Central Science: Chapter 23
Chalcocite, chalcopyrite, and malachite are sources of which
metal?
A) manganese
B) copper
C) titanium
D)
iron
E) zinc
B
Which mineral contains titanium?
A) pyrolusite
B)
chalcopyrite
C) galena
D) rutile
E) sphalerite
D
A mineral is ________.
A) a solid inorganic compound that
contains one or more metals
B) a vitamin
C) metal in its
elemental form
D) a transition metal ion
E) a source of carbon
A
What two oxidation states are more frequently observed in the first
transition series than in the third?
A) +3 and +7
B) +2 and
+3
C) +2 and +7
D) +5 and +6
E) +3 and +5
B
A substance with unpaired electrons will be ________.
A)
slightly attracted to a magnet
B) slightly repelled by a
magnet
C) permanently magnetic
D) brightly colored
E) nonmetallic
A
The lanthanide contraction is responsible for the fact that
________.
A) Zr and Y have about the same radius
B) Zr and
Nb have similar oxidation states
C) Zr and Hf have about the same
radius
D) Zr and Zn have similar oxidation states
E) Zr and
Hf have the same oxidation states
C
Which one of the following is not true about transition
metals?
A) They frequently have more than one common oxidation
state.
B) Their compounds are frequently colored.
C) Their
compounds frequently exhibit magnetic properties.
D) They are
found in the d-block of the periodic table.
E) They typically
have low melting points.
E
Which one of the following species is paramagnetic?
A)
Fe3+
B) Cu+
C) Zn
D) Mg
E) Au+
A
Paramagnetic solids ________.
A) have atoms with one or more
unpaired electrons
B) show very slight magnetic character when
placed in a magnetic field
C) have atoms with randomly oriented
magnetic moments
D) have atoms with strongly aligned electrons
when placed in a magnetic field
E) both A and D
E
Formation of a complex species of Mn+ metal ion with ligands often
________.
A) "masks" original chemical properties of
both the Mn+ ion and the ligands
B) reduces availability of the
free Mn+ ions in solution
C) may cause changes in the ease with
which Mn+ is reduced or oxidized
D) alters original physical
properties of Mn+
E) all of the above
E
What is the most common geometry found in four-coordinate
complexes?
A) square planar
B) octahedral
C)
tetrahedral
D) icosahedral
E) trigonal bipyramidal
C
The minimum number of unshared valence electron pairs in the ligands
of a coordination compound is ________.
A) 1
B) 2
C)
3
D) 4
E) 5
A
The coordination number of cobalt in CoCl3 ∙ 6NH3 is
________.
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 6
E) 8
D
What is the oxidation number of Fe in [Fe(CN)5]3-?
A)
1+
B) 2+
C) 3+
D) 4+
E) 5+
B
Changes in the coordination sphere of a complex compound may lead to
changes in ________.
A) color
B) physical properties
C)
chemical properties
D) stability
E) all of the above
E
In the compound, CaNa[Fe(CN)6], what ligands are in the coordination
sphere?
A) Ca2+
B) Na+
C) CN-
D) H2O
E) none
of the above
C
What are the respective central-metal oxidation state, coordination number, and overall charge on the complex ion in
Na2[Cr(NH3)2 (NCS)4]?
A) +3; 6; -1
B) +3; 6; +1
C) +2; 6; -2
D) +2; 4;
-1
E) +1; 6; -2
C
Which of the following complexes has a coordination number of
6?
A) [Co(NH3)2Cl2]
B) [Co(NH3)4]2+
C)
[Co(en)3]3+
D) [Co(NH3)2]3+
E) None of these complexes has
coordination number 6.
C
How many ligands are there in the coordination sphere of
[Co(en)2Cl2]+?
A) 3
B) 6
C) 4
D) 1
E) 0
C
What is the charge on the complex ion in Ca2[Fe(CN)6]?
A)
3-
B) 2+
C) 2-
D) 1-
E) 4-
E
A ligand with a single donor atom is called ________.
A) a
chelon
B) a chelate
C) polydentate
D)
monodentate
E) bidentate
D
Which of the following is not a chelating
agent?
