Anatomy Block III- Wrist and Hand
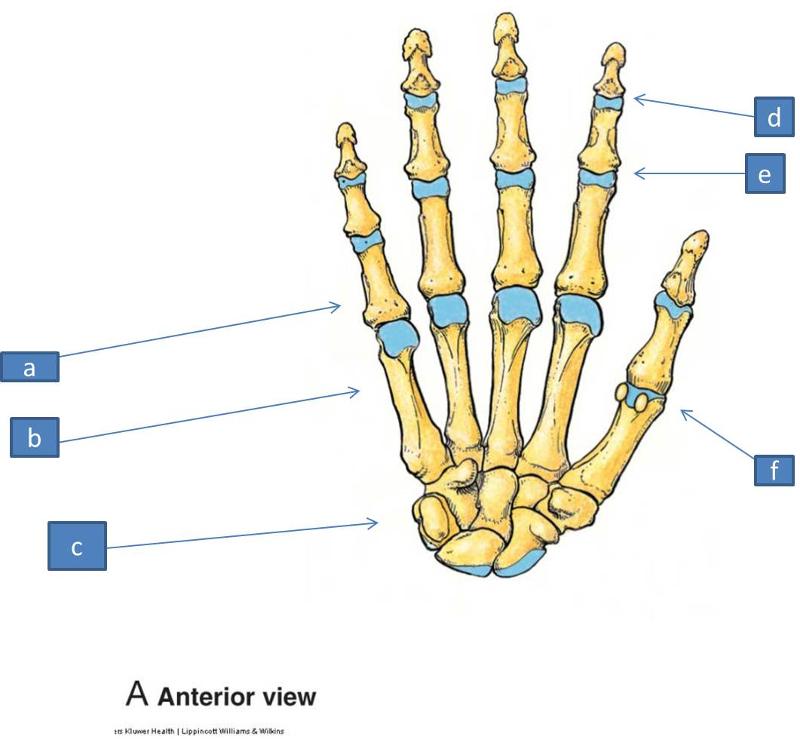
a. phalanges
b. metatarsals
c. tarsals
d. distal interphalangeal joint
e. proximal interphalangeal joint
f. metacarpophalangeal joint
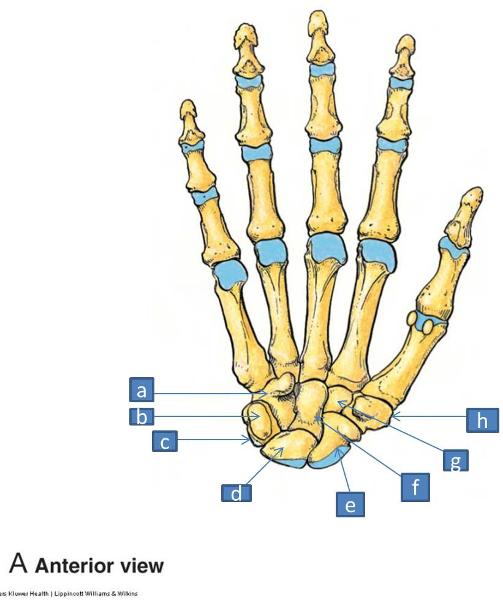
a. hamate (with hook of hamate
b. pisiform
c. triquetrum
d. lunate
e. scaphoid (with tubercle)
f. capitate
g. trapezoid
h. trapezium (with tubercle)
where is the most lateral finger in the hand
thumb, finger 1
what are the bones of the hand generally
carpals
metacarpals
phalanges
how many carpals are there
8
how many metacarpals are there
5
how many phalanges are there
14
how many rows of carpals are there
2, from lateral to medial
what are the two rows of carpals
proximal and distal
what are the proximal carpals
scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform
what are the distal carpals
trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
what is on top of the triquetrum
pisiform
what bone of the hand can you not see from the dorsum
pisiform
what did the scaphoid use to be called
navicular bone
what is interesting about the hamate
has a hook, extends anteriorly off palm and forms medial border of carpal tunnel
what forms lateral border of carpal tunnel
tubercles of scaphoid and trapezium
how many phalanges are in each finger
23333
what are the joints of the fingers
metacarpophalangeal joints
proximal interphalangeal joints
distal interphalangeal joints
what is a scaphoid fracture usually the result of
falling on outstretched hand
this is because the scaphoid is a protruding bone on the palmar side
what can often result from a scaphoid fracture
avascular necrosis proximally
why are scaphoid fractures susceptible to avascular necrosis
lack of adequate proximal blood supply
where can a scaphoid tubercle fracture be palpated
