CH 460 Final Exam Review
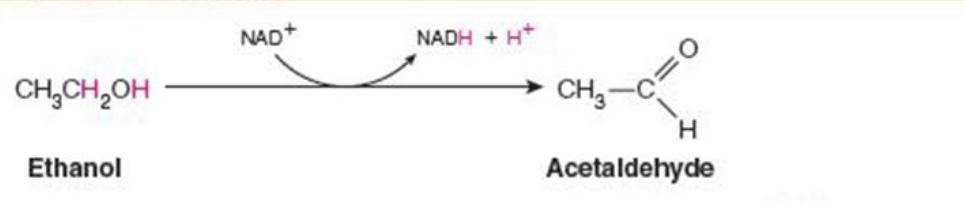
Name the enzyme: catalyze oxidation reduction reactions
Oxidoreductases
Ex. alcohol dehydrogenase (oxidation with NAD+)
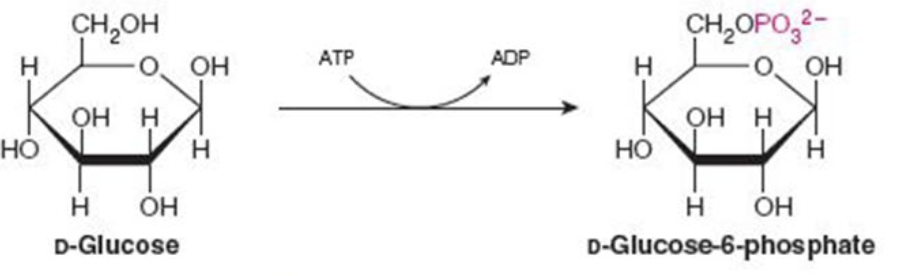
Name the enzyme: catalyze transfer of functional groups from one molecule to another
Transferases
Ex. Hexokinase (phosphorylation)
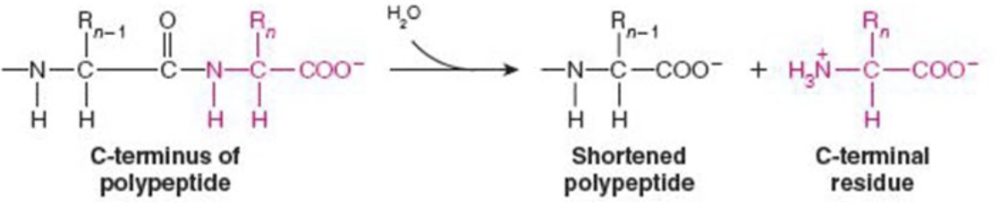
Name the enzyme: catalyze hydrolytic cleavage
Hydrolases
Ex. carboxypeptidase A (peptide bond cleavage)
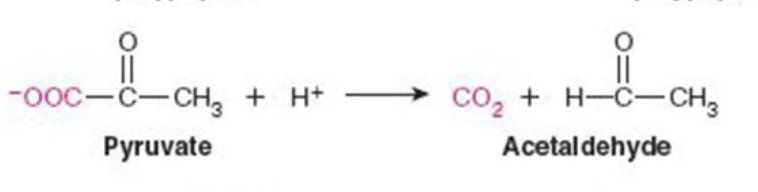
Name the enzyme: Catalyze removal of a group from or addition of a group to a double bond or other cleavage involving electron rearrangement
Lyases
Ex. Pyruvate decarboxylase (decarboxylation)
