Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Module I
front 1 In Griffith’s experiments, what made the harmless R cells grow capsules when exposed to heat-killed S cells? | back 1 DNA |
front 2 In the Hershey-Chase experiment radioactive Sulfur was used to: | back 2 Be incorporated into the phage protein coat because some amino acids contain sulfur |
front 3 The experiments by Hershey and Chase helped confirm that DNA was the hereditary material on the basis of the finding that: | back 3 Radioactive phosphorus was found inside the cell |
front 4 If DNA of a particular species was analyzed and it was found that it contains 27 percent of adenine (A), what would be the percentage of cytosine (C)? | back 4 23 percent |
front 5 Four nucleic acid samples are analyzed to determine the percentages of the nucleotides they contain. Which of the following DNA sample(s) could be double-stranded DNA? Sample 1: A(22%), G(28%), T(22%), U(0%), C(28%); Sample 2: A(30%), G(30%), T(0%), U(20%), C(20%); Sample 3: A(18%), G(32%), T(0%), U(18%), C(32%); Sample 4: A(29%), G(29%), T(21%), U(0%), C(21%) | back 5 Sample 1 |
front 6 Your chromosomes are located _______ and they are made of ___________ . | back 6 inside the nucleus, DNA |
front 7 A nucleotide is made of _______. | back 7 sugar + phosphate + nitrogen base |
front 8 A molecule of RNA (ribonucleic acid) contains the bases _______. | back 8 adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil |
front 9 Which of the following does cytosine pair with? | back 9 Guanine |
front 10 Prokaryotes contain a _________ chromosome, and eukaryotes contain ________ chromosomes. | back 10 double-stranded circular; double stranded linear |
front 11 How long would the peptide be that is translated from this mRNA sequence: 5'- AUGGGCUACCGA -3'? | back 11 4 amino acids |
front 12 What is the correct sequence of steps in the central dogma? | back 12 DNA->RNA->Protein |
front 13 Where does transcription take place in human cells? | back 13 Nucleus |
front 14 Where does translation take place in eukaryotic cells? | back 14 Cytoplasm |
front 15 Transcribe the following DNA sequence (non template strand): 5'-ATGGCCGGTTATTAAGCA-3' | back 15 5'-AUGGCCGGUUAUUAAGCA-3' |
front 16 In which of the following pairs do both evolutionary processes introduce new genetic variation into a population? | back 16 Mutation and gene flow |
front 17 Mutation can be defined as the addition of genetic variation that increases the hereditary diversity of a population. T/F | back 17 True |
front 18 If an allele has a frequency of 1: | back 18 It is found in 100% of the population |
front 19 When male lions reach sexual maturity, they leave their group in search of a new pride. This can alter the allele frequencies of the population through which of the following mechanisms? | back 19 Gene flow |
