Fat Seals
1) In cats, black fur color is caused by an X-linked allele; the other allele at this locus causes orange color. The heterozygote is tortoiseshell. What kinds of offspring would you expect from the cross of a black female and an orange male?
- orange females; black males
- black females; orange males
- tortoiseshell females; tortoiseshell males
- tortoiseshell females; black males
✅ Answer: tortoiseshell females; black males
2) Red-green color blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait in humans. Two people with normal color vision have a color-blind son. What are the genotypes of the parents?
- XnXn and XnY
- XNXn and XNY
- XNXN and XnY
- XNXN and XNY
✅ Answer: XᴺXⁿ and XᴺY
- 3) Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a serious condition caused by
a recessive allele of a gene on the human X chromosome. The patients
have muscles that weaken over time because they have absent or
decreased dystrophin, a muscle protein. They rarely live past their
twenties. How likely is it for a woman to have this condition?
- One-half of the daughters of an affected father and a carrier mother could have this condition.
- One-fourth of the daughters of an affected man would have this condition.
- Women can never have this condition.
- Only if a woman is XXX could she have this condition.
✅ Answer: One-half of the daughters of an affected father and a carrier mother could have this condition.
4) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD) is inherited as a recessive allele of an X-linked gene in humans. A woman whose father suffered from G6PD marries a normal man. What proportion of their sons is expected to be G6PD? If the husband was not normal but was G6PD deficient, would you change your answer in part (a)?
- A) (a) 1/2; (b) yes
- (a) zero; (b) no
- (a) 100%; (b) no
- (a) 1/2; (b) no
✅ Answer: (a) 1/2; (b) no
5) If cell X enters meiosis, and nondisjunction of one chromosome occurs in one of its daughter cells during meiosis II, what will be the result at the completion of meiosis?
- 1/4 of the gametes descended from cell X will be n + 1, 1/4 will be n - 1, and 1/2 will be n.
- All the gametes descended from cell X will be diploid.
- Two of the four gametes descended from cell X will be haploid, and two will be diploid.
- Half of the gametes descended from cell X will be n + 1, and half will be n - 1.
✅ Answer: 1/4 of the gametes descended from cell X will be n + 1, 1/4 will be n - 1, and 1/2 will be n.
6) One possible result of chromosomal breakage is for a fragment to join a nonhomologous chromosome. What is this alteration called?
- inversion
- duplication
- deletion
- translocation
✅ Answer: translocation
7) Of the following human aneuploidies, which is the one that generally has the most severe impact on the health of the individual?
- trisomy 21
- XO
- XXX
- XXY
✅ Answer: trisomy 21
8) A phenotypically normal prospective couple seeks genetic counseling because the man knows that he has a translocation of a portion of his chromosome 4 that has been exchanged with a portion of his chromosome 12. Although his translocation is balanced, he and his wife want to know the probability that his sperm will be abnormal. What is your prognosis regarding his sperm?
- 1/4 will carry the two normal chromosomes, 4 and 12, 1/4 will have only the two translocation chromosomes and no normal chromosomes 4 and 12, and 1/2 will have both normal and translocated chromosomes.
- 1/2 will be normal and the rest will have the father's translocation.
- None will carry the translocation.
- All will carry the same translocation as the father.
✅ Answer: 1/4 will carry the two normal chromosomes, 4 and 12, 1/4 will have only the two translocation chromosomes and no normal chromosomes 4 and 12, and 1/2 will have both normal and translocated chromosomes.
9) Abnormal chromosomes are frequently found in malignant tumors. Errors such as translocations may place a gene in close proximity to different control regions than normal. Which of the following might then occur to make the cancer worse?
- expression of inappropriate gene products
- a decrease in mitotic frequency
- failure of the cancer cells to multiple
- an increase in nondisjunction
✅ Answer: expression of inappropriate gene products
10) A couple has a child with Down syndrome.The mother is 39 years old at the time of delivery. Which of the following is the most probable cause of the child's condition?
- The woman inherited this tendency from her parents.
- The mother most likely underwent nondisjunction during gamete production.
- One member of the couple underwent nondisjunction in somatic cell production.
- The mother had a chromosomal duplication.
✅ Answer: The mother most likely underwent nondisjunction during gamete production.
1)A possible sequence of nucleotides in the template strand of Dna that would cide for the polypeptide sequence phe-leu-ile-val would be ___.
- 5' TTG-CTA-CAG-TAG 3'
- 5' AUG-CTG-CAG-TAT 3'
- 3' AAA-GAA-TAA-CAA 5'
- 3' AAA-AAT-ATA-ACA 5'
✅ Answer: 3' AAA-AAT-ATA-ACA 5'
2) What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the following mRNA codon sequence?
5' AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG 3'
- met-ser-leu-ser-leu-ser
- met-arg-glu-arg-glu-arg
- met-glu-arg-arg-glu-leu
- met-ser-ser-leu-ser-leu
✅ Answer: met-ser-ser-leu-ser-leu
3) Refer to the figure above. What would the anticodon be for a tRNA that transports phenylalanine to a ribosome?
- TTT
- UUU
- AAA
- CCC
✅ Answer: AAA
4) In the process of transcription,___.