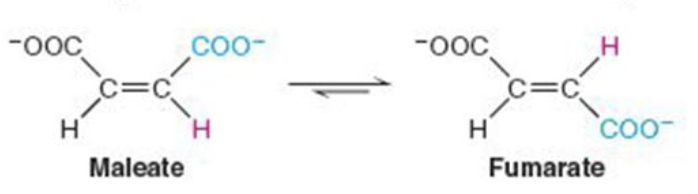
Name the enzyme: catalyze intramolecular arrangement of molecule
Isomerases
Ex. maleate isomerase (cis-trans isomerization)
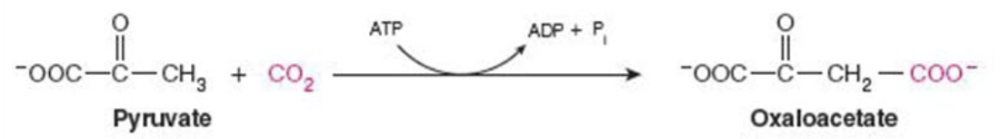
Name the enzyme: Catalyze reactions in which 2 molecules are joined
Ligase
Ex. pyruvate carboxylase
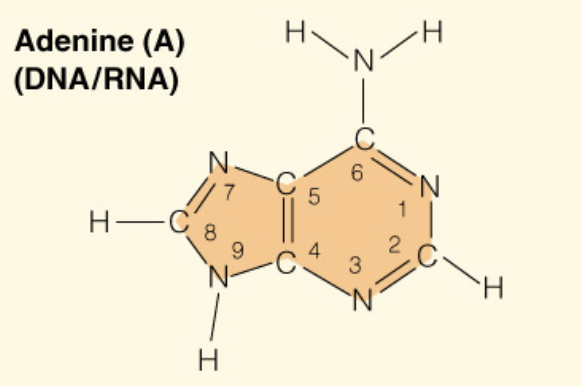
Name the base:
Adenine (Purine - 2 rings)
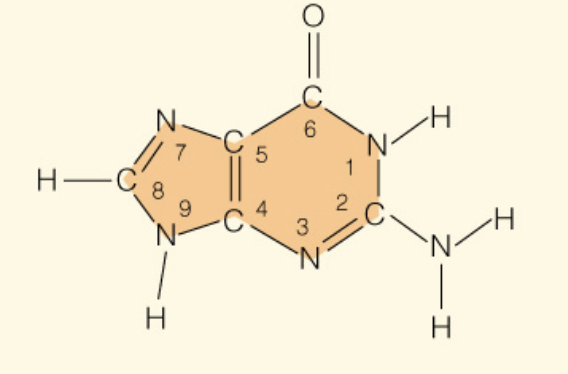
Name the base:
Guanine (Purine - 2 rings)
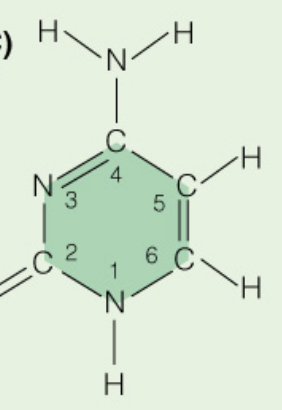
Name the base:
Cytosine (Pyrimidine)
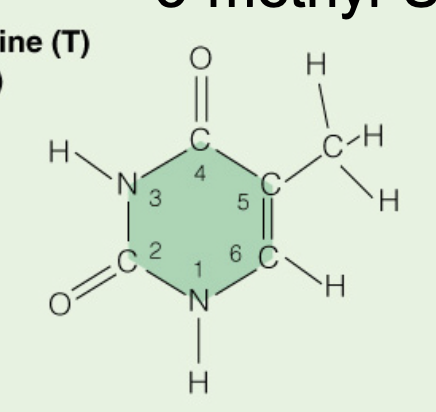
Name the base:
Thymine (Pyrimidine)
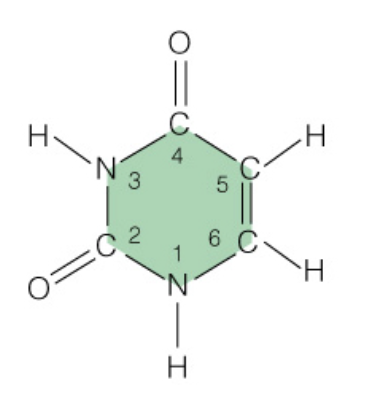
Name the base:
Uracil (RNA Only - Pyrimidine)
