Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Neurons, the Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
front 1 What are the three major functional classes of neurons? | back 1 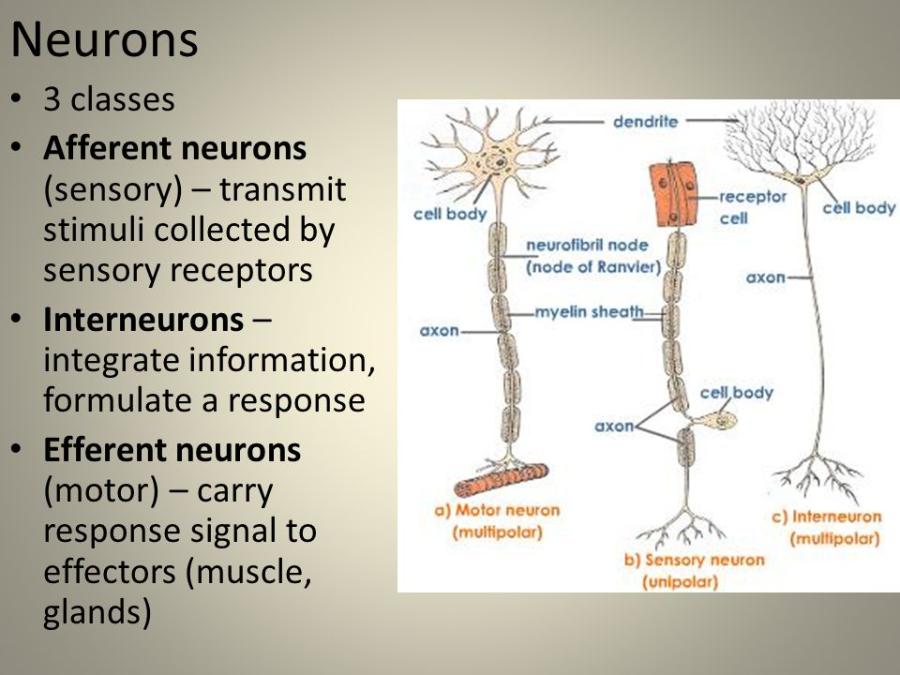 3 Types of Neurons 1) Afferent neurons (sensory) transmit stimuli collected by receptors and sends to the central nervous system, 2) Interneurons (integrate information) sends information between sensory and motor neurons within the central nervous system, 3) Efferent neurons (motor) sends response signal from central nervous system to muscles and glands. |
front 2 Neuron | back 2 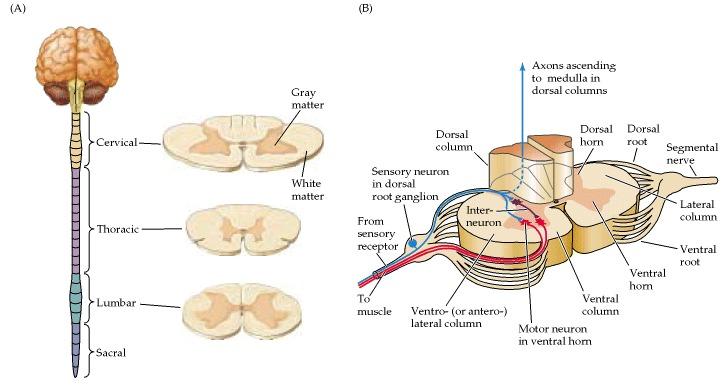 Neurons:
|
front 3 Spinal Cord (Function) | back 3 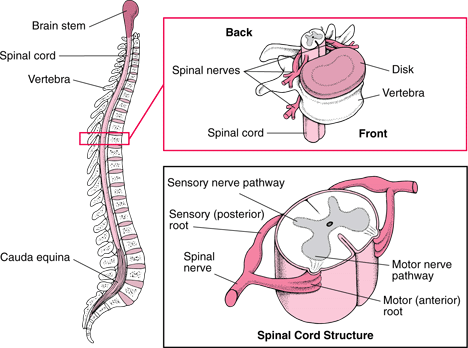 Spinal Cord Functions:
|
front 4 Spinal Cord (function) | back 4  The spinal cord is:
|
front 5 Spinal Nerve | back 5 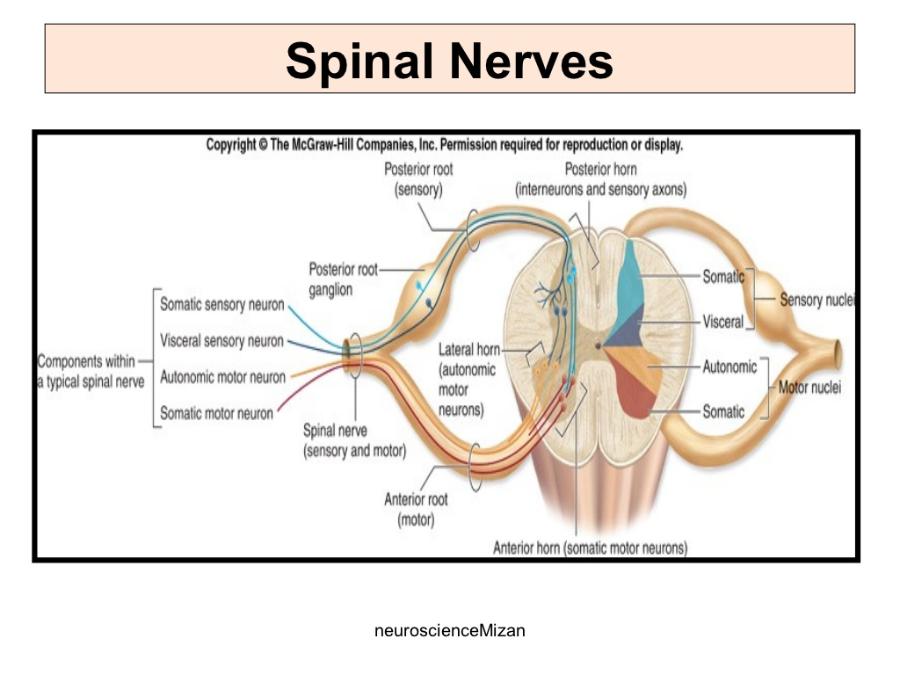 The posterior/dorsal (contain sensory axons) and anterior/ventral (contain motor axons) nerve roots fuse to form a spinal nerve. |
