Psychology on the brain Dr Mason
Pituitary gland
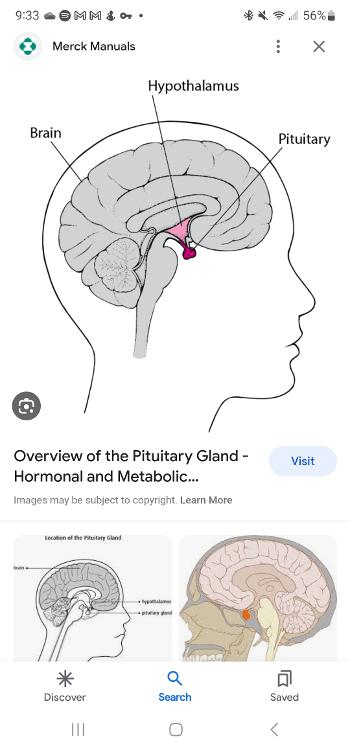
Gland located in the brain that secretes human growth hormones and influences all other hormones-seceting glands
Cerebellum
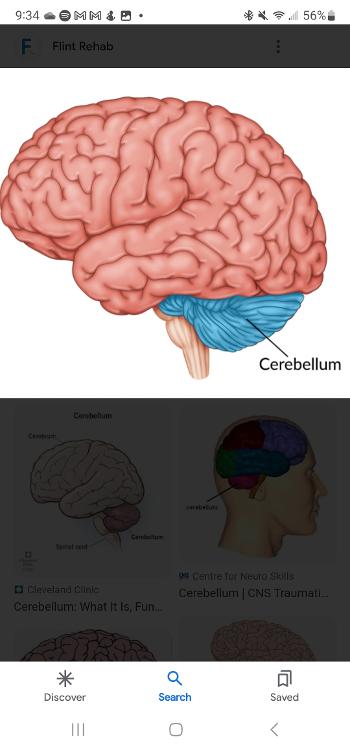
Part of the lower brain located behind the pond that controls and coordinates involuntary, rapid, fine motor movement
White matter
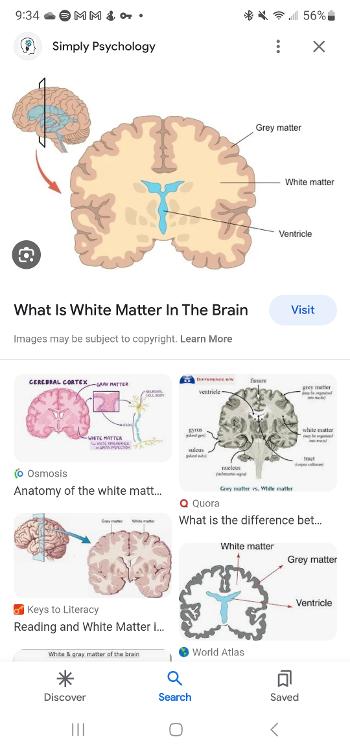
Is made up of a large network of nerve fibers (axons) in your brain that allows the exchange of info and communication between different areas of your brain
Temporal lobe
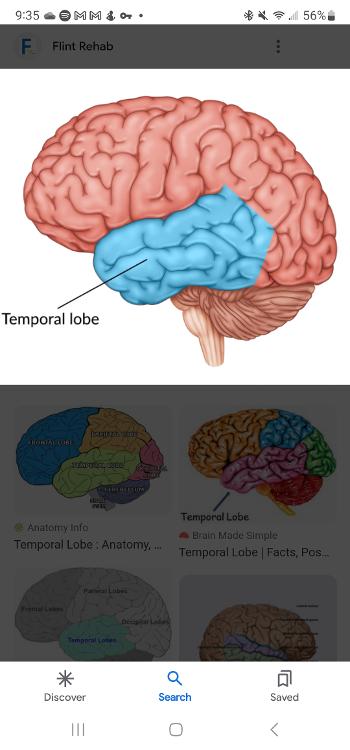
It forms the cerebral cortex in conjunction with the occipital, parietal, and frontal lobe
Cerebral cortex
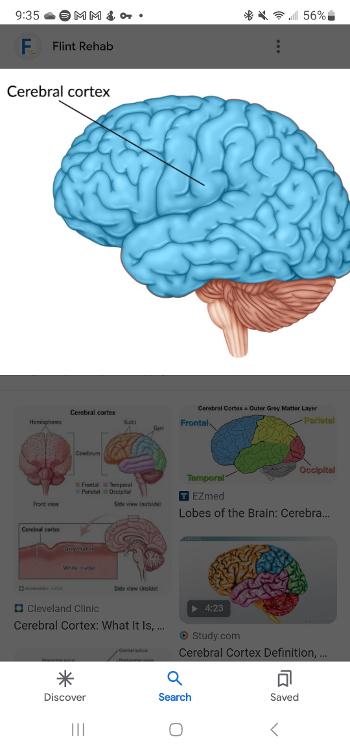
The outer layer that lies on top of the cerebrum
Parietal lobe
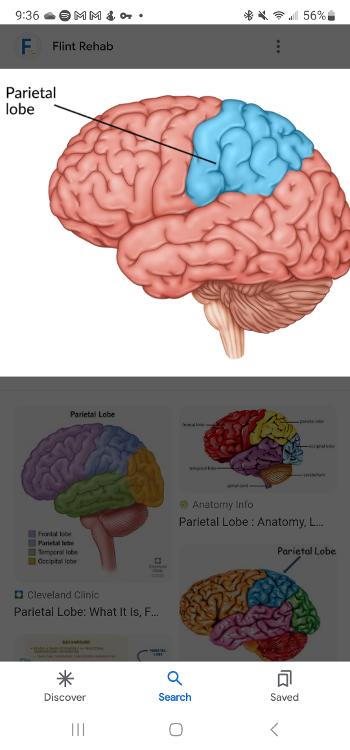
Sections of the brain located at the top and the back of each cerebral hemisphere containing the centers for touch, taste, and temperature sensations
Hippocampus
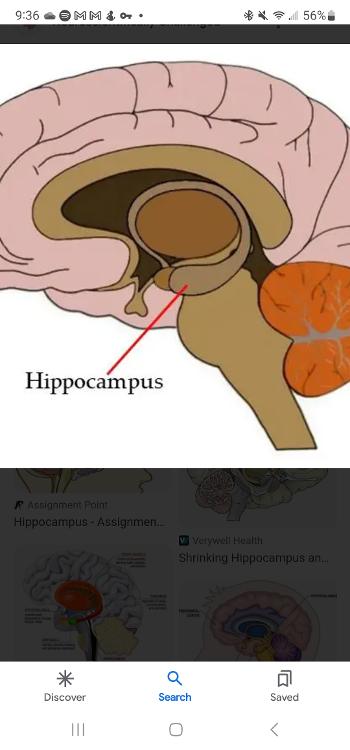
Curved structure located within each tempors lobe, responsible for the formation of long term memories and the storage of memory location of objects
Grey matter
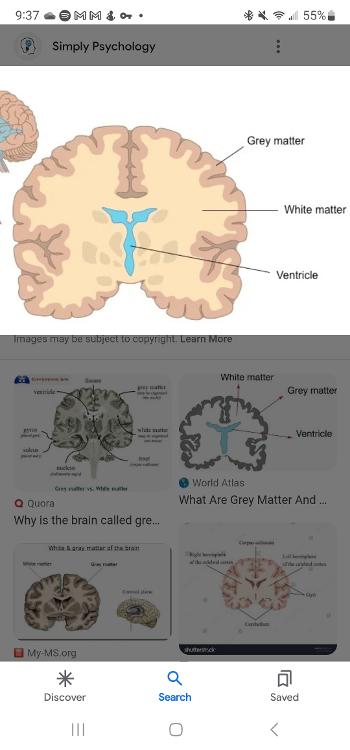
A type of tissue in your brain and spinal cord that plays a crucial role in allowing you to function normally day to day
Motor control
The process of initiating, directing, and grading purposeful voluntary movement