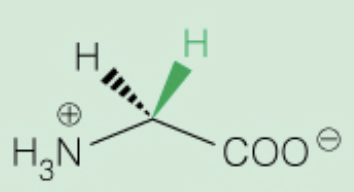
Name the amino acid
Glycine (Gly, G)
- smallest molecule, achiral
- Nonpolar, aliphatic
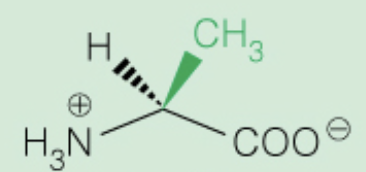
Name the amino acid
Alanine (Ala,A)
- Nonpolar, alipathic
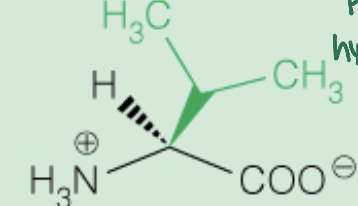
Name the amino acid
Valine (Val,V)
Nonpolar, Aliphatic
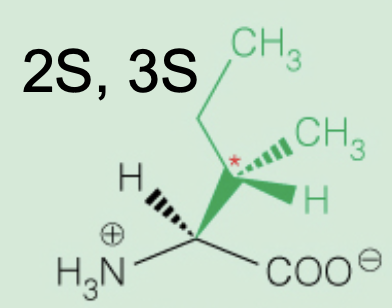
Name the amino acid
Isoleucine (2S,3S)
Nonpolar, Aliphatic
Ile, I
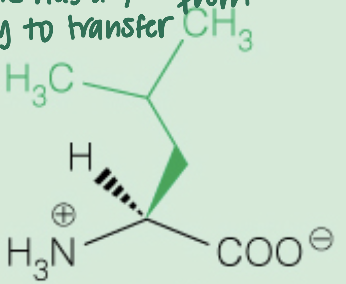
Name the amino acid
Leucine (Leu,L)
Nonpolar, Aliphatic
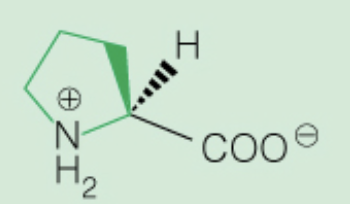
Name the amino acid
Proline (Pro, P)
Nonpolar, only amino acid with secondary amine ring in backbone
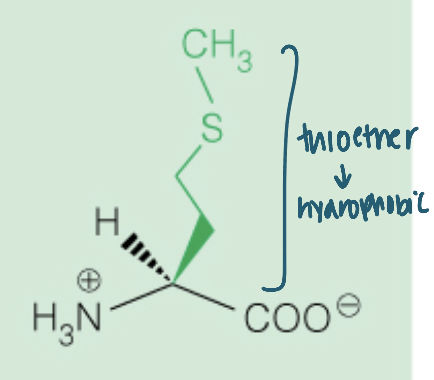
