of ________.
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Three to six rows of cells covering a tissue in which the cells may be the same shape from the basement membrane to the surfaces would be ________ epithelia.
transitional
How is epithelial tissue the opposite of connective tissue?
Epithelial versus connective distinctions include: tight cell packing versus wide cell spacing, avascular versus vascular (except cartilage), polar versus nonpolar orientation, no matrix versus matrix (with important fibers), limited versus numerous cell types, and surface versus subsurface purposes.
Cardiac muscle tissue is uninucleated, has intercalated discs, and is ________.
branched
The ________ muscle cells are multinucleated due to the fusion of myoblasts.
Skeletal
The tissue that forms the framework for the lamina propria of mucous membranes is ________ connective tissue.
Areolar
Mesenchymal cells are most commonly found in ________ connective tissue.
A)areolar
B)reticular
C)dense regular
D)embryonic
Answer: D
Macrophage-like cells are found in many different tissues, and may have specific names that reflect their location or specializations. What is the one functional characteristic common to all macrophage-like cells?
phagocytosis
Which cells are commonly found wedged between simple columnar epithelial cells?
A)Restoration of blood supply
B)Inflammation
C)Formation of new stem cells
D)Regeneration and fibrosis.
Answer: A
Select the correct statement regarding epithelia.
A)Stratified epithelia are present where protection from abrasion is important. B)Pseudostratified epithelia consist of at least two layers of cells stacked on top of one another. C)Stratified epithelia are tall, narrow cells. D)Simple epithelia form impermeable barriers.
Answer: A
Answer: A
Select the correct statement regarding tissue repair.
A)Stratified epithelia are present where protection from abrasion is important. B)Pseudostratified epithelia consist of at least two layers of cells stacked on top of one another. C)Stratified epithelia are tall, narrow cells. D)Simple epithelia form impermeable barriers.
Answer: B
Select the correct statement regarding the stem cells of connective tissue
A)"Blast" cells are undifferentiated, actively dividing cells .
B)Chondroblasts are the main cell type of connective tissue proper.
C)Connective tissue cells are nondividing.
D)Connective tissue does not contain cells.
Answer: A
Which of the following statements is true of connective tissue?
A)When connective tissue is stretched, collagen gives it the ability to snap back.
B)Reticular fibers form thick, ropelike structures.
C)Elastin fibers are sometimes called white fibers.
D)Collagen fibers provides high tensile strength.
A nswer: D
What are the three main components of connective tissue?
A)ground substance, fibers, and cells
B)fibroblasts, chondroblasts, and osteoblasts
C)collagen, elastin, and reticular fibers
D)alveoli, fibrous capsule, and secretory cells
Answer: A
The first step in tissue repair involves ________. A)inflammation
A)are mature cartilage cells located in spaces called lacunae
B)remain in compact bone even after the epiphyseal plate closes
C)within the cartilage divide and secrete new matrix
D)never lose their ability to divide
Answer: A
Which is true concerning muscle tissue?
A)contains contractile units made of collagen
B)is a single-celled tissue
C)cuboidal shape enhances function
D)highly cellular and well vascularized
Answer: D
Arteries, veins, and lymphatics keep clots from sticking as long as their ________ is intact and healthy.
A)mesothelium
B)simple cuboidal epithelium
C)endothelium
D)transitional epithelium.
Answer: C
Heart muscle cells would tend to separate without ______
A)stroma
B)flana
C)myofilaments
D)intercalated discs
Answer: D
A many-layered epithelium with cuboidal basal cells and flat cells at its surface would be classified as ________.
A)transitional
B)simple cuboidal
C)stratified squamous
D)simple squamous
Answer: C
________ epithelium appears to have two or three layers of cells, but all the cells are in contact with the basement membrane.
A)Pseudostratified columnar
B)Stratified cuboidal
C)Stratified columnar
D)Transitional
Answer: A
Groups of cells that are similar in structure and perform a common or related function form a(n) ________.
A)organism
B)organ
C)organ system
D)tissue
Answer: D
Chondroblasts ________.
A)are mature cartilage cells located in spaces called lacunae
B)remain in compact bone even after the epiphyseal plate closes
C)within the cartilage divide and secrete new matrix
D)never lose their ability to divide
Answer: C
Glands, such as the thyroid, that secrete their products directly into the blood rather than through ducts are classified as ________.
A)ceruminous
B)exocrine
C)sebaceous
D)endocrine
Answer: D
Which of the following is true about epithelia?
A)Pseudostratified epithelia are commonly keratinized.
B)Stratified epithelia are associated with filtration.
C)Simple epithelia are commonly found in areas of high abrasion.
D)Endothelium provides a slick surface lining all hollow cardiovascular organs.
Answer: D
Which tissue type arises from all three embryonic germ layers?
A)nervous tissue
B)muscle tissue
C)connective tissue
D)epithelial tissue
Answer: D
Groups of cells that are similar in structure and perform a common or related function form a(n) ________.
