GIS test two, environmental monitoring
The afternoon constellation (A-Train) makes near simultaneous observations of CO2, precipitation, the water cycle energy fluxes, temperature and more. What two things can be said about its orbit?
Sun-synchronous and near-polar
Do satellites have to sense shortwave or longwave radiation to monitor Earth's temperature?
Longwave
What is the name of the sensors specifically designed to measure atmospheric conditions in 3D and create atmospheric profiles?
Sounders
To measure air quality satellites collect data at wavelengths ranging from UV to _____________?
microwave
Ozone absorbs which harmful portion of the electromagnetic spectrum?
UV light
Which famous chemical was banned in the Montreal Protocol (1987) that was depleting the ozone layer?
CFCs
GRACE and GRACE-FO are two satellites measuring differences in gravity through their location relative to one another as they pass over Earth. how does this relate to water?
More water in the soil means more gravity over that portion of the Earth's surface. When each satellite is pulled closer to the Earth (relative to each other) while passing over land there is more water in the ground at those spots.
By how much is the burned area of Canada expected to increase by in 2025?
It's supposed to double
There are four Remote Sensing Applications for Wildfires listed in the lecture slides, name two.
1. Monitoring fire conditions and detecting wildfires
2.
Monitoring fire spread and behaviour
3. Smoke impacts and air
quality
4. Post-fire Impacts
There are six Factors that contribute to wildfires listed in the lecture slides which can be monitored with remote sensing. Name three.
• Vegetation type and extent
• Stage of vegetation growth
• Vegetation structure
• Topography
• Moisture
content
• Available fuels
What are the two ways remote sensing can be used to detect wildfires?
Temperature anomalies and smoke
Do you want coarse or fine thermal resolution to detect fires? Is a pixel size of 1 by 1 km very helpful to detect new, small fires?
Fine, probably not
MODIS tracks surface temperature and could be very useful to detect new, small wildfires as it's thermal resolution is 30m by 30m. What is the caveat to this?
It needs contrast with the surroundings to detect an anomaly.
What does NBR stand for?
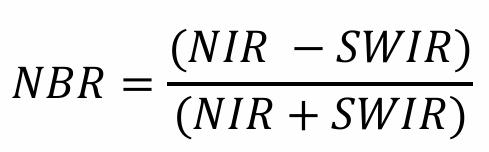
Normalized Burn Ratio
WildFireSat Mission is planned to launch in 2029 as a part of future Wildfire Monitoring efforts in Canada. What two types of resolution need to be fine (as oppposed to coarse) for these satellites to be helpful?
Temporal resolution and spatial resolution
Why might data management be a challenge in the future as we implement satellites into wildfire monitoring solutions?
Because of the time it might take to get relevant data quickly and consistently from storage to firefighting organizations.