Mammillary body
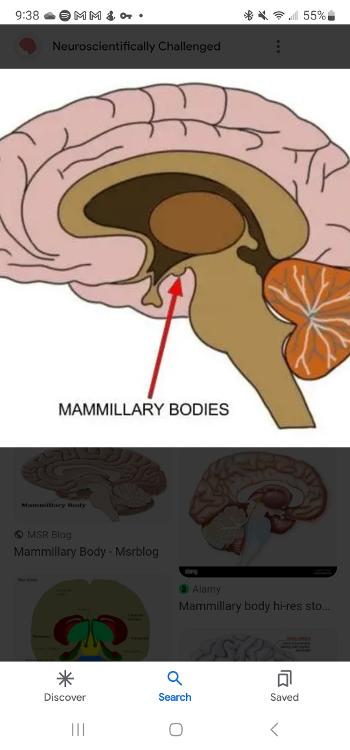
Is a recollective memory
Limbic system
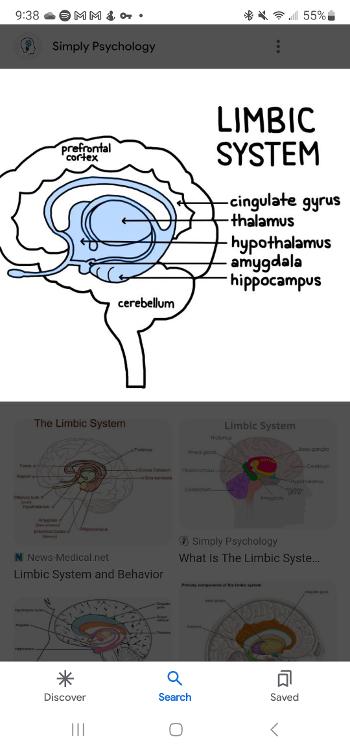
A group of several brain structures located under the cortex and involved in learning, emotion, memory, and motivation
Glial cell
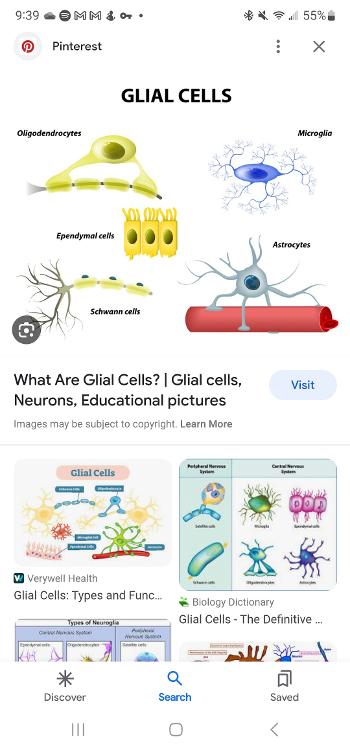
A type of cell that provides physical and chemical support neurons and maintain their environment
Frontal lobe
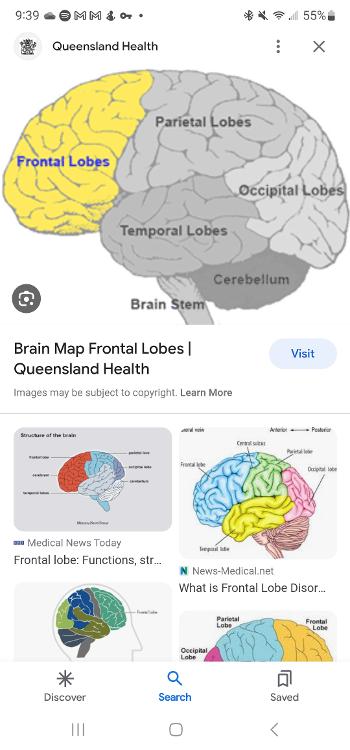
Area of the cortex located in the front and top of the brain, responsible for higher mental processes and decision making, as well as the protection of fluent speech
Corpus callosum
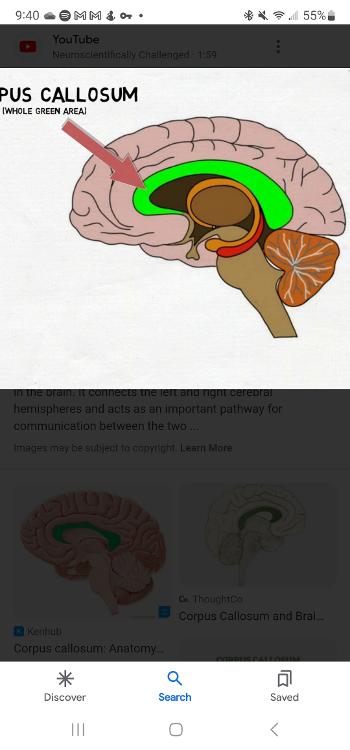
Thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemisphere
Occipital lobe
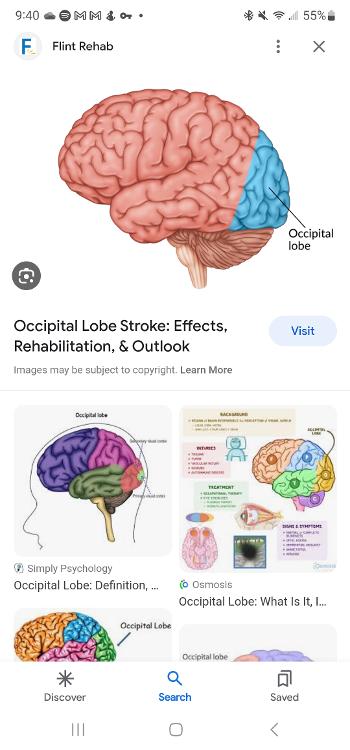
Section of the brain located at the rear and bottom of each cerebral hemisphere containing the visual centers of the brain
Deep leisoning
Insertion of a thin, insulated wire into the brain through which an electrical current is sent that destroys the brain cells at the tip of the wire
Computed tomography (CT)
Brain-imaging method using computer-contolled X-rays of the brain
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Brain-imaging method using radio waves and magnetic fields of the body to produce detailed images of the brain
Positron emission tomography (PET)
