Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
The Respiratory System
front 1 Which of the following is not part of the upper respiratory system?
| back 1 D |
front 2 The conducting zone does NOT act to
| back 2 E |
front 3 The nose connects with the pharynx through the
| back 3 C |
front 4 Which of the following is a passageway for air, food and water?
| back 4 A |
front 5 The opening to the pharynx from the mouth is called
| back 5 D |
front 6 This structure prevents food or water from entering the trachea.
| back 6 B |
front 7 During swallowing, which structure rises?
| back 7 A |
front 8 These are triangular pieces of mostly hyaline cartilage located at the posterior and superior border of the cricoid cartilage.
| back 8 B |
front 9 Pitch is controlled by
| back 9 B |
front 10 This is located anterior to the esophagus and carries air to the bronchi.
| back 10 A |
front 11 This is the primary gas exchange site.
| back 11 D |
front 12 Which of the below tissues maintains open airways in the lower respiratory system?
| back 12 C |
front 13 Which of the below tissues provides the functions of the inner layer of the conducting organs?
| back 13 B |
front 14 The point where the trachea divides into right and left primary bronchi is a ridge called
| back 14 A |
front 15 Which of the below tissues forms the exchange surfaces of the alveolus?
| back 15 C |
front 16 These are cells of the alveoli that produce surfactant.
| back 16 B |
front 17 This is direction of diffusion of gases at capillaries near systemic cells.
| back 17 B |
front 18 This is direction of diffusion of gases at the alveoli of the lungs.
| back 18 C |
front 19 Exhalation begins when
| back 19 A |
front 20 This means the lungs and the chest wall expand easily.
| back 20 C |
front 21 The conducting airways with the air that does not undergo respiratory exchange are known as the
| back 21 E |
front 22 This is the sum of the residual and the expiratory reserve volume.
| back 22 B |
front 23 Which of the following is not a factor that the rate of pulmonary and systemic gas exchange depends on.
| back 23 E |
front 24 Which is the dominant method of carbon dioxide transport?
| back 24 D |
front 25 When blood pH drops then the amount of oxyhemoglobin _______ and oxygen delivery to the tissue cells ________________.
| back 25 C |
front 26 Which is a factor that does NOT affect hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen?
| back 26 E |
front 27 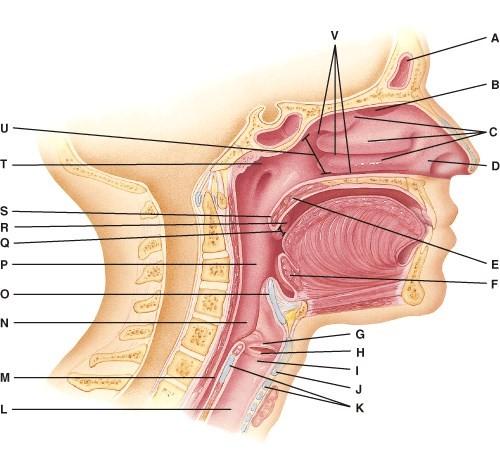 Where are the nasal conchae?
| back 27 B |
front 28  This portion of the pharynx has five openings in its wall.
| back 28 E |
front 29  Which tonsils are found in the oropharynx?
| back 29 B |
front 30  What is also referred to as the Adam’s Apple?
| back 30 D |
front 31  Where is the larynx?
| back 31 A |
front 32  This is a ring of hyaline cartilage that forms the inferior wall of the larynx.
| back 32 B |
front 33  Where is the uvula?
| back 33 D |
front 34  Where are the palatine tonsils?
| back 34 C |
front 35  Where is the soft palate?
| back 35 B |
front 36  Where is the epiglottis?
| back 36 A |
front 37  Where are the olfactory receptors found?
| back 37 B |
front 38 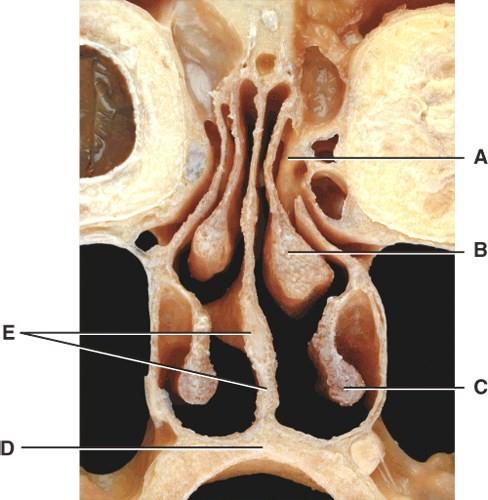 Where is the middle nasal concha?