A) chloride anion
B) EDTA
C) porphine
D)
ethylenediamine
E) oxalate anion
A
What is the purpose of adding EDTA to prepared foods?
A) to keep
ions such as Ca2+ in solution so the foods look
good
B) to complex trace metal ions that catalyze decomposition
reactions
C) to complex iron (III) ions so they can catalyze
protein decomposition on cooking
D) to aid in browning of the
surface during cooking
E) to prevent dissolution of the container
in the food when stored for long periods of time
B
In humans, what percent of absorbed iron is found in blood?
A)
15
B) 25
C) 40
D) 60
E) 75
E
The coordination number and oxidation number of the central atom in
[Fe(H2O)4Cl2] are ________ and ________, respectively.
A) 4,
+1
B) 6, +1
C) 6, +2
D) 5, +2
E) 4, +2
C
What are the donor atoms in a porphine molecule?
A) N
B)
O
C) S
D) Br
E) F
A
What metal is complexed in chlorophyll?
A) iron
B)
chromium
C) manganese
D) vanadium
E) magnesium
E
What form of hemoglobin is purplish-red?
A) myoglobin
B)
deoxyhemoglobin
C) heme
D) oxyhemoglobin
E) none of the above
B
How many bonds can ethylenediamine form to a metal ion?
A)
1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 6
B
Based on entropy considerations alone, which homogeneous aqueous
equilibrium would be expected to lie to the right?
A) AgI2- +
2Br- ⇔ AgBr2- + 2I-
B) Ni(H2NC2H4NH2)32+ + 6NH3 ⇔ Ni(NH3)62+ +
3H2NC2H4NH2
C) CoCl42+ + 6H2O ⇔ Co(H2O)62+ + 4Cl-
D)
Fe(NH3)62+ + C20H10N42- ⇔ Fe(NH3)2(C20H10N4) + 4NH3
E) Cu(NH3)42+
+ 6H2O ⇔ Cu(H2O)62+ + 4NH3
D
The chelate effect is best attributed to considerations of which
type?
A) hydration
B) enthalpy
C) entropy
D)
hydrogen bonding
E) resonance
C
Which one of the following species is a potential polydentate ligand
(chelating agent)?
A) NH3
B) Cl-
C) CN-
D)
H2O
E) C2O42-
E
What are the donor atoms in ferrichrome and how many of them are in
one molecule?
A) Cr, 5
B) N, 4
C) O, 6
D) Fe,
4
E) S, 6
C
Which of the following is a polydentate ligand?
A)
ammonia
B) oxalate ion
C) chloride ion
D) water
E)
hydroxide ion
B
A complex of correctly written formula [Pt(NH3)3Br]Br ∙ H2O has which
set of ligands in its inner coordination sphere?
A) 3 NH3
B)
3 NH3 and 2 Br-
C) 3 NH3 and 1 Br-
D) 3 NH3, 1 Br-, and 1
H2O
E) 3 NH3, 2 Br-, and 1 H2O
C
Which one of the following is the correct formula for potassium
diaquatetrachloromolybdate (III)?
A) K2[Mo(H2O)2Cl4]
B)
K[Mo(H2O)2Cl2]Cl2
C) K[Mo(H2O)2Cl4]
D)
Mo[K(H2O)2]Cl4
E) K3[Mo(H2O)2Cl4]
C
Does either or both cis- or trans-[Mn(en)2Br2] have optical
isomers?
A) cis only
B) trans only
C) both cis and
trans
D) neither cis nor trans
E) [Mn(en)2Br2] does not
exhibit cis-trans isomerism.
A
Linkage isomerism would most likely occur when which of the following
ligands is present?
A) H2O
B) NH3
C) Cl-
D)
PF3
E) NCS-
E
Isomers whose ligands can bind directly to a metal or be outside the
lattice are called ________.
A) linkage isomers
B)
rotational isomers
C) coordination sphere isomers
D)
geometric isomers
E) optical isomers
C
Which of the following will display optical isomerism?
