PCB 3063: Genetics
The structures within all living cells that contain the genetic material are called
chromosomes
Which of the following are the major components of a chromosome?
Protein, DNA
A chromosome contains a very long segment of_______ , which is bound to _____that provide structure.
DNA , Proteins
What is chromatin?
A complex between DNA and proteins that is found in eukaryotic cells
Which term best describes organisms whose chromosomes are not contained within a membrane-bound nucleus?
prokaryotes
The ____of a prokaryotic cell is the region of cytoplasm that contains the chromosome.
Nucleotid
Chromosomes are best defined as ______.
the structures within living cells that contain the genetic material
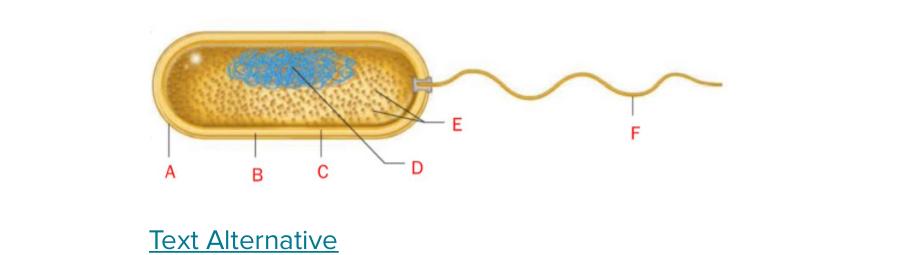
In this figure of a bacterial cell, which of the following labels are correctly matched with their appropriate structures?

Answer: C, E

Chromatin
Prokaryotes, which include the _____ and the ______, are organisms that lack a membrane-bound nucleus.
Bacteria, Archaea
Prokaryotes usually have a single type of circular chromosome in a region of the cytoplasm called the ______.
nucleoid
Which of the following are eukaryotes?
Fungi
Protists
Plants

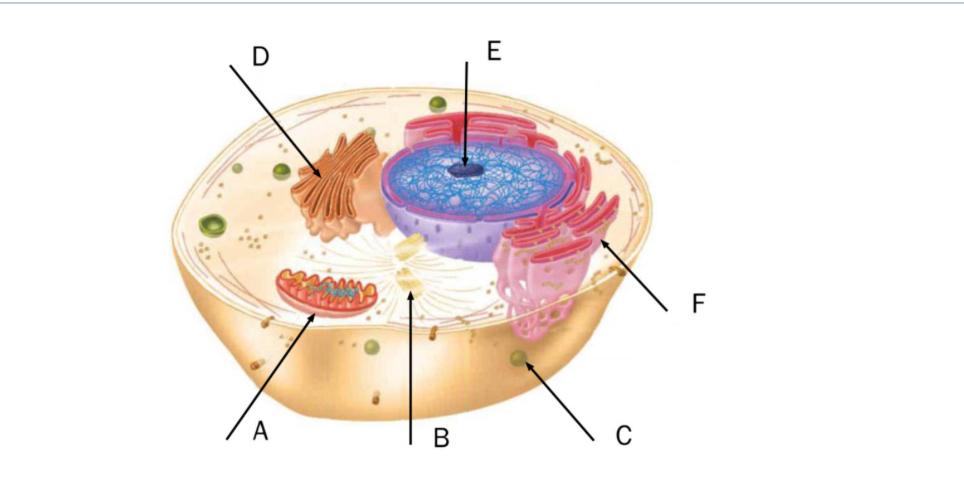
This diagram depicts a eukaryotic cell. Match the letter to the correct structure.
Which term best describes organisms whose chromosomes are not contained within a membrane-bound nucleus?
prokaryotes
An organelle is ______.
a structure within the cytoplasm with a specific function.
Organisms, such as protists and fungi, that have a true nucleus are called
Eukaryotes
The _____of a eukaryote is the organelle that contains most of the genetic material found in the cell.
nucleus
Which of the following organelles contain their own DNA?