anatomical snuff box
what is a Boxer's fracture
distal metacarpal fracture
what is a barfight fracture
fractores of 4th or 5th metacarpal
what is a telltale sign of a barfight fracture
sunken knuckle
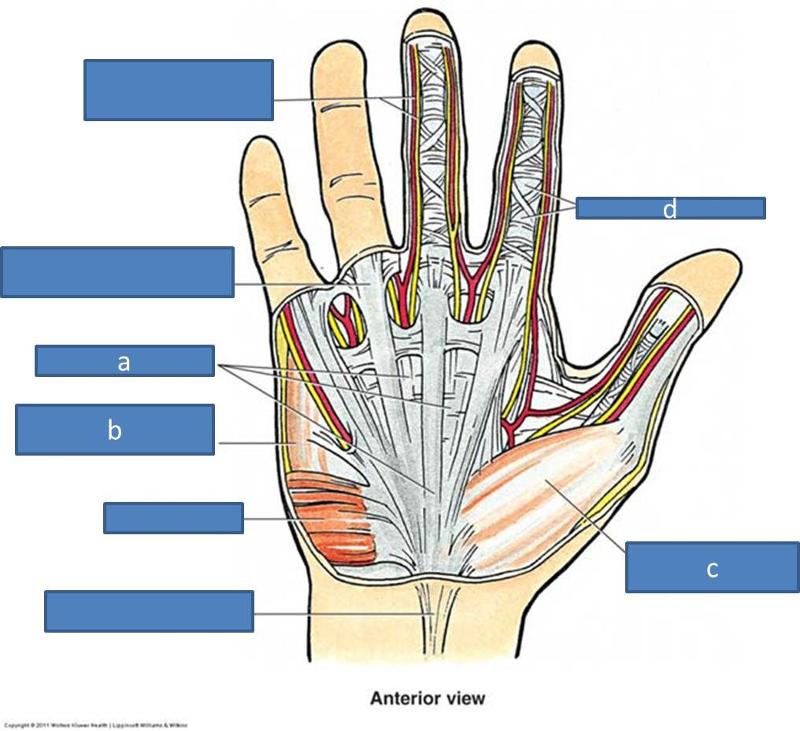
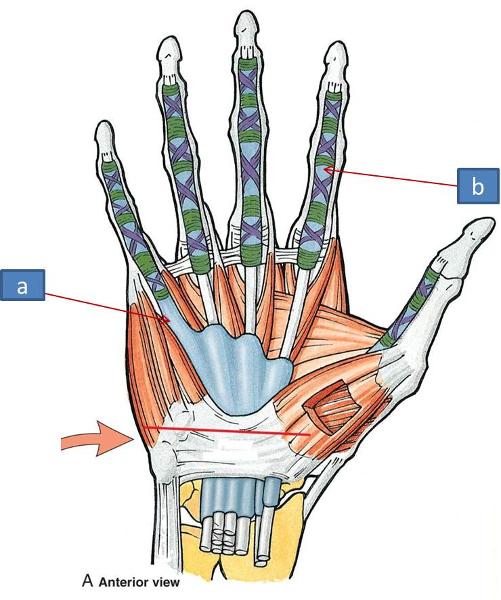
a. palmar aponeurosis
b. hypothenar eminence
c. thenar eminence
d. fibrous digital sheath
what is the palmar aponeurosis
thickening of palmar fascia; triangle like tissue with palmaris longus blends with it
what are the fascias of the hand
palmar aponeurosis
thenar eminence
hypothenar eminence
dorsal fascia
fibrous digital sheaths
what are the spaces in the hand
midpalmar space
thenar space
what are the septa in the hand
medial fibrous septum
lateral fibrous septum
what does the palmar aponeurosis allow
union with overlying skin and for better grip
what is the palmar aponeurosis continuous with
fibrous digital sheaths supporting digits and flexor tendons underneath
what are the thickest aponeuroses
dorsal fascia
palmar aponeurosis
what is the thenar fascia
fascia around respective muscles at base of thumb
what is the hypothenar fascia
fascia around respective muscles at base of pinky
what is the role of the fibrous digital sheaths
covers flexor tendons extending to the fingers
what is tenosynovitis
infection/inflammation of synovial sheath
what is digital tenovaginitis stenosans
swollen tendon of a finger, doesn't want to go back into fibrous sheath, swelling will pop it in and out
what spinal segments innervate all of the hand muscles
C8-T1
what is the midpalmar space continuous with
carpal tunnel
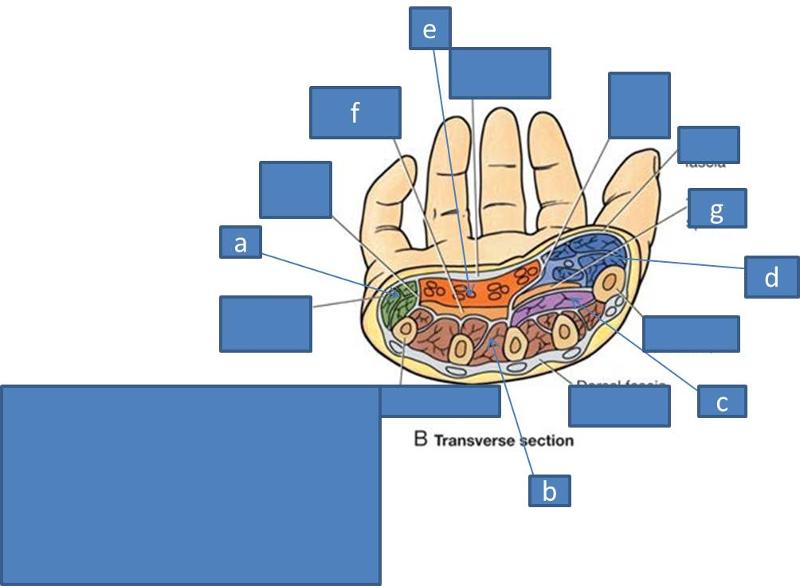
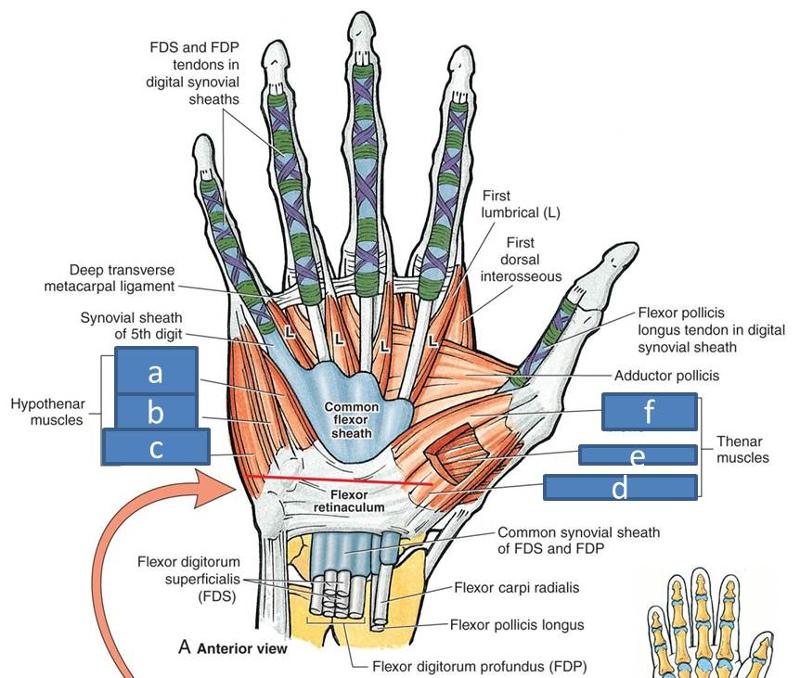
a. hypothenar compartment
b. interosseous compartment
c. adductor compartment