front 20 When closely related individuals mate with each other, or inbreed, the offspring are often not as fit as the offspring of two unrelated individuals. Why? | back 20 Inbreeding can bring together rare, deleterious mutations that lead to harmful phenotypes. |
front 21 Which statement about analogies is correct? | back 21 They are derived by similar environmental constraints. |
front 22 What do scientists use to apply cladistics? | back 22 homologous traits |
front 23 What is true about organisms that are a part of the same clade? | back 23 They evolved from a shared ancestor. |
front 24 Why do scientists apply the concept of maximum parsimony? | back 24 to decipher accurate phylogenies |
front 25 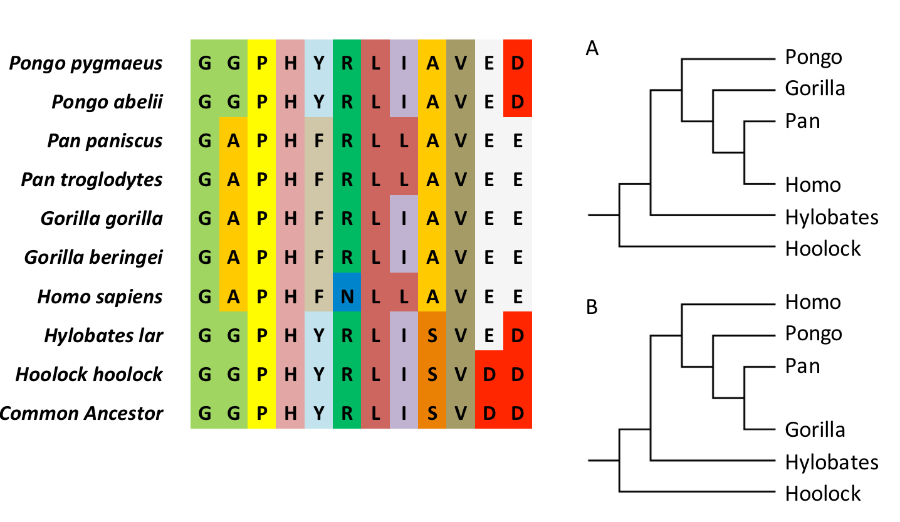 Which one is the correct tree? | back 25 Tree A |
front 26 Alternate forms of a gene are called _______. | back 26 alleles |
front 27 Describing a person as having hemophilia is to indicate his or her ______. | back 27 phenotype |
front 28 Why do your chromosomes come in pairs? | back 28 Because one member of each pair came from my mother and the other from my father. |
front 29 How did Mendel get the peas to cross-fertilize? | back 29 He kept them apart and pollinated them by hand. |
front 30 The observable traits expressed by an organism are described as its ________. | back 30 phenotype |
front 31 Half of the gametes produced by an organism with the genotype Aa will receive the A allele, while half will receive the a allele. This is a demonstration of ______. | back 31 segregation |
front 32 Which of the following is true about genes that are located on different chromosomes? | back 32 These genes are inherited independently of each other. |
front 33 A recessive trait will be observed in individuals that are ________ for that trait. | back 33 homozygous |
front 34 What are the types of gametes that can be produced by an individual with the genotype AaBb? | back 34 AB, Ab, aB, ab |
front 35 How many different types of gametes could an organism with the genotype AABbCc produce? | back 35 4 |
front 36 Genetic inheritance is being studied in a certain species of plant in which orange flower color (O) is dominant to white (o) and round leaf shape (S) is dominant to oval (s). A true-breeding orange-flowered, round-leaved male plant (Plant A) is mated with a true-breeding white-flowered, oval-leaved female plant (Plant B) to produce dihybrid offspring plant (Plant C). Assuming normal Mendelian genetics and independent inheritance of these two traits, which gametes might be produced by Plant C? | back 36 Both OS and oS |