- proteins are synthesized
- RNA is synthesized
- DNA is replicated
- mRNA attaches to ribosomes
✅ Answer: RNA is synthesized
5) What does it mean when we say the genetic code is redundant?
- The genetic code is different for different domains of organisms.
- A single codon can specify the addition of more than one amino acid.
- The genetic code is universal (the same for all organisms).
- More than one codon can specify the addition of the same amino acid
✅ Answer: More than one codon can specify the addition of the same amino acid
6) Once researchers identified DNA as the unit of inheritance, they asked how information was
transferred from the DNA in the nucleus to the site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. What is the mechanism of information transfer in eukaryotes?
- Transfer RNA takes information from DNA directly to a ribosome, where protein synthesis takes place.
- DNA from a single gene is replicated and transferred to the cytoplasm, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis.
- Proteins transfer information from the nucleus to the ribosome, where protein synthesis takes place.
- Messenger RNA is transcribed from a single gene and transfers information from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where protein synthesis takes place.
✅ Answer: Messenger RNA is transcribed from a single gene and transfers information from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where protein synthesis takes place.
7)According to the central dogma, what molecule should go in the blank?
DNA → _ → Proteins
- rRNA
- mtDNA
- mRNA
- tRNA
✅ Answer: mRNA
8) Which of the following occurs in prokaryotes but not in eukaryotes?
- simultaneous transcription and translation
- translation in the absence of a ribosome
- post-transcriptional splicing
- gene regulation
✅ Answer: simultaneous transcription and translation
9) Which of the following best describes the significance of the TATA box in eukaryotic promoters?
- It is the recognition site for transcription factors and RNA polymerase
- Its significance has not yet been determined.
- It is the recognition site for ribosomal binding.
- It sets the reading frame of the mRNA.
✅ Answer: It is the recognition site for transcription factors and RNA polymerase
10) Alternative RNA splicing___.
- is a mechanism for increasing the rate of translation
- can allow the production of similar proteins from different RNAs
- can allow the production of proteins of different sizes and functions from a single mRNA
- increases the rate of transcription
✅ Answer: can allow the production of proteins of different sizes and functions from a single mRNA
11) In an experimental situation, a student researcher inserts an mRNA molecule into a eukaryotic cell after she has removed its 5' cap and poly-A tail. Which of the following would you expect her to find?
- The mRNA attaches to a ribosome and is translated, but more slowly.
- The mRNA is quickly converted into a ribosomal subunit.
- The cell adds a new poly-A tail to the mRNA.
- The molecule is digested by enzymes because it is not protected at the 5' end.
✅ Answer: The molecule is digested by enzymes because it is not protected at the 5' end.
12) Which one of the following statements about RNA processing is true?
- RNA splicing can be catalyzed by tRNA.
- A primary transcript is often much shorter than the final RNA molecule that leaves the nucleus.
- Splicesomes may function in RNA splicing.
- Exons are cut out before mRNA leaves the nucleus.
✅ Answer: Splicesomes may function in RNA splicing.
13) A primary transcript in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell is___ the functional mRNA,
while a primary transcript in a prokaryotic cell is___the functional mRNA.
- larger than; smaller than
- the same size as; smaller than
- larger than; the same size as
- the same size as; larger than
✅ Answer: larger than; the same size as
14) Translation requires
- mRNA, DNA, and rRNA
- mRNA, tRNA, and DNA
- mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA
- mRNA, tRNA, DNA, and rRNA
✅ Answer: mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA
15) How does termination of translation take place?
- The end of the mRNA molecule is reached.
- A stop codon is reached.
- The poly-A tail is reached
- The 5' cap is reached.
✅ Answer: A stop codon is reached.
16) Which of the following types of mutation, resulting in an error in the mRNA just after the AUG start of translation, is likely to have the most serious effect on the polypeptide products?
- A deletion of a codon
- a deletion of two nucleotides
- a substitution of the third nucleotide in an ACC codon
- a substitution of the first nucleotide of a GGG codon
✅ Answer: a deletion of two nucleotides
17) A nonsense mutation in a gene___.
- has no effect on the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein
- introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA
- alters the reading frame of the mRNA
- changes an amino acid in the encoded protein
✅ Answer: introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA
18) How might a single base substitution in the sequence of a gene affect the amino acid sequence of a protein encoded by the gene, and why?
- All amino acids following the substitution would be affected, because the reading frame would be shifted.
- Only a single amino acid could change, because the reading frame is unaffected.
- It is not possible for a single base substitution to affect protein structure, because each codon is three bases long.
- The amino acid sequence would be substantially altered, because the reading frame would change with a single base substitution.
✅ Answer: Only a single amino acid could change, because the reading frame is unaffected.
19) An original section of DNA has the base sequence AGCGTTACCGT. A mutation in this DNA stand results in the base sequence AGGCGTTACCGT. This change represents___.