A)organism B)organ C)organ system D)tissue
Answer: D
The fiber type that gives connective tissue great tensile strength is ________.
A)collagen
B)elastic
C)reticular
D)muscle
Answer: A
Cell type not found in areolar connective tissue.
A)fibroblasts B)chondrocytes C)macrophages D)mast cells
Answer: B
Answer: B
Connective tissue matrix is composed of ________.
A)cells and fibers
B)fibers and ground substance
C)all organic compounds
D)ground substance and cells
Answer: B
Which statement best describes connective tissue?
A)usually contains a large amount of matrix
B)usually lines a body cavity
C)typically arranged in a single layer of cells
D)primarily concerned with secretion
Answer: A
Which of the following is a single-celled layer of epithelium that forms the lining of serous membranes?
A)simple cuboidal B)simple columnar C)pseudostratified columnar D)simple squamous
Answer: D
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium ciliated variety ________.
A)aids in digestion
B)possesses no goblet cells
C)is not an epithelial classification
D)lines most of the respiratory tract
Answer: D
The simple columnar epithelium that form absorptive cells of the digestive tract have which characteristic?
A)cilia
B)fibroblasts
C)a rich vascular supply
D)dense microvilli
Answer: D
Tendon tears or breaks are difficult to repair both physiologically and surgically. Why?
Tendons are composed of dense regular connective tissue, which consists of densely packed, parallel connective tissue fibers. This type of tissue has relatively few cells and vascular supply is poor; consequently, repair is slow. Because of the structure of the tissue, surgical repair can be compared to attempting to suture two bristle brushes together. The broken ends of existing collage fibers will not reunite and can still slip past each other. Furthermore, any scar that forms has an irregular pattern with less one-way strength than parallel fibers.
Which of the following would be of most importance to goblet cells and other glandular epithelium?
A)Golgi bodies B)lysosomes C)microvilli D)multiple nuclei
Answer: A
The blast cell for blood production is the ________.
A)fibroblast B)hemocytoblast C)chondroblast D)osteoblast Answer: B
How is hyaline cartilage different from elastic or fibrocartilage?
A)It forms most of the embryonic skeleton.. B)It contains more nuclei. C)Fibers are not normally visible. D)It is more vascularized.
Answer: C
The reason that intervertebral discs exhibit a large amount of tensile strength, which allows them to absorb shock, is because they possess ________.
A)elastic fibers B)collagen fibers C)reticular fibers D)hydroxyapatite crystals
Answer: B
What tissue has lacunae, calcium salts, and blood vessels?
A)osseous tissue B)areolar tissue C)cartilage tissue D)fibrocartilaginous tissue
Answer: A
Which of the following is not found in the matrix of cartilage but is found in bone?
A)organic fibers B)lacunae C)blood vessels D)living cells
Answer: C
Blood is considered a type of connective tissue.
Answer: True
Squamous cells are flattened and scalelike when mature.
Answer: True
Functions of connective tissues include binding, support, insulation, and protection.
Answer: True
Nervous tissue consists mainly of neurons and collagen fibers.
Answer: False
The shock-absorbing pads between the vertebrae are formed of fibrocartilage.
Answer: True
Endocrine glands are often called ducted glands. Answer:
ANSWER: False
Healing of a surgical incision through the body wall will tend to increase the amount of areolar tissue.
Answer: FLASE
Cartilage has good regenerative capacity, while most epithelial tissues do not.
Answer: False
Smooth muscle cells possess central nuclei but lack striations.
Answer: True
Intercalated discs and striations are found in skeletal muscle.
Answer:FLASE
Cartilage tissue tends to heal less rapidly than bone tissue.
Answer: TRUE
A major characteristic of fibrocartilage is its unique amount of flexibility and elasticity
Answer: TRUE
Tendons and ligaments are composed mainly of dense irregular connective tissue.
Answer: FLASE
Connective tissues that possess a large quantity of collagen fibers often provide the framework for organs such as the spleen and lymph nodes..
ANSWER: flase
Salivary glands exhibit simple tubuloalveolar glandular arrangement.
Answer: FLASE
Merocrine glands produce their secretions by accumulating their secretions internally until the cell ruptures.
Answer: FLASE
Aging tends to increase bony spread within the body as chondrocytes die.
Answer: FLASE
Elastic cartilage tissue is found in the walls of the large arteries that leave the heart.
Answer: True
Depending on the functional state of the bladder, transitional epithelium may resemble stratified squamous or stratified cuboidal epithelium.
Answer: TRUE
Simple cuboidal epithelia are usually found in areas where secretion and absorption occur.
Answer: TRUE
Epithelial tissues always exhibit polarity; that is, they have a free surface and a basal surface.
Answer: True
Goblet cells are found within pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
Answer: TRUE
Macrophages are found in areolar and lymphatic tissues.
Answer: True
The role of brown fat is to warm the body; whereas, the role of white fat is to store nutrients.
Answer: True