Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
AP Biology
front 1 One category of a virus is the retroviruses, like HIV, | back 1 They use reverse transcriptase to make DNA |
front 2 If a virus has an envelope, it is usually made out of: | back 2 Membrane taken from host cells |
front 3 In the LYTIC cycle of bacteriophages – | back 3 Host DNA is degraded |
front 4 what would result in greater activity | back 4 Lower levels of ubiquitin |
front 5 In eukaryotic cells, the addition of ____ groups to | back 5 Acetyl |
front 6 In eukaryotic cells, the signal that often tells the | back 6 The attaching of ubiquitin to the protein. |
front 7 If an operon is under positive repressible regulation: | back 7 It is normally transcribing and removing an |
front 8 If a single base pair mutation in the DNA changes the | back 8 Silent |
front 9 What is a polyribosome? | back 9 An mRNA being translated by more than one |
front 10 What would happen if a cell was missing SRP? | back 10 Ribosomes could not be attached to the |
front 11 How is transcription terminated in eukaryotic cells? | back 11 Proteins cut the RNA free from the RNA |
front 12 The P site of the ribosome usually holds | back 12 A tRNA with a polypeptide attached to it |
front 13 Transcription in eukaryotes begins when transcription | back 13 A TATA box in the promoter region |
front 14 During the copying of DNA, what action happens | back 14 DNA Helicase attaches at a site of origin |
front 15 _____ is the process that makes new copies of DNA | back 15 Replication |
front 16 Primers are synthesized where on the lagging strand? | back 16 At the beginning of every Okazaki fragment |
front 17 What is the job of DNA polymerase I in the process | back 17 Replacing RNA primers with DNA |
front 18 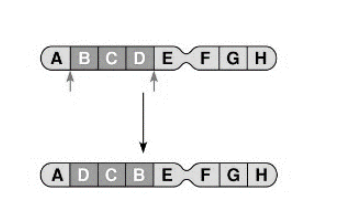 The figure above shows an example of a chromosomal | back 18 inversion |
front 19 If homologous chromosomes fail to separate during | back 19 Nondisjunction |
front 20 What is polygenic Inheritance? | back 20 When multiple genes contribute to the |
front 21 What is the probability that an AABBCC x AaBbCc | back 21 1/8 |
front 22 In tigers, the absence of fur pigmentation is caused by A) Pleiotropy | back 22 A) Pleiotropy |
front 23 During gamete formation the segregation of the alleles | back 23 Law of independent assortment |
front 24 What is the probability of Aabb x aaBb parents | back 24 3/4 |