02 Software Development - methodologies
Formal methods of working on a programming project
-Creation of a specification
-breaking down the work (decomposition)
-allocating tasks
-clear timescales
-milestones
-agreed deliverables
What is a feasibility study?
What are 3 types of feasibility the study includes?
-Feasibility studies are used if the project is likely to be successful. Reasons it could fail include:
-Economic feasibility - budget isn't large enough, or the cost of the project outweighs the benefits
-Legal feasibility - project would break laws about data protection or privacy
-Technical feasibility - the project is overly ambitious and goes beyond what current hardware and/or algorithms can achieve
-The methodology used by a development team will likely depend on this feasibilities
What are the 5 different methodologies?
1. Waterfall method
2. Spiral method
3. Agile methodologies
4. Extreme programming
5. Rapid application development (RAD)
Methodology philosophies
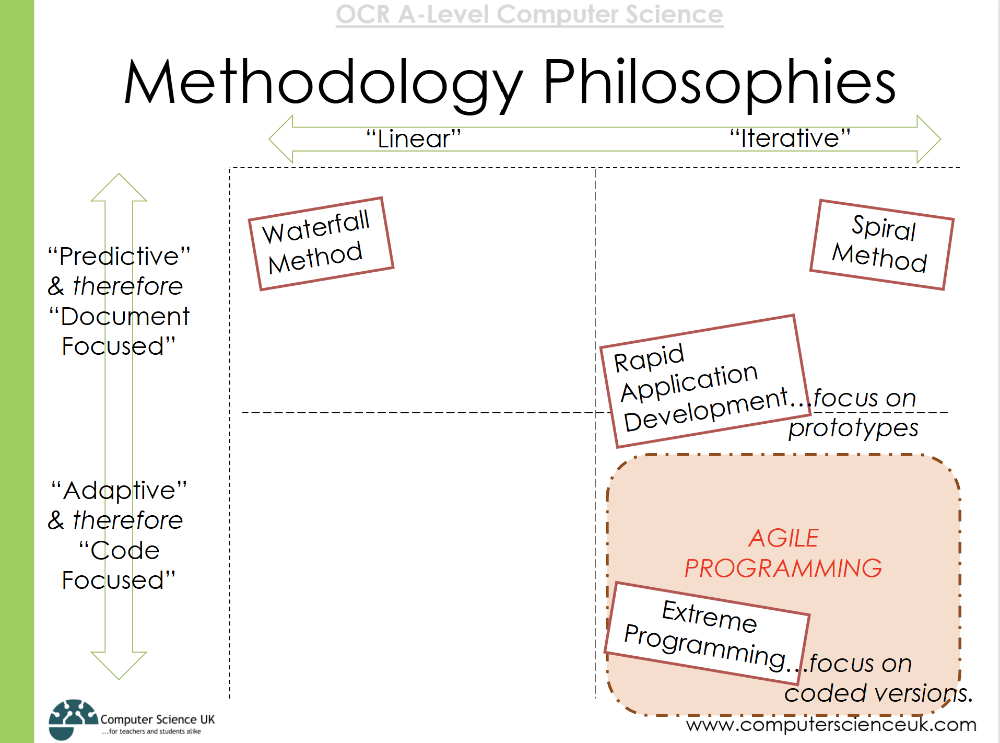
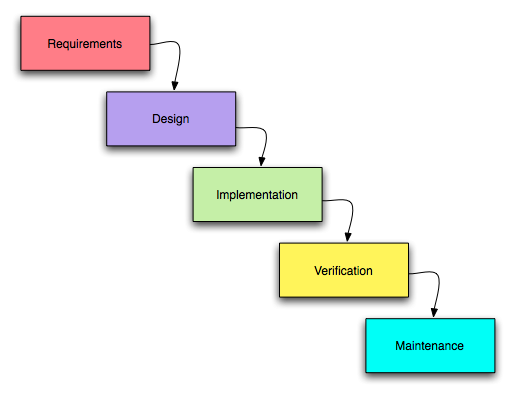
Describe the waterfall method
-the development team work through each section in turn until the product/system is developed
-rigid, structured
-extremely document focused & relies on accurate and meticulous planning
-once a section is complete, the next is started - little chance of going back if there are errors
-great for keeping control of a project and meeting deadlines
-difficult to ensure that end-user requirements are met as there is no product to show until the end
Stages of waterfall method
Describe the spiral method
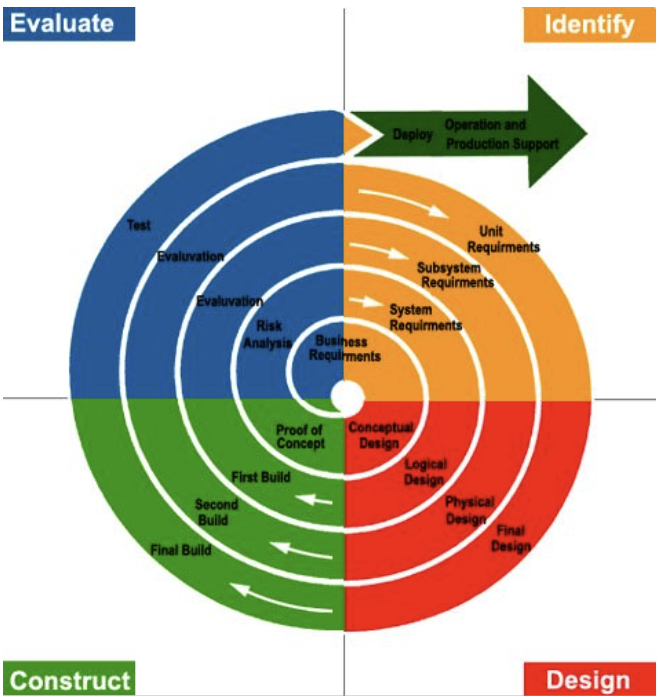
-more iterative than waterfall
-continually working through stages of system development life cycle to ensure 'risk of not meeting end user's needs' is kept to a minimum
-initial risks or analysed & user requirements checked before the system is designed and developed
