Histology of Nervous Tissue
Nervous Tissue
-the master integrating and coordinating system
-monitors and processes sensory info
-divided into central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
Central Nervous System

-consists of brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System

-includes all nervous elements located outside the central nervous system
*ex: nerves, sensory receptors, and some cluster of nerve cells
Nervous Tissue
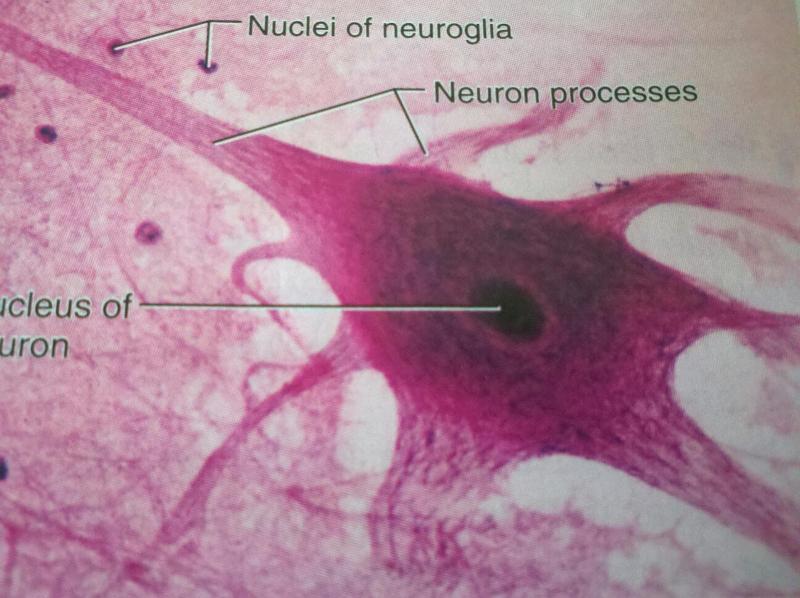
-made up of neurons and neuroglia cells
Neuroglia/ Glial Cells

-serves the needs of the delicate neurons by bracing and protecting them
CNS: astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglial cells, and ependymal cells
PNS: Schwann cells and satellite cells
Microglial Cells

-acts as phagocytes
Oligodendrocytes & Schwann Cells
-myelinate the cytoplasmic extensions of the neurons
Astrocytes
-play a role in capillary-neuron exchanges and control the chemical environment around neurons
Neuron/Nerve Cells
-basic functional units of nervous tissue
-transmit messages from one part of the body to another in the form of nerve impulses
Cell Body of Neuron

-slender processes extend
-both the biosynthetic center of the neuron and part of its receptive region
-make up the gray matter of the CNS and form clusters there called nuclei and ganglia in PNS
-contains a large round nucleus surrounded by cytoplasm
Nuclei

-cluster of neuron cell bodies in CNS
Ganglia
-cluster of neuron cell bodies in PNS
Two structures found in the cytoplasm
Neurofibrils and Chromatophilic Substance
Neurofibrils
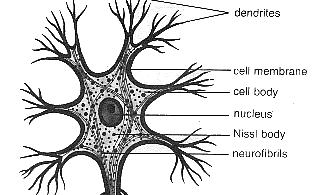
-provide support for the cell and a means to transport substances throughout the neuron
Chromatophilic Substance/Nissl Bodies

-an elaborate type of rough endoplasmic reticulum involved in the metabolic activities of the cell
Two Types of Neuron Processes.
1.Dendrites
2.Axons
Dendrites

-receptive regions that bear receptors for neurotransmitters released by the axon terminals of other neurons
Axons/Nerve Fibers

-form the impulse generating and conducting region of the neuron
-the white matter of the nervous system
Tracts
-bundles of axons in the CNS
Nerves
-bundles of axons in PNS
Neurons may have several dendrites, but they only have a single _____________.
Axon
Axon Collaterals

-branch off of the main axon forming more processes
Axon Hillock

-conical area of origin of the axon from the nerve cell body
Axon Terminals
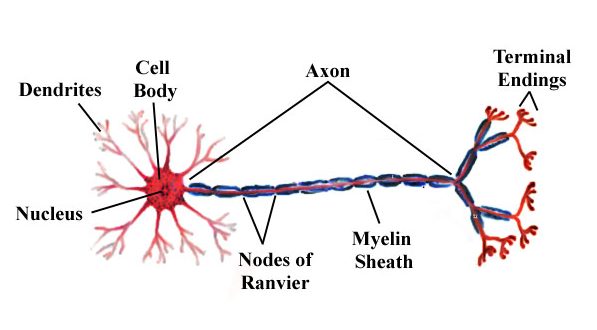
club-shaped endings by which axons make synaptic contacts with other nerve cells or effector cells
-stores the neurotransmitter chemical in tiny vesicles
Synaptic Cleft

- a narrow extracellular cleft between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes
Neuromuscular Junction
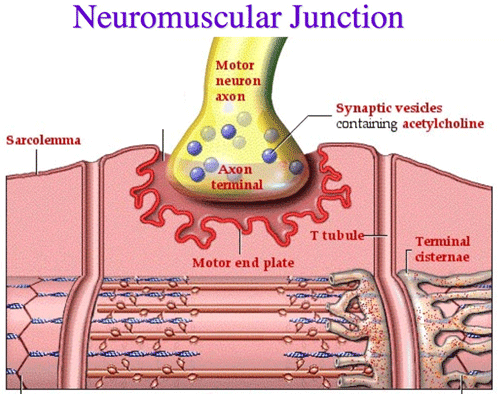
-specialized synapses between neurons and skeletal muscles
Myelinated Fibers

-long nerve fibers that are covered by fatty material (myelin)
Axons in the PNS are typically heavily myelinated by special supporting cells called ______________.

Schwann Cells
Schwann Cells

-wrap themselves tightly around the axon in jelly roll fashion, this wrapping is the myelin sheath
Nodes of Ranvier

-gaps or indentations in the myelin sheath
Within the CNS myelination is accomplished by neuroglia called ________________.
Oligodendrocytes
Unipolar Neurons

-one very short process which divides into peripheral and central processes, extends from cell body
Bipolar Neurons

-have two processes attached to the cell body
-rare
Multipolar Neurons

-many processes
Sensory (Afferent) Nerves
- conduct impulses only toward the CNS
Motor (Efferent) Nerves
-carry impulses only away from the CNS
Mixed Nerves
-nerves carrying both sensory and motor fibers
Endoneurium

-delicate connective tissue enveloping individual nerve fibers
Perineurium

-sheath of connective tissue enclosing a bundle of nerve fibers
-forming fascicles
Epineurium

sheath of connective tissue around all fascicles of nerve fibers