Evolutionary Relationships
Evolutionary Relationships
It is based on shared characteristics.
Which describes the modern classification system?
based on evolutionary relationships
Why was modern classification invented?
Scientists understood that species share a common ancestor.
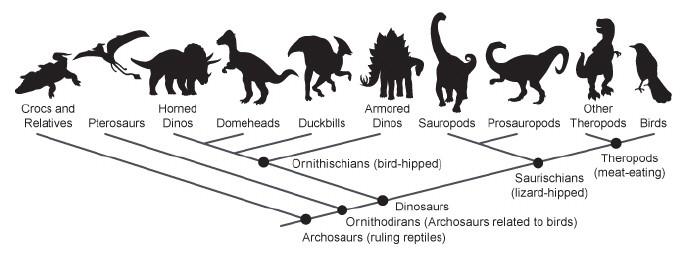
Consider the diagram.
Josiah says this is a phylogenetic tree of the dinosaurs. Maleek says it is a cladogram of the dinosaurs. Who is correct?
Both are correct.
A scientist is trying to determine how closely related a moth species (Species Z) is to four other moth species (Species A, B, C, and D). He examined the DNA of each species and compared it to the study subject. He then created this table.
Which species is most closely related to the moth species (Species Z)?
Species # of genetic differences
Species A 12
Species B 3
Species C 14
Species D 28
species B
Dr. Digger, a paleontologist, finds a fossil that he describes in his
journal.
The creature was approximately 1 meter
long, with its backbone fused into a large shell covering the body
cavity. It had a beaklike mouth, without teeth, and all four limbs
were in the form of flippers.
Based on
anatomical similarities, to which modern animal is Dr. Digger’s
creature most closely related?
sea turtle
If two organisms are in the same clade, what can you predict about their relationship?
They share a common ancestor.
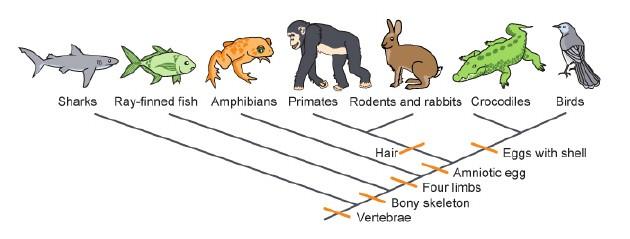
According to the cladogram, which organisms are in the smallest clade with birds?
Crocodiles
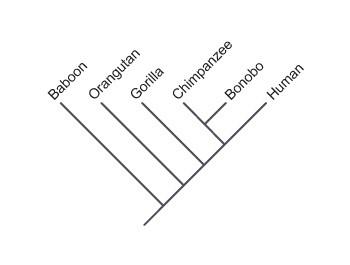
Consider the phylogenetic tree of Old World primates.
According to the tree, which primates share the most recent common ancestor with humans?
bonobos and chimpanzees
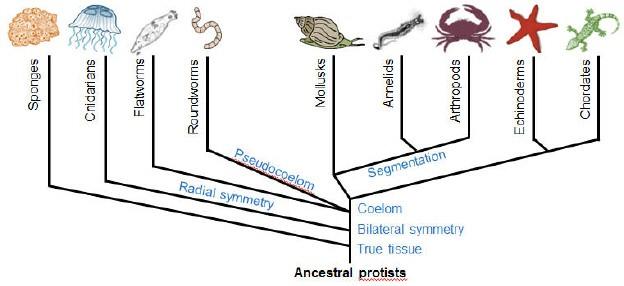
According to the cladogram, which organisms have roundworms as a common ancestor?
.
mollusks, echinoderms, chordates, and annelids

Consider the cladogram. Which group of organisms has the derived characteristics of true tissues, bilateral symmetry, and a pseudocoelom?
Roundworms
In a cladogram, what occurs at a node?
A derived trait appears.
Which best describes derived characteristics?
They are newly evolved traits.
A scientist discovers a new organism that is related to clownfish. What can the scientist discover by using molecular clocks?
the amount of time that the two species have been evolving apart
Julia is trying to place a duckbilled platypus, lizard, bear, and monkey on a phylogenetic tree. She learns that the duckbilled platypus, bear, and monkey are classified as mammals. She also learns that mammals share a common ancestor with reptiles. Which additional piece of information will be most helpful to Julia to properly build her phylogenetic tree?
The platypus lays eggs like a reptile.
Protists are a group of organisms that are characterized as eukaryotes (they have cells with nuclei) that are neither plants nor animals nor fungi. They are very diverse, and there are many hypotheses about their classification. The cladogram for protists is constantly changing and, sometimes, there are opposite hypotheses that both have data to support them. What is the implication of a changing hypothesis?
It is acceptable because data are still being collected.
Which of the following are Phylogenetic trees also know as ?
Cladogram