Name the amino acid
Methionine (Met, M)
Nonpolar
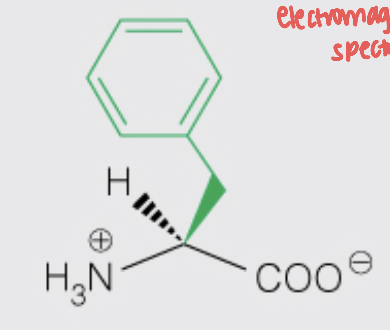
Name the amino acid
Phenylalanine (Phe, F)
- Nonpolar, Aromatic
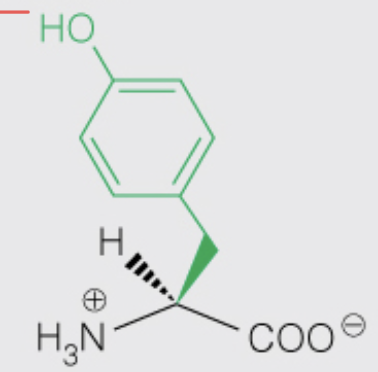
Name the amino acid
Tyrosine (Tyr, Y)
- Nonpolar, Aromatic
- OH can be phosphorylated
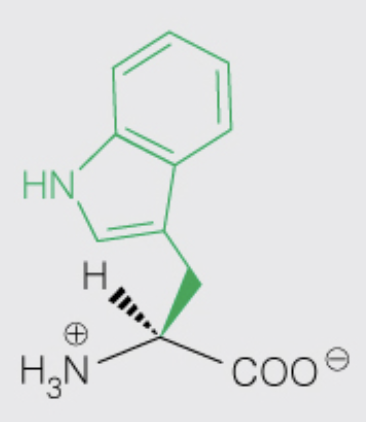
Name the amino acid
Tryptophan (Trp, W)
- Nonpolar, Aromatic
- contributes the most to UV absorbance at 280 nm compared to Tyr
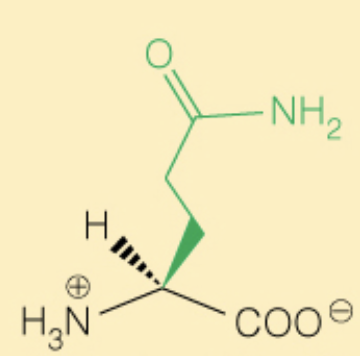
Name the amino acid
Glutamine (Gln, Q)
- Polar
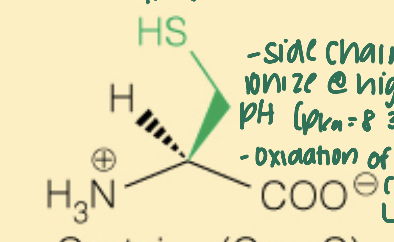
Name the amino acid
Cysteine (Cys, C)
- Polar
- 2 cysteine molecules can form a disulfide bond (with -SH, thiol)
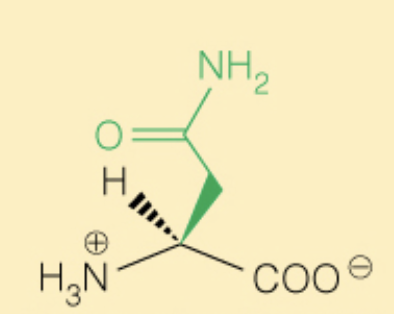