front 6 Spinal Nerves | back 6 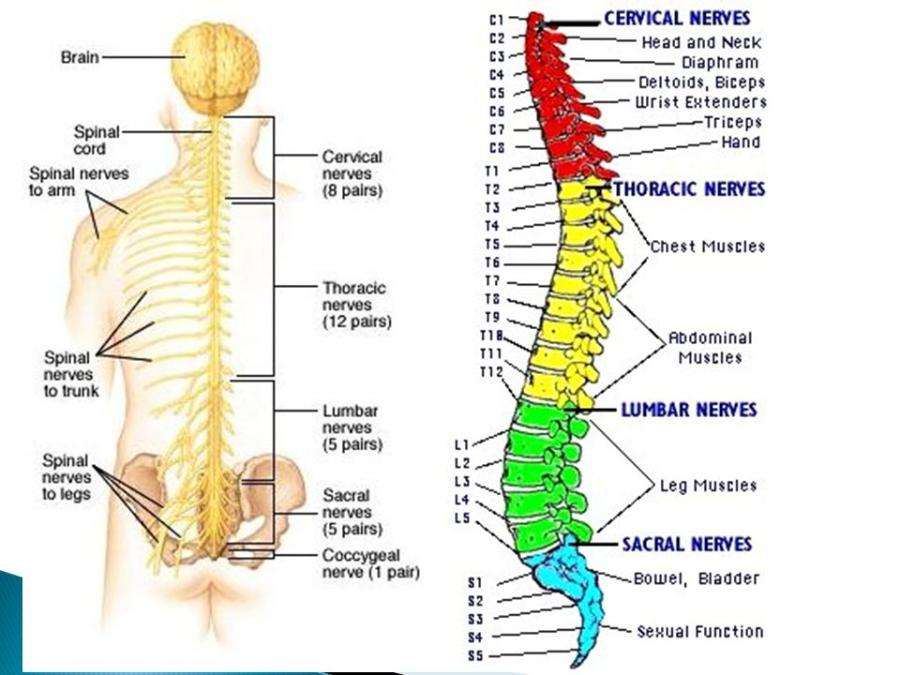 Spinal nerves are attached to the spinal cord and carry information directly to and from the spinal cord. The spinal nerve contains motor and sensory nerve fibers to and from all parts of the body. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. They are mixed nerves carrying sensory and motor information. The spinal cord is divided into four regions: cervical (C), thoracic (T), lumbar (L) and sacral (S), |
front 7 Somatic Motor Neurons | back 7 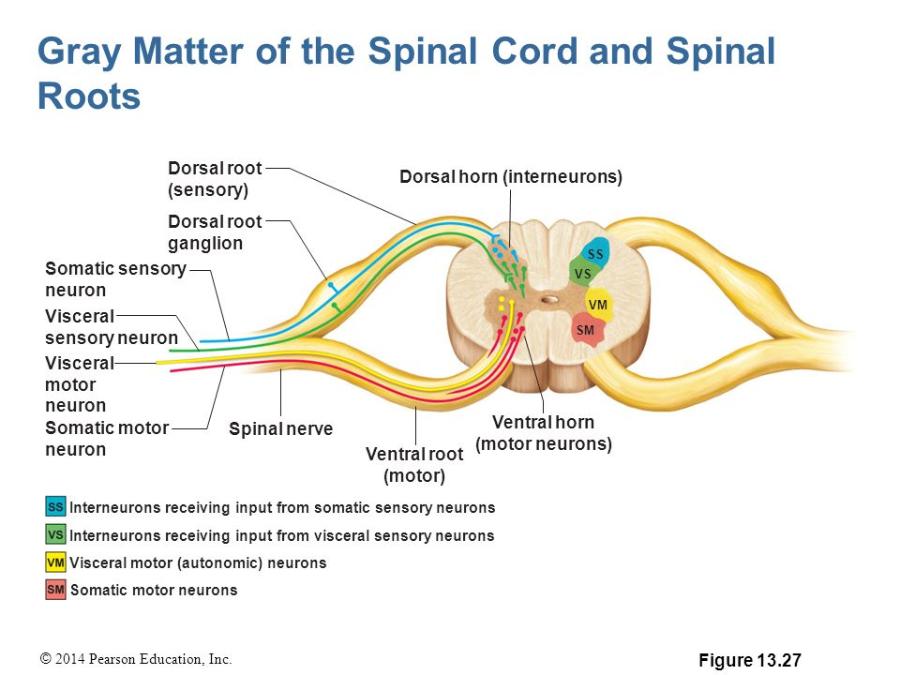 Somatic Motor Neurons: Somatic motor neurons are multipolar neurons. That means each somatic motor neuron has numerous dendrites and a single axon extending from its soma. Somatic (sensory) motor neurons sends signals to skeletal muscle cells. The axon of a somatic motor neuron extends into the |
front 8 Visceral Motor Neurons | back 8  Visceral Motor Neurons: Visceral (efferent) motor neurons send signals to glands, cardiac muscle cells and smooth muscle cells. |
front 9 Dendrite | back 9 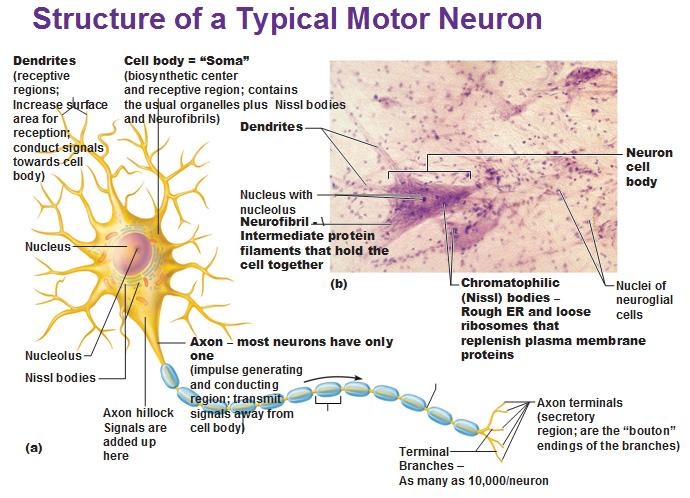 Dendrites: Dendrites bring electrical signals to the cell body. |