A)
square-planar [Rh(CO)2Cl2]-
B) square-planar
[Pt(H2NC2H4NH2)2]2+
C) octahedral [Co(NH3)6]3+
D) octahedral
[Co(NH3)5Cl]2+
E) octahedral [Co(H2NC2H4NH2)3]3+
E
Which one of the following complexes would most likely have
tetrahedral geometry?
A) [NiCl4]2-
B) [Co(H2O)6]2+
C)
[Cr(NH3)6]3+
D) [Fe(CN)6]3+
E) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
A
Which one of the following complexes can exhibit geometrical
isomerism?
A) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] (square planar)
B) [Zn(NH3)2Cl2]
(tetrahedral)
C) [Cu(NH3)4]2+ (square planar)
D)
[Cu(NH3)5Cl]2+ (octahedral)
E) All of the above can exhibit
geometrical isomerism.
A
Coordination sphere isomers ________.
A) have the same molecular
formula and coordination number
B) have the same molecular
formula but different coordination numbers
C) have different
molecular formulas but the same coordination number
D) have
different molecular formulas and different coordination
numbers
E) are the same as resonance structures
A
A racemic mixture is ________.
A) an equal mixture of both
enantiomers of an optically active species
B) a mixture of an
optically active species with an optically inactive species
C) an
equal mixture of cis- and trans-isomers
D) a mixture of metal
ions and ligands in equilibrium
E) a mixture of structural isomers
A
Which compound is most likely white/colorless?
A)
[Cu(H2O)4]2+
B) [Ni(H2O)6]2+
C) [Cr(H2O)5Cl]2+
D)
[Cd(H2O)4]2+
E) [Co(H2O)6]2+
D
A complex that absorbs light at 700 nm will appear ________.
A)
red
B) green
C) yellow
D) orange
E) violet
B
A metal complex absorbs light mainly at 420 nm. What is the color of
the complex?
A) green
B) yellow
C) red
D)
orange
E) purple
B
Which one of the following substances has three unpaired d
electrons?
A) [Zn(NH3)4]2+
B) [V(H2O)6]4+
C)
[Ag(NH3)2]+
D) [Cu(NH3)4]2+
E) [Cr(CN)6]3-
E
Which one of the following complex ions will be paramagnetic?
A)
[Fe(H2O)6]2+ (low spin)
B) [Fe(H2O)6]3+ (low spin)
C)
[Co(H2O)6]3+ (low spin)
D) [Zn(H2O)4]2+
E) [Zn(NH3)4]2+
B
Complexes containing metals with d10 electron
configurations are typically white/colorless because ________.
A)
there is no d electron that can be promoted via the absorption of
visible light
B) the empty d orbitals absorb all of the visible
wavelengths
C) there are no d electrons to form bonds to
ligands
D) a complex must be charged to be colored
E) d
electrons must be emitted by the complex in order for it to appear colored
A
Complexes containing metals with d10 electron
configurations are typically ________.
A) violet
B)
blue
C) green
D) yellow
E) white/colorless
E
Complexes containing metals with which one of the following electron
configurations are usually white/colorless?
A) d2
B) d1
C) d5
D) d8
E) d10
E
Consider a complex in which manganese (III) is bonded to six
identical ligands. Which one of the following ligands will result in
the smallest value of Δ?
A) Cl-
B) NH3
C) H2O
D)
F-
E) CN-
A
Based on the crystal-field strengths F- < CH2CN < NH3 < NO2-
< CN-, which Co (III) complex is most likely high-spin?
A)
[Co(NH3)6]3+
B) [Co(NO2)6]3-
C) [Co(CN)6]3-
D)
[CoF6]3-
E) [Co(CH3CN)6]3+
D
The attraction of a metal to a neutral ligand is due to ________
bonding.
A) ionic
B) covalent
C) ion-dipole
D)
dipole-dipole
E) hydrophobic
C
Which of the following statements is (are) false?
A) The greater
the energy gap in a metal complex, the shorter the wavelength of light
the complex will absorb.
B) Complex color depends on both the
metal and the ligand.
C) Metal complexes with an ammonia ligand
have a larger energy gap than the corresponding fluoride
complexes.
D) Strong field ligands are associated with low energy
gaps.
