Bio Ch 41
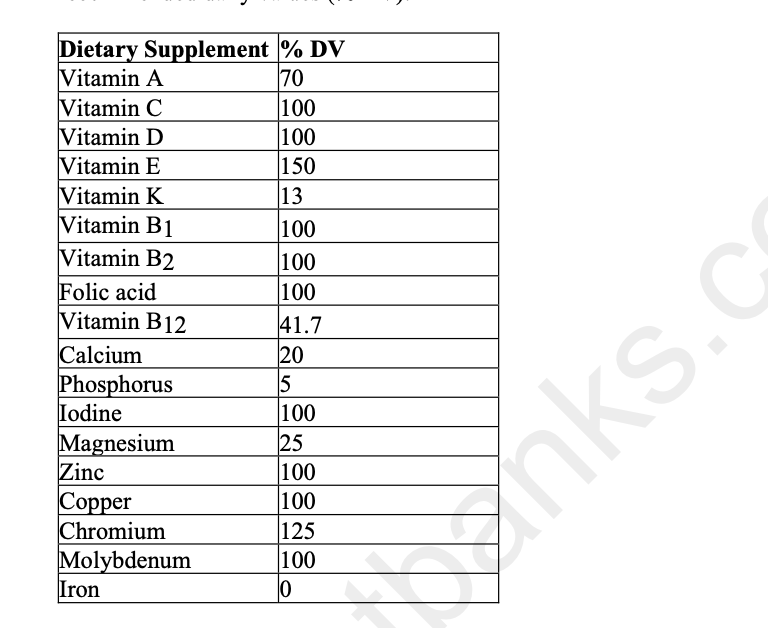
The following table shows the contents of a multivitamin supplement and its percentage of recommended daily values (% DV).
The most likely reason that some of the vitamins and minerals in this supplement are found at
less than 100% is that ________.
A) it would be chemically impossible to add more
B) these vitamins and minerals are too large in size to reach 100%
C) it is too easy to overdose on minerals such as phosphorus and calcium
D) it is dangerous to ingest more than the recommended daily value of fat-soluble vitamins such
as A and K
D
Iodine deficiency in mammals will most likely result in: A) decreased production of thyroid hormones B) decreased enzyme function C) weak bones D) decreased muscle function
A
Lysine is an essential amino acid for animals. An animal that lacked lysine in its diet ________. A) would make lysine from other amino acids B) could not make many necessary proteins C) could not synthesize phospholipids D) would be very healthy
B
Which of the following is a difference between vitamins and minerals? A) Vitamins are involved in regulating enzyme activity, but minerals are not. B) Vitamins are organic molecules, but minerals are inorganic molecules. C) Vitamins are made by the animal, but minerals are obtained by an animal through dietary sources. D) Vitamins are only obtained by digesting plants, whereas minerals are only obtained by digesting meat.
B
It is important for pregnant women to consume folic acid supplements because ________. A) the fetus is not able to acquire oxygen by breathing on its own B) the fetus stores folic acid in high quantities C) folic acid deprivation is associated with neural tube defects in a fetus D) folic acid deprivation is a cause of heart abnormalities in a newborn
C
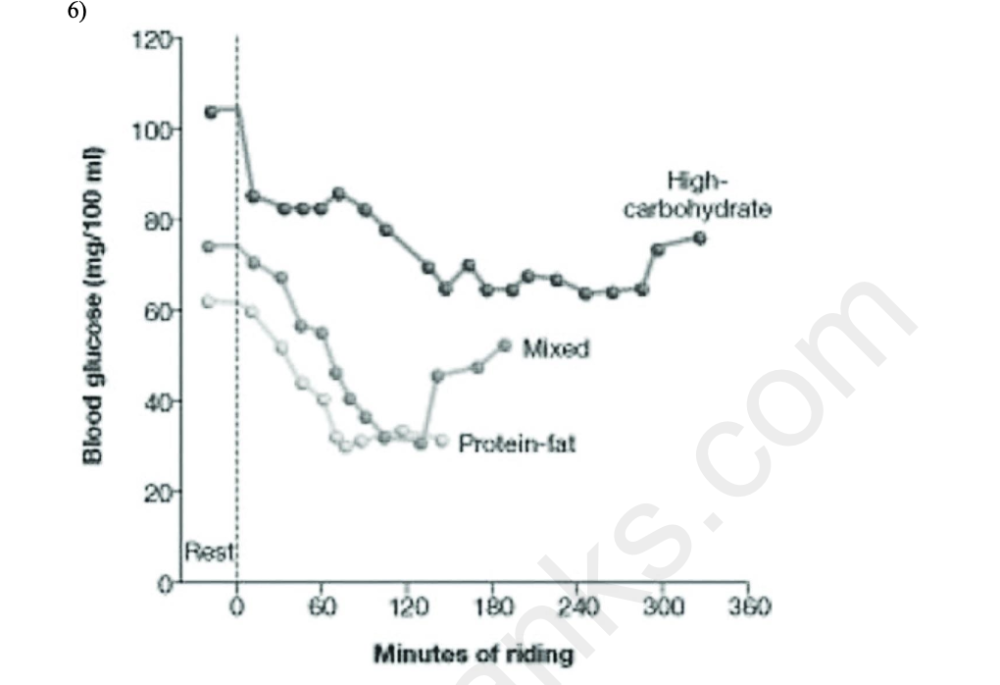
Each of three groups of cyclists had a different diet: high-carbohydrate; a mix of carbohydrates,
fat, and protein; or high in protein and fat. The blood glucose levels of the riders over a six-hour
period after consuming each diet is shown in the accompanying graph. Which statement best
summarizes the data in the graph?
A) Endurance is entirely related to diet.
B) Maintaining elevated blood sugar improves endurance.
C) An early 50 percent drop in blood glucose is associated with improved endurance.
D) Diet is not at all related to endurance.
B
Megaloblastic anemia results from a vitamin deficiency and causes abnormalities in red blood cell production and neurological issues. Megaloblastic anemia may be caused by a deficiency in which of the following vitamins? A) vitamin A B) vitamin B12 C) vitamin C D) vitamin K
B
Jasmine, a 36-year-old female, visits her personal care physician complaining of muscle cramps and reduced appetite. Which of the following options would a doctor likely advise her to do to reduce her symptoms? A) eating a banana (high in potassium) B) drinking a sports drink (high in sodium and chlorine) C) eating dark green leafy vegetables (high in magnesium, iron, and calcium) D) drinking water from the kitchen sink (high in fluoride)
