Control growth
The multidrug resistant pumps in many bacterial cell membranes function by
Bacterial chromosomal mutations
Synthesis of enzymes that
alter drug structure
Removing the drug from the cell when it
enters
Alteration of drug receptors on cell targets
Removing the drug from the cell when it enters
The cellular basis for bacterial resistance to antimicrobials include
Bacterial chromosomal mutations
Synthesis of enzymes that
alter drug structure
Prevention of drug entry into the
cell
Alteration of drug receptors on cell targets
All of the
choices are correct
All of the choices are correct
Antiviral drugs that target reverse transcriptase would be used to treat
Influenza A virus
HIV
Herpes zoster virus
Respiratory syncytial virus
Hepatitis C virus
HIV
An antiviral that is a guanine analog would have an antiviral mode of action that
Blocks penetration
Blocks transcription and translation
Inhibits DNA synthesis
Blocks maturation
Bonds to
ergosterol in the cell membrane
Inhibits DNA synthesis
1. Commercial products containing which types of chemicals are more
effective at killing
microorganisms?
Bacteriostatic
Lead
Bacteriocidal
Carbohydrate
None
of these are correct
Bacteriocidal
2.Using toilet bowl cleaner and nonionizing radiation to inanimate
surfaces only removes or kills vegetative bacteria. The term that best
describes this action is
_________.
Disinfection
Sterilization
Antisepsis
Degermation
None
of these are correct
Disinfection
3. Which of these metals have antimicrobial properties associated
with them?
Silver
Gold
Aluminum
Tin
Both A
and B are correct
Both A and B are correct
4.Which of the following types of agents targets protein
conformation?
Alcohol
Hydrogen peroxide
Ultraviolet
light
Detergents
Crystal violet
Alcohol
5.All of the following are correct about the autoclave, except
_________.
Sterilization is achieved when steam condenses against
the objects in the chamber and raises their temperatures
It is
effective for sterilizing powders, oils, and waxy substances
It
is the temperature that kills the microbes, not the pressure
itself
The duration of the process depends on how full the
chamber is
It is important not to overload the chamber
It is effective for sterilizing powders, oils, and waxy substances
6.Which common hospital pathogen is able to grow abundantly in soap
dishes?
Salmonella
Mycobacteria
tuberculosis
Escherichia coli
Hemophilus influenza
Pseudomonas
Pseudomonas
7.Historically, which of the following was instilled into the eyes of
newborn infants to prevent gonococcal
infections?
Mercurochrome
Triclosan
Silver nitrate
Phenol
Formaldehyde
Silver nitrate
8.All of the following are methods of disinfection or sterilization,
except _________.
Lyophilization
Gamma
radiation
Ethanol
Dry oven
Triclosan
Lyophilization
9.All of the following are benefits of food irradiation, except
_________.
It can inhibit the sprouting of white potatoes
It
makes the food less nutritious
It can kill bacterial pathogens on
the food
In can reduce the number of food-borne deaths each
year
It can kill insects on the food
It makes the food less nutritious
10. All of the following are correct about food irradiation, except
_________.
The World Health Organization does not endorse this
process
No irradiated food can be sold without clear
labeling
food is not made radioactive by the process
it is
approved in the U.S. for beef, chicken, and pork
it can lead to a
longer shelf life for the irradiated food
The World Health Organization does not endorse this process
11.Which of the following is officially accepted as a sterilant and
high-level disinfectant?
Cresol
Glutaraldehyde
Silver
nitrate
Benzalkonium chloride
Triclosan
Glutaraldehyde
12.Which of the following chemicals is a disinfectant for soft
contact lenses?
Hypochlorite
Hydrogen peroxide
Hexachlorophene
Glutaraldehyde
Alcohol
Hydrogen peroxide
13.Which of the following is being used to replace hypochlorites in
treating water because of the possibility of cancer-causing substances
being produced?
Hydrogen peroxide
Chloramines
Sodium
iodide
Quaternary ammonium compounds
Fluorine
Chloramines
14.The sterilizing gas used in a special chamber is
_________.
Glutaraldehyde
Iodophor
Chlorine
dioxide
Ethylene oxide
Formaldehyde
Ethylene oxide
15.Alcohols _________.