| back 38 B |
front 39  Where is the inferior nasal concha?
| back 39 C |
front 40  What is E pointing to?
| back 40 D |
front 41 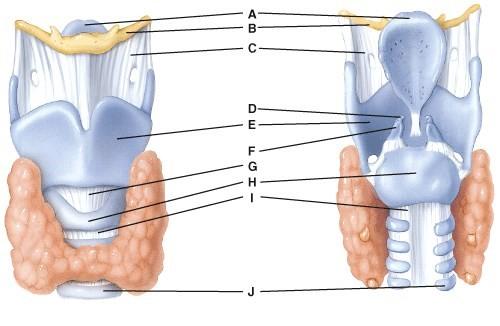 What is line D pointing to?
| back 41 B |
front 42  Where is the cricoid cartilage?
| back 42 E |
front 43  Where is the tracheal cartilage?
| back 43 A |
front 44  What is line A pointing to?
| back 44 E |
front 45 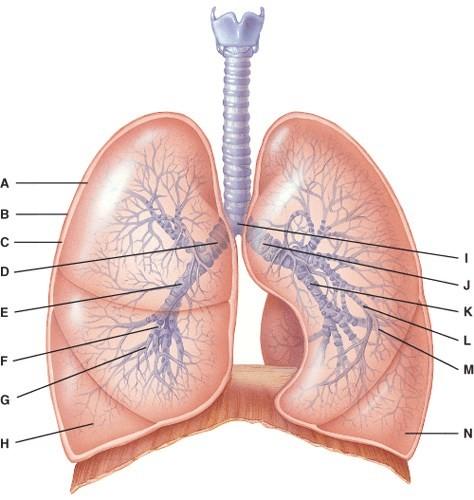 Where is the structure that regulates air flow to the alveolus?
| back 45 B |
front 46  What is line J pointing to?
| back 46 D |
front 47  Where is the right bronchiole?
| back 47 B |
front 48  What lines are pointing to tertiary bronchi?
| back 48 C |
front 49  What is line B pointing to?
| back 49 C |
front 50 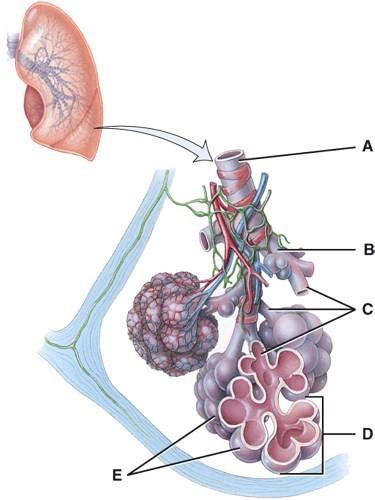 In this portion of the lungs, the epithelial lining is simple squamous.
| back 50 E |
front 51  This is the primary gas exchange structure.
| back 51 E |
front 52  What is line C pointing to?
| back 52 C |
front 53  Where is the terminal bronchiole?
| back 53 A |
front 54 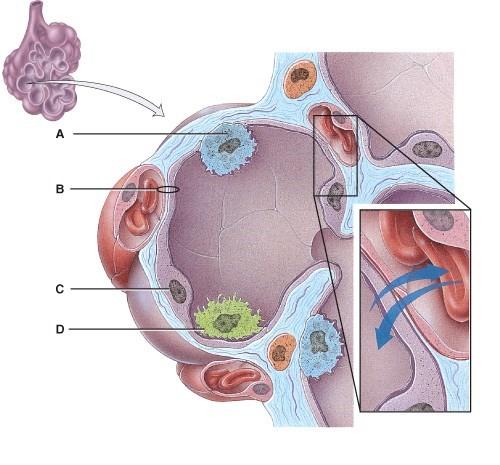 This provides disease resistance within the lungs.
| back 54 D |
front 55  Which cells are the main sites of gas exchange?
| back 55 C |
front 56  Which cell secretes surfactant?
| back 56 A |