B
Ticks are parasites that obtain nutrients by ingesting blood from a host animal. Ticks would be classified as ________. A) filter feeders B) substrate feeders C) fluid feeders D) bulk feeders
C
In a hydra, digestion is completed ________. A) intracellularly B) extracellularly C) in the alimentary canal D) in the gastrovascular cavity
A
Which of the following is an advantage of a complete digestive system? A) It excludes the need for extracellular digestion. B) It allows for specialized regions with specialized functions. C) It allows extensive branching. D) It facilitates intracellular digestion.
B
Fat digestion yields fatty acids and glycerol, whereas protein digestion yields amino acids. Which of the following statements is true regarding these processes? A) Both are catalyzed by the same enzyme B) Both use water molecules when breaking bonds (hydrolysis) C) Both require the presence of hydrochloric acid to lower the pH D) Both initially occur in the mouth of an animal
B
The process by which digested dietary substances cross cell membranes to be used by the body is known as ________. A) ingestion B) digestion C) hydrolysis D) absorption
D
Which statement best describes why mechanical digestion, the process of breaking down large chunks of food into smaller pieces, is an important digestive process? A) Because smaller pieces of food do not pass through the small intestine whereas larger pieces of food do B) Because smaller pieces of food have more surface area for chemical digestion than do larger pieces of food C) Because smaller pieces of food are easier to excrete than are larger pieces of food D) Because smaller pieces of food are more easily stored in the stomach than are larger pieces of food
B
Termites are insects that eat a variety of dead plants, but they are most well-known for burrowing into wooden structures (including houses!) and eating the cellulose within the wood. What type of feeding mechanism do termites use? A) Filter feeding B) Fluid feeding C) Bulk feeding D) Substrate feeding
D
Gastroliths are stones that are used by the digestive systems of some animals to perform mechanical digestion. Fossilized gastroliths have been found with dinosaur skeletons. What does this evidence suggest about the digestive systems of dinosaurs? A) that dinosaurs had gastrovascular cavities B) that dinosaurs had gizzards C) that dinosaurs had crops D) that dinosaurs had intestines
B
Which process does the large surface area in the intestine make more efficient? A) secretion B) absorption C) filtration D) temperature regulation
B
Which of the following statements correctly describes peristalsis? A) It is a process of fat emulsification in the small intestine. B) It triggers voluntary control of the urethral sphincters regulating urination. C) It causes the transport of nutrients to the liver through the hepatic portal vessel. D) It results from smooth muscle contractions that move food along the esophagus.