front 10 Axon (Function) | back 10  Axons sends electrical signals away from the cell body to muscles or glands. |
front 11 Soma | back 11  The Soma, or cell body, is where the signals from the dendrites are joined. The soma and the nucleus do not play an active role in the transmission of the neural signal. Instead, these two structures serve to maintain the cell and keep the neuron functional. |
front 12 Anterior horn (also called ventral horn) of spinal cord | back 12 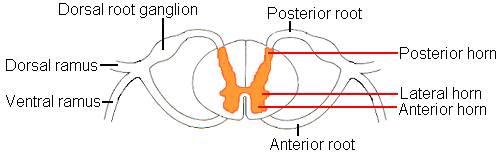 Anterior horn - Is located in the front of the spinal cord (near inside of body). Is the anterior grey matter that contain motor neurons that affect the skeletal muscles. |
front 13 Posterior horn (also called dorsal horn) of spinal cord | back 13  Posterior horn - is located in the back of the spinal cord (outside of back). Is the posterior of grey matter that contains bodies of interneurons. It receives several types of sensory information from the body, including touch and sensation. This information is sent from receptors of the skin, bones, and joints through sensory neurons whose cell bodies lie in the dorsal root ganglion. |
front 14 Lateral horn of the spinal cord | back 14  Lateral horn projects to the side in a triangular shape in the thoracic and upper lumbar spinal sections. Contain the bodies of visceral motor neurons. |
front 15 Dorsal Root Ganglia | back 15 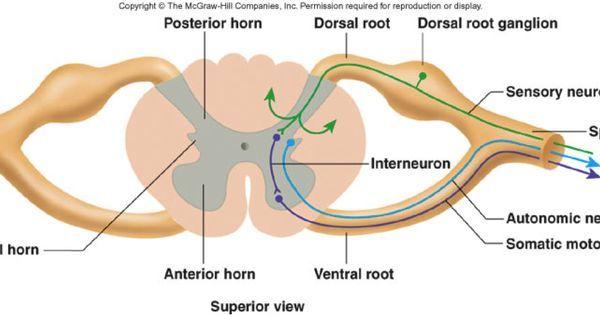 The dorsal root ganglion contains the cell bodies of sensory neurons that bring axons to the spinal cord. |
front 16 Dorsal Root (posterior/back root) | back 16 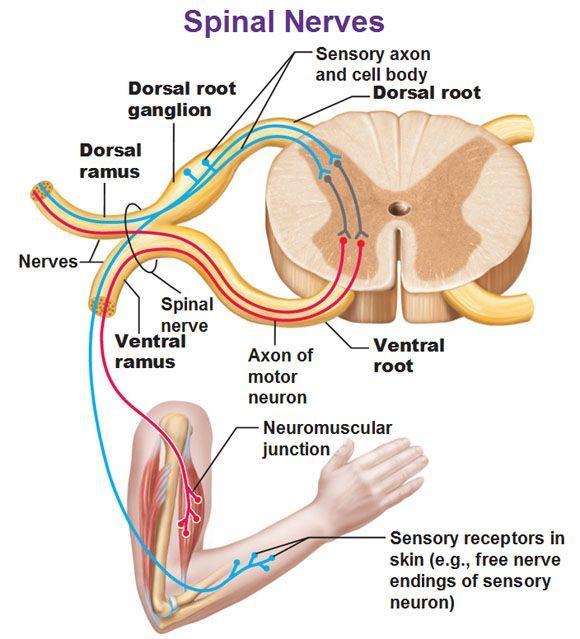 The dorsal roots are nerves where axons travel into the back of the spinal cord into the gray matter of the spinal cord. |
front 17 Ventral Root (anterior root) | back 17 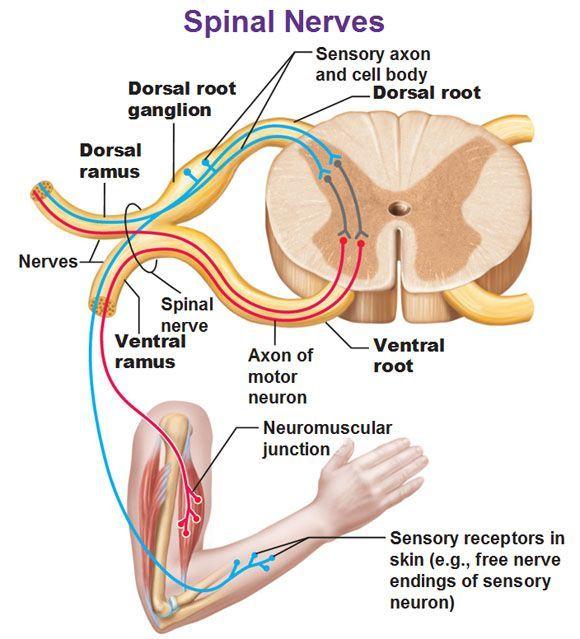 The ventral root contain motor neutron axons that exit the front of the spinal cord into the gray matter of the spinal cord. |
front 18 Spinal Meninges | back 18 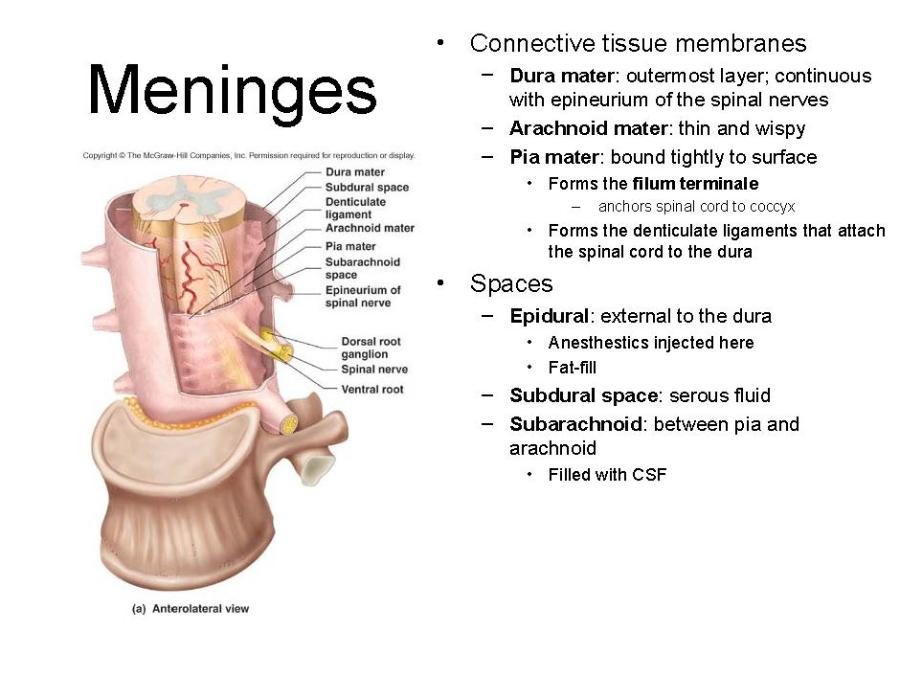 Spinal Meninges the three membranes enclosing the spinal cord, comprising the dura mater, the pia mater, and the arachnoid membrane. |
front 19 Posterior | back 19 Posterior means dorsal or back/outside |
front 20 Anterior | back 20 Anterior means ventral or inside |