- Frameshift mutation
- A point mutation
- A silent mutation
- A missense mutation
✅ Answer: Frameshift mutation
20) Rank the following one base point mutations from most likely to least likely with respect to their likehood of affecting the structure of the corresponding polypeptide
- insertion mutation deep within an intron
- Substitution mutation as a third position of an exon codon
- Substitution mutation of the second position of an exon code on
- Deletion mutation within the first exon of the gene
- 1,2,3,4
- 3,1,4,2
- 4,3,2,1
- 2,1,4,3
✅ Answer: 4, 3, 2, 1
1) Prior to the work of Lyell and Darwin, the prevailing belief was that Earth is
- millions of years old, and populations are unchanging
- a few thousand years old, and populations are unchanging
- millions of years old, and populations rapidly change
- a few thousand years old, and populations gradually change
A1: A few thousand years old, and populations are unchanging
2) During a study session about evolution, one of your fellow students remarks, "The giraffe stretched its neck while reaching for higher leaves; its offspring inherited longer necks as a result." Which statement is most likely to be helpful in correcting this student's misconception?
- Characteristics acquired during an organism's life are generally not passed on through genes.
- Disuse of an organ may lead to its eventual disappearance.
- Only favorable adaptations have survival value.
- Spontaneous mutations can result in the appearance of new traits.
A2: Characteristics acquired during life are generally not passed on through genes.

3) If x indicates the location of fossils of two closely related species, then fossils of their most-recent common ancestor are most likely to occur in which stratum?
- B
- D
- A
- C
A3: Stratum C
4) Which of these conditions are always true of populations evolving due to natural selection?
Condition 1: The population must vary in traits that are heritable.
Condition 2: Some heritable traits must increase reproductive success.
Condition 3: Individuals pass on most traits that they acquire during their lifetime.
- Condition 2 only
- Conditions 1 and 2
- Conditions 2 and 3
- Condition 1 only
A4: Conditions 1 and 2 (Heritable variation; Some traits improve reproductive success)
5) A farmer uses triazine herbicide to control pigweed in his field. For the first few years, the triazine works well and almost all the pigweed dies; but after several years, the farmer sees more and more pigweed. Which of these explanations best explains what happened?
- The herbicide company lost its triazine formula and started selling poor-quality triazine.
- Triazine-resistant pigweed has less-efficient photosynthesis metabolism.
- Natural selection caused the pigweed to mutate, creating a new triazine-resistant species.
- Triazine-resistant weeds were more likely to survive and reproduce.
A5: Triazine-resistant weeds were more likely to survive and reproduce.
6) A biologist studied a population of squirrels for fifteen years. During that time, the population was never fewer than thirty squirrels and never more than forty-five. Her data showed that over half of the squirrels born did not survive to reproduce, because of both competition for food and predation. In a single generation, 90% of the squirrels that were born lived to reproduce, and the population increased to eighty. Which inference(s) about this most recent surge in the population size might be true?
- The number of predators that prey upon squirrels may have decreased
- The parental generation of squirrels developed better eyesight due to improved diet; the subsequent squirrel generation inherited better eyesight.
- The amount of available food may have increased and/or the predators that prey upon squirrels may have decreased.
- The amount of available food may have increased.
A6: Food availability may have increased and/or predators decreased.
7) Which of the following must exist in a population before natural selection can act upon that population?
- genetic variation among individuals
- variation among individuals caused by environmental factors
- sexual reproduction
- the population has predators
A7: Genetic variation among individuals
8) Which of Darwin's ideas had the strongest connection to his reading of Malthus's essay on human population growth?
- descent with modification
- variation among individuals in a population
- that the ancestors of the Galápagos finches had come from the South American mainland
- struggle for existence
A8: Struggle for existence
9) If Darwin had been aware of genes and their typical mode of transmission to subsequent generations, with which statement would he most likely have been in agreement?
- If an organism's somatic cell genes change during its lifetime, making it more fit, then it will be able to pass these genes on to its offspring.
- If an organism acquires new genes by engulfing, or being infected by, another organism, then a new genetic species will result.
- A single mutation in a single gene in a single gamete, if inherited by future generations, will produce a new species.
- If natural selection can change gene frequency in a population over generations, given enough time and genetic diversity, then natural selection can cause sufficient genetic change to produce new species from old ones.
A9: Natural selection can change gene frequency enough to produce new species over time.
10) Many crustaceans (for example, lobsters, shrimp, and crayfish) use their tails to swim, but crabs have reduced tails that curl under their shells and are not used in swimming. This is an example of___.
- natural selection
- convergent evolution
- a vestigial trait
- a homologous structure
A10: A vestigial trait
11) If the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus experiences a cost for maintaining one or more antibiotic-resistance genes, what would happen in environments that lack antibiotics?
- These bacteria would be outcompeted and replaced by bacteria that have lost these genes.
- The number of genes conveying antibiotic resistance would increase in these bacteria.
- These bacteria would try to make the cost worthwhile by locating and migrating to microenvironments where traces of antibiotics are present.
- These genes would be maintained in case the antibiotics appear.
A11: Bacteria with resistance genes are outcompeted by those without them.
12) Of the following anatomical structures, which is homologous to the bones in the wing of a bird?
- bones in the hind limb of a kangaroo
- bones in the flipper of a whale
- bony rays in the tail fin of a flying fish
- chitinous struts in the wing of a butterfly
A12: Bones in the flipper of a whale
13) Over long periods of time, many cave-dwelling organisms have lost their eyes. Tapeworms have lost their digestive systems. Whales have lost their hind limbs. How can natural selection account for these losses?