front 37 In guinea pigs coat color is determined by a single gene with two alleles. A guinea pig from a true-breeding black strain is mated with a guinea pig from a true-breeding white strain. The F1 progeny are all black. Two of the F1 progeny are mated with each other. What proportion of the F2 progeny is expected to be white? | back 37 1/4 |
front 38 In guinea pigs coat color is determined by a single gene with two alleles. A guinea pig from a true-breeding black strain is mated with a guinea pig from a true-breeding white strain. The F1 progeny are all black. Two of the F1 progeny are mated with each other. What proportion of the black F2 progeny is expected to be homozygous? | back 38 1/3 |
front 39 The presence of short hairs on leaves is controlled by dominant allele H. Plants with genotype hh have smooth leaves. Two parental plants with unknown genotype were crossed. What are the parental genotypes if F1= 32 Hairy and 11 smooth? | back 39 Hh x Hh |
front 40 The presence of short hairs on leaves is controlled by dominant allele H. Plants with genotype hh have smooth leaves. Two parental plants with unknown genotype were crossed. What are the parental genotypes if F1= 0 Hairy and 24 smooth? | back 40 hh x hh |
front 41 Mendel imagined that seed color in pea plants is influenced by a gene with two alleles in which the allele for yellow seeds (Y) is dominant over the allele for green seeds (y). What would Mendel predict the seed colors would be from a cross of a male plant with the mixed Yy genotype with a female plant with the yy genotype? | back 41 There should be 1 green seed for every 1 yellow seed. |
front 42 In apples, the allele A is dominant for a big size apple and the allele R is dominant for red color. You cross one tree that produces big yellow apples and another tree that produces small red apples. Half of the offspring trees produce big red apples and half produce big yellow apples. What are the genotypes of the parents? | back 42 AArr and aaRr |
front 43 You have flipped a standard quarter 10 times and had four head and six tails come up. With that experience, what will be the chances of you getting a heads on the next flip? | back 43 50% |
front 44 If a student randomly guesses at five multiple-choice questions during a BIO 340 exam, find the probability that the student gets exactly three correct. Each question has five possible choices. | back 44 0.05 |
front 45 What is the probability of having 4 girls in a row? | back 45 1 in 16 |
front 46 In a cross between two heterozygous plants (Tt x Tt), what is the probability of a plant being homozygous given that it is tall? | back 46 0.33 |
front 47 What is the probability that the following pair of parents will produce the indicated offspring? TTRrYy x TtRrYy -> TTrrYY | back 47 1/32 |