front 21 Anterior Funiculi (or ventral funiculi) | back 21 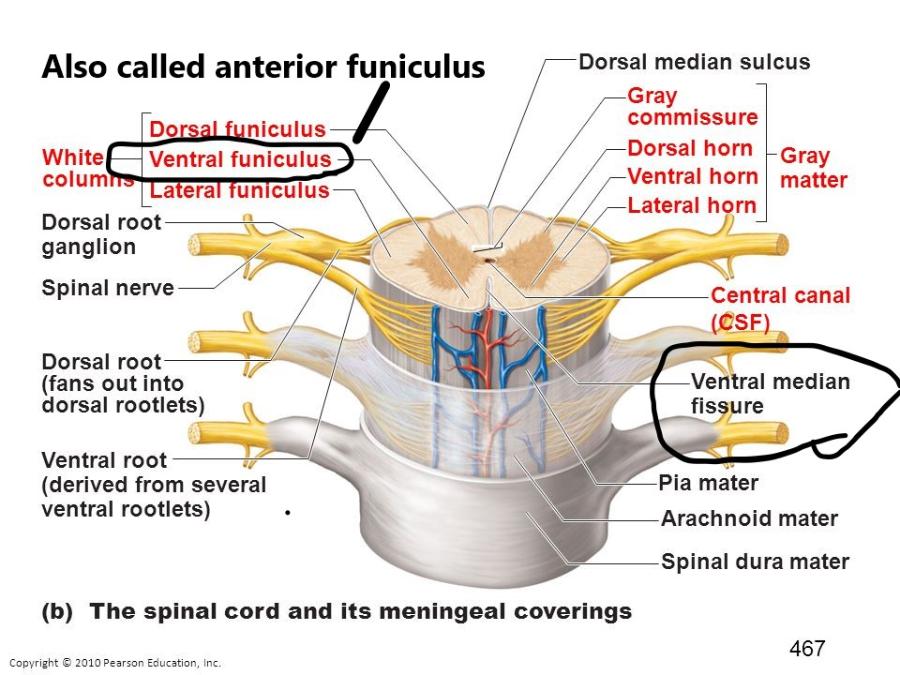 Anterior Funiculi: white matter of the anterior section of the spinal cord. Axons in the anterior funiculi carry signals down the spinal cord from the brain. |
front 22 Lateral Funiculi | back 22 Lateral Funiculi contain a mix of anterior and posterior funiculi. |
front 23 Posterior Funiculi (or dorsal funiculi) | back 23 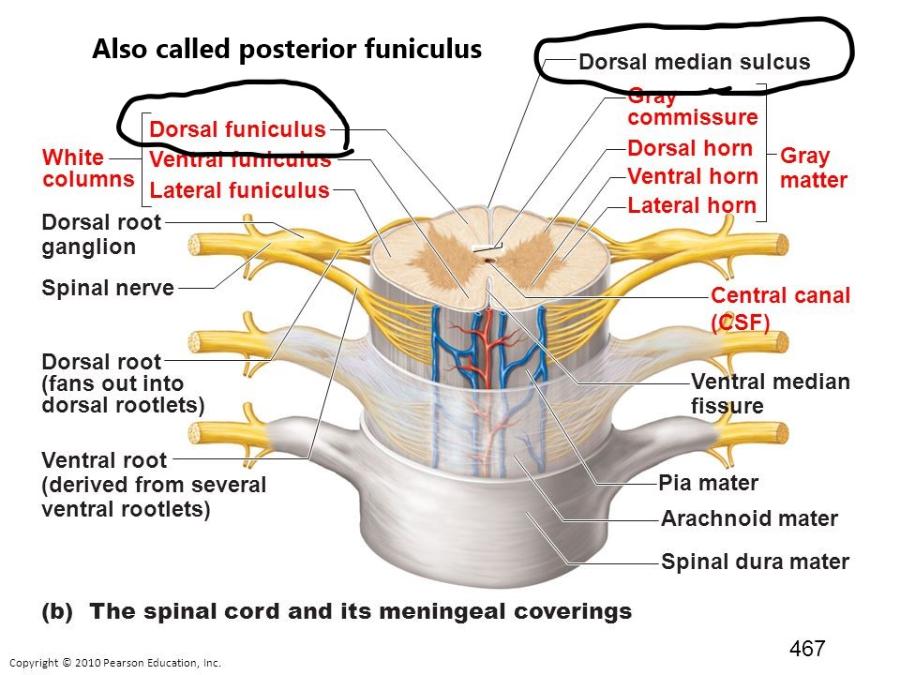 Posterior Funiculi: white matter of the posterior section of the spinal cord. Axons in the posterior funiculi carry signals up the spinal cord. |
front 24 Funiculi | back 24 Funiculi: also called columns |
front 25 Gray Matter | back 25 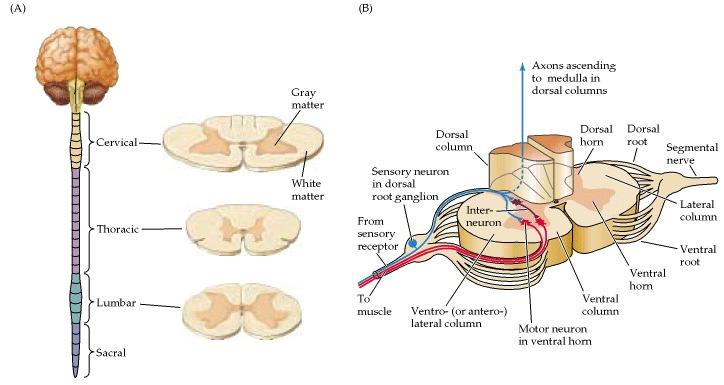 Gray Matter: area of the spinal cord rich in nerve cell bodies that has a butterfly shape. |
front 26 White Matter | back 26  White Matter: area of the spinal cord that consist primarily of glial cells and axons, which gives the tissue a white coloring. It contains sensory and motor neurons. The glial cells is a type of cell, in the nervous system, that provides support for the neurons. |