- Under particular circumstances that persisted for long periods, each of these structures presented greater costs than benefits.
- The ancestors of these organisms experienced harmful mutations that forced them to lose these structures.
- Natural selection accounts for these losses by the principle of use and disuse.
- Natural selection cannot account for losses, but accounts only for new structures and functions.
A13: These structures became costly and provided no advantage in certain environments.
14) Which of the following evidence most strongly supports the common origin of all life on Earth? All organisms
- use essentially the same genetic code
- require energy
- reproduce
- show heritable variation
A14: All organisms use essentially the same genetic code.
15) Members of two different species possess a similar-looking structure that they use in a similar way to perform about the same function. Which of the following would suggest that the relationship more likely represents homology instead of convergent evolution?
- The two species live at great distances from each other.
- The two species share many protein common, and the nucleotide sequence that code for these proteins are almost identical.
- Both species are well adapted to their particular environments.
- The structures in adult members' species are similar in size.
A15: They share many proteins and nearly identical nucleotide sequences.
16) It has been observed that organisms on islands are different from, but closely related to, similar forms found on the nearest continent. This is taken as evidence that___.
- The island forms and mainland forms are converging
- Island forms and mainland forms have identical gene pools
- Island forms are descended from mainland forms
- Common environments are inhabited by the same organisms
A16: Island forms are descended from mainland forms.
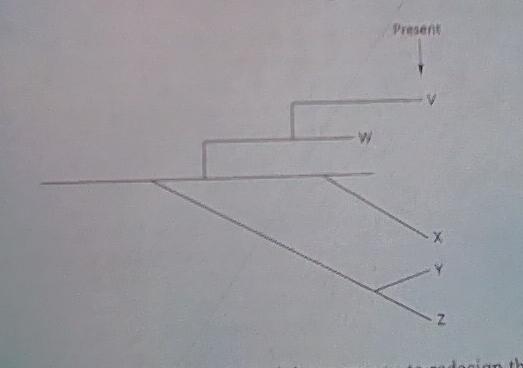
17) Which of the following might cause you to redesign this evolutionary tree?
- The skeletal remains of the organisms depicted by the tree were incomplete (in other words, some bones were missing.)
- Transitional fossils had not been found
- Relationships between DNA sequences among the species did not match relationships between skeletal patterns
- Some of the organisms depicted by the tree had lived in different habitats.
A17: DNA sequence relationships don’t match skeletal relationships.
1) Which of the following choices includes all of the others in creating global terrestrial climates?
- ocean currents
- differential heating of Earth's surface
- global wind patterns
A1: Differential heating of Earth's surface
2) Why is the climate drier on the leeward (downwind) side of mountain ranges that are subjected to prevailing winds?
- Deserts create dry conditions on the leeward side of mountain ranges.
- The sun illuminates the leeward side of mountain ranges at a more direct angle, converting to heat energy, which evaporates most of the water present.
- Pushed by the prevailing winds on the windward side, air is forced to rise, cool, condense, and drop its precipitation, leaving drier air to descend the leeward side.
A2: Air rises on the windward side, cools, and loses moisture; drier air descends on the leeward side.
3) The main reason polar regions are cooler than the equator is that
- the poles are permanently tilted away from the sun
- the polar atmosphere is thinner and contains fewer greenhouse gases
- sunlight strikes the poles at an angle
- the poles are farther from the sun
A3: Sunlight strikes the poles at an angle.
4) Coral reefs can be found on the southeast coast of the United States but not at similar latitudes on the southwest coast. Differences in which of the following most likely account for this?
- Ocean currents
- Day lengths
- Salinity
- precipitation
A4: Ocean currents
5) When climbing a mountain, we can observe transitions in biological communities that are analogous to the changes___.
- in an ecosystem as it evolves over time
- in a community through different seasons
- in biomes at different latitudes
- across the United States from east to west
A5: Changes in biomes at different latitudes
6) Which statement describes how climate might change if Earth was 75 percent land and 25 percent water?
- Summers would be longer and winters shorter at midlatitude locations.
- Earth's daytime temperatures would be higher and nighttime temperatures lower.
- Terrestrial ecosystems would likely experience more precipitation.
A6: Daytime temperatures would be higher and nighttime temperatures lower.
7) If global warming continues at its present rate, which biomes will likely take the place of the coniferous forest (taiga)?
- desert and chaparral
- chaparral and temperate broadleaf forest
- tropical forest and savanna
- temperate broadleaf forest and grassland
A7: Temperate broadleaf forest and grassland
12) In deep water, which of the following abiotic factors would most limit productivity (photosynthesis)?
- temperature
- light availability
- solute concentration
A12: Light availability
13) Which of the following is the greatest physiological challenge for a fish swimming from a river into an estuary?
- The low oxygen content would give the fish difficulty in swimming aerobically.
- The change in water solute content would challenge the osmotic balance of the fish.
- The temperature change would stress the fish by denaturing its proteins.
- The high water flow would make the fish expend more energy.
A13: Change in water solute content affects osmotic balance.