Mitochondria
Chloroplasts
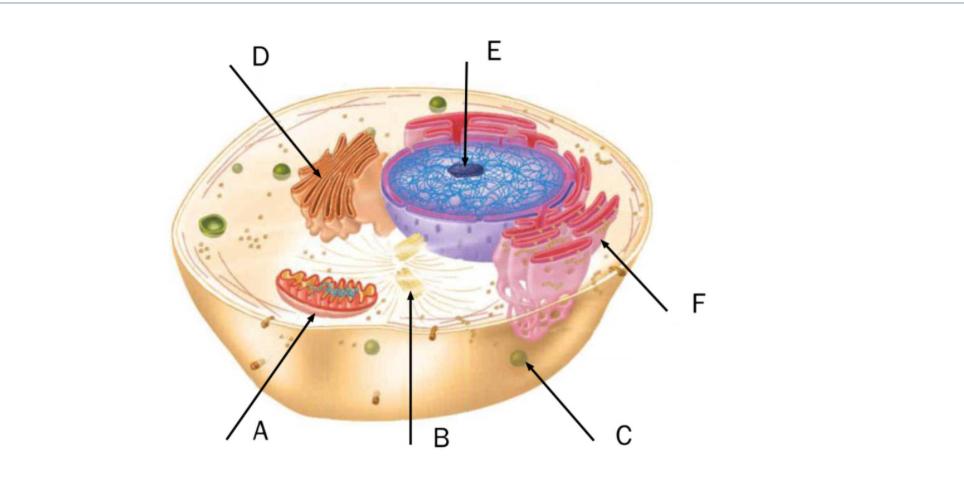
In this figure of a eukaryotic cell, which of the following labels are correctly matched with their appropriate structures?
C = Lysosome
A = Mitochondrion
B = Centriole
What is cytogenetics?
The field of genetics that involves the microscopic examination of chromosomes.
In eukaryotes, ______are membrane-bound structures that have specific functions.
Organelles
Which of the following best describes the nucleus?
An organelle of eukaryotes that is surrounded by two membranes.
In general, the chromosome number of a particular species ______.
is the same for all individuals of the species
In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic organelles called the____ and the ____contain a small amount of their own DNA.
mitochondria,Chloroplast
The following are steps used in the procedure for making a karyotype. Arrange them in order, starting with the first step at the top.

The field of genetics that involves the microscopic examination of chromosomes is called .
cytogeneticist
Which is the best definition of a karyotype?
An organized representation of the chromosomes within a cell
True or false: Most eukaryotic species are haploid or have such a phase as a significant part of their life cycle.
False
Organisms, such as protists and fungi, that have a true nucleus are called
Eukaryotes
A diploid cell is defined as a cell that has ______.
two sets of chromosomes
True or false: Each species has a particular chromosome composition.
True
The procedure for making a karyotype includes all of the following steps except______.

A normal human somatic cell carries ______ pairs of chromosomes for a total of ______.
23 ; 46
An organized representation of the chromosomes within a cell is called a(n)
Karyotype
Which of the following statements about eukaryotes is true?
Most eukaryotic species are diploid or have a diploid phase to their life cycle.
In a ______ cell, each type of chromosome is a member of a pair.
diploid
In a diploid cell, each member of a pair of chromosomes is called a(n) ______.
homolog
The two members of a homologous pair of chromosomes may carry different versions of a given gene, which are called ____
Alleles
Insert a number into the blank: Most human somatic cells contain a total of chromosomes.
46
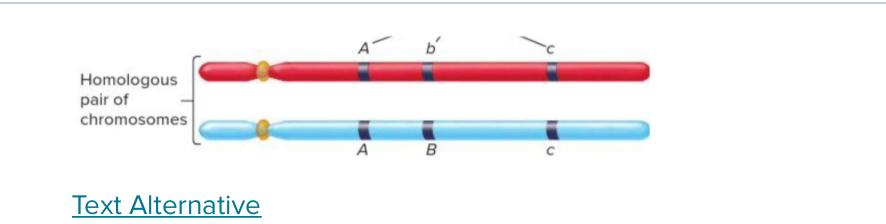
The position of a gene on a chromosome, such as gene A in the image, is called its ______.
locus
Unicellular prokaryotic organisms proliferate by ____ reproduction, in which a preexisting cell divides to produce two new cells.
Asexual
Each type of chromosome in a diploid cell is found in a homologous pair. Each chromosome in such a pair is referred to as a(n)
Homologos
Most bacterial cells divide by ______.
binary fission
______ are different versions of the same gene.
Alleles
The eukaryotic cell cycle is composed of ______ phases called ______.
four; G1, G2, S, and M
A(n)____ refers to the physical location of a gene.
Locus
Which of the following best describes asexual reproduction?
A mother cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells
Which of the following are part of interphase?
