Exam 3 questions
Ouabain, an inhibitor of the Sodium Potassium Pump, is a _________ that inhibits the pump by binding to the _______ part of the transporter.
cardiac glycoside, extracellular
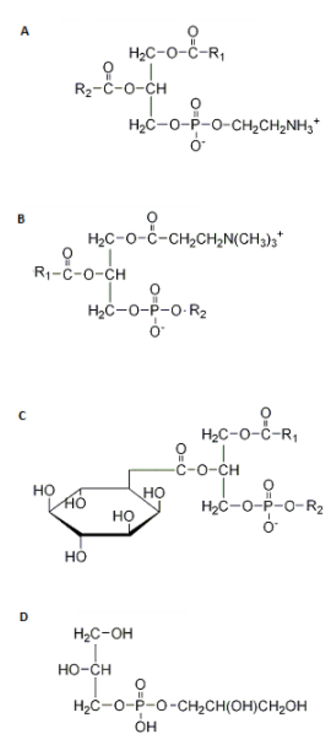
Which of these structures correctly represents a glycerophospholipid?
Structure A
The convention for drawing the structure of disaccharides is to draw the _______ end on the left, and the ______ end on the right.
non-reducing, reducing
All of the following is (are) found as covalently attached anchors in lipid-linked proteins, EXCEPT:
A) glycosylphosphatidyl inositol
B) cholesterol and other sterols
C) isoprenes
D) All of the above are found as covalently attached anchors in lipid-linked proteins.
E) fatty acids
cholesterol and other sterols
Peptidoglycans are primarily found in
Bacterial cell walls
Which of the following is true about membrane glycoproteins?
A) They increase the hydrophobicity of the membrane.
B) They function primarily in energy storage.
C)They are located exclusively on the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane.
D)They serve as solute transporters in the membrane.
E)They play a key role in cell recognition and communication.
They play a key role in cell recognition and communication.
What describes why plant oils are generally healthier for human consumption than animal fats?
Plant oils usually contain more unsaturated fatty acids than animal fats
Lactose is made up of which of the following monosaccharides?
Glucose and Fructose
Which of the following segments of the integral membrane protein glycophorin most likely contains the transmembrane alpha helix?
A) SQTNDTHKRDTYAATPRA
B) LSTTEVAMHTTTSSSVSKSY
C) ITLIIFVMAILVIAFMILLI
D) VSEISVRTVYPPEEETGE
E) YGIRRLIKKSPSDVKPLP
C) ITLIIFVMAILVIAFMILLI
What correctly describes monosaccharide isomers?
Formation of a hemiacetal, or a hemiketal, creates a new chiral center.
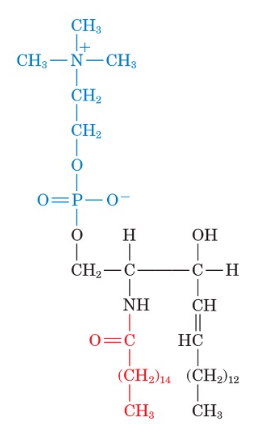
Identify the compound
sphingomylelin
Which of the following are used for energy storage?
A) Fatty Acids
B) Glycerophospholipds
C) Cholesterol
D) Sphingolipids
E)Triacylglycerols
Triacylglycerols
How many reducing ends does glycogen have?
One
What can form a cyclic hemiketal?
Fructose
What does transverse asymmetry mean in the context of membrane structure?