14) The oceans affect the biosphere by__
I producing a substantial amount of the biosphere's oxygen
Il) adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere
III) being the source of most of Earth's rainfall
- IV) regulating the pH of freshwater biomes and terrestrial groundwater
- only I and III
- only I, II, and IV
- only I, Il, and III
- only II and IV
A14: Only I, II, and III (Produce oxygen, add CO₂ to atmosphere, source of rainfall)
Match the description with the structure:
- Salivary glands
- Gallbladder
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Esophagus
- Liver
- ac. Mouth
- ad. Pancreas
- ae. Cardiac sphincter
- bc. Stomach
Produces bile.
Site of protein, carbohydrate and lipid digestion.
Site of protein digestion, has a pH of 2.
Site of carbohydrate digestion and mechanical digestion.
Produces enzymes for protein, lipid and carbohydrate digestion.
Site of nutrient absorption.
Absorbs water and vitamins.
Site where bile is stored and concentrated.
Muscle that controls movement of food from between esophagus and stomach.
Produce enzymes that partially break down carbohydrates.
- Produces bile. → Liver
- Site of protein, carbohydrate and lipid digestion. → Small intestine
- Site of protein digestion, has a pH of 2. → Stomach (bc)
- Site of carbohydrate digestion and mechanical digestion. → Mouth (ac)
- Produces enzymes for protein, lipid and carbohydrate digestion. → Pancreas (ad)
- Site of nutrient absorption. → Small intestine
- Absorbs water and vitamins. → Large intestine
- Site where bile is stored and concentrated. → Gallbladder
- Muscle that controls movement of food from between esophagus and stomach. → Cardiac sphincter (ae)
- Produce enzymes that partially break down carbohydrates. → Salivary glands
Describe how insulin and glucagon work as a pair to control blood glucose levels and maintain homeostasis. Use the following answer options:
- Glucagon
- Insulin
- This hormone raises blood glucose levels.
- This hormone lowers blood glucose levels.
- This hormone causes glycogen to be broken down into glucose molecules and released into the bloodstream.
- This hormone is necessary for cells to transport glucose from the blood into the cell.
- People who have type I diabetes are not producing this hormone.
25. This hormone raises blood glucose levels.
→ a. Glucagon
26. This hormone lowers blood glucose levels.
→ b. Insulin
27. This hormone causes glycogen to be broken down into
glucose molecules and released into the bloodstream.
→ a. Glucagon
28. This hormone is necessary for cells to transport glucose
from the blood into the cell.
→ b. Insulin
29. People who have type I diabetes are not producing this
hormone.
→ b. Insulin
- Which structure in Figure 30-2 removes excess water, urea and metabolic waste from the blood?
- kidney
- renal vein
- ureter
- urinary bladder
→ kidney
2 The function of the excretory system is to control homeostasis and
- absorb nutrients.
- prevent infection,
- remove wastes.
- break down nutrients.
removes waste
- A patient is diagnosed with kidney failure and visits a clinic to receive dialysis treatments three times a week. What does the process of dialysis do?
- filters waste from the blood
- forces water into cells and tissues by osmosis
- pumps blood throughout the body
- carries urine to the urinary bladder
filters waste from the blood
- Which of these is a function of the circulatory system?
- transferring electrical impulses from one cell to another
- removing carbon dioxide wastes from tissues
- delivering carbon dioxide to cells for cellular respiration
- all of the above
removing carbon dioxide wastes from tissues
5 Which are the components of the circulatory system?
- blood vessels, heart, and lungs
- blood, blood vessels, and heart
- heart and lungs
blood, blood vessels, and heart
- Which of the following pathways is the largest of the circulatory system?
- systemic circulation
- pulmonary circulation
- coronary circulation
systemic circulation
7 Which is the correct direction of blood flow?
- left ventricle → pulmonary artery → aorta
- right atrium → left atrium → pulmonary
- artery left ventricle → left atrium → aorta
- right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary artery
→ right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary artery
Compared with the walls of arteries, the walls of capillaries
- are thinner.
- lack valves.
- are thicker.
are thinner
- Through which path does blood typically flow through the circulatory system?
- arteries → capillaries → veins
- arteries → veins → capillaries veins → capillaries → arteries
- capillaries → arteries → veins
- → arteries → capillaries → veins
10. Which type of blood vessel carries blood
away from the heart?
a. Capillaries
b.
Arteries
c. Lymph nodes
d. Veins
✅ b. Arteries
11. Which of the following is true about blood
pressure?
a. It drops a great deal when traveling through
arteries.
b. Diastolic pressure is higher than systolic
pressure.
c. It is typically lower in veins than in
arteries.
d. It is not affected by atherosclerosis (blocking of
blood vessels).
✅ c. It is typically lower in veins than in arteries.
12. Uncontrolled hypertension (high blood pressure)
can lead to:
a. Kidney damage
b. Stroke
c. Heart
attack
d. All of the above
✅ d. All of the above
13. The sudden death of brain cells when their blood
supply is interrupted is called:
a. A heart attack
b. A
stroke
c. Hypertension
d. Atherosclerosis
✅ b. A stroke
14. Which of these structures provides the muscle
cells in the heart with a constant supply of oxygen?
a. Coronary
arteries
b. The pulmonary artery
c. Systemic veins
d. Capillaries
✅ a. Coronary arteries
15. What structure serves as a passageway for both
air and food?
a. Bronchus
b. Larynx
c. Pharynx
d. Trachea
✅ c. Pharynx
16. Because there is more oxygen in an alveolus than
in the blood around it, oxygen diffuses:
a. From capillaries
into the veins
b. From alveoli into capillaries
c. From
veins into the alveolus
d. From arteries into the capillaries
✅ b. From alveoli into capillaries
17. When you take a deep breath, air is forced into
your lungs by the contraction of your:
a. Alveoli
b.