d. thenar compartment
e. central compartment
f. midpalmar space
h. thenar space
what does the thenar compartment of the hand form
thenar eminence
what innervates the intrinsic muscles of the thumb
recurrent branch of median nerve
what muscles are within the thenar compartment of the hand
intrinsic muscles of thumb:
abductor pollicis brevis
flexor pollicis brevis
opponens pollicis
where is the abductor pollicis brevis in the hand relative to the other thumb muscles
more lateral
where is the flexor pollicis brevis in the hand relative to other thumb muscles
more medial
where is the opponens pollicis in the hand
deep to flexor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis brevis
what does the opponens pollicis do
helps with opposition along with palmaris brevis
thenar eminence rotates and comes in with it, allowing thumb to come over and touch pinky finger

a. recurrent branch of median nerve
b. abductor pollicis brevis
c. flexor pollicis brevis
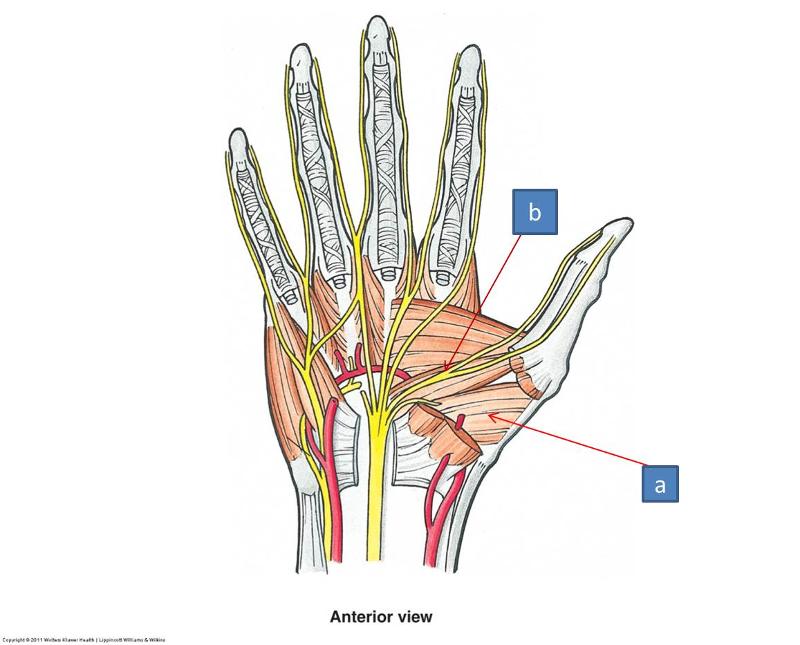
a. opponens pollicis
b. recurrent branch of median nerve
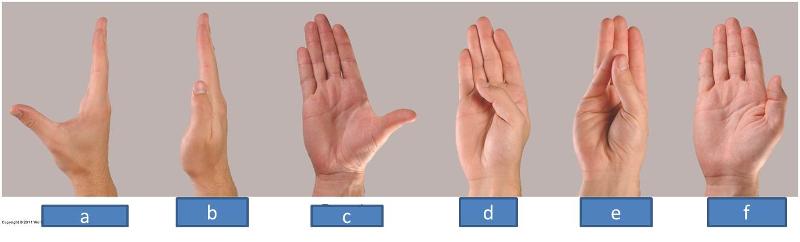
a. abduction
b. adduction
c. extension
d. flexion
e. opposition
f. reposition
wwhat does the hypothenar compartment form
hypothenar eminence
what muscles are within the hypothenar eminence
intrinsic muscles of 5th digit:
abductor digiti minimi
flexor digiti minimi
oppponens digiti minimi
where is the abductor digiti minimi in the hypothenar compartment
lateral
what does the abductor digiti minimi do
draws pinky away from middle of hand
where is the flexor digiti minimi in the hypothenar compartment
middle
what is the role of the flexor digiti minimi
works on flexing fifth finger
where is the opponens digiti minimi
most lateral
what is the role of the opponens digiti minimi
assists in finger opposition