The composition of the inner leaflet and outer leaflet of the bilayer are different
Which of the following pairs are epimers?
glucose and mannose
AcrB is a(n) ____ that transport drugs out of the cell ____ their concentration gradient using energy from protons entering the cell ____ their concentration gradient.
secondary active transporter; up; down
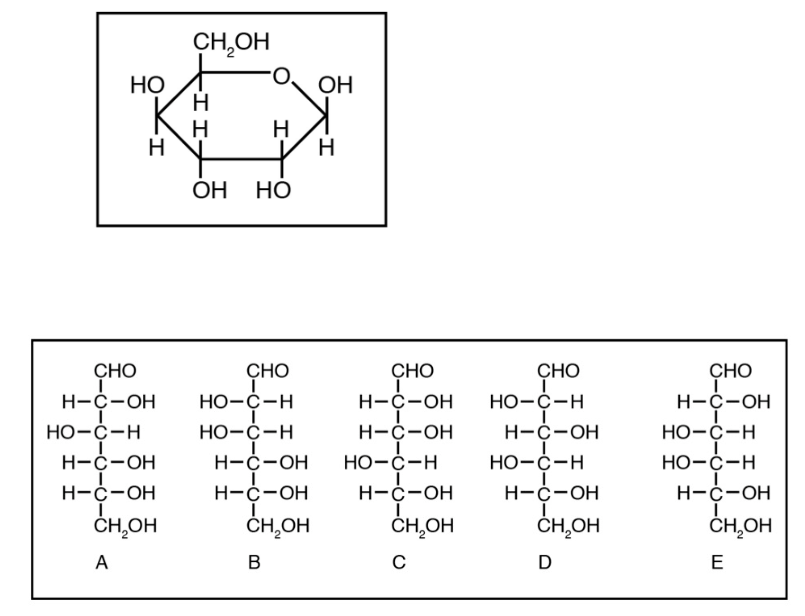
Which Fisher Projection represents the same monosaccharide as the Haworth Projection?
C
What is the position of the hydroxyls on the chiral carbons of D-fructose in the linear structure (Fischer projection)?
Left, right, right
Amide-linked ____ anchors are covalently attached to the ____ of ____ residues on proteins.
myristoyl; alpha amino group; glycine
The sodium potassium pump transports 3 Na+ ions ___ and 2 K+ ions ___ for every 1 molecule of ATP hydrolyzed.
out of the cell; into the cell
Which of the following is an example of a monosaccharide?Correct answer:
A)Galactose
B) Sucrose
C) Maltose
D)Amylose
E)Lactose
A)Galactose
Which of the following statement about cell membrane states is TRUE?
A) Lipid rafts phase separate in single monolayers in the liquid-ordered state.
B) The liquid-ordered state predominates below the melting temperature of a membrane.
C) The solid-ordered state predominates above the melting temperature of a membrane.
D)Thioether linked proteins are found in the liquid-ordered state.
E) The liquid-ordered state can only be made up of lipids with unsaturated fatty acid tails.
A) Lipid rafts phase separate in single monolayers in the liquid-ordered state.
____ and ____ increase melting temperatures of fatty acids and lipids that contain them
Saturation; longer acyl chains
What polysaccharide is a branched polymer?
amylopectin
Starch is a mixture of
amylose and amylopectin
The monosaccharide used to make glycogen is _____, while the monosaccharide used to make RNA is _____ and DNA is _____.
glucose; ribose; deoxyribose
Peripheral membrane proteins are
Bound to integral membrane proteins or polar head groups of lipids
O-linked oligosaccharides are important on glycoproteins in order to
lift the protein functional domains above the glycocalyx.
What type of glycosidic bond is found in maltose?
α(1→4)
In glycoproteins, O-linked oligosaccharides are commonly attached to the —OH group of _____.
threonine
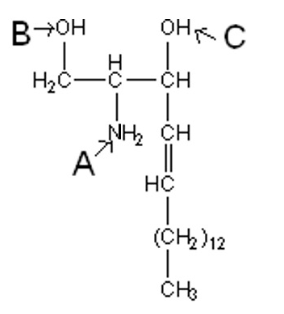
Which label points to the point of attachment for a fatty acid to yield a ceramide?