front 27 Efferent: | back 27 Efferent: The conduction of impulses outward from/away the brain or spinal cord. Efferent means to act. |
front 28 Afferent | back 28 Afferent: The conduction of impulses inwards to the brain or spinal cord. Afferent means to receive. |
front 29 Central Nervous System | back 29 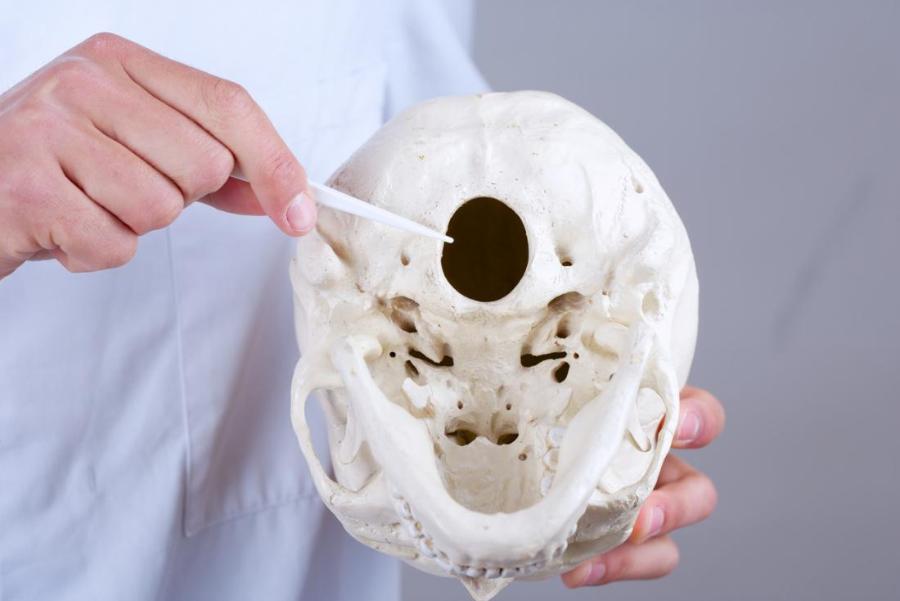 Central Nervous System (CNS)- The brain and the spinal cord are the two organs that make up the CNS. The foramen magnum divides the brain and the spinal cord. The foramen magnum is the hole in the base of the skull through which the spinal cord passes. |
front 30 What is CSF? | back 30 CSF: cerebral spinal fluid |
front 31 What is a motor unit? | back 31 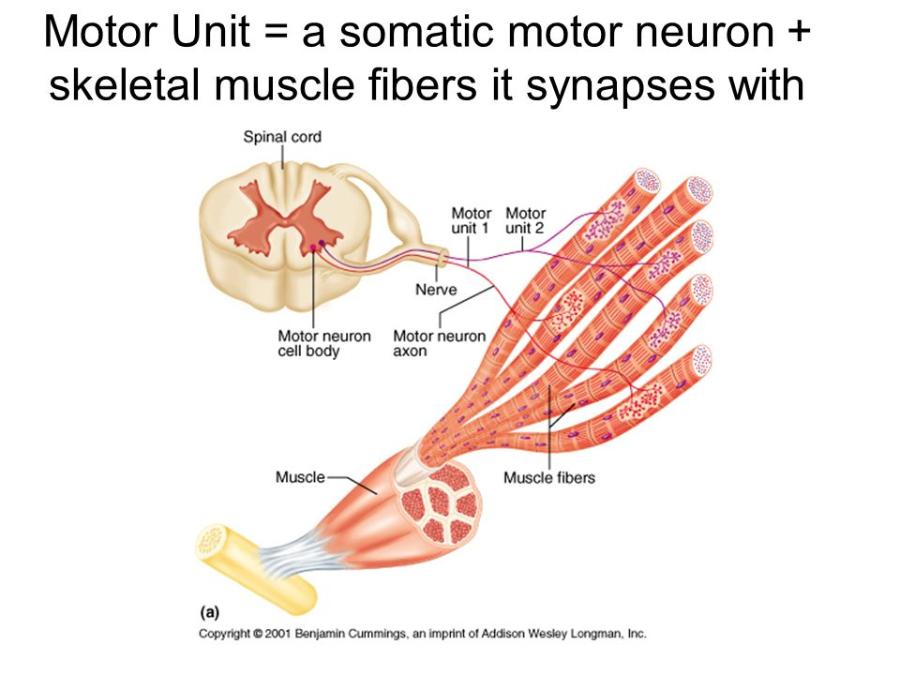 a motor unit = a somatic motor neuron + skeletal muscle fibers it synapses with |
front 32 What is a synapse? | back 32 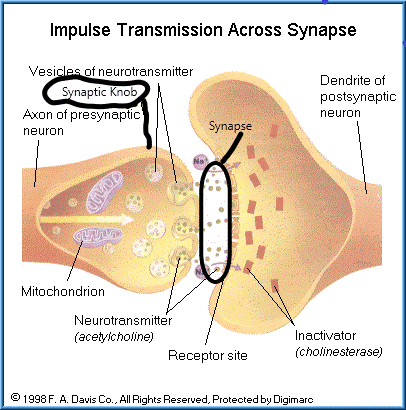 A synaptic knob usually lies adjacent to another cell. The neighboring cells and the gap that separates them is called a synapse. Neurotransmitters travel down the axon to synaptic knobs where it signals the synaptic vesicles to release stored neurotransmitters. |