what innervates the hypothenar compartment muscles
deep branch of ulnar nerve
a. opponens digiti minimi
b. flexor digiti minimi
c. abductor digiti minimi
d. abductor pollis brevis
e. opponens pollicis
f. fleoxr pollicis brevis

a. transverse head of adductor pollicis
b. oblique head of adductor pollicis
c. ulnar nerve
what is in the adductor compartment of the hand
adductor pollicis
what are the two heads of the adductor pollicis
oblique head and transverse head
what is the role of the adductor pollicis
two heads help draw the thumb back to normal position from sticking out anteriorly
where is the transverse head of the adductor pollicis
webbing of thumb
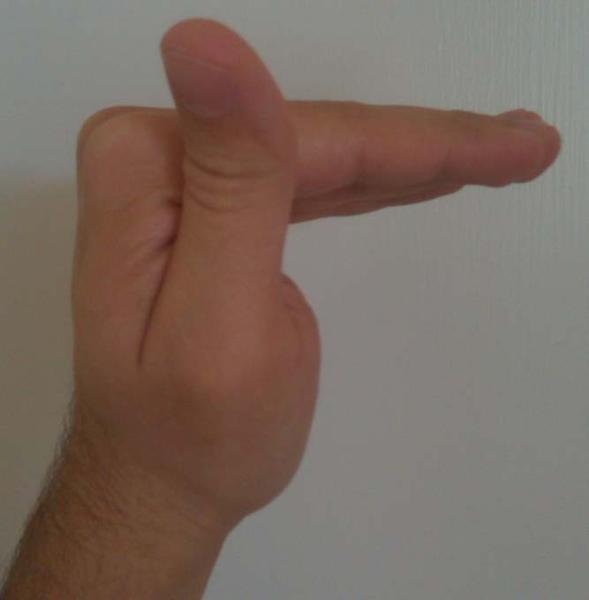

what muscles assist in this motion
lumbricals
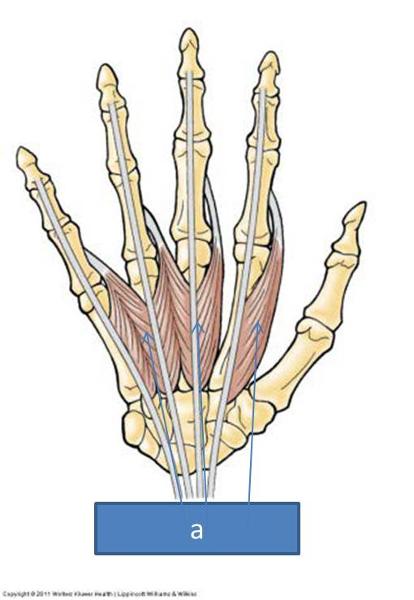
a. lumbricals
what is in the central compartment of the hand
lubricals
tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus
superficial and deep palmar arches
bracnhes of median and ulnar nerve
where are the lumbricals located
flexor digitorum profundus tendons; cross metacarpal phalangeal joint and go to dorsal side of digits and go into extensor sheaths on backside of fingers
what is the role of the lumbricals
flex joint but help extend and stabilize interphalangeal joints
what do the lateral 2 lumbricals control
middle and index finger
what innervates the lateral two lumbricals
median nerve
what do the medial two lumbrical control
pinky and ring finger
what innervates the medial two lumbricals
ulnar nerve
what are the arteries of the central compartment
superficial and deep palmar arches
a. common flexor sheath
b. digital synovial sheaths
what is the common flexor sheath continuous with
digital synovial sheath of pinky
what covers up the digital synovial sheaths
