Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal Muscle/Voluntary Muscle

-attaches to the skeleton
-shapes the body and gives you the ability to move
-most of the muscle tissue in the body
-consciously controlled
-striated
Fibers

-large, long cylindrical cells that makes up skeletal muscle
-multinucleated
Sarcolemma

-membrane enclosing a striated muscle fiber
Myofibrils

-a contractile fibril of skeletal muscle
-made up of myofilaments
Myofilaments

-composed of actin and myosin, which slide past each other during muscle activity to bring about shortening and contracting of the muscle cells
Sarcomere

-contractile units of muscle
-extends from the middle of one I band (its Z disc) to the middle of the next along the length of the myofibrils
Transverse Tubule (t tubule)

-deep invagination of the sarcolemma
Terminal Cisterns

-pairs of tranversely oriented channels that are confluent with the sarcotubules, which together with an intermediate T tubule constitute a triad of skeletal muscle
Triads
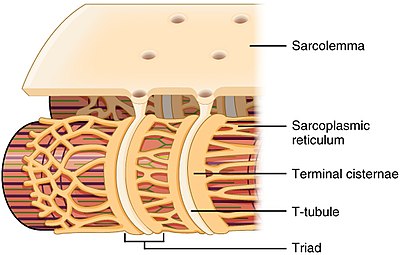
-regions where the sarcoplasmic reticulum terminal borders a t tubule on each side.
Endomysium

-delicate areolar connective tissue that encloses each muscle fiber
Perimysium

-collagenic membrane surrounding several muscle fibers
Fascicle

-bundle of fibers
Epimysium

- large number of fascicles bounded together by dense connective tissue
Deep Fascia
-coarser sheets of dense connective tissue that bind muscles into functional groups
Insertion

-a muscles more movable attachment
Origin

- a muscles immovable attachment
Neuromuscular/Myoneural Junction
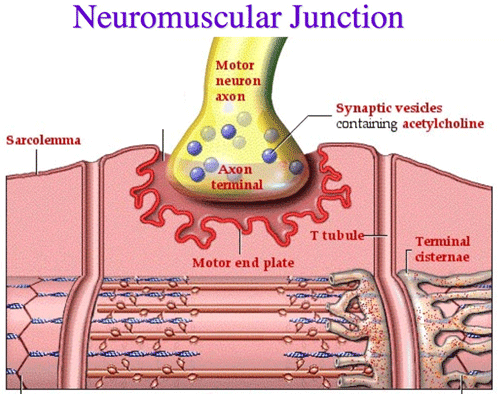
- junction between an axon of a motor neuron and a muscle cell
Motor Unit
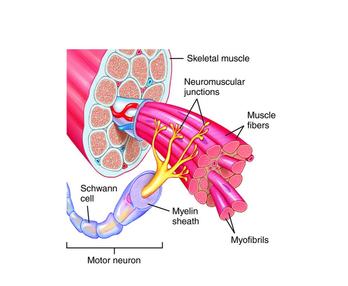
-a neuron and all the muscle fibers it stimulates
Synaptic Cleft

-small fluid-filled gap separating the neuron and muscle fiber membranes