Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 1
front 1 Drag the images to arrange them by level of complexity from least to most complex, in order from left to right. Tissue Level Organ Level Cellular Level Organ system level Chemical level | back 1 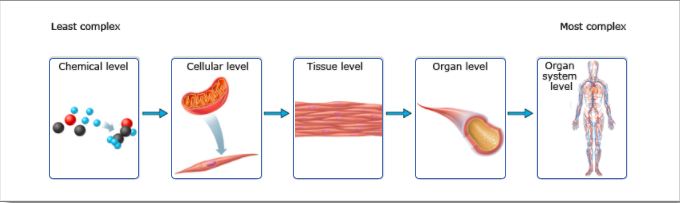 |
front 2 Which of the following is true regarding the anatomical position? -It is a visual reference point only used in the various imaging techniques. -The feet are placed at exactly 45 degrees outward. -The person is seated with head facing forward. -The palms face posteriorly with the thumbs pointed toward the body. -Directional terminology refers to the body in this position. | back 2 Directional terminology refers to the body in this position. |
front 3 Which of the following statements are accurate concerning light microscopy? -It provides three-dimensional pictures of whole, unsectioned surfaces. -It is limited because it cannot produce sharp images of structures within cells. -It uses acidic and basic dyes to stain structures. -Tissues are stained with heavy metal salts. -It uses a beam of electrons to view cellular structures. | back 3 It is limited because it cannot produce sharp images of structures within cells. |
front 4 Choose between chemical level, cellular level, tissue level, organ level, or organ system level.
| back 4  |
front 5 Which of the following best represents an example at the organ level? -Smooth muscle in the large intestine -Hydrochloric acid -Digestive enzymes -Stomach -Enterocytes (cells that line the small intestine) | back 5 Stomach |
front 6 The proximal convoluted tubule is a structure within the kidney nephron that plays a significant role in the reabsorption of important products that have been filtered from the blood. One of the key features of this structure is its lining. The cells that line the tubule are responsible for the transport of substances across the membrane. These cells and their collective efforts would be an example of which of the following levels? -Tissue level -Organ level -Organismal level -Molecular level -Cellular level | back 6 Tissue level |
front 7 Drag and drop each of the organizational levels so that they are in the correct order, ranking them from the simplest to the most complex. chemical level, cellular level, tissue level, organ level, organ system level, or organismal level | back 7 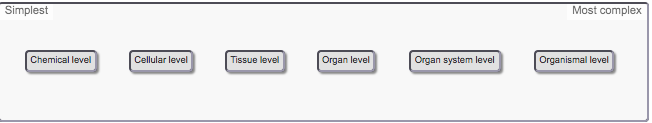 |
front 8 Choose between organ level, chemical level, tissue level, cellular level, or organ system level.
| back 8 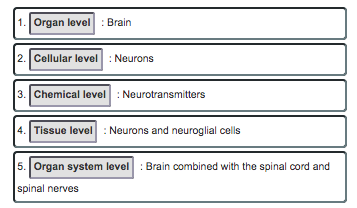 |
front 9 Choose between organ level, chemical level, tissue level, cellular level, or organ system level.