-then, the product is evaluated and end user gets to check that their needs are being [starting to be] met
-then after the evaluation, designs are refined and development is continued until the product satisfies the client
-also document focused & relies on accurate & meticulous planning and evaluation
-ensures risk is kept to a minimum and product is high quality
-but can be long-winded and projects can go overtime and over budget, esp if risk analysis and evaluations are not thorough enough
Describe agile development
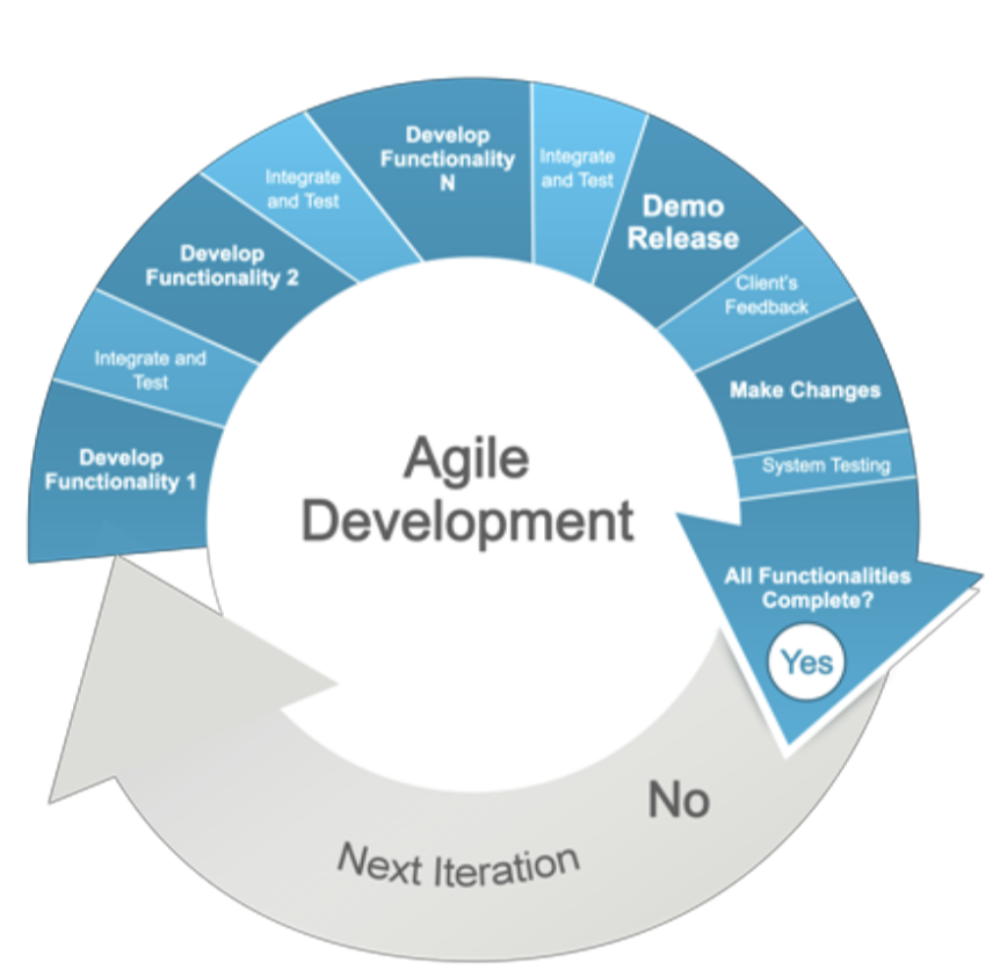
-describes a group of methodologies, including 'extreme programming'
-focus on developing versions of the product which can be evaluated by the end user - specifically useful if clients often change their mind on requirements
-As each version is developed, more of the client's requirements are added until the solution is developed
-allows flexibility of development when some requirements aren't known until mid-way through the project
Describe extreme programming
-an example of an agile methodology
-focuses heavily on producing 'versions' of coded software
-speed is important - versions developed quickly and given to client to be evaluated
-clients will discuss version and if improvements are required, the programmer will develop the software accordingly in order to produce a newer and better version
-important to recognise that each version uses code which is good enough to be in the final version - they are actual programs which are created, NOT prototypes
Describe rapid application design (RAD)
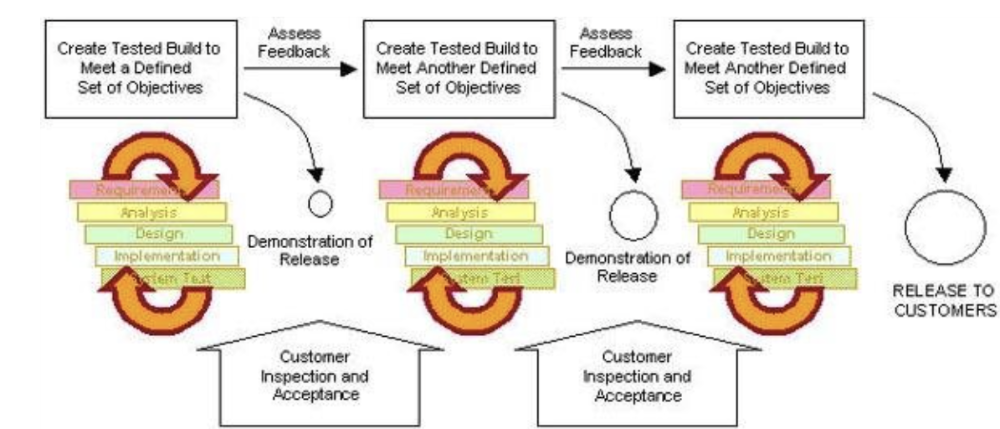
-production of prototypes (a form of the system w/out full functionality) are the focus
-the development team work through each section of the system development life cycle rapidly to produce a prototype to get client feedback on
-it can then be rapidly developed again and so forth until the product is complete
