The Water Cycle

Absorb
To soak up or take something in.
Atmosphere
The layer of gas surrounding a planet that is held in place by gravity.

Condensation
The change from a gas state to a liquid state.
Crystallization
The formation of highly ordered, solid structures from particles in a solution.
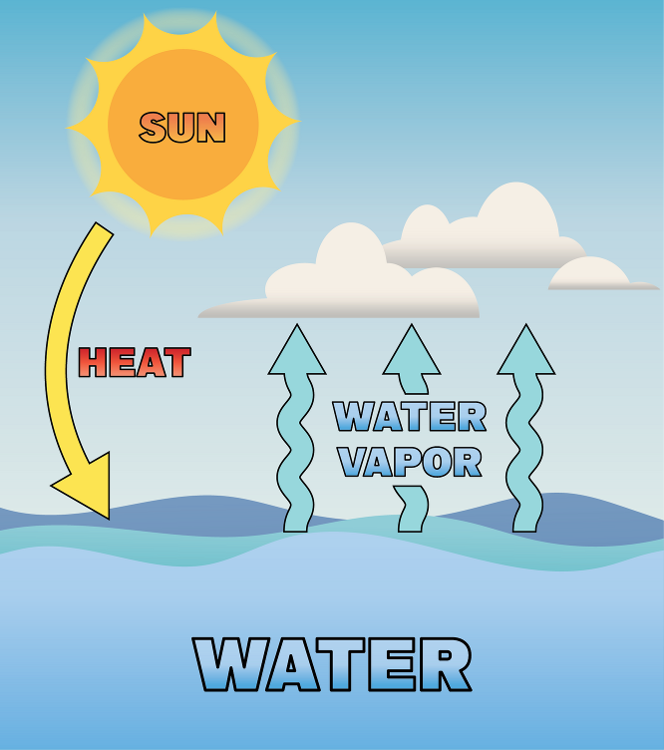
Evaporation
Change of a liquid to a vapor or gas.
Gravity
The force that causes objects with mass to attract one another.
Groundwater
Water that collects in cracks and pores in underground soil and rock layers.
Percolation
When water soaks into the ground and moves downward through spaces in soil and rocks.
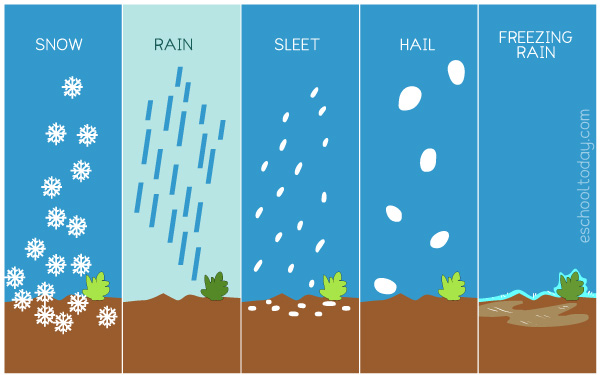
Precipitation
Rain, snow, sleet, or hail that falls from clouds in the sky.
Radiant Energy
Energy from the Sun that reaches Earth as visible light, ultraviolet radiation and infrared (heat) radiation.

Runoff
Rainfall and surface water that drains or flows from the land into streams, rivers, lakes or the ocean.

Thermal Energy
The total kinetic (motion) energy of the tiny particles that make up matter; the faster the particles move, the warmer the matter becomes.

Transpiration
The process by which plants lose water (water vapor) through that stomata in their leaves
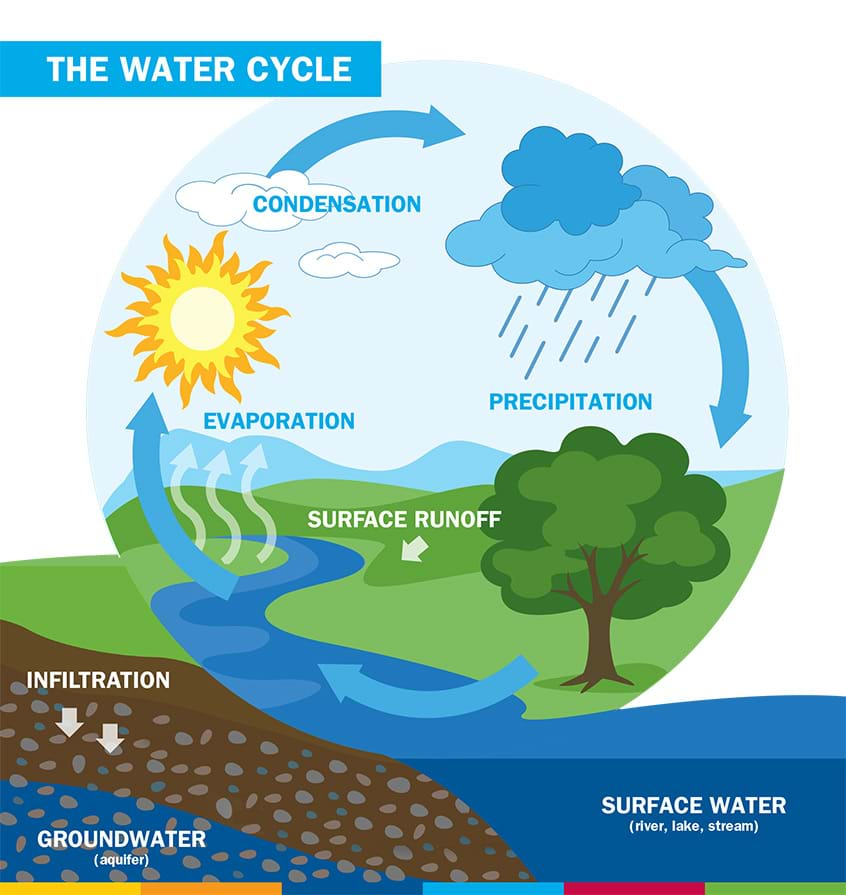
Water Cycle
The constant movement of water through the land, air, oceans, and living things.