| back 9  |
front 10 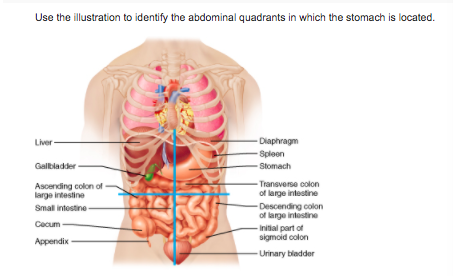 right upper quadrant and right lower quadrant left upper quadrant and left lower quadrant right upper quadrant and left upper quadrant left lower quadrant and right lower quadrant | back 10 right upper quadrant and left upper quadrant |
front 11 All vertebrates have specific identifying characteristics during some point of development. A partial listing of these characteristics is __________. -ventral hollow nerve cord, radial symmetry, and tube-within-a-tube -pharyngeal pouches, coronal symmetry, and anatomical position -tube-within-a-tube, notochord, and ventral hollow nerve cord -radial symmetry, vertebrae, and dorsal hollow notochord -pharyngeal pouches, dorsal hollow nerve cord, and segmentation | back 11 pharyngeal pouches, dorsal hollow nerve cord, and segmentation |
front 12 Bones lie __________ to muscles. | back 12 deep |
front 13 What is the advantage of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) over positron emission tomography (PET)? -fMRI uses sound waves rather than radioactive tracers. -fMRI uses radioactive tracers rather than magnets. -fMRI is better for determining the age of a fetus. -fMRI is better for observing bones.fMRI pinpoints smaller brain areas, does not use radioactive tracers, and works faster. | back 13 fMRI pinpoints smaller brain areas, does not use radioactive tracers, and works faster. |
front 14 Sonography is effectively used for viewing all of the following EXCEPT __________. -arteries -a developing fetus -the gallbladder -the brain and spinal cord | back 14 the brain and spinal cord |
front 15 The right nostril and right ear are __________. | back 15 ipsilateral |
front 16 The word __________ always refers to the part of the serosa that lines a body cavity. | back 16 parietal |
front 17 The levels of structural organization in order of decreasing complexity are __________ -organ system, organism, organ, tissue, chemical, cellular organ, organ system, tissue, cellular, molecular, atomic -organism, organ system, organ, tissue, cellular, chemical -chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism -kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species | back 17 organism, organ system, organ, tissue, cellular, chemical |
front 18 Cells, organelles, and tissues are usually measured in __________. milliliters micrometers centimeters meters | back 18 micrometers |
front 19 Which set of orientation and directional terms is NOT correctly matched with its opposite? contralateral: ipsilateral proximal: distal posterior: anterior superficial: deep distal: superior | back 19 distal: superior |
front 20 Levels of Structural Organization | back 20 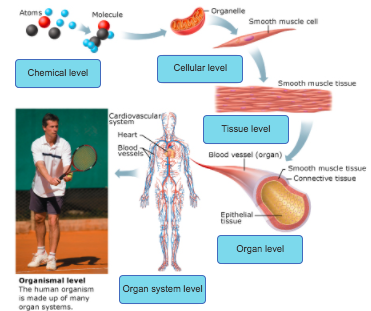 |
front 21 Dorsal and ventral body cavities and their subdivisions cranial cavity, vertebral cavity, thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, and pelvic cavity | back 21 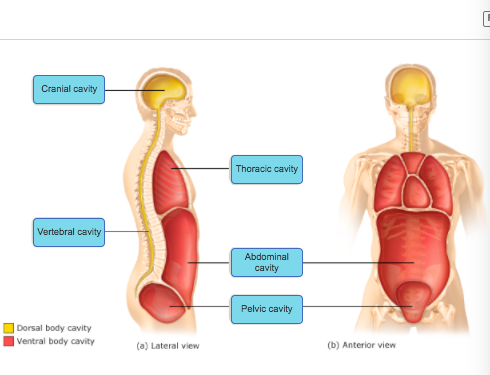 |
front 22 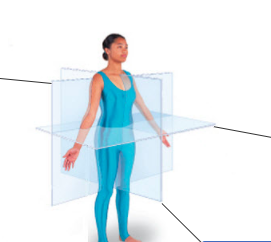 frontal plant, transverse plane and median plane | back 22 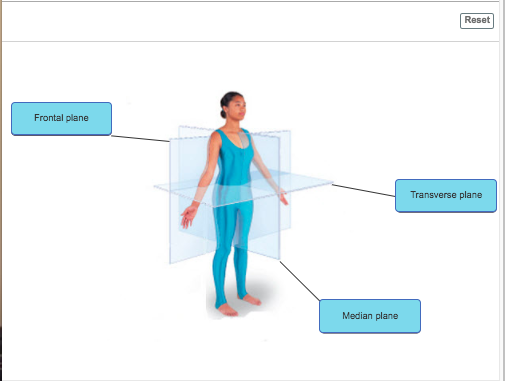 |
front 23 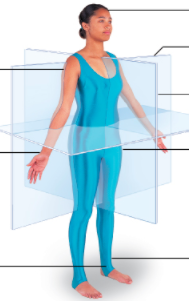 Superior frontal plane proximal distal inferior median plane medial lateral | back 23 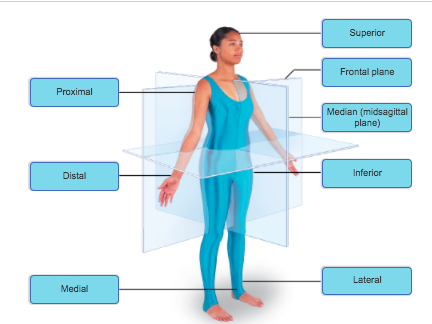 |
front 24 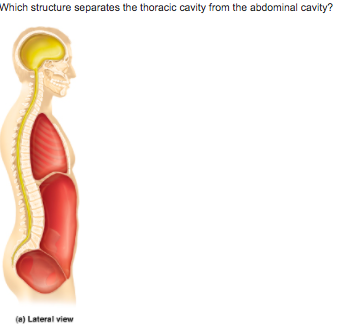 ventral body cavity mediastinum vertebral column diaphragm | back 24 diaphragm |
front 25 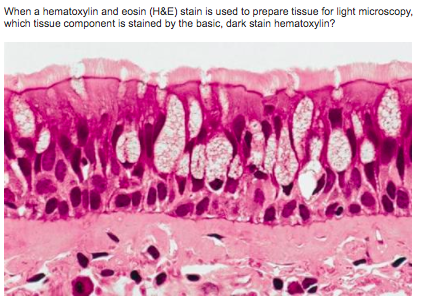 cilia cellular cytoplasm cellular nuclei extracellular material | back 25 cellular nuclei |
front 26 During the process of ________, noncellular artifacts can be introduced into histology samples. -time -observation -staining -photography | back 26 staining |