Lungs
c. Diaphragm
d. Heart
✅ c. Diaphragm
18. How does movement of the rib cage change air
pressure in the chest cavity?
a. When the rib cage raises, a
decrease in air pressure in the chest cavity causes air to rush into
the lungs.
b. When the rib cage relaxes, a decrease in air
pressure in the chest cavity causes air to rush out of the
lungs.
c. When the rib cage raises, an increase in air pressure
in the chest cavity causes air to rush into the lungs.
d. When
the rib cage relaxes, an increase in air pressure in the chest cavity
causes air to rush into the lungs.
✅ a. When the rib cage raises, a decrease in air pressure in the chest cavity causes air to rush into the lungs.
19. How does tobacco smoke affect the body?
a.
It blocks hemoglobin from binding to oxygen, thus affecting gas
exchange in the lungs.
b. It causes an increase in heart rate
and blood pressure.
c. It paralyzes cilia in the trachea,
allowing inhaled particles to enter the lungs.
d. All of the above
✅ d. All of the above
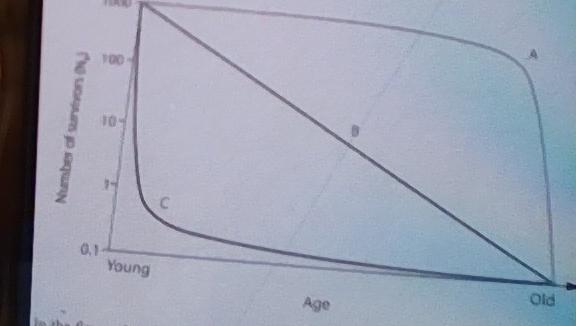
1) In the figure above, which of the following survivorship
curves implies that an animal may lay many eggs, of which a regular
number die each year?
A) Curve A
B) Curve
C
C) Curve B
Curve B

2) In the figure above, which of the survivorship curves most
applies to living in developed countries?
A) Curve
A
B) Curve A or Curve B
C) Curve C
D) Curve B
Curve A
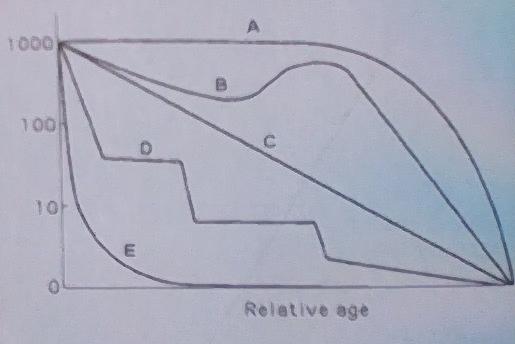
3) Refer to the figure above. Which curve best describes
survivorship in marine mollusks?
A) Curve A
B) Curve C
C) Curve B
D) Curve E
Curve C

4) Refer to the figure above. Which curve best describes
survivorship in elephants?
A) Curve E
B)
Curve A
C) Curve D
D) Curve B
Curve A
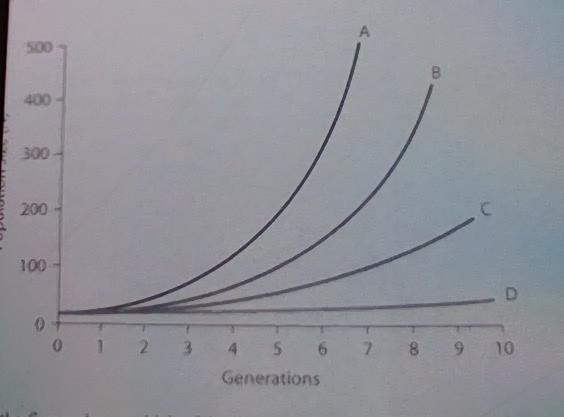
5) In the figure above, which of the lines represents the
highest per-capita rate increase (r)?
A)
Line C
B) Line B
C) Line A
D) Line D
Line A
The symbols +, –, and 0 are used to show the results of interactions between individuals or groups.
- + = positive effect
- – = negative effect
- 0 = no effect The first symbol refers to the first organism mentioned.
6) What interactions exist between a lion pride and a hyena
pack?
A) 0 / 0
B) + / +
C) + / –
D)
– / –
D) -/-
The symbols +, –, and 0 are used to show the results of interactions between individuals or groups.
- + = positive effect
- – = negative effect
- 0 = no effect The first symbol refers to the first organism mentioned.
7) What interactions exist between a tick on a dog and the
dog?
A) + / –
B) 0 / 0
C) – / +
D)
+ / 0
C) – / +
8) Which of the following statements is consistent with the
principle of competitive exclusion?
A) Even a
slight reproductive advantage will eventually lead to the elimination
of the less well-adapted of two competing species.
B) Natural
selection tends to increase competition between related
species.