Name the amino acid
Asparagine (Asn, N)
- Polar
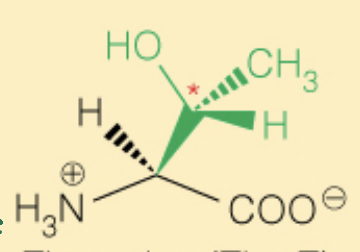
Name the amino acid
Threonine (Thr, T)
- OH can be phosphorylated
- Polar
- 2S, 3R
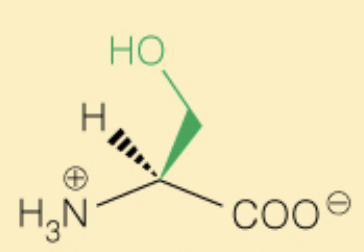
Name the amino acid
Serine (Ser, S)
- OH can be phosphorylated
- Polar
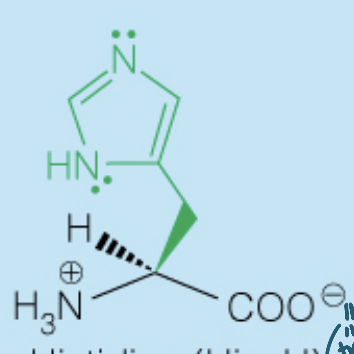
Name the amino acid
Histidine (His, H)
- Polar, Positively-Charged, Basic
- Used in many enzymes catalysis since the side chain pKa (6) is around the physiological pH
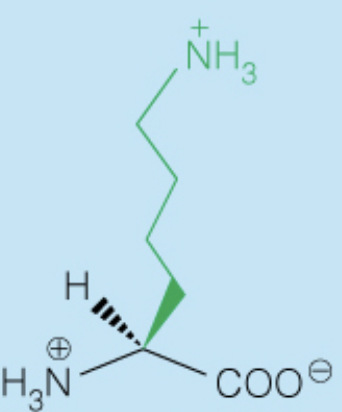
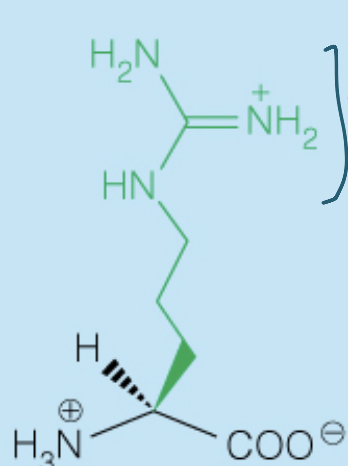
Name the amino acid
Arginine (Arg, R)
- Polar, Positively-Charged, Basic
Name the amino acid
Lysine (Lys, K)
- Polar, Positively-Charged, Basic
