Quiz Practice Questions
Four Properties of Water
cohesive behavior
moderate temperature
expansion upon freezing
versatility as a solvent
Cohesion
hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together
Adhesion
an attraction between different substance
Evaporating cooling
as a liquid evaporates, its remaining surface cools
Moderation of Temperature
heat is absorbed and released
evaporating cooling
Solvent
the dissolving agent of the solution
Solute
substance that is dissolved
Solution
a liquid that is a homogenous mixture of substances
Aqueous solution
water is solvent
Hydration shell
ion surrounded by a sphere of water molecules when dissolved in water
Hydrophobic substance
substance that does not have affinity for water
Hydrophilic substance
substance that has affinity for water
Colloid
a stable suspension of fine particles in a liquid
Is oil hydrophobic, hydrophilic, or a colloid?
hydrophobic
Is paper hydrophobic, hydrophilic, or a colloid?
hydrophilic
Is cotton hydrophobic, hydrophilic, or a colloid
hydrophilic and colloid
What allows water molecules to form hydrogen molecules with each other?
polarity
What is used to describe whether a solution is acidic or basic?
pH scale
A substance that reduces H+ ion conc is called a base. True or False
true
What is the pH for a neutral solution?
pH 7
A substance which has more OH- conc and less H+ conc is _____________
basic substance
Buffers
substances that minimize concentrations of H+ and OH- in a solution
Acid precipitation
rain, snow, or fog with a pH lower than 5.6
What is the valence for Carbon?
four
What are frequent partners of Carbon?
Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen
Name the different types of variations in Carbon skeletons
Length
Branching
Double Bonds
Rings
What are isomers?
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures
Different types of isomers
Structural, geometric, enantiomers
What are structural isomers?
different covalent arrangements
What are geometric isomers
differ in spatial arrangements
What are enantiomers?
mirror images of each other
What are functional groups?
components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions
Name the seven functional groups discussed in class
Hydroxyl group
Carbonyl group
Carboxyl group
Amino group
Sulfhydryl group
Phosphate group
Methyl group
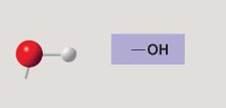
Hydroxyl group
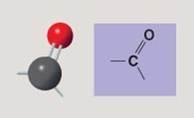
Carbonyl group
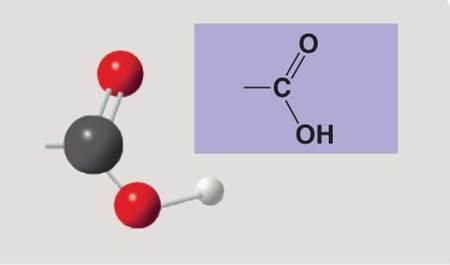
Carboxyl group
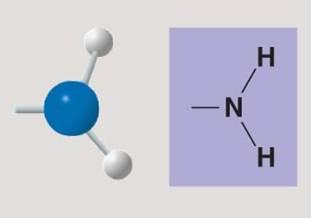
Amino
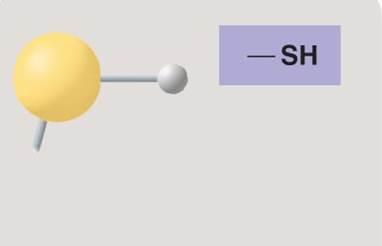
Sulfhydryl
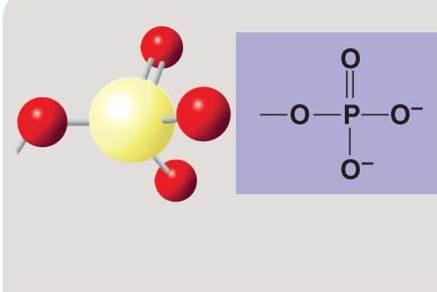
Phosphate
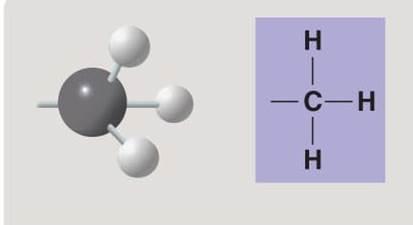
Methyl