C) The random distribution of one competing species
will have a positive impact on the population growth of the other
competing species.
D) Two species with the same fundamental
niche will exclude other competing species.
A) Even a slight reproductive advantage will eventually lead to the elimination of the less well-adapted of two competing species.
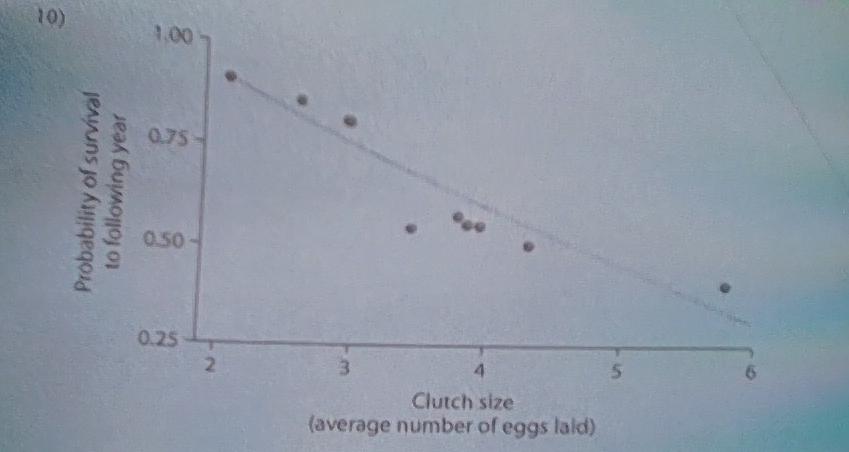
9) Looking at the data in the figure above, what can be said
about survival and clutch size?
A) Animals with low
survival tend to have smaller clutch sizes.
B) Animals with
high survival tend to have larger clutch sizes.
C) Probability
of survivorship does not correlate with clutch size.
D) Large
clutch size correlates with low survival.
✅ D) Large clutch size correlates with low survival.
10) You observe two female fish of the same species breeding.
One female lays 100 eggs and the other lays 1000 eggs. Which one of
the following is LEAST likely given the limits of fitness
trade-offs?
A) The female laying 100 eggs lives
longer than the female laying 1000 eggs.
B) The eggs from the
female laying 1000 eggs have larger yolks than the yolks of the eggs
from the female laying 100 eggs.
C) The female laying 1000 eggs
is larger than the female laying 100 eggs.
D) The female laying
100 eggs breeds more often than the female laying 1000 eggs.
✅ B) The eggs from the female laying 1000 eggs have larger yolks than the yolks of the eggs from the female laying 100 eggs.
11) Which of the following is characteristic of
K-selected populations?
A) Offspring with
good chances of survival
B) Many offspring per reproductive
episode
C) Small offspring
D) A high intrinsic rate of increase
✅ A) Offspring with good chances of survival
12) In the global nitrogen cycle depicted in the figure above,
what is the limiting portion of the cycle for plants?
A) Industrial nitrogen fixation
B) Nitrogen fixation by
bacteria
C) Nitrogen lost to the atmosphere
D) Internal
nitrogen cycling in the oceans
B) Nitrogen fixation by bacteria
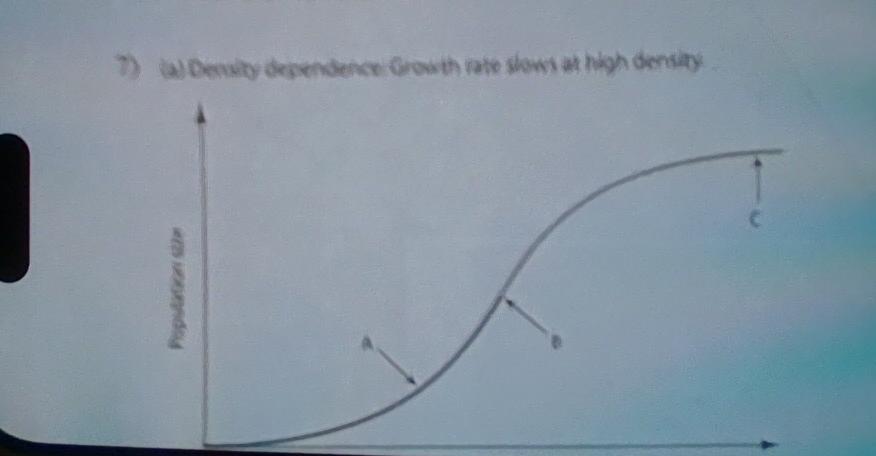
7) In the figure above, which of the arrows represents the
carrying capacity?
A) Carrying capacity cannot be
found in the figure because species under density-dependent control
never reach carrying capacity.
B) Arrow C
C) Arrow
D
D) Arrow A
Arrow C
8) As N (population size) approaches K (carrying capacity) for
a certain population, which of the following is predicted by the
logistic equation?
A) The growth rate will not
change.
B) The growth rate will approach zero.
C) The
carrying capacity of the environment will increase.
D) The
population will increase exponentially.
B) The growth rate will approach zero
9) Which of the following causes populations to shift most
quickly from an exponential to a logistic population
growth?