E) Both A and C
D
Based on the crystal-field strengths Cl- < F- < H2O < NH3
< H2NC2H4NH2, which octahedral Ti (III) complex below has its d-d
electronic transition at shortest wavelength?
A)
[Ti(NH3)6]3+
B) [Ti(H2NC2H4NH2)3]3+
C) [Ti(H2O)6]3+
D)
[TiCl6]3-
E) [TiF6]3-
B
Which of the following ions can form both a high spin and a low spin
octahedral complexes?
A) Fe3+ and Co2+ only
B) Fe3+, Mn3+,
and Co2+
C) Cr3+ only
D) Fe3+, Cr3+, and Co2+
E) Mn3+,
Cr3+, and Co2+
B
Using the following abbreviated spectrochemical series, determine which complex ion is most likely to absorb light in the red region of the visible spectrum.
small splitting Cl- < H2O < NH3 < CN- large splitting
A) [CuCl4]2-
B) [Cu(H2O)4]2+
C) [Cu(NH3)4]2+
D)
[Cu(CN)4]2-
E) not enough information given to determine
A
Which of the following cannot form both high- and
low-spin octahedral complexes?
A) Mn2+
B) V2+
C)
Co3+
D) Cr2+
E) All of the above can form both high- and
low-spin complexes.
B
Which of the following can form both high- and low-spin octahedral
complexes?
A) Cr2+
B) Cr3+
C) Zn2+
D) Cu+
E)
All of the above can form either high- or low-spin complexes.
A
How many d electrons are associated with the metal ion in
[Cr(NH3)3+?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
C
The coordination numbers of cobalt (III) and of chromium (III) in
their complexes are always ________.
A) 4
B) 5
C)
2
D) 3
E) 6
E
The coordination number of platinum in complexes is always
________.
A) 4
B) 5
C) 2
D) 3
E) 6
A
During the formation of a coordination compound, the ________ acts as
a Lewis acid.
A) metal
B) ligand
A
During the formation of a coordination compound, the ________ acts as
a Lewis base.
A) metal
B) ligand
B
The coordination sphere of a complex consists of ________.
A)
the central metal ion only
B) the ligands
C) the central
metal ion and the ligands bonded to it
D) the primary and
secondary valencies
E) coordination and steric numbers
C
In the following reaction, Ni2+ is acting as a(n) ________.
Ni2+ (g) + 6H2O (l) → Ni(H2O)62+ (aq)
A) oxidizing agent
B) Lewis acid
C) precipitating
agent
D) solvent
E) ligand
B
How many d electrons are in the iron ion of K3[Fe(CN)6]?
A)
3
B) 5
C) 6
D) 7
E) 4
B
What is the charge on the complex ion in Mg2[FeCl6]?
A)
2-
B) 2+
C) 3-
D) 3+
E) 4-
E
What is the oxidation number of chromium in Cr[(NH3)4Cl2]Cl?
A)
-3
B) +3
C) +2
D) -2
E) 0
B
What is the ligand in Ca3[Fe(CN)6]2?
A) Ca2+
B)
Fe3+
C) CN-
D) Fe(CN)63-
E) Fe2+
C
What is the charge of the central metal ion in Ca3[Fe(CN)6]2?
A)
0
B) 1+
C) 2+
D) 3+
E) 6+
D
What is the oxidation number of cobalt in [Co(NH3)4F2]?
A)
-3
B) +2
C) +1
D) +3
E) +6
B
The charge of the complex ion in [Zn(H2O)3Cl]Cl ________.
A)
0
B) 1-
C) 2+
D) 1+
E) 2-
D
The coordination number for [Zn(H2O)3Cl]Cl is ________.
A)
5
B) 4
C) 2
D) 1
E) 6
B
What is the oxidation state of iron in CaNa[Fe(CN)6]?
A)
0
B) +2
C) +3
D) +4
E) +6
C
What is the oxidation state of iron in K3[Fe(CN)6]?
A) 0
B)
+2
C) +3
D) +4
E) +6
C
What is the coordination number of iron in CaNa[Fe(CN)6]?
A)
2
B) 8
C) 4
D) 6
E) 12
D
What is the coordination number of cobalt in
[Co(NH3)5Cl](NO3)2?