front 33 Why is the spinal cord enlarged in two places? | back 33 Why is the spinal cord enlarged in two places because the cervical and lumbar enlargements of the spinal cord result from enlargement of the gray matter that contains the neural machinery necessary to operate the limbs. |
front 34 Label the three meninges of the spine. Label the subarachnoid space and epidural space | back 34 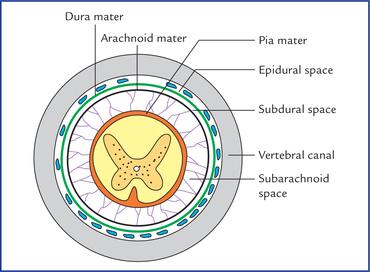 Label the three meninges of the spine. Label the subarachnoid space and epidural space. |
front 35 What structure are the bodies of sensory neurons found? | back 35 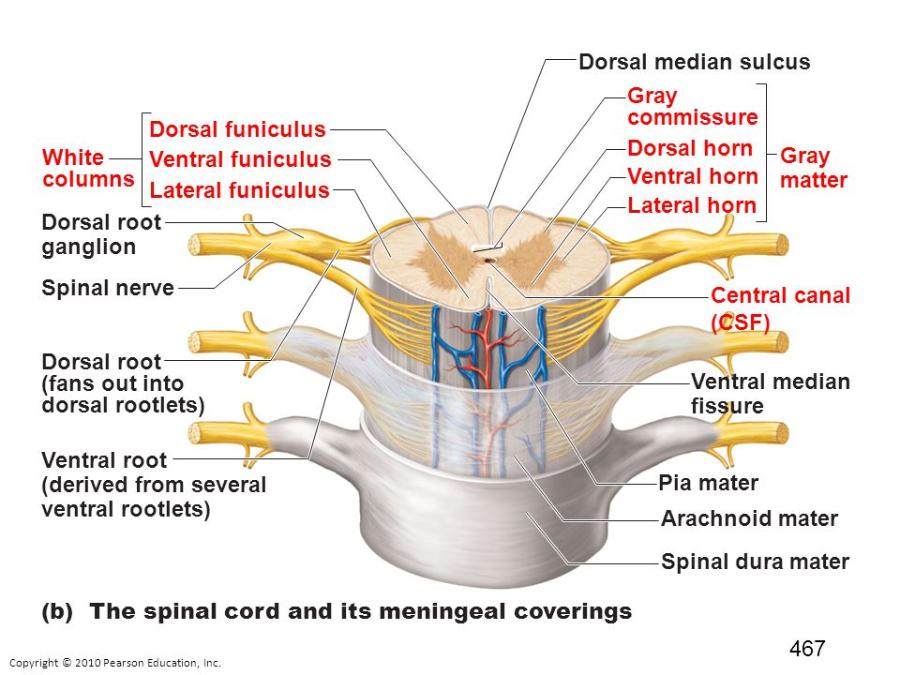 The cell bodies of sensory neurons are found in clusters in the dorsal root ganglia, next to the spinal cord. |
front 36 In what part of the spinal cord are bodies of somatic motor neurons found? | back 36  Cell bodies of somatic motor neurons are found in the anterior (or ventral) gray horns (gray matter) of the spinal cord. They provide nerve impulses for contraction of skeletal muscles. |
