Chapter 18: The Heart
Describe the size, shape, location, and orientation of the heart in the thorax.
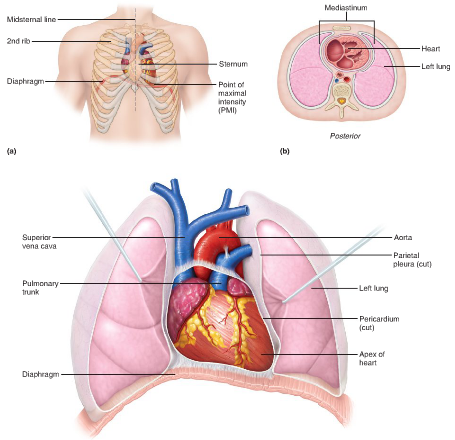
Size: fist, weighs less than a pound
Shape: broad, flat base (9cm) and apex points toward left hip
Location: frontal plane, between lungs, most mass is on left, but projects out more to right to balance the heart
Orientation: rests on superior surface of diaphragm, anterior to vertebral column, posterior to sternum
Coverings of the heart.
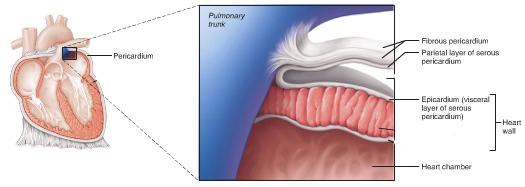
Fibrous Pericardium
Serous Pericardium
Fibrous Pericardium
Structure: superficial part of double-walled sac surrounding the heart; consists of dense connective tissue
Function: (1) protects heart (2) anchors it to surround structures (3) prevents overfilling of heart with blood
Serous Pericardium
parietal: lines internal surface of fibrous pericardium; attaches to large arteries exiting the heart
visceral (epicardium): thin membrane that continues over the external heart surface
Pericardial Cavity
between the parietal and visceral layers; slitlike cavity that contains a film of protein-rich fluid
Stroke Volume (SV)
Amount of blood ejected by one contraction of the heart.
End Diastolic Volume (EDV)
Amount of blood in the ventricle at the end of relaxation
End Systolic Volume (ESV)
Amount of blood in the ventricle at the end of contraction
Cardiac Output (CO)
The amount of blood ejected from the heart in one minute
Heart Rate (HR)
The frequency at which the heart beats