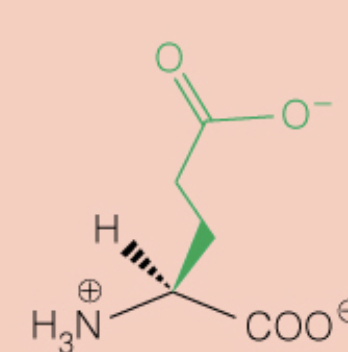
Name the amino acid
Glutamic Acid (Glu, E)
- Polar, Negatively Charged, Acidic
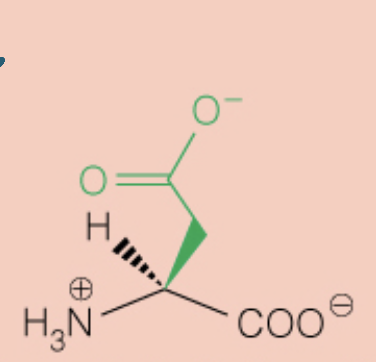
Name the amino acid
Aspartic Acid (Asp, D)
- Polar, Negatively Charged, Acidic
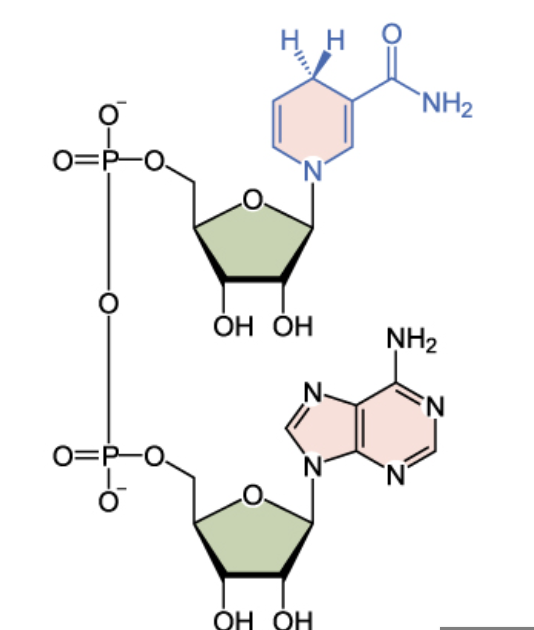
Name the structure
NAD+
Name the structure
NADH
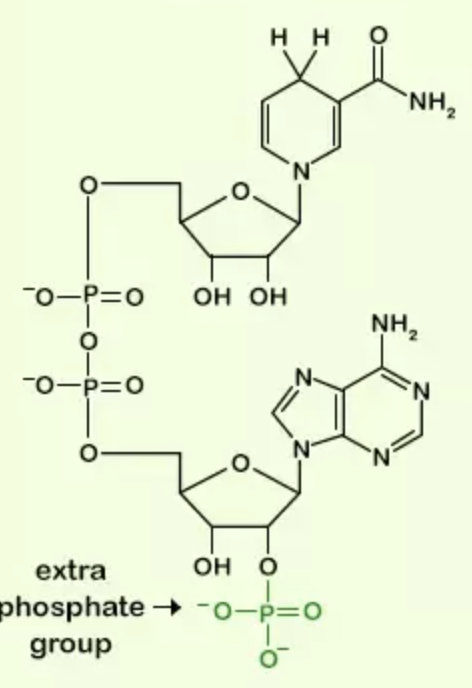
Name the structure
NADPH
Name the structure
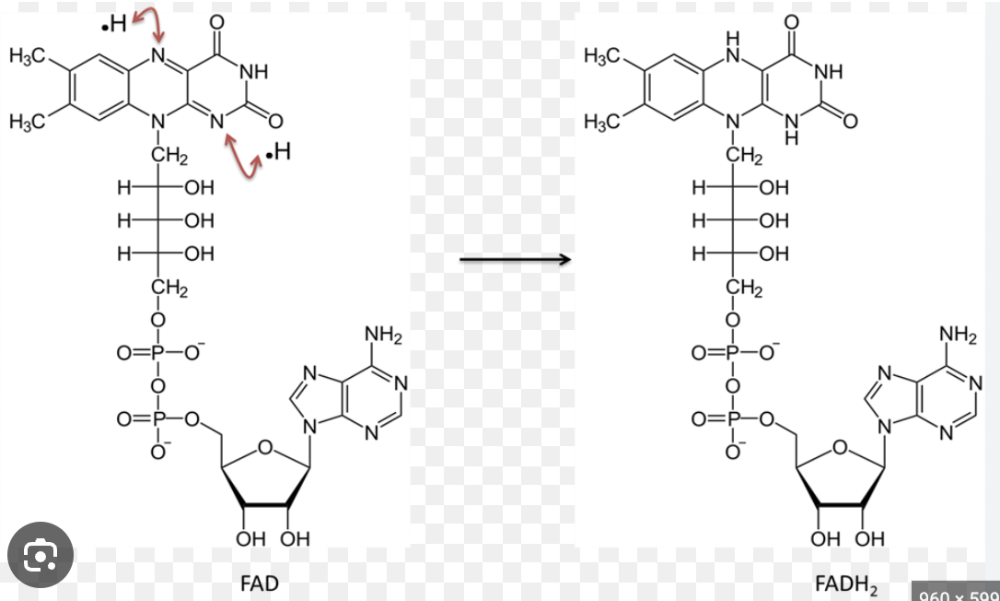
FAD+ vs. FADH
Name the structure
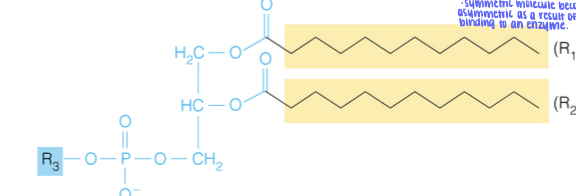
Glycerophospholipid
- lipid with phosphate containing head group
- When R3 is is H, the structure is a phosphatidic acid.
- Part of membrane lipids
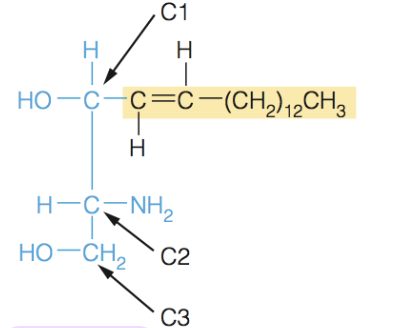