At 50% or higher concentrations dissolve
cell membrane lipids
Denature proteins when in a 50-95%
solution
Are used to disinfect items by soaking
Are skin
degerming agents
All of the choices are correct
All of the choices are correct
16.Which control method would not be a suitable choice for killing
Mycobacteria in a capped culture tube?
121oC at 15 psi for 15
minutes
Ultraviolet (germicidal) light
160oC for 2
hours
Gamma rays
All of the choices are correct
Ultraviolet (germicidal) light
17.The easiest microbial forms to kill or inhibit are
_________.
Protozoan cysts
Endospores
Vegetative
bacteria and fungi
Mycobacterium and Staphylococcus
Naked viruses
Vegetative bacteria and fungi
18.HEPA filters are used to remove microbes from
_________.
Human tissues
Liquids
Air
Medical
instruments
All of the choices are correct
Air
19.Disinfection of beverages, such as apple juice, milk, and wine, is
optimally achieved by
_________.
Pasteurization
Chlorination
Moist heat
autoclave
Boiling water
Filtration
Pasteurization
20.The shortest time required to kill all the microbes in a sample at
a specified temperature is called the __________.
Sporicidal
time
Death phase point
Thermal death point
(TDP)
Thermal death time (TDT)
None of the choices are correct
Thermal death time (TDT)
21.Dry heat _________.
Is used in devices called
autoclaves
Is less efficient than moist heat
Includes
tyndallization
Cannot sterilize
Will sterilize at 121oC for
15 minutes
Is less efficient than moist heat
22.Sterilization is achieved by _________.
Flash
pasteurization
Steam autoclave
Boiling water
Hot
water
All of the choices are correct
Steam autoclave
23.Scrubbing or immersing the skin in chemicals to reduce the numbers
of microbes on the skin is _________.
Sanitization
Degermation
Sterilization
Disinfection
Antisepsis
Degermation
24.The use of chemical agents directly on exposed body surfaces to
destroy or inhibit vegetative pathogens is _________.
Sterilization
Degermation
Antisepsis
Sanitization
Disinfection
Antisepsis
25.Microbiological contaminants are best described as
_________.
Vegetative microbes present on or in a
substance
Any and all microbes present on or in a
substance
Pathogenic microbes present on or in a
substance
Unwanted microbes present on or in a
substance
None of the choices are correct
Unwanted microbes present on or in a substance
26.Which of the following antimicrobials is contraindicated for
children due to permanent tooth discoloration?
Penicillin G
Erythomycin
Gentamicin
Vancomycin
Tetracycline
Tetracycline
27.Which organ is responsible for metabolizing and detoxifying
foreign chemicals in the blood, including
drugs?
Kidneys
Liver
Stomach
Gall bladder
Spleen
Liver
28.A nurse preparing a section of skin for an injection is an example
of __________.
sanitization
disinfection
sterilization
degerming
disinfection
29.the eradication of all organisms including bacterial endospores and viruses (although not prions) in or on an object.
disinfection.
sanitization
sterilization
degerming
sterilization
30.the removal of microbes from a surface by scrubbing
disinfection
sanitization
sterilization
degerming
degerming
31.The process of filtration is a(n) _______________.
antiseptic procedure
ineffective method for removing
microbes
sterilizing method
disinfectant method
sanitization method
sterilizing method
32.Damage to the cell wall will adversely affect a bacterial cell by
making it more susceptible to __________.
alcohols
radiation
osmotic pressure
high temperature
osmotic pressure
33.The process of filtration is a(n) _______________.
antiseptic
procedure
ineffective method for removing
microbes
sterilizing method
disinfectant method
sanitization method
sterilizing method
34-the process of disinfecting surfaces and utensils used by the public
disinfection
sanitization
sterilization
degerming
sanitization
35.the use of physical or chemical agents to inhibit or destroy microorganisms on inanimate objects
disinfection
sanitization
sterilization
degerming
disinfection
36.Which of the following is not a mode of action of an
antiviral?