Brain-imaging method in which a radioactive sugar is injected into the subject, and a computer complies a color coded image of the activity of the brain, with lighter color indicating more activity
Functional MRI (fMRI)
A type of MRI scan that can show which areas of your brain are most active
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
A test that measures electrical activity in the brain using small, metal discs (electrodes) attached to the skull
Neuroplasticity
The ability of the brain to form and reorganize synaptic connections EX. Response to learning, experience or following injury
Stem cells
Cells with potential to develop into many different types of cells in the body
Medulla
The inner region of the organ or tissue, especially when it is distinguishable from the outer region or cortex (as in kidney, and adrenal gland, or hair)
Pons
The part of the brainstem that links the medulla oblongata and the thalamus
Reticular formation (RF)
A complex network of brainstem nuclei and neurons that serve as a major integration and relay center for many vital brain systems to coordinate functions necessary for survival
Thalamus
A paired grey matter structure of the diencephalon located near the center of the brain
Hypothalamus
Coordinates both the autonomic nervous system and the activity of the pituitary, controlling body temp, thirst, hunger, and other homeostatic systems, and involved in sleep and emotional activity
Homeostasis
The tendency toward a relatively stable equilibrium between interdependent elements
Amygdala
Region of the brain primarily associated with emotional processes
Cortex
The outer layer of the cerebrum composed of folded grey matter and playing an important role in the consciousness
Cerebral hemispheres
Controls the somatosensory, motor, language, cognitive thout, memory, emotions, hearing, and vision
Somatosensory cortex
It detects sensory info from the body regarding temp, proprioception, touch, texture, and pain
Motor cortex
Plan and create electrical impulses that cause voluntary muscle contractions
Association areas
Parts of the cerebral cortex that receive inputs from multiple areas
Nature
Genetic influence an individual's personality
Nuture
How the environment impacts their development
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
The fundamental and distinctive characteristics or qualities of someone or something
Gene
A unit of heredity which is transferred from parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the offspring
Chromosome
A thread like structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus, carrying genetic info in the form of genes
Dominant
The relationship of two versions of a gene also called allele
Recessive
The relationship between two versions of a gene but is masked a dominant allele
Predisposition
The state of being likely to behave in a particular way or to suffer from a particular disease
Evolution
The gradual development of an organism overtime
Natural selection
The process through which populations of living organisms adapt and change