Name the structure
Spingosine
- sphingolipids are built on the amino alcohol spingospine, rather than glycerol
- includes long chain tail, so it requires the addition on one fatty acid tail to make a suitable membrane lipid
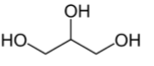
Name the structure
Glycerol
- does not have any stereocenters. When it is derivatized, the symmetric molecules becomes asymmetric (pro-chiral) when bound to enzyme
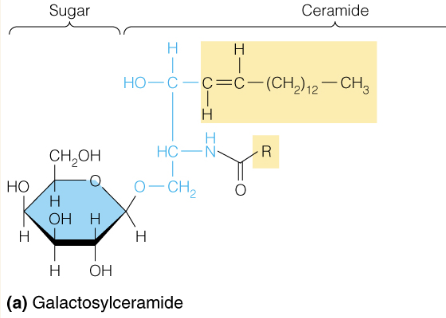
Name the structure
Glycospingolipids
- includes cerebrosides, gangliosides which are common in membranes of the brain and nerve cells
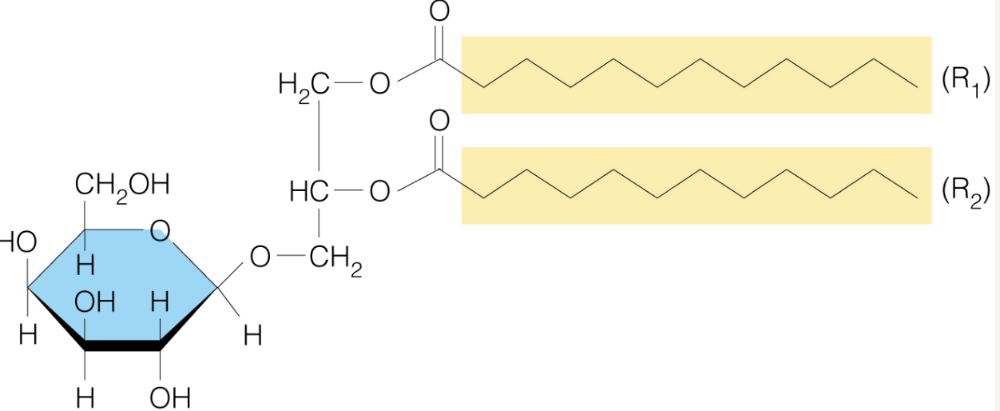
Name the structure
Glycoglycerolipids
- widespread in plants and bacterial membrane