front 48 John has alkaptonuria; it "runs in the family". John and his grandmother are both homozygous for alkaptonuria. John's grandmother has two brothers and a sister. One of the brothers had alkaptonuria and his daughter is John's mother. Based on this information, John's parents are: | back 48 Both heterozygous for the alkaptonuria gene. |
front 49 If John marries someone who is heterozygous for alkaptonuria, then which of the following statements is true? Remember alkaptonuria is a recessive disorder. | back 49 All of the children will inherit at least one copy of the alkaptonuria gene. |
front 50 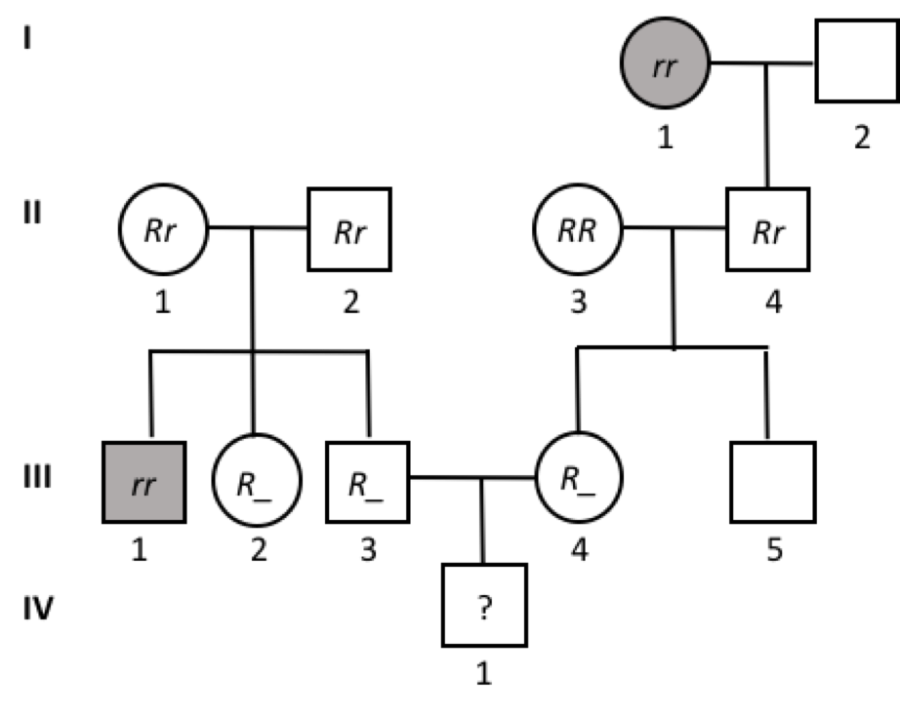 What is the probability that III-3 is a carrier (Rr)? | back 50 2/3 |
front 51 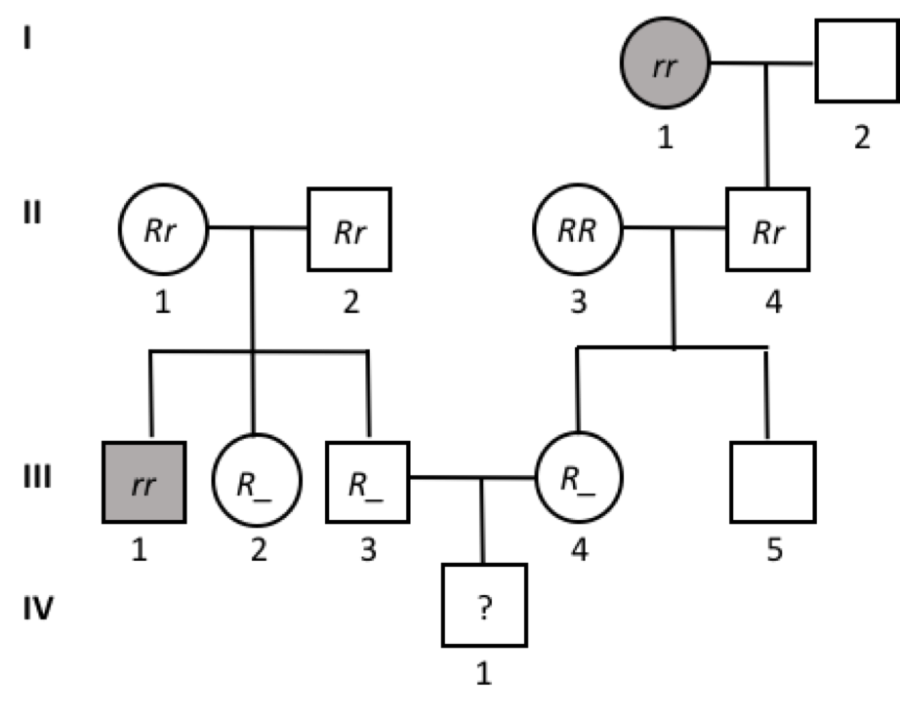 What is the probability that III-4 is a carrier (Rr)? | back 51 1/2 |
front 52 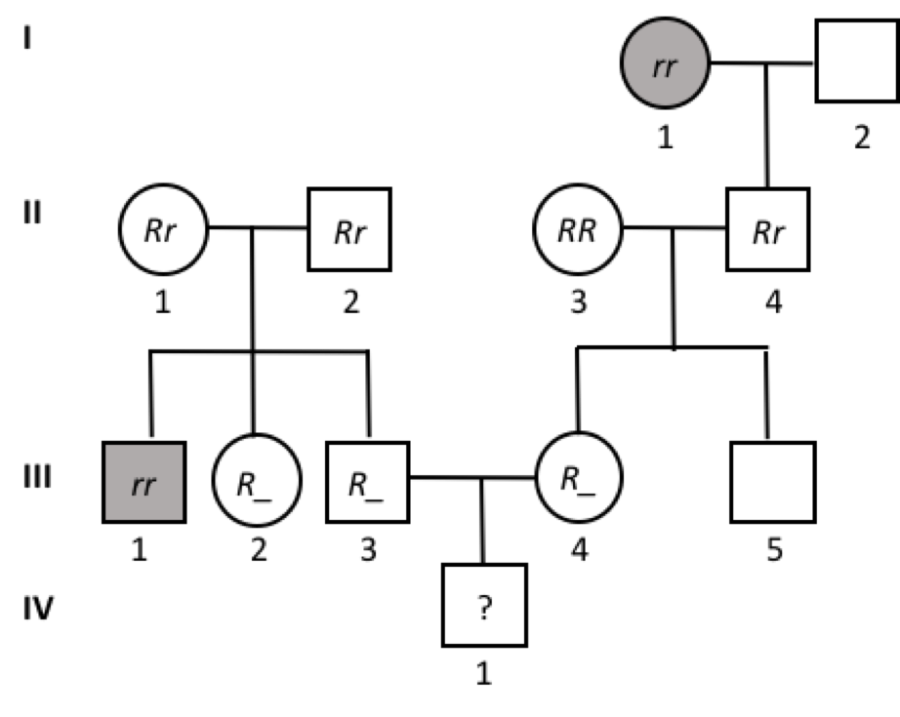 What is the probability that IV-1 is affected (rr)? | back 52 1/12 |
front 53 Daughter cells produced by mitosis _______. | back 53 are genetically identical to the parent cell |
front 54 Besides growth, what must happen before a cell divides? | back 54 DNA replication. |
front 55 The division of the cytoplasm following mitosis to form two new cells is called? | back 55 Cytokinesis |
front 56 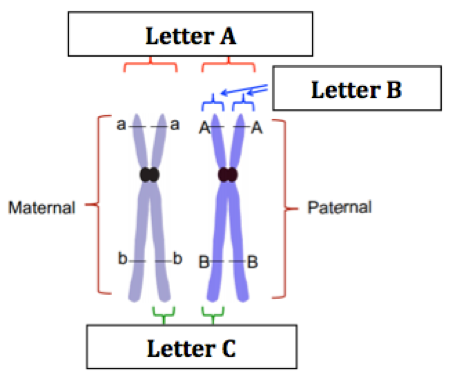 In the figure, "Letter B" represents: | back 56 Sister chromatids |
front 57 Which of the following is the correct order of events in mitosis? | back 57 The kinetochore becomes attached to the mitotic spindle. Sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate. Cohesin proteins break down and the sister chromatids separate. The nucleus reforms and the cell divides. |
front 58 Meiosis produces ________ daughter cells. | back 58 four haploid |
front 59 If a muscle cell of a typical organism has 32 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will be in a gamete of that same organism? | back 59 16 |
front 60 Which of the following events is unique to prophase I of meiosis? | back 60 Pairing of homologous chromosomes. |
front 61 At metaphase I, homologous chromosomes are connected only at what structures? | back 61 Chiasmata |
front 62 In which nuclear division process do sister chromatids segregate? | back 62 In mitosis and meiosis II. |
front 63 In a cross between a homozygous red-eyed female fruit fly and a white-eyed male fruit fly, what is the expected outcome? | back 63 All offspring with red eyes. |
front 64 In a cross between a white-eyed female fruit fly and a red-eyed male fruit fly, what is the expected outcome? | back 64 All male offspring with white eyes. |
front 65 Hemophilia has an X-linked recessive pattern. It is carried on the “X” chromosome. It is only expressed phenotypically as homozygous recessive in women but men that inherit the affected chromosome will suffer from the disorder. A carrier woman (one affected X chromosome) married a man with hemophilia, and they have children. What percent of their boy children will be affected with hemophilia? | back 65 50% of the boy children. |