A) 12
B) 8
C) 4
D) 2
E) 6
E
What is the oxidation state of cobalt in [Co(NH3)5Cl](NO3)2?
A)
0
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 6
C
What is the oxidation state of chromium in [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]+?
A)
0
B) +2
C) +3
D) -2
E) -3
C
What is the coordination number of chromium in
[Cr(H2O)4Cl2]+?
A) 8
B) 6
C) 4
D) 2
E) 12
B
The "dentation" of a ligand is defined by ________.
A)
how many "dents" or "deceptions" there are in the
coordination sphere of a complex species it forms
B) how many
electron donor atoms it utilizes to form coordinate bonds to the
central metal ion
C) the total number of lone pairs of electrons
it possesses
D) how many metal ions it can sequester from
solution
E) none of the above
B
EDTA is ________-dantate ligand.
A) mono
B) bi
C)
tri
D) tetra
E) hexa
E
What is the metal ion in the porphyrin of heme?
A) iron
B)
calcium
C) molybdenum
D) magnesium
E) chlorophyll
E
How many iron atoms are coordinated in a hemoglobin molecule?
A)
1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
D
The correct name for [Ni(NH3)6](NO3)3 ________.
A)
dinitrohexaamminenickel (II)
B) hexaamminenickel (III)
trinitrate
C) dinitrohexaamminenickelate (III)
D)
hexaamminenickel (II) nitrate
E) hexaamminenickel (III) nitrate
E
The correct name for [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+ is ________.
A)
diwaterquatraamminecopper (II)
B) tetraamminediaquacopper
(II)
C) diaquatetraammoniumcopper (II)
D) tetraamminecopper
(II) dihydrate
E) copper (II) tetraamminediaqueous
B
The correct name for [Al(H2O)2(OH-)4]- is ________.
A)
diwaterquatrahydroxyaluminum
B) tetrahydroxydiaquaaluminum
(III)
C) diaquatetrahydroxoaluminate
D) aluminum (IV)
hydroxide dihydrate
E) aluminumdihydratetetrahydroxide
C
The correct name for [Fe(NH3)5]Cl3 is ________.
A)
pentaamineiron (II) chloride
B) pentaamineiron (I)
chloride
C) pentaamineiron (III) chloride
D) pentaamineiron
(IV) chloride
E) pentaamineiron (0) chloride
C
The names of complex anions end in ________.
A) -o
B)
-ium
C) -ate
D) -ous
E) -ic
C
The correct name for Na3[CoF6] is ________.
A) trisodium
hexakisfluorocobalt (III)
B) trisodium hexakisfluorocobalt
(II)
C) trisodium hexakisfluorocobalt (IV)
D) sodium
hexafluorocobaltate (III)
E) sodium hexafluorocobaltate (IV)
D
Triphenylphosphine is often given the abbreviated formula PPh3. The
correct name for Rh(PPh3)3Cl is ________.
A)
chlorotriphenylphosphinerhodium
B)
chlorotriphenylphosphinerhodium (I)
C)
tris(triphenylphosphine)chlororhodium (I)
D)
chlorotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium (I)
E)
chlorotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodate (I)
D
In ________, the bonds are the same but the spatial arrangement of
the atoms is different.
A) structural isomers
B) linkage
isomers
C) coordination-sphere isomers
D)
stereoisomers
E) resonance structures
D
A geometrical isomer with like groups located on opposite sides of
the metal atom is denoted with the prefix ________.
A)
cis-
B) trans-
C) bis-
D) tetrakis-
E) d-
B
The complex [Zn(NH3)2Cl2]2+ does not exhibit cis-trans isomerism. The
geometry of this complex must be ________.
A) tetrahedral
B)
trigonal bipyramidal
C) octahedral
D) square planar
E)
either tetrahedral or square planar
A
How many isomers exist for the octahedral complex ion
[Co(NH3)4F2]+?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
B
Trans-[Fe(H2O)2Cl4]2- must be ________.
A) tetrahedral
B)
octahedral
C) square planar
D) trigonal bipyramidal
E) linear
B
Linkage isomerism can only occur ________.