D
Which of the following statements is true regarding the digestive system in mammals? A) all types of foods begin their enzymatic digestion in the esophagus B) after leaving the oral cavity, the bolus enters the larynx C) the epiglottis prevents swallowed food from entering the trachea D) the trachea leads to the esophagus and then to the stomach
C
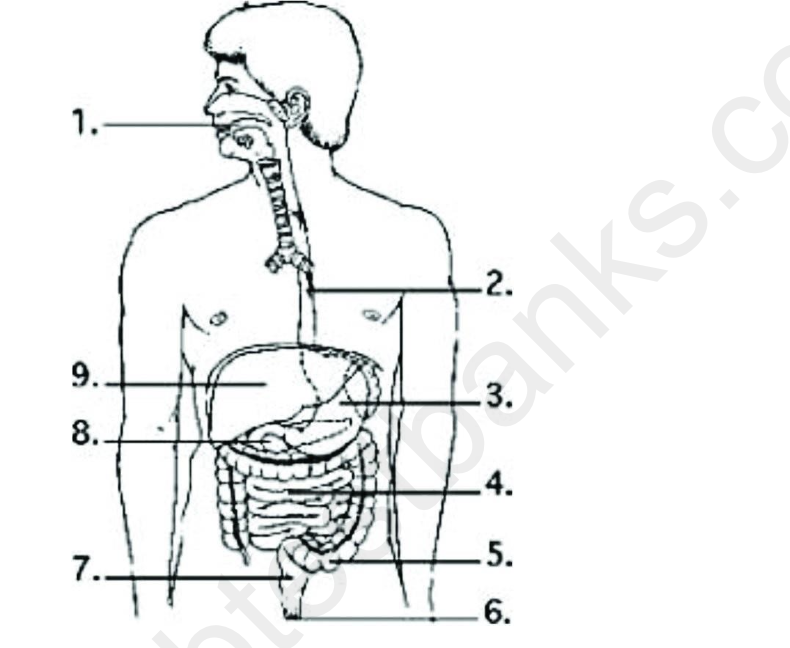
Examine the digestive system structures in the figure. In which labeled structure is the rate of
nutrient absorption the highest?
A) 1
B) 4
C) 5
D) 8
B

Examine the digestive system structures in the figure. In which labeled structure does the
digestion of fats occur?
A) 3 only
B) 4 only
C) 1 only
D) 7 only
B

Examine the digestive system structures in the figure. In which labeled structure are bacteria that
produce vitamins found in the greatest concentration?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 8
C
Which of the following organs is correctly paired with its function? A) stomach–fat digestion B) large intestine–bile production C) small intestine–polysaccharide digestion D) pancreas–starch digestion
C
Which statement best describes how stomach cells survive the acidity and protein-digesting activities in the stomach? A) because they are surrounded by large colonies of H. pylori B) because they are covered by a thick, mucous secretion and rapidly undergo active mitosis C) because they are protected by a high level of secreted enzymes from chief cells D) because they have cell walls impermeable to acid
B
Which of the following correctly describes the function of chylomicrons? A) to digest nucleic acids in the intestine B) to break down carbohydrates in the mouth C) to transport lipids from the intestine to adipose tissue D) to move proteins across plasma membranes of cells
C
Which statement best describes what secretions of the parietal cells do upon activation by stomach acidity? A) break peptide bonds of proteins in the stomach B) slow the mechanical digestion of lipids in the stomach C) initiate the chemical digestion of lipids in the stomach D) delay digestion until the food arrives in the small intestine
A
What is the importance of the mucus that is released by salivary glands? A) It aids in degradation of triglycerides to fatty acids and monoglycerides. B) It assists with mechanical digestion by the teeth. C) It contains hormonal molecules that stimulate the release of gastric juice by the stomach in anticipation of receipt of the contents of the mouth. D) It consists of glycoproteins that make food slippery enough to slide easily through the esophagus.