S
G2
G1
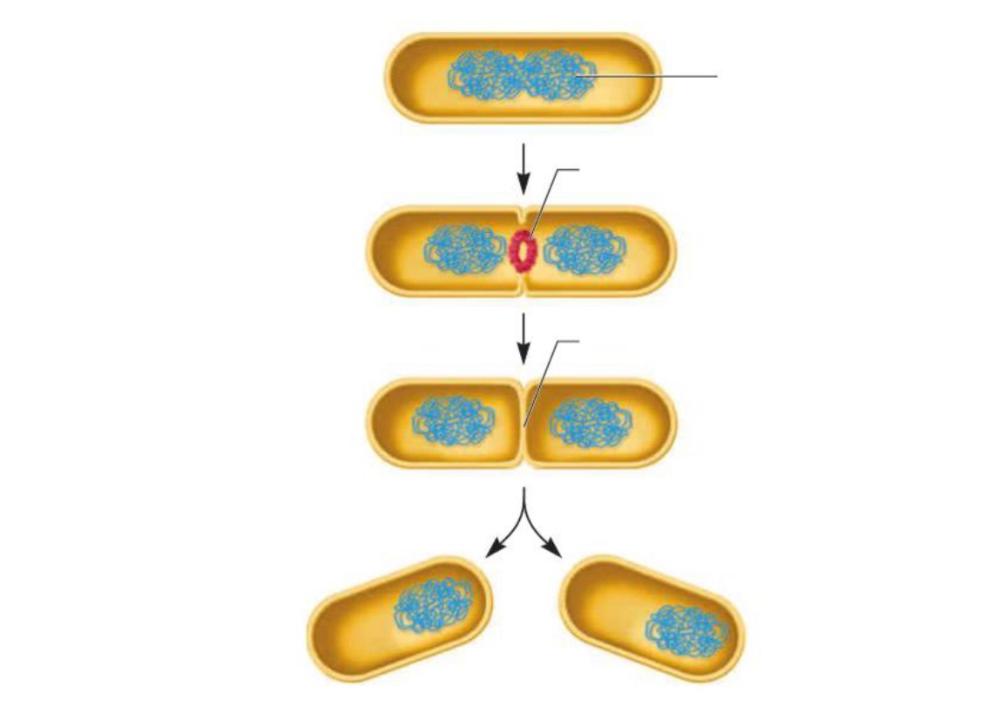
This figure shows a bacterium reproducing asexually by a process known as
binary fission
A cell, such as most nerve cells in an adult mammal that will never divide again, is in the ______ phase.
G0
Eukaryotic cells that are destined to divide progress through G1, S, G2, and M phases, which are collectively known as the
Cell cycle
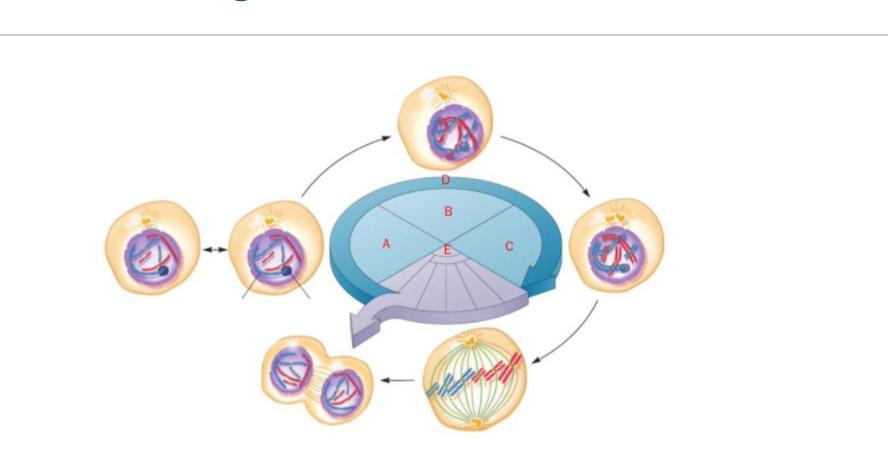
The following is a diagram of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Match the letter to the appropriate phase.