A) in cis-isomers of
octahedral complexes
B) with cobalt complexes
C) with
coordination number 6
D) with tetrahedral complexes
E) with
ligands that have more than one possible donor atom
E
Metals with ________ electron configurations characteristically form
diamagnetic, square planar complexes.
A) d0
B) d9
C) d6
D) d8
E) d10
D
Which mineral contains mercury?
A) cinnabar
B)
sphalerite
C) rutile
D) chromite
E) cassiterite
A
Which one of the following species is paramagnetic?
A)
Cu
B) Ne
C) Y3+
D) Ra
E) Zn2+
A
Which element has the largest bonding atomic radius?
A)
scandium
B) titanium
C) vanadium
D) chromium
E) manganese
A
What is the most common geometry found in five-coordinate
complexes?
A) trigonal bipyramidal
B) octahedral
C)
tetrahedral
D) linear
E) icosahedral
A
The coordination number of cobalt in CoCl3 ∙ 6NH3 is
________.
A) 6
B) 7
C) 8
D) 1
E) 2
A
What is the oxidation number of Ni in [Ni(CN)4]2-?
A) +2
B)
+1
C) 0
D) +3
E) +4
A
Which ion shown below does not exist?
A) Y4+
B) Y2+
C) Y+
D) Zr4+
E) Nb3+
A
Which ion shown has empty 5s orbitals?
A) Mo2+
B) Y3+
C) Zr4+
D) Nb2+
E) All choices have empty 5s orbitals.
E
Which ion shown has empty 4d orbitals?
A) Y3+
B) Zr2+
C) Nb+
D) Mo3+
E) Zr3+
A
A ligand with a single donor atom is called ________.
A)
monodentate
B) bidentate
C) polydentate
D) a
chelate
E) a chelon
A
Which of the following is not a chelating
agent?
A) water
B) ethylenediamine
C)
ortho-phenanthroline
D) carbonate ion
E) triphosphate ion
A
How many bonds can carbonate ion form to a metal ion?
A)
2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 1
E) 5
A
Which of the following is a polydentate ligand?
A)
ethylenediamine
B) water
C) cyanide ion
D) nitrite
ion
E) ammonia
A
The ligand with the formula Br– is named ________ in complexes with
transition metals.
A) bromo
B) bromide
C)
fluoro
D) carbonato
E) azido
A
The ligand with the name aqua when used in complexes with transition
metals has the formula ________.
A) H2O
B) H2O2
C) HO-
D) N3-
E) H3O+
A
Which one of the following is the correct formula for
pentaamminechlorocobalt (III) chloride?
A) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
B) [Co(NH3)4Cl]Cl2
C) [Co(NH3)6Cl]Cl2
D)
[Co(NH3)5]Cl4
E) [Cl(NH3)5Co]Co2
A
Which of the following can form both high- and low-spin octahedral
complexes?
A) Ru2+
B) Cr3+
C) Cr4+
D)
Zr
E) Ag+
A
How many d electrons are associated with the metal ion in
[Cr(NH3)6]3+?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 2
D) 1
E) 0
A
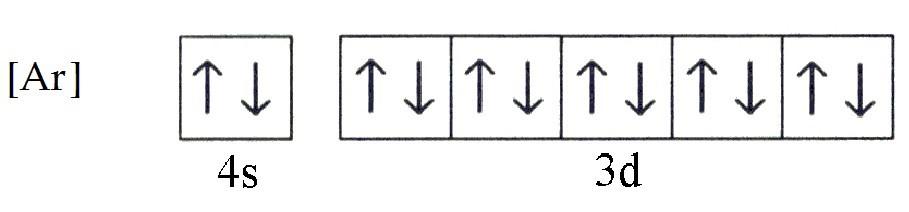
Draw a diagram of the short-hand ground state electron configuration of zinc.
Most transition metal ions contain partially occupied ________ subshells.
d
A substance is ________ if its ions or atoms have zero unpaired electrons.
diamagnetic
The two more common oxidation states of lead are ________ and ________.