D
What is the most likely cause for the neurological complications after gastric bypass surgery? A) sudden weight loss and caloric deficiency interfering with neurological function B) nutrient (for example, vitamin and mineral) deficiencies C) sloppy surgical technique of physicians performing the bypass surgery D) infections following surgical intervention
B
Why do digestive system cells secrete proteolytic enzymes like pepsin in inactive forms? A) These proteolytic enzymes, in active form, would digest the very tissues that synthesize them. B) By secreting inactive enzymes, the catalytic activity of the enzymes is maintained for a longer time. C) The stomach is too acidic to maintain these enzymes in their active form. D) Inactive pepsin and trypsin are more easily transported across the cell membrane
A
Over-the-counter medications for acid reflux block production of stomach acid. Which cells are directly affected? A) goblet cells B) chief cells C) parietal cells D) smooth muscle cells
C
Orlistat reduces fat absorption by targeting: A) salivary amylase B) pepsidase C) pancreatic lipase D) secretin
C
Nutrient-rich blood from the intestine is carried to the liver via: A) lacteal vessels B) hepatic portal artery C) hepatic portal vein D) lymphatic system
C
How does fat absorption differ from carbohydrate absorption? A) fat absorption occurs in the stomach B) carbs must be emulsified first C) most fats enter the lymphatic system first; carbs go directly into blood D) fats are digested by bacteria before absorption
C
Constipation can result from consumption of a substance that: A) promotes water reabsorption in the large intestine B) speeds up movement of material in the large intestine C) decreases water reabsorption in the small intestine D) increases chemical digestion in the small intestine
A
What converts pepsinogen to its active form in the stomach? A) HCl B) chief cells C) high pH conditions D) parietal cells
A
How do termites access the nutrients in cellulose? A) specialized mouthparts B) cellulose enzymes in plant material C) intracellular digestion in the hindgut D) mutualistic bacteria in the hindgut digest cellulose
D
Which group of animals have a relatively long cecum? A) carnivores B) herbivores C) autotrophs D) omnivores
B
Why can cattle survive on a diet consisting almost entirely of plant material? A) because cattle are autotrophic B) because cattle re-ingest their feces C) because they synthesize amino acids in the liver D) because they have cellulose-digesting symbiotic microorganisms
D
How did the zoologist likely determine the extinct mammal was an herbivore? A) assessed muscle attachment sites B) assessed the shape of the teeth C) assessed the size of the mouth opening D) assessed the number of neck bones
B
If you found a vertebrate skull with sharp, scissor-like teeth, what would the animal most likely eat? A) grass stems and leaves B) animal flesh C) plant nectar D) animal blood
B
Which benefit do intestinal bacteria gain from living in a mutualistic relationship with an animal? A) The bacteria are provided with a regular source of nutrients. B) Temperature is always regulated. C) The bacteria can easily infect intestinal cells. D) The bacteria can avoid the immune system.
A
What is one concern when using antibiotics? A) Antibiotics damage animal cells. B) Antibiotics make viruses more effective. C) Each antibiotic only works on one bacteria. D) Antibiotics may kill beneficial microbiome bacteria, disrupting digestion.
D
Varsha discovers a mammal skull with wide molars and thin incisors, but no canines. What did the mammal likely eat? A) prey animals B) leafy plants, trees, and shrubs C) fish and mollusks D) grasses and small birds
B
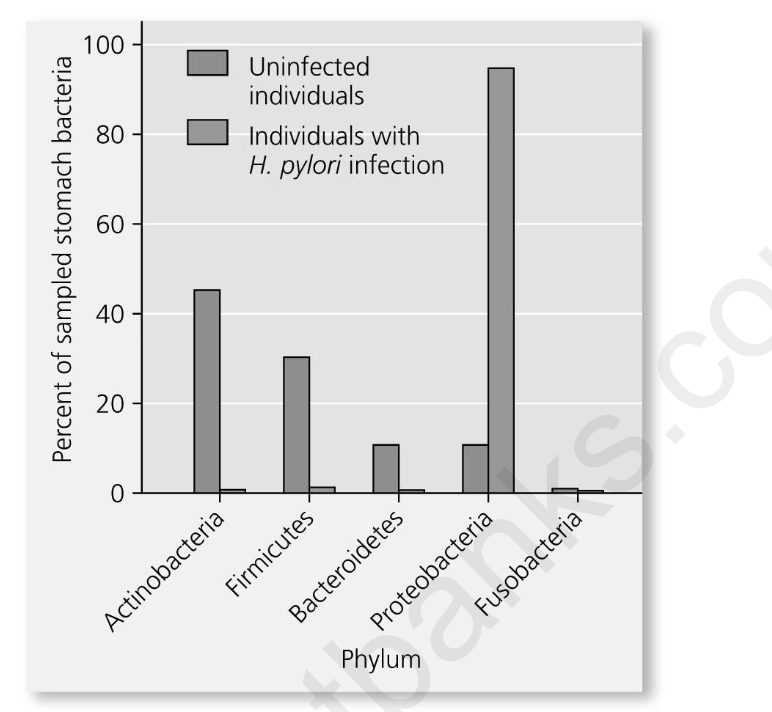
Researchers sequenced bacterial DNA found in the stomachs of humans to analyze the
human microbiome. They compared the microbiomes of stomachs from healthy humans to those
of stomachs from humans infected by H. pylori. What can you conclude from these data?