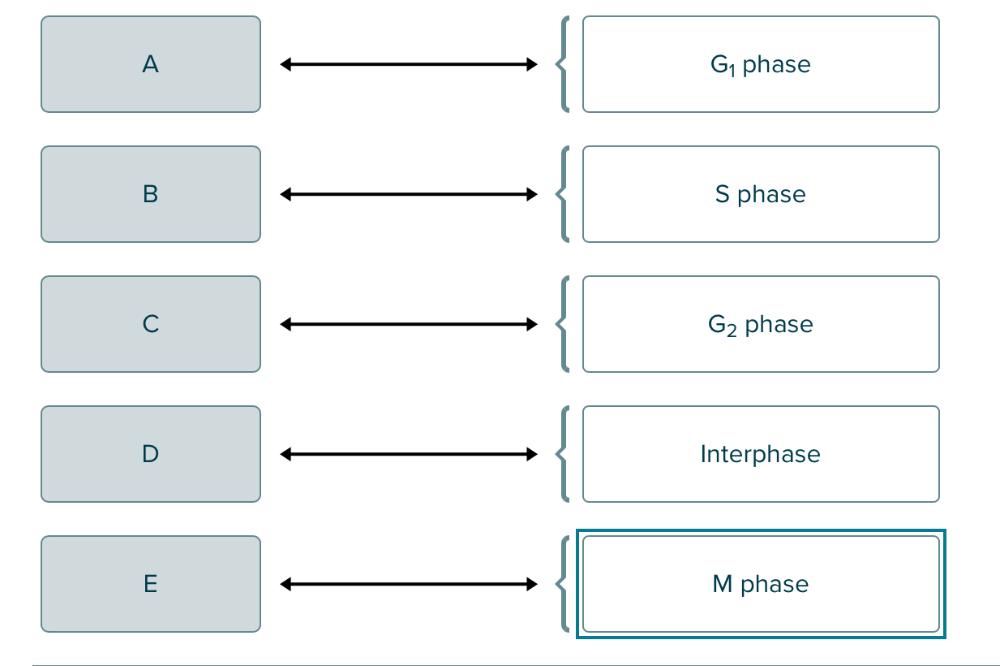
In mitosis, the restriction point is ______.
the time in the G1 phase at which the cell becomes “committed” to the cell cycle
In actively dividing cells, the G1, S, and G2 phases are collectively known as
Interphase
After replication, each chromosome consists of two copies called
Chromatids
Which of the following phases of the cell cycle is considered a "resting" stage, where cells can remain permanently, or for long periods of time?
G0
This figure depicts the cell cycle in eukaryotes, including the M phase. Match the letter to the appropriate phase.
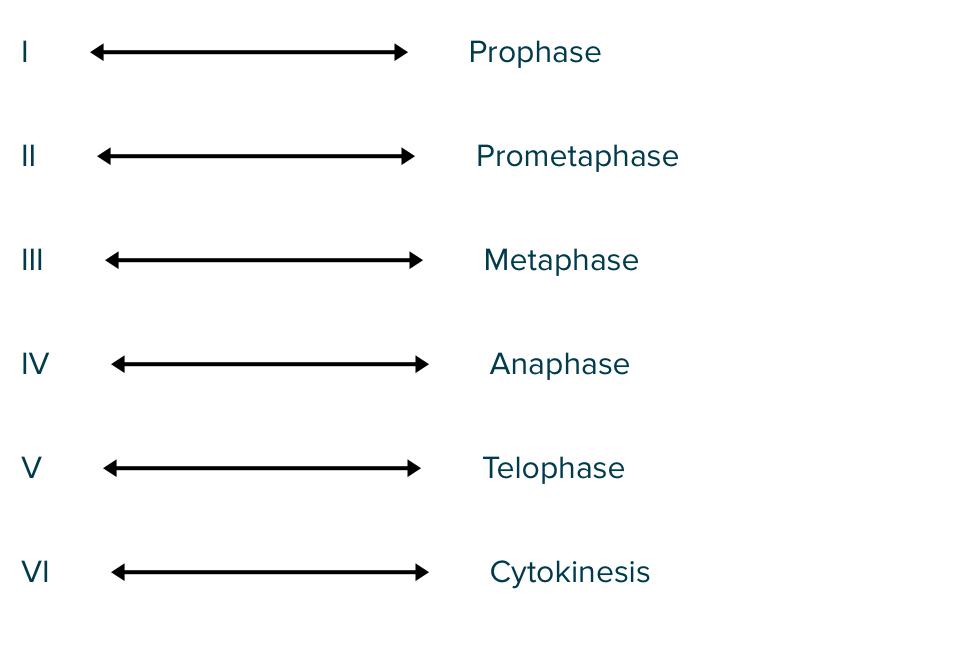