A
Which of the following is an example of a heteropolysaccharide?
hyaluronic acid
The bonding of alcohols to the anomeric center of a carbohydrate results in the formation of a(n) __________ bond.
glycosidic
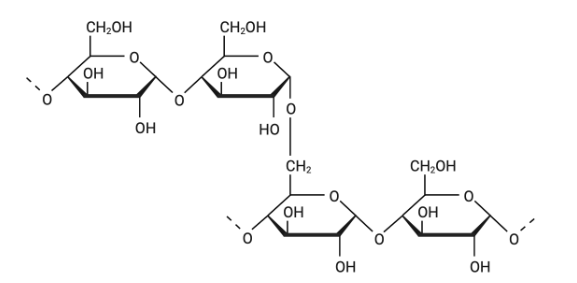
What is true concerning the polysaccharide shown above?
The branch point illustrated occurs more often in glycogen than it does in amylopectin.
Which type of lipid-anchor is an isoprene-based lipid and connected to side-chain Cys residues?
Thioether-linked anchors
The role of cartilage matrix proteoglycan is
to expel water upon compression and absorb water upon decompression.
Which of the following structures is formed by fatty acids and other single tailed amphiphiles?
micelles
Lipid bilayers with high concentrations of gangliosides are rare. Which of the following explanations is correct?
A)The hydrophobic tails on gangliosides form a conical shape rather than a cylindrical shape making close packing difficult.
B) Gangliosides contain trans fatty acids resulting in a bent hydrophobic tail making close packing difficult.
D) None of the above is correct.
E) Gangliosides contain large headgroups making close packing difficult.
Gangliosides contain large headgroups making close packing difficult.
Which of the following modes of transport exhibits saturation, at very high solute concentration?
-Facilitated diffusion
- Secondary active transport
-Primary active transport
-Ion channels
All of the following describe the solid ordered (So) phase of a lipid bilayer EXCEPT:
A) Tight packing
B) Maximal bilayer thickness
C) Found at temperatures below Tm
D)Lipid chains likely to be bent
D) lipid chains likely to be bent
ALL of the following are components of the cartilage matrix proteoglycan, EXCEPT:
A) O-linked oligosaccharides, Not SelectedCorrect answer:
B)Transmembrane domain
C)Chondroitin sulfate
D)N-linked oligosaccharides
E)Keratan sulfate
B)Transmembrane domain
All of the following are components of membranes EXCEPT:
A)Triacylglycerols
B) Proteins
C) Sphingolipids
D)Glycerophospholipids
E) Cholesterol
Triacylglycerols
A membrane surface protein with a keratan sulfate linkage is classified as a
Proteoglycan
Which of the following amino acid residues is thermodynamically favored at the lipid-water interface of a membrane?
Tryptophan
Proteins that bind to specific carbohydrates are called ______.
lectins
Two of the following are linear polysaccharides made up of glucose
monomers:
______ is a structural polysaccharide, while _____ is
for storage.
cellulose, amylose
Which carbon in D-glucose determines its D or L configuration?
C-5
Which of the following can be predicted using hydropathy plots?
Transmembrane alpha helices
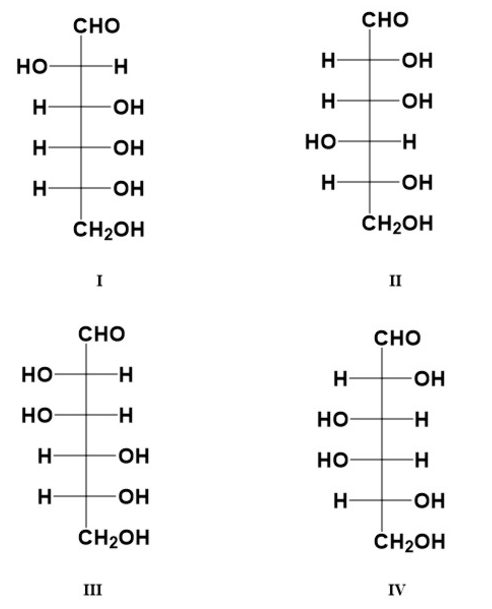
Which of the these is the C-2 epimer of D-glucose?
Note that the identifying Roman Numeral is below each monosaccharide structure.
III