A) H. pylori killed the other types of bacteria in the stomach.
B) The number of H. pylori bacteria in infected stomachs is larger than the number of Firmicutes
bacteria in uninfected stomachs.
C) H. pylori infections result in reduced diversity of stomach bacteria.
D) Mechanical digestion is negatively affected in infected stomachs.
C
Which of the following molecules provides the greatest energy storage for animals? A) proteins B) minerals C) carbohydrates D) fats
D
If you exercise, which stored fuel do you use first? A) muscle proteins B) liver glycogen and muscle glycogen C) fat stored in adipose tissue D) blood proteins
B
Food being digested in the stomach is in a highly acidic environment. The pH of the small intestine is higher than that of the stomach. Why? A) Secretin increases the flow of bicarbonate ions from the pancreas into the small intestine to neutralize the stomach acid. B) Trypsinogen is activated, thus neutralizing the stomach acid. C) Bile salts from the gallbladder neutralize the stomach acid. D) Pepsin activation results in stomach acid neutralization.
A
Which of the following happens to the production of insulin and glucagon in a healthy person after eating a carbohydrate-rich meal? A) insulin levels increase and glucagon levels increase B) insulin levels increase and glucagon levels decrease C) insulin levels decrease and glucagon levels increase D) insulin levels decrease and glucagon levels decrease
A
If there is a strong genetic link for type II diabetes mellitus in your family, which option might you take to minimize your risk of developing the disorder? A) monitor your blood glucose levels daily B) take oral insulin daily C) maintain a healthy weight, eat a balanced diet, and exercise D) eat complex carbohydrates like starch instead of sweets
C
What is the fate of organic molecules that are absorbed in digestion but not immediately used for metabolism? A) eliminated in the feces B) stored as starch in the liver C) stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles D) oxidized and converted to ATP
C
A fasting animal whose energy needs exceed those provided in its diet will draw on its stored resources in which order? A) fat, then glycogen, then protein B) glycogen, then protein, then fat C) liver glycogen, then muscle glycogen, then fat D) muscle glycogen, then fat, then liver glycogen
C
Fat digestion yields fatty acids and glycerol. Protein digestion yields amino acids. Both digestive processes ________. A) occur inside cells in most animals B) add a water molecule to break bonds C) require a low pH resulting from HCl production D) consume ATP
B
The mammalian trachea and esophagus both connect to the ________. A) pharynx B) stomach C) large intestine D) rectum
A
In which organ does almost all enzymatic digestion of food occur? A) stomach B) small intestine C) large intestine D) pancreas
B
In which digestive system organ does nearly all nutrient absorption occur? A) stomach B) small intestine C) large intestine D) pancreas
B
If you put the following events in the order they occur in the human digestive system, which would be the third event in the series? A) Cells in gastric pits secrete protons. B) Pepsin activates pepsinogen. C) HCl activates pepsinogen. D) Partially digested food enters the small intestine.
B
After surgical removal of the gallbladder, a person might need to limit his or her dietary intake of ________. A) starch B) protein C) sugar D) fat
D
If you were to jog 1 km a few hours after lunch, which stored fuel would you probably tap? A) muscle proteins B) muscle and liver glycogen C) fat in the liver D) fat in adipose tissue
B