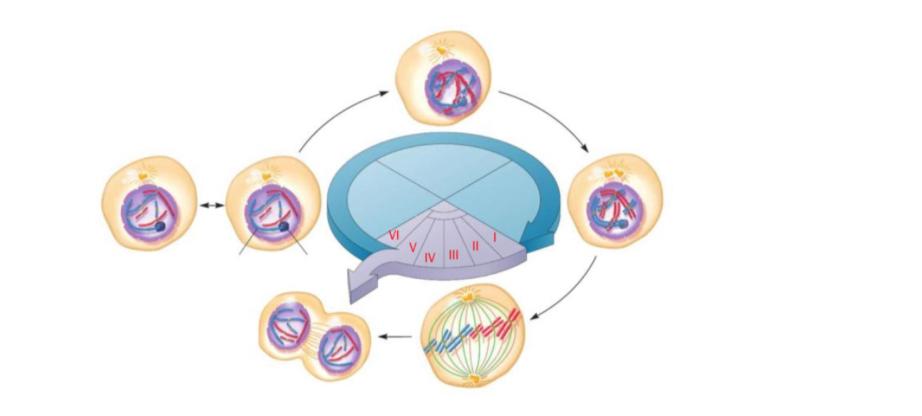
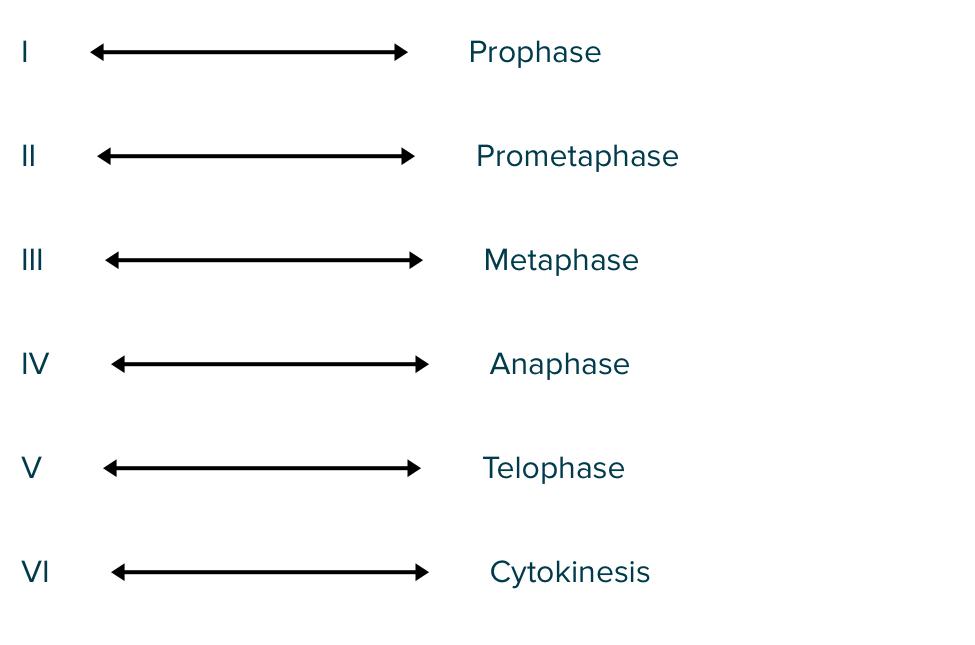
Late in the G1 phase, many cell types become committed to progress through the rest of the cell cycle. When this occurs, the cell has reached a(n)
Restriction point
A pair of sister chromatids is also called a ______.
dyad
The centromere is a ______.
region of the chromosome where the sister chromatids join
The two copies of a replicated chromosome are called ______.
sister chromatids
The kinetochore serves which of the following functions?
It aids in chromosome sorting during mitosis.
A cell, such as most nerve cells in an adult mammal that will never divide again, is in the ______ phase.