front 27 The main purpose of fixation is -to make an organ easier to section. -to preserve the tissue. -to stick tissue sections to a glass slide. -to mend breaks in tissue sections. | back 27 to preserve the tissue. |
front 28 What is the major difference in scanning electron microscopy (SEM) when compared to light microscopy (LM) or transmission electron microscopy (TEM)? -SEM is not good at viewing higher magnifications. -SEM uses whole, unsectioned surfaces that are covered in carbon and gold dust. -SEM uses a beam of light to view specimens. -The original image is in black and white. | back 28 SEM uses whole, unsectioned surfaces that are covered in carbon and gold dust. |
front 29 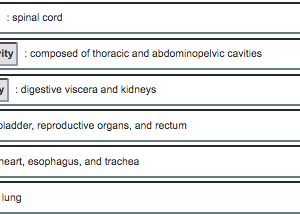 choose between vertral, ventral body, abdominal, pelvic, mediastinum, or pleural | back 29 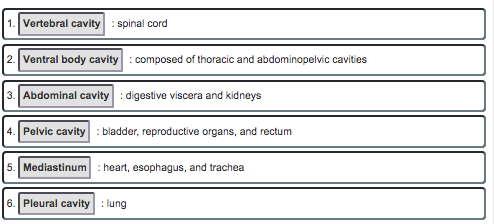 |
front 30 Patients with appendicitis often complain of abdominal pain in the right lower abdominopelvic quadrant. The appendix itself is in the__________. -right lumbar region -umbilical region -hypogastric region -right iliac region | back 30 right iliac region |
front 31 The smallest living unit is a human being. an organ. a cell. a molecule. | back 31 a cell. |
front 32 Which branch of anatomy studies the structural changes that occur as one ages? regional anatomy developmental anatomy pathological anatomy surface anatomy | back 32 developmental anatomy |
front 33 A histologist examines a specimen that has an epithelium overlying some smooth muscle. This specimen is part of a molecule. an organ. a tissue. a cell. | back 33 an organ. |
front 34 An example of a tissue in the body is epithelium. a muscle cell. a macromolecule. the stomach. | back 34 epithelium. |
front 35 An example of an organ is a fat cell. epithelium. the intestine. the cardiovascular system (but not the circulatory system). | back 35 the intestine. |
front 36 Large molecules such as proteins are called macromolecules. multi-atom units. cells. cellular organelles. | back 36 macromolecules. |
front 37 The roots of anatomical terminology lie mainly in Latin and Greek. German and French. Esperanto. Russian and Old English. | back 37 Latin and Greek. |
front 38 How many centimeters are there in a meter? 100 10 1,000,000 1,000 | back 38 100 |
front 39 EM has much greater resolution than LM. True False | back 39 True |
front 40 Most adults are between 1.5 and 2 meters tall. True False | back 40 true |
front 41 The chest is ________ to the abdomen. superior lateral anterior proximal deep | back 41 superior |
front 42 The knee is ________ to the foot. superior lateral anterior proximal deep | back 42 proximal |
front 43 The brain is ________ to the skull. superior lateral anterior proximal deep | back 43 deep |
front 44 The thumb is ________ to the index finger. superior lateral anterior proximal deep | back 44 lateral |
front 45 Muscles are ________ to the skin. superior lateral anterior proximal deep | back 45 deep |
front 46 The eye is ________ to the occipital region. superior lateral anterior proximal deep | back 46 anterior |
front 47 The heart is ________ to the sternum. superior lateral anterior proximal deep | back 47 deep |
front 48 A coronal section through the human body can -pass through both ears. -provide mirror right and left images. -lie in a horizontal plane. -pass through both the nose and the occipital region. | back 48 -pass through both ears. |
front 49 What is the function of serous membranes? -They act like wrapping paper to hold visceral organs together. -They halt the spread of infection. -They contain gland cells that secrete mucus. -They reduce friction so that viscera move freely. | back 49 -They reduce friction so that viscera move freely. |
front 50 Which organ system covers the external surface of the body, but not the internal surface of the mouth? -lymphatic -cutaneous -digestive -integumentary | back 50 -integumentary |