Inhibit DNA synthesis
Bond to ergosterol in the
cell membrane
Block transcription and translation
Block
penetration
Block mutation
Bond to ergosterol in the cell membrane
37.There are fewer antifungal, antiprotozoan, and antihelminth drugs
compared to antibacterial drugs because these organisms
_________.
Do not cause many human infections
Are parasites
found inside human cells
Are not affected by
antimicrobics
Are so similar to human cells that selective drug
toxicity is difficult to achieve
Have fewer target sites compared
to bacteria
Are so similar to human cells that selective drug toxicity is difficult to achieve
38.Antibiotics are derived from all the following, except _________.
Staphylococcus
Bacillus
Streptomyces
Cephalosporium
Penicillium
Staphylococcus
39.Drug-resistant population of microbes arise when
_________.
Resistant cells become numerous in a population due to
their greater vigor
Exposure to drugs selectively kills sensitive
cells allowing overgrowth of resistant cells
Synergy between
medications occurs
Exposure to drugs causes mutation that produce
resistance
That patient becomes immune to the drug
Exposure to drugs selectively kills sensitive cells allowing overgrowth of resistant cells
40.Bacterial DNA replication requires the enzyme gyrase, but
eukaryotic replication does not. Ciprofloxacin (“Cipro”) inhibits
gyrase activity. This is an example of _________.
Use of an
analog
An antimetabolite
Synergism
Selective
toxicity
Antimicrobial resistance
Selective toxicity
41.Synthetic antimicrobials that block protein synthesis by binding
to the mRNA are
_________.
Macrolides
Aminoglycosides
Nucleic acid
analogs
Antisense nucleic acids
Beta-lactams
Antisense nucleic acids
42.Most drugs that inhibit the synthesis of the cell wall act by
_________.
Disrupting the formation of the mycolic acid layer of
the cell wall
Preventing the formation of the alanine-alanine
bridges
Preventing the cross-linkage of NAM
subunits
Blocking the secretion of cell wall molecules from the
cytoplasm
Prevent the formation of β-lactamases
Preventing the cross-linkage of NAM subunits
43.The CDC issued alerts about a bacterial strain known as NDM1 (New
Delhi metalo-lactamase 1). What type of antibiotic resistance is
indicated by the name?
Removal of the drug via a
pump
Alteration of the target of the drug
Change in the
permeability of the drug
Overproduction of an enzyme in a key
metabolic pathway
Inactivation of the drug
Inactivation of the drug
44.In the compound lamivudine, an –SH group replaces an –OH group
found in cytosine. When used as a medication it will
_________.
Disrupt lipid membrane structure
Disrupt membrane
structure
Interfere with nucleic acid synthesis
Interfere
with cell wall synthesis
Interfere with protein synthesis
Interfere with nucleic acid synthesis
45.The first synthetic antimicrobial widely available for treatment
of infections _________
Was an attachment
antagonist
Disrupted cytoplasmic membranes
Interfered with
bacterial cell wall synthesis
Was a nucleotide analog
Was an antimetabolite
Was an attachment antagonist
46.Which of the following is a primary advantage of semisynthetic
drugs?
They work faster
They are not readily absorbed, so
they persist longer
They must be administered
intravenously
They are less stable and consequently have fewer
side effects
They have a broader spectrum of action
They have a broader spectrum of action
47.Beta-lactam antibiotics have an effect on which of the following
types of cells?
Bacterial cells
Virus-infected
cells
Animal cells
Fungal cells
Both animal and fungal cells
Bacterial cells
48.An antimicrobial that inhibits cell wall synthesis will result in
which of the following?
Cells cannot attach to their
hosts
The replication of cell, including cancer cells slows
down.