front 37 What is the difference between sensory neuron and a motor neuron? | back 37 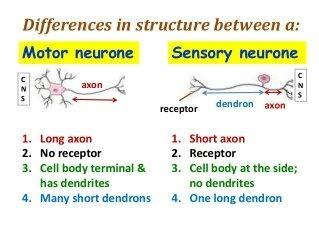
|
front 38 In what structures are afferent axons found? | back 38 Afferent nerves conduct signals from sensory neurons to the central nervous system, for example from mechanoreceptors in skin |
front 39 In what structures are efferent axons found? | back 39 Efferent axons (nerves) conduct signals away from the central nervous system to target muscles and glands. Therefore efferent axons can be found in muscles or glands. |
front 40 What is an axon and it's function? | back 40 An axon or nerve fiber, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. |
front 41 Describe the gross anatomy of the spine. | back 41 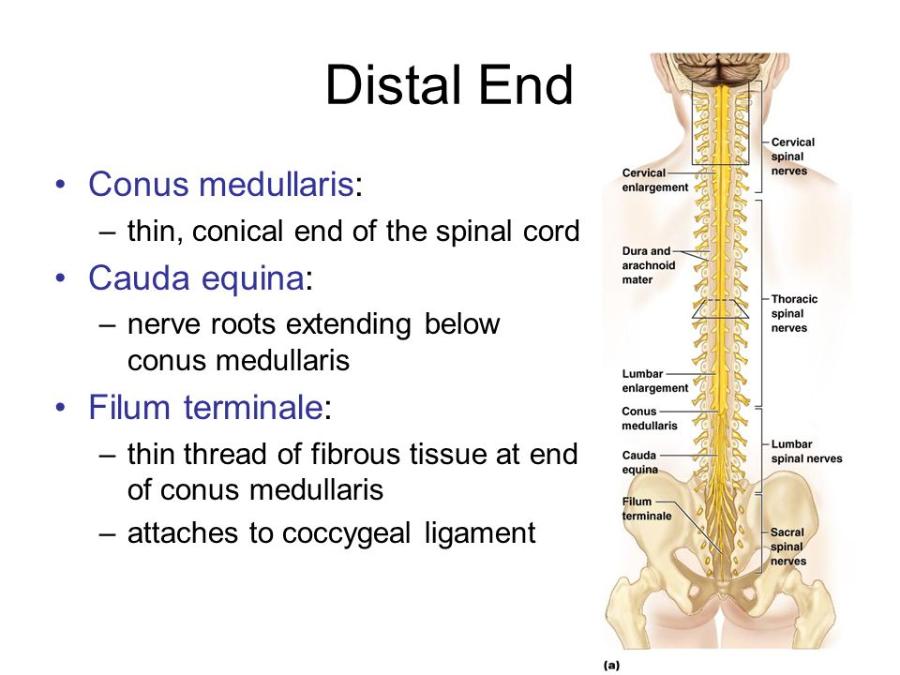 The top of the spine begins at the foramen magum and ends near the L1 vertebra. The spinal cord does not extend all the way down the vertebrae. Conus medullaris - is the top tip of the spinal cord Cauda equina - nerve roots extending below the conus medullaris Filum terminale - is an extension of the pia mater of the spinal cord and attaches to the conus medullaris to the coccyx (tail bone). |