-still a rigid focus on documentation due to in depth nature of planning and prototyping
-> tldr; several increasingly refined prototypes produced until the final working solution is achieved
Pros and Cons of waterfall methodology
Pros:
-simple, clear 7 structured
-easy to manage and ensure deadlines are met
-workers have clear roles
Cons:
-Risk - due to rigidness, its not known until the end whether the product fully meets client requirements
Pros and Cons of spiral methodology
Pros:
-focuses on risk, so reduced risk by ensuring client is happy with the development at all stages
Cons:
-If risk analysis is inaccurate, issues can still arise
-Can be lengthy process due to evaluative nature
Pros and Cons of RAD (Rapid Application Development)
Pros:
-if a client is uncertain of project outcome at the onset, this method (due to focus on prototyping) can help ensure the client is getting the software they require
-> usability focus
Cons:
-Demand for continued feedback/communication with client
-Unsuitable for large projects - more end users so harder to communicate effectively
Pros and Cons of Agile methods
Pros:
-Focuses on product and gets versions of software to clients to ensure requirements are met
-If requirements change, easily flexible (code focus rather than documentation)
Cons:
-Can be hard to control agile projects which go on for longer than originally planned for
-this can lead to budgeting issues
Pros and Cons of extreme programming
Pros:
-Same as agile methods (focus on product to ensure client req are met, flexible due to being code based) but with rapid development of versions
Cons:
-Can be difficulty with communication as these projects are often carried out by teams of programmers who have to integrate their code with the others or develop another piece of code - issues can arise if they dont all follow the same standards or programming standards