Ribosomes lose their function
Cells become more
susceptible to osmotic pressure
The sterols in the cell wall
become nonfunctional
Cells become more susceptible to osmotic pressure
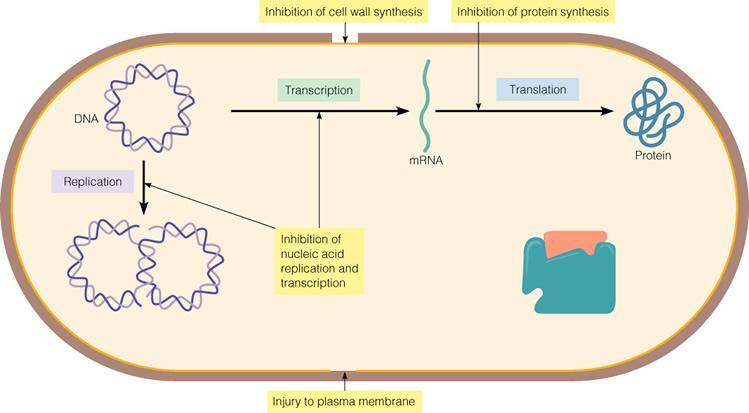
49Which mode of antibiotic activity is the most selective target for antibiotics since it will not affect eukaryotic cells?
Inhibition of transcription
Inhibition of cell wall
synthesis
Inhibition of translation
Inhibition of DNA replication
Injury to the plasma membrane
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
50.Which antibiotic pictured is not recommended for children due to possible discolorations of their teeth?
Penicillin
Amphotericin B
Tetracycline
Chloramphenicol
Tetracycline
51.A chemical that kills gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria is described as:
selectively toxic.
inhibitory.
broad spectrum.
narrow spectrum.
broad spectrum.
52.A drug that inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis is:
antibacterial.
antifungal.
antiprotozoal.
antiviral.
antibacterial.
53.An antiviral that is a guanine analog would have an antiviral mode
of action that
blocks penetration.
blocks transcription
and translation.
inhibits DNA synthesis.
blocks
maturation.
bonds to ergosterol in the cell membrane.
inhibits DNA synthesis.
54.The multidrug resistant pumps in many bacterial cell membranes
function by
bacterial chromosomal mutations.
synthesis of
enzymes that alter drug structure.
removing the drug from the
cell when it enters.
alteration of drug receptors on cell targets.
removing the drug from the cell when it enters.
55.Each of the following result in drug resistance except
drug
pumped out of the cell.
drug used as a nutrient by the
cell.
drug binding site altered.
drug inactivated.
drug blocked from entering cell.
drug used as a nutrient by the cell.
56.Each of the following is a mechanism for drug resistance transfer
between microorganisms except
transposons.
R-plasmids.
conjugation.
mutation.
mutation.
57.Nutrients that encourage the growth of beneficial microbes in the intestines are known as
prebiotics.
probiotics.
lantibiotics.
phytobiotics.
probiotics.
58.Which therapeutic index value would be the drug of choice?
20
10
1
0.1
20
59.Important characteristics of antimicrobial drugs include
low toxicity for human tissues.
high toxicity against microbial
cells.
do not cause serious side effects in humans.
stable
and soluble in body tissues and fluids.
All of the choices are correct.
All of the choices are correct.
60.Selective toxicity refers to
damage to pathogenic
organisms.
damage to prokaryotic cell membranes.
damage to
the target organisms but not host cells.
damage to nucleic acids.
damage to the target organisms but not host cells.
61.Drugs that insert on the _____ ribosomal subunit prevent peptide
bond formation or inhibit translocation of the subunit during
translation.
30S
40S
50S
60S
50S
62. Drugs that act by mimicking the normal substrate of an enzyme,
thereby blocking its active
site, are called
inhibitors.
blockers.
competitive
inhibitors.
noncompetitive inhibitors.
competitive inhibitors.
63.What type of chemical will allow some bacteria to be resistant to
many penicillins?
synercid
penicillinase
aztreonam
clavulanic acid
penicillinase
64.Antibiotics that disrupt bacterial ribosomes can also affect
eukaryotic large ribosomal subunit.
eukaryotic small ribosomal subunit.
ribosomal RNA.
eukaryotic mitochondrial ribosomes.
eukaryotic mitochondrial ribosomes.
65.Drugs that act by mimicking the normal substrate of an enzyme, thereby blocking its active site, are called
______.
inhibitors
blockers
competitive inhibitors
noncompetitive inhibitors
competitive inhibitors
66-Which of the following is the third stage of a disease?