fibrous digital sheath
what aare the interosseous compartmetns separated by
metacarpals

a. deep branch of ulnar artery and nerve
what are interosseous compartments innervated by
deep branch of ulnar nerve
what finger does the palmar interossei not attach to
third finger
what are the muscles of the interosseus compartments
palmar interossei
dorsal interossei
how many palmar interossei are there
three
what is the role of the palmar interossei
adduct; draw fingers back toward midline
how many dorsal interossei are there
4
what is the role of the dorsal interossei
help abduct (bring fingers out)
what abducts the pinky finger
abductor digiti minimi
what is this injury and where is it and when is this
median nerve at wrist
under normal conditions
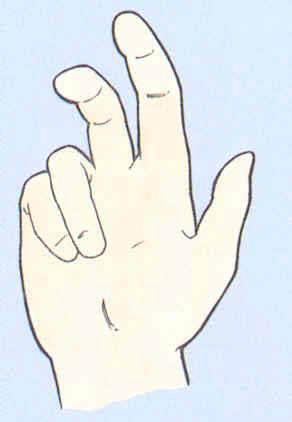
what is this injury
where is this injury
when is this
benediction deformity
median nerve at elbow
when asked to make a fist
what are symptoms of median nerve injury at the wrist
loss of two lateral lumbricals and thenar muscles (ape hand deformity where thumb rotate and is stuck next to hand) and loss of sensation over thumb and 2-4.5 digits
what is always affected in a median nerve injury
thumb and lumbricals
what types of injuries could affect the median nerve at the wrist
carpal tunnel syndrome and laceration of wrist
what types of injuries could afefct the median nerve at the elbow
anterior puncture would
what does the ulnar nerve injury alwasy affect
digits
what could result from ulnar nerve injury
claw hand deformity: loss of flexion of 4th and 5th metacarpophalangeal joints, extension of both proximal interphalangeal joints, and flexion of distal interphalangeal joints
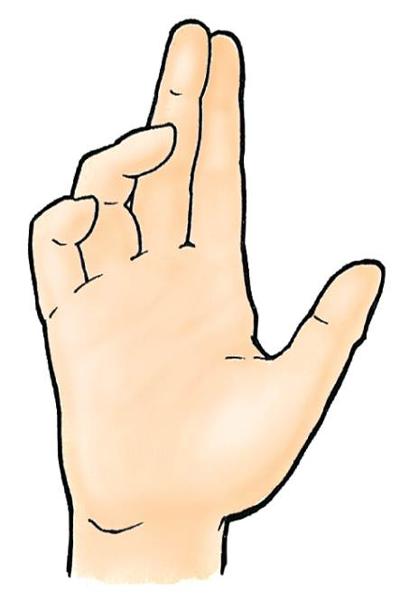
what type of deformity is this? when is it made? and where is the injury?