G0
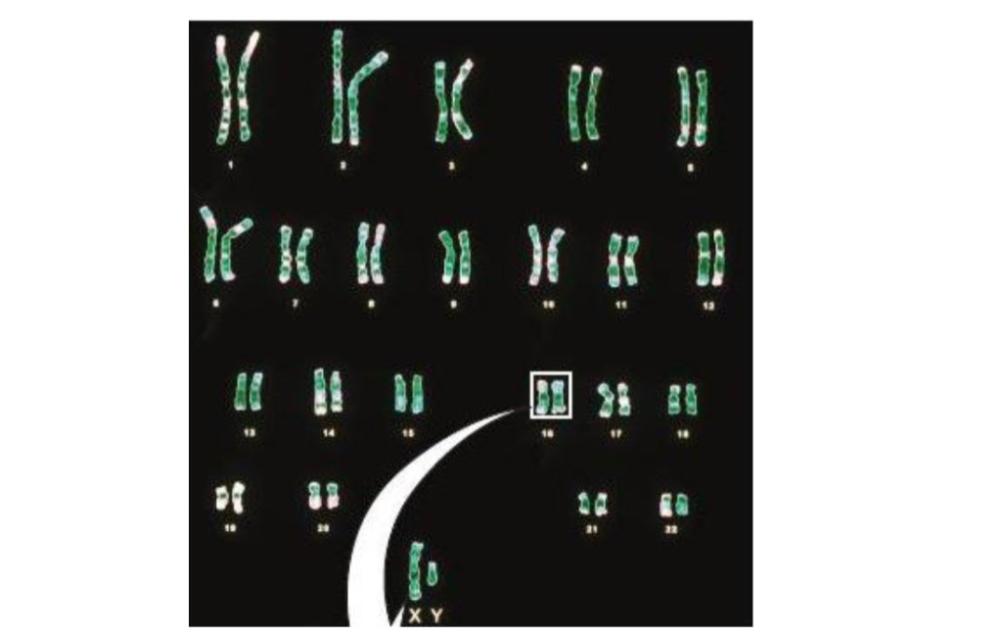
The box in this karyotype highlights which of the following?
A pair of homologous chromosomes
A monad can be described as ______.
an unreplicated chromosome
The two chromatids of a chromosome are joined together at a region of DNA called the
centromere
When S phase is completed, a cell has _______ in the G1 phase.
twice as many chromatids as chromosomes
The ____is a protein-complex that is bound to the centromere, and which plays a key role in the separation of chromosomes during cell division.
kinetochore
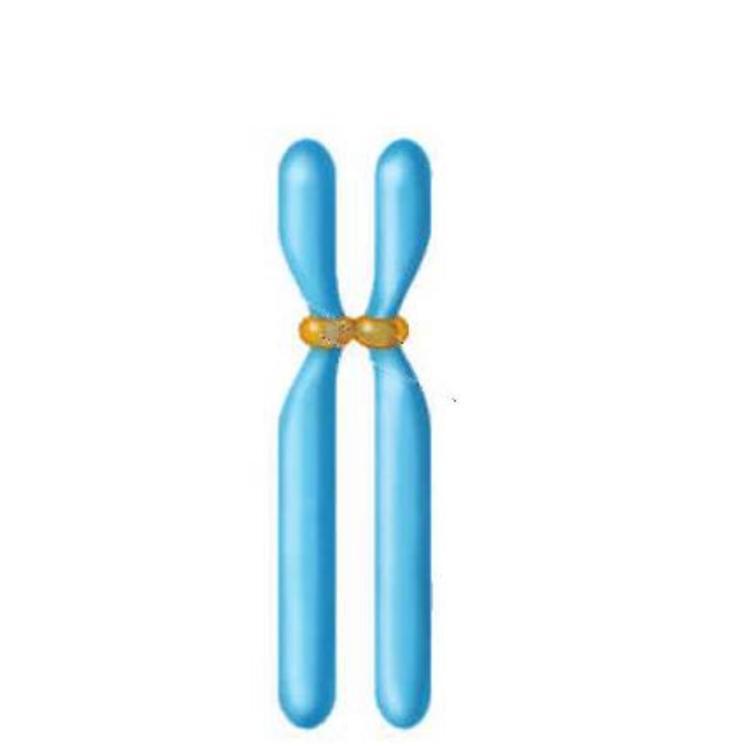
This diagram shows a pair of .
sister chromatids
After a mitotic division is complete, a daughter cell has 40 chromosomes. Which of the following best describes the chromosome composition of the mother cell in the G2 phase?
The term that can refer to either a dyad (pair of sister chromatids) or a monad (single chromatid) is a(n)
chromosome
The primary purpose of mitosis is to ______.
distribute the replicated chromosomes equally into the two daughter cells