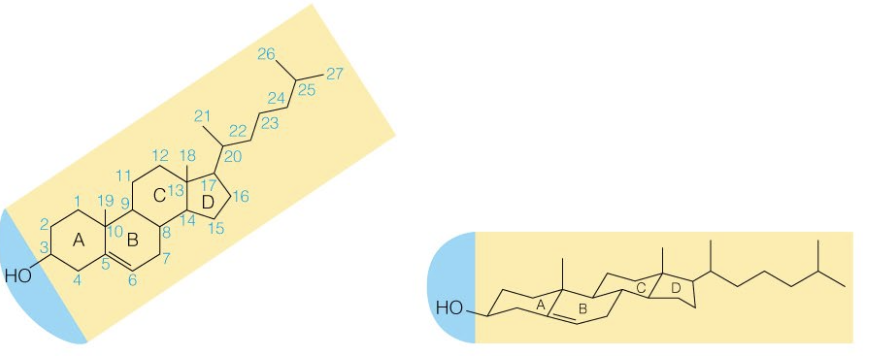
Name the structure
Cholesterol
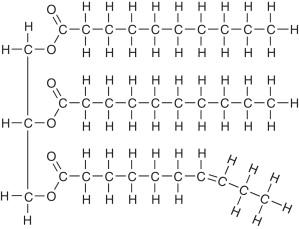
Name the structure
triaglycerol
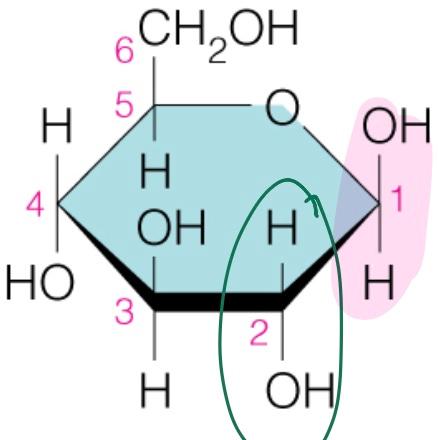
Name the sugar
Glucose
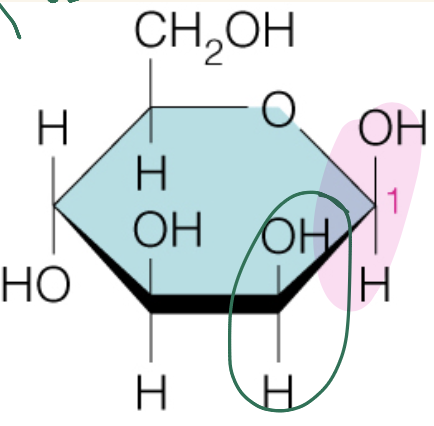
Name the sugar
Mannose
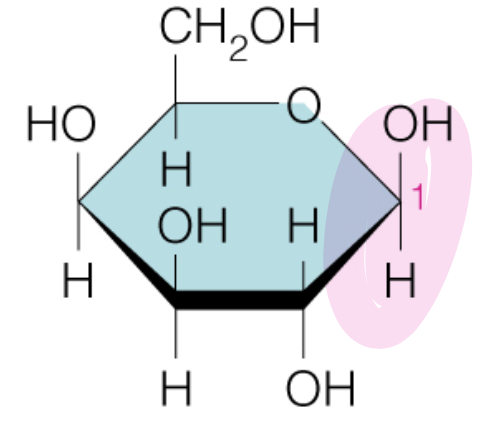
Name the sugar
Galactose
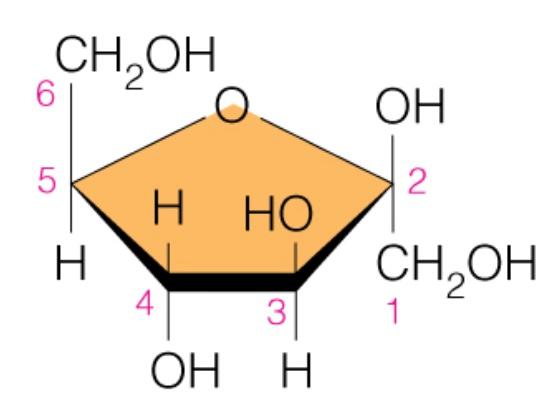
Name the sugar
Fructose
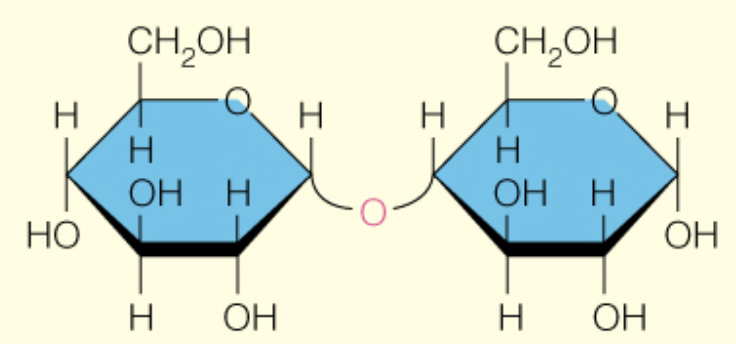
Name the disaccharide
Maltose
B-d-glcp (1 to 4) B-d-glcp
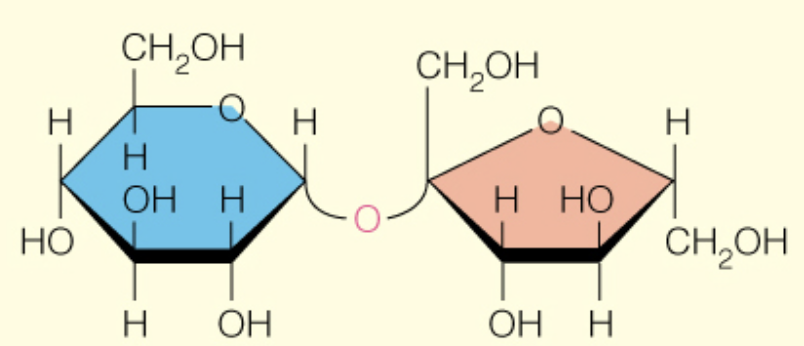
Name the disaccharide
Sucrose
a - D -glcp (1 to 2) B-D-fruf
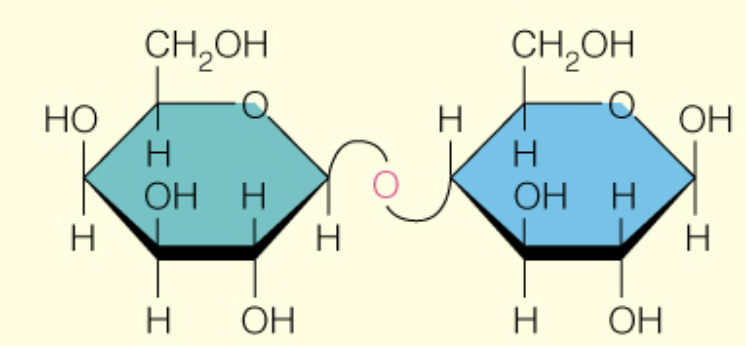
Name the disaccharide
Lactose
B-d-Galp (1 to 4) B-d-Glcp