claw hand deformity
under normal conditions
injury is at wrist to ulnar nerve
what could reult from elbow level ulnar nerve injury
wrist abducts when asked to flex
what would an elbow level ulnar nerve injury result in
loss of flexor carpi ulnaris and sensory loss to medial side of hand and half of 4th and 5th digit
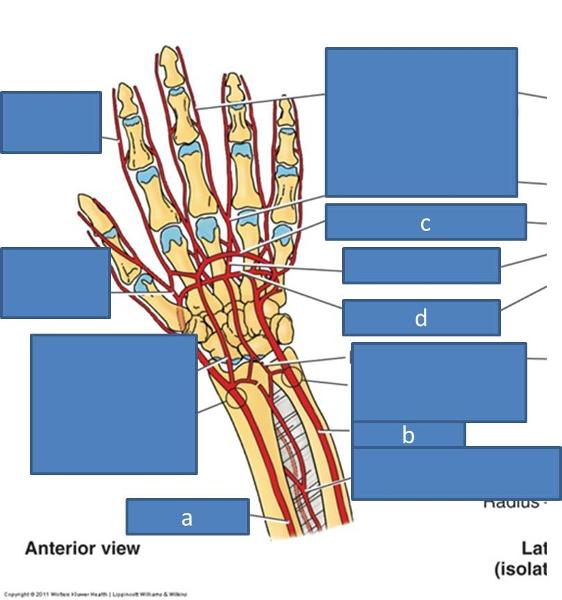
a. radial artery
b. ulnar artery
c. superficial palmar arch
d. deep palmar arch
what supplies the superficial palmar arch with blood
mainly from ulnar artery
what supplies the deep palmar artch with blood
mainly from radial artery
what are teh braches of the ulnar artery and which one is larger
superficial and deep; superficial is usually larger
what does the superficial ulnar branch usually anastomose with
superficial radial branch
what does the deep palmar arch anastomose with
deep branch of ulnar artery
what do the deep palmar and superficial palmar arteries usually anastomoes with
palmar metacarpal arteries
what cutaneous innervatino does the ulnar nerve's superficial branch supply
medial hand and medial 4th and 5th digit
what cutaneous innervation does the radial nerve's superficial branch supply
lateral dorsum of hand, proximal 1/2 of 1st-3rd digit

a. median nerve
b. radial nerve
c. ulnar nerve
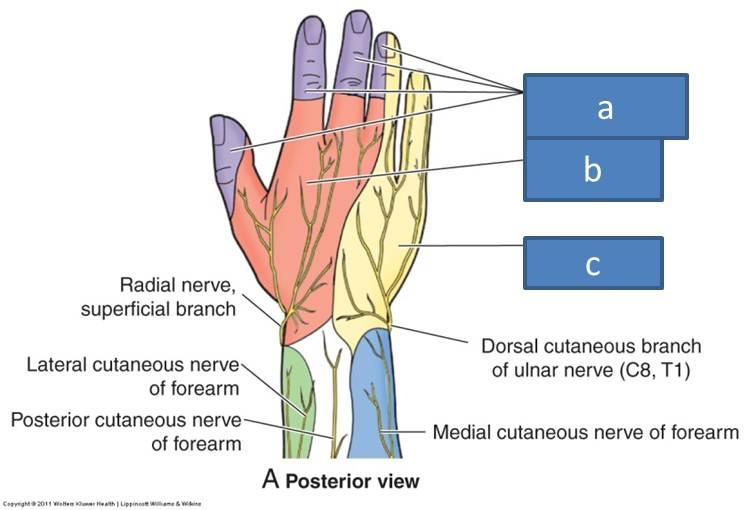
a. median nerve
b. radial nerve
c. ulnar nerve
what cutaneous innervation does the median nerve supply
latreal palm of hand and first 3.5 digits, distal portion of palmar side of 1st 3.5 digits