A) Decreased death rate
B) Favorable
climatic conditions
C) Competition for resources
D)
Removal of predators
C) Competition for resources
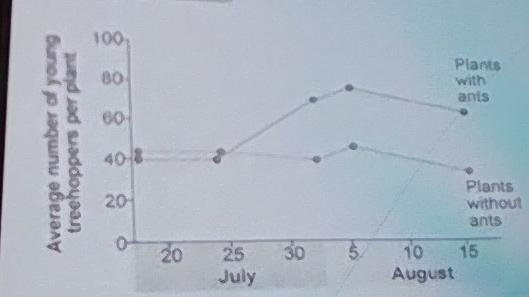
10) Treehoppers (a type of insect) produce honeydew, which
ants use for food. Treehoppers have a major predator, the jumping
spider. Researchers hypothesized that the ants would protect the
treehoppers from the spiders. In an experiment, researchers followed
study plots with ants removed from the system and compared them to a
control plot. In the figure above, what can you conclude?
A) Ants eat the honeydew produced by treehoppers
B) Ants
do somehow protect the treehoppers from spiders
C) No specific
conclusions can be drawn from this figure
D) Ants reduce the
numbers of treehoppers
B) Ants do somehow protect the treehoppers from spiders
11) Dwarf mistletoes are flowering plants that grow on certain
forest trees. They obtain nutrients and water from the vascular
tissues of the trees. The trees derive no known benefits from the
dwarf mistletoes. Which of the following best describes the
interactions between dwarf mistletoes and trees?
A)
Facilitation
B) Mutualism
C) Competition
D) Parasitism
D) Parasitism
12) In some circumstances, grasses benefit from being grazed.
Which of the following terms would best describe such a
plant-herbivore interaction?
A) Predation
B)
Commensalism
C) Mutualism
D) Parasitism
C) Mutualism
13) How does inefficient transfer of energy among trophic
levels result in the typically high endangerment status of many
top-level predators?
A) Top-level predators are
more likely to be stricken with parasites.
B) Top-level
predators are destined to have small populations that are sparsely
distributed.
C) Predators have relatively large population
sizes.
D) Predators are more disease-prone than animals at
lower trophic levels.
B) Top-level predators are destined to have small populations that are sparsely distributed.
14) Why does a vegetarian leave a smaller ecological footprint
than an omnivore?
A) Eating meat is an inefficient
way of acquiring photosynthetic productivity.
B) Vegetarians
need to ingest less chemical energy than omnivores.
C) There is
an excess of plant biomass in all terrestrial ecosystems.
D)
Fewer animals are slaughtered for human consumption.
A) Eating meat is an inefficient way of acquiring photosynthetic productivity.
15) For most terrestrial ecosystems, pyramids composed of
species abundances, biomass, and energy are similar in that they
have a broad base and a narrow top. The primary reason for this
pattern is that:
A) Secondary consumers and top
carnivores require less energy than producers.
B) Top
carnivores and secondary consumers have a more general diet than
primary producers.
C) Biomagnification of toxic materials
limits the secondary consumers and top carnivores.
D) At each
step, energy is lost from the system.
D) At each step, energy is lost from the system.
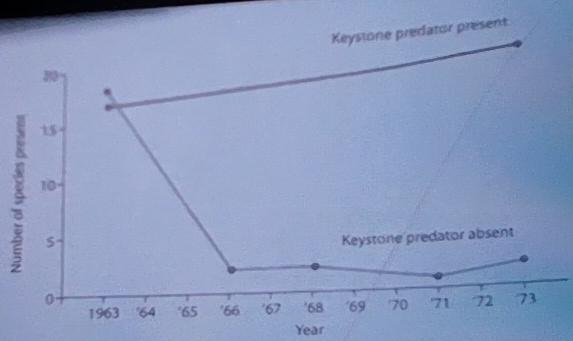
16) What does the graph in the figure above tell you about the
definition of a keystone species?
A) A keystone
species has little interaction with other species in an
environment.
B) Adding a keystone species to the community will
make it more diverse.
C) Removing a keystone species from the
community drastically reduces diversity.
D) Removing a keystone
species from the community will eventually allow for the invasion of
a new species.
C) Removing a keystone species from the community drastically reduces diversity.
17) Approximately how many kilograms (kg) of carnivore
(secondary consumer) biomass can be supported by a field plot
containing 1000 kg of plant material?
A) 10
B) 1000
C) 100
D) 1
A) 10
18) In a tide pool, fifteen species of invertebrates were
reduced to eight after one species was removed. The species removed
was likely a(n):
A) Keystone species
B)
Resource partitioner
C) Herbivore
D) Pathogen
A) Keystone species
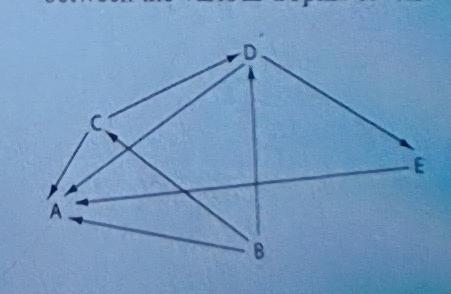
19) Use the following diagram of a hypothetical food web to
answer the question: Which letter represents an organism that could
be a producer?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D)
D
E) E
A) B