2+, 4+
________ arises when the unpaired electrons of the atoms or ions in a solid are influenced by the orientations of the electrons of their neighbors.
Ferromagnetism
What is the oxidation state of the central atom in CaK[Co(CN)6]?
+3
The most common coordination numbers are ________.
4 and 6
What is the coordination number of the iron atom in CaNa[Fe(CN)6]?
6
Six-coordinate complexes generally have ________ geometry.
octahedral
The number of "free" chloride ions in an ionic coordination compound can be determined by treating the compound with ________.
AgNO3
The secondary valence in metal ion complexes is called the ________.
coordination number
Werner's theory of primary and secondary valences for transition metal complexes has given us the concepts of ________ and ________.
oxidation state, coordination number
Transition metal ions with empty valence orbitals act as ________.
Lewis acids
What is the oxidation number of the central metal in [Mo(H2O)5NO3]Cl2
+3
Define the chelate effect.
Chelate effect = an increased stability of complex compounds formed with chelating (polydentate) ligands compared to those formed with monodentate ligands.
The chelate effect is enhanced by polydentate ligand binding because of the change in ________.
entropy
List three of the ten transition metals required for human life.
Co, Cu, Cr, Fe, Mn, V, Zn, Ni, Mo, Cd
Myoglobin has ________ heme group(s) that bind(s) ________.
1,oxygen
In photosynthesis, ________ moles of photons are required to form one mole of ________.
48, glucose
In the leaves of plants, visible light is absorbed by a compound known as ________, and is aided by a ________ ion bonded to a porphyrin ring.
chlorophyll, Mg
What is the mechanism used in humans to combat blood bacterial growth via deprivation of iron?
fever
A large difference in formation constant (Kf) of a poly- versus monodentate ligand is called ________.
chelate effect
A compound that can occupy two coordination sites is a (an) ________.
bidentate ligand
The porphyrin compound that contains Mg (II) is called ________.
chlorophyll
The transport of iron into bacteria is facilitated by the formation of the complex ________.
ferrichrome
Name the compound: K2[Cr(H2O)4(CO3)2].
potassium tetraaquadicarbonatochromate (II)
Name Na [Ru(H2O)2 (C2O4)2].
sodium diaquadioxalatoruthenate (III)
Two compounds have the same formula and contain an ligand. In one compound the ligand is bonded to the metal atom via the N atom and in the other it is bonded via the S atom. These two compounds are examples of ________ isomers.
linkage
Non superimposable isomers are ________ isomers.
optical, chiral, enantiomeric
How can high-spin and low-spin transition metal complexes be distinguished from each other?
Magnetic properties and absorption spectra can be compared.
If chloride is a ligand to a transition metal, it will not be precipitated by silver nitrate.
true
The chelate effect must always occur with positive enthalpy change.
false
The color of hemoglobin changes from purple to red when water displaces oxygen on the molecule.
false
The heme unit of myoglobin is bound to the protein via a nitrogen-containing ligand.
true
To separate racemic mixtures, the isomers must be in a chiral environment.
true
Green and orange are complementary colors.
false
The energy of a metal ligand complex is higher than the energy of the separated components.
false
What is the purpose of adding sodium tripolyphosphate to a detergent?
to sequester the metal ions in hard water to prevent their interference with the action of the detergent
What colors of light does chlorophyll-a absorb?
red and blue
How does an elevated body temperature deprive some bacteria in the body of iron?
In some bacteria, siderophore production decreases as temperature increases.
What is a siderophore?
a ligand that forms an extremely stable water-soluble complex, such as ferrichrome, with iron
What is meant by the prefix tetrakis-, and when is it used?
It means 4 and is used when there are 4 of a ligand whose name includes a Greek prefix.
Name the compound, Ca[AlH4]2.
calcium tetrahydroaluminate
Name the compound, [Os(en)3]2 [NiCl2Br2]3.
tris(ethylenediamine)osmium(III) dibromodichloronickelate(II)
Name the compound, Cu(H2O)42+.
tetraaquacopper(II)
In what two ways can an object appear blue?
absorb all wavelengths except blue and reflect or transmit only blue, or absorb the complementary color of blue and reflect or transmit all others