front 51 Which statement concerning the anatomical position is FALSE? -The knees, elbow, and neck are straight (not bent). -The person is lying down, as straight as possible. -The palms face anteriorly. -The toes point anteriorly, but the fingers point inferiorly | back 51 -The person is lying down, as straight as possible. |
front 52 Bilateral symmetry can apply to objects as well as to animal bodies. Which of the following capital letters of the alphabet is not bilaterally symmetrical? A M L O | back 52 L |
front 53 A frontal plane is the same as a ________ plane. coronal sagittal transverse midsagittal | back 53 coronal |
front 54 Another name for the midsagittal plane is oblique. coronal. parasagittal. median. | back 54 median |
front 55 Which of the following pairs of organs/structures is located ipsilateral? mouth : navel right lung : left lung cecum : sigmoid colon descending colon : spleen | back 55 descending colon : spleen |
front 56 The ________ body cavity contains the brain. ventral dorsal serous lateral | back 56 dorsal |
front 57 The ________ cavity contains the heart and lungs. thoracic dorsal abdominopelvic lateral | back 57 thoracic |
front 58 Which structures are evidence of the vertebrate characteristic of segmentation? branches of the blood vessels multiple joints of fingers subdivisions of the gastrointestinal tract vertebral column | back 58 vertebral column |
front 59 Which statement about visceral serosa is false? -It clings to the surface of organs. -It lines the internal surface of hollow organs. -It is deep to the parietal serosa. -It is continuous with the membrane that covers the outer body wall. | back 59 It lines the internal surface of hollow organs. |
front 60 The ankle lies ________ to the thigh. distal proximal lateral inferior | back 60 distal |
front 61 Serous cavities include the pleural cavity. True False | back 61 True |
front 62 Serous cavities contain air. True False | back 62 False |
front 63 In anatomical position, the palms of the hands face medially toward the thighs. True False | back 63 False |
front 64 A transverse plane could cut the head off the body! True False | back 64 true |
front 65 Hormones are regulatory proteins that are secreted by the ________ system. integumentary lymphatic urinary endocrine | back 65 endocrine |
front 66 Which organ system keeps blood constantly supplied with oxygen, removes carbon dioxide, and contains many air tubes? urinary respiratory endocrine circulatory | back 66 respiratory |
front 67 Someone studying anatomy using the systemic approach could study __________. all the digestive organs landmarks on the surface of the body all the muscles, nerves, and blood vessels of individual areas of the body changes in cells and tissues caused by disease | back 67 all the digestive organs |
front 68 The words anatomy and dissection both derive from Greek word meaning __________. functional morphology cut apart structure landmark | back 68 cut apart |
front 69 Pathological anatomy deals with structural changes caused by disease. True False | back 69 True |
front 70 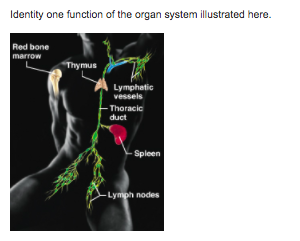 regulates water and electrolyte balance delivers white blood cells to the body tissues carries fluid from body tissues back to the blood vascular system produces bile, which is used to break down ingested fats | back 70 carries fluid from body tissues back to the blood vascular system |
front 71 Which system of the body eliminates nitrogenous wastes and regulates water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance of the blood? urinary lymphatic digestive cardiovascular endocrine | back 71 urinary |
front 72 Which organ system includes the spinal cord? muscular nervous integumentary skeletal | back 72 nervous |