Period of convalescence
Incubation period
Period of
decline
Prodromal period
Period of illness
Period of illness
67.Which of these disease stages is most likely to be altered in length if the number of infecting organisms at the start of the infection is very high?
Period of convalescence
Prodromal period
Period of
illness
Incubation period
Period of decline
Incubation period
68.Microorganisms that typically colonize a host without causing disease are referred to as the __________.
pathogens
opportunistic pathogens
normal
microbiota
transient microbes
normal microbiota
69. occurs when someone come into direct contact with the infectous lesion or infected body fluid.
direct transmission
70.involves the transfer organisms to a person through handling of contaminated instruments and then touching face, eyes, or mouth.
indirect transmission
71. spread of disease through moisture containing bacteria or virus.
ex: coughing through the air
droplet infection
72.What occurs during vehicle transmission?
Nonliving media transmit the pathogen
73.Vehicle Transmission, how does media transmit the pathogen?
Through contaminated water that is ingested, inhaling spores from dust, droplet nuclei of mucus, or eating contaminated food
74.What is a biological vector?
Active transmission that is purposeful and part of the microbes life cycle, such as, a bite.
75.Contact Transmission, What is the distance in which a droplet nuclei would travel to achieve the spread of disease?
Less than 1 meter
76. A disease which develops rapidly but lasts only a short time, like influenza
Acute
77. A disease which develops slowly, & the symptoms may be less severe but it is likely to continue or recur for periods with continuous shedding of the pathogen. likeGlandular fever, Hepatitis B
Chronic
78.The pathogen remains inactive for a time but may be re-activated
under certain conditions. Herpes virus
(cold sores)
Latent
79. The infection produces an immune response without recognisable symptoms. Rubella (German measles)
Subclinical
80. "contagious" an INFECTIOUS disease that is readily transmitted from one individual to another..either directly or indirectly. infectious disease transmissible from one human to another (ex: gonorrhea)
communicable disease
81. What is a noncommunicable disease?
a disease that cannot spread and is not caused by a pathogen
82. - Primary infection:
initial infection that is later complicated by additional, secondary infections
83. Localized infection:
microbe remains in area of entrance (fungal skin infection or wart)
84 - Systemic infection:
microbe spreads to several sites, including blood (septicemia, bacteremia, viremia, toxemia)
85. Mixed infection (polymicrobial):
infection involves more than one microbe (wound infection, dental caries)
86. Secondary infection :
an infection that complicates the primary infection (HIV-primary → pneomonia-secondary)
87.The reservoir of infection for botulism and tetanus is
humans.
soil.
water.
animals.
soil AND water.
soil
88.The popular name for tetanus is
hydrophobia.
lockjaw.
whooping cough.
consumption.
lockjaw.
89.The exotoxin produced by C. tetani is
tetanoxin.
exotetanus.
tetanospasmin.
endospasmin.
tetanospasmin.
90.The disease that involves the muscles and often manifests itself
first with spasms of the jaw muscles is
polio.
rabies.
tetanus.
gastritis.
tetanus.
91.Tetanus prevents the release of neurotransmitters from
muscle cells.
excitatory neurons.
inhibitory neurons.
tetano cells.
inhibitory neurons.
92. The normal habitat of Clostridium tetani is
humans.
animals.
plants.
soil and dust.
soil and dust.
93.Production of a neurotoxin that binds to target sites on spinal
cord neurons responsible for inhibiting skeletal muscle contraction is
a characteristic of
Clostridium botulinum.
Clostridium
perfringens.
Clostridium difficile.
Clostridium tetani.
Clostridium tetani.
94.What does Polio invade?
the central nervous system producing from a subclinical or mild febrile illness to aseptic meningitis, muscle weakness, and paralysis.
95.What is polio caused by?
3 distinct types of Enteroviruses (poliovirus 1,2,3)
96.Which of the following diseases is NOT caused by an organism that
enters the body through the gastrointestinal
tract?
leprosy
polio
infant botulism
adult listeriosis
leprosy