front 66 What would a female genotype have to be for her to have the genetic disease hemophilia? | back 66 Both her X chromosomes would have to have the recessive hemophilia gene. |
front 67 Congenital generalized hypertrichosis is an X-linked dominant disease. If an affected male marries an unaffected female, what is the probability of passing the hypertrichosis gene to his offspring? | back 67 p=0.5, all daughters will be affected. |
front 68 Human sex-linked transmission | back 68 In X-linked recessive inheritance, females homozygous In X-linked dominant traits, heterozygous females and |
front 69 X-linked inheritance is theterm for traits carried on the X chromosome; males have only one X and so are called hemizygous for X-linked traits | back 69 no data |
front 70 X-linked dominant trait transmission | back 70 The distinctive characteristics of X-linked dominant
traits |
front 71 List below all probable transfers proposed by Dr. Crick. | back 71 DNA > DNA RNA > RNA DNA > RNA RNA > Protein |
front 72 List below all possible transfers proposed by Dr. Crick. | back 72 DNA > Protein RNA > DNA |
front 73 List below all impossible transfers proposed by Dr. crick | back 73 Protein > DNA Protein > RNA Protein > Protein |
front 74 The basis of Dr. Crick’s 1970 paper was to clarify the central dogma of molecular biology in response to the “Central Dogma Reversed” publication put forth by Dr. Howard Temin. According to Dr. Crick, the work of Dr. Temin suggests what? | back 74 Tumor viruses containing RNA as their genetic material can use viral RNA as a template for DNA synthesis. |
front 75 The alleles of a particular gene segregate independently into individual gametes (sex cells) during meiosis. T/F | back 75 True |
front 76 You cross a pea plant with purple flowers to a plant with white flowers. The resulting offspring have a mixture of purple and white flowers. What were the possible genotypes of the parents if the purple allele is dominant (B) and the white allele is recessive (b)? (Hint: draw Punnett squares). | back 76 Parent 1: Bb, Parent 2: bb |
front 77 Two diploid individuals, one homozygous and the other heterozygous at a particular gene, make babies. Which of the following statements about the offspring genotype is correct? (Hint: draw Punnett squares) | back 77 1/2 of the offspring are homozygotes and 1/2 are heterozygotes |
front 78 The DNA sequence of a gene is a phenotype. T/F | back 78 False |
front 79 Consider a plant character, leaf shape. In a tree species, it has been determined that leaf shape is controlled by a single gene segregating two alleles, and havingrounded leaves is dominant to elongated leaves. An experiment that crossed a rounded-leaf plant with an elongated-leaf plant, both from true-breeding lines, found the following results: all F1 offspring have rounded leaves. F2 offspring, which came from selfing of F1 individuals, also all have rounded leaves. A hypothesis suggests that the law of _______ is most likely violated in this mating. Fill in the blank. | back 79 Segregation |
front 80 Mendel's law of Independent Assortment describes the independent movement of _______ into ______ during meiosis. | back 80 alleles of different genes, gametes |
front 81 Consider a diploid organism. What is the phenotypic ratio expected to be observed in the offspring produced by two homozygous recessive parents? | back 81 0 dominant: 1 recessive |
front 82 What are the possible values for the probability "P(A)"? | back 82 Between 0 and 1, including both 0 and 1 |
front 83 Under what conditions should you use the addition/sum rule and what notion should you use? | back 83 With mutually exclusive events; P(A or B) |
front 84 In the binomial probability distribution formula, there are three unique variables. What does each one stand for (in the order of p, n, k)? | back 84 Probability of success, number of trials, number of successes |
front 85 Cross together two heterozygous parents for pea color (genotypes: Gg for both parents; G = yellow, g = green.) What is the probability that a plant in the F1generation has yellow peas? | back 85 3/4 |
front 86 Cross together two double heterozygous parents for plant height and flower color (genotypes: SsWw for both parents; S = tall, s = short, W = purple/violet, and w = white.) What is the probability that a randomly selected offspring will be short and have purple/violet flowers? | back 86 3/16 |
front 87 Under what conditions should you use the multiplication/product rule and what notation should you use? | back 87 With independent events; P(A and B) |
front 88 DNA replication is classified as _______________ replication | back 88 Semi-conservative |
front 89 Given this DNA template strand (3'-CTGAGGCATATCAC-5'), select the correct RNA transcript. | back 89 5'-GACUCCGUAUAGUG-3' |
front 90 I mentioned an exception to the classic Central Dogma in my video. What was the exception? | back 90 RNA to DNA |
front 91 The Central Dogma states DNA turns into RNA and RNA turns into protein. T/F | back 91 False |
front 92 Translate the following mRNA transcript: 5'-AUGCCGUCAGGGUGA-3' | back 92 Met - Pro - Ser - Gly - Stop |
front 93 What is the process by which RNA is synthesized from a DNA template? | back 93 Transcription |
front 94 What is the process by which protein is synthesized from a RNA template? | back 94 Translation |
front 95 Who proposed the Central Dogma of molecular biology? | back 95 Francis Crick |