Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Biology Final Exam
front 1 Choose the correct order of classification from most inclusive to exclusive. | back 1 Domain-Kingdom-Phylum-Class-Order-Family-Genus-Species |
front 2 Biodiversity in a particular ecosystem. A. is the total number of species in that ecosystem B. includes the variability of the individual genes C. impacts the function of the ecosystem in which the species live D. All of the choices are correct. | back 2 All of the choices are correct. |
front 3 Which listing correctly indicates a sequence of increasing biological organization? | back 3 atom, molecule, organelle, cell |
front 4 Living and nonliving entities share some characteristics. Which statements are TRUE and which are FALSE about both living and nonliving entities? Both living and nonliving entities exhibit homeostatic controls | back 4 False |
front 5 Which of the following concepts is NOT one of the unifying theories of biology? | back 5 Life may arise through spontaneous generation. |
front 6 A cell is to a tissue as an atom is to a: | back 6 molecule |
front 7 Some members of Daphnia, a water flea, have a genetic mutation that causes them to prefer warmer environments. These members reproduce and pass these genetic changes to their offspring. The next generation will occupy warmer environments not previously occupied by this species. This is an example of: | back 7 adaptation |
front 8 Which of the following does NOT represent homeostasis? | back 8 Energy is captured by plants, then transferred to consumers and decomposers, and eventually lost as heat. |
front 9 Which definition best describes a population? | back 9 the members of a species in a given area |
front 10 (T or F) The classification system most commonly used by biologists today contains five domains. | back 10 False |
front 11 Living organisms on Earth share many common characteristics. Which statements are TRUE and which are FALSE about nearly all living things? Living things are composed only of organic elements, whereas nonliving things are made up of inorganic elements | back 11 False |
front 12 (T or F) Extinction can occur if a species is unable to adapt to a changing environment. | back 12 True |
front 13 Which of the following terms best describes the collection of scientific data through observation in the field, such as observing the behavior of birds? | back 13 descriptive research |
front 14 Which of the following organisms is NOT ultimately dependent on the sun as a source of energy? | back 14 All of the choices ARE ultimately dependent on the sun. |
front 15 Which of the following domains contains the most primitive prokaryotes that live in extreme environments? | back 15 Archaea |
front 16 Which of the following is/are an atom, an isotope and an ion? | back 16 H+ |
front 17 An atom's atomic mass is best described as the mass of | back 17 protons and neutrons it contains. |
front 18 Which statement is NOT true about subatomic particles? | back 18 All electrons in an atom contain the same amount of energy. |
front 19 Which type of covalent bond is the strongest? | back 19 triple |
front 20 Which of the following elements is NOT one of the six most common elements in living organisms? | back 20 iron |
front 21 Which substances are on the basic side of the pH scale? | back 21 baking soda, oven cleaner & human blood |
front 22 If you place the corner of a paper towel into a droplet of water the water moves across the paper towel. Which of the following would explain the movement of the water? | back 22 both cohesion and adhesion |
front 23 Which term refers to the attraction to water molecules? | back 23 hydrophilic |
front 24 Which statement is NOT true about covalent bonds? | back 24 Covalent bonds form when an electron is completely lost or gained from an atom. |
front 25 Which is NOT true about the electrical charges in chemistry? | back 25 In an atom, the number of protons and neutrons must be equal. |
front 26 (T or F) Which of the following statements is/are true about the pH scale? The scale ranges from 1 to 15. | back 26 False |
front 27 The electrons are unequally shared in _______, and transferred in __________. | back 27 CH4, Na+Cl- |
front 28 All of the following are examples of damage caused by acid deposition from rain EXCEPT | back 28 increased agricultural yields |
front 29 An orbital is best described as | back 29 the volume of space in which electrons are most often found. |
front 30 A polysaccharide is a polymer made up of which kind of monomers? | back 30 simple sugars |
front 31 Which carbohydrate is found in the exoskeleton of insects and crabs? | back 31 chitin |
front 32 Which functional group will attach to a hydrocarbon chain to form alcohol? | back 32 hydroxyl |
front 33 Which carbohydrate is found in the cell walls of plants? | back 33 cellulose |
front 34 Saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids differ in: | back 34 all of the choices are differences between saturated and unsaturated fatty acid |
front 35 Which of the following are structural carbohydrate molecules? | back 35 cellulose and chitin |
front 36 A lipid is a polymer made up of which kind of monomers? | back 36 fatty acids and glycerol |
front 37 (T or F) ATP is a protein that supplies energy to the cell. | back 37 False |
front 38 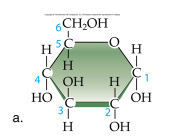 Identify this molecule: | back 38 carbohydrate |
front 39 What is the molecular formula for 5 glucose molecules? | back 39 C30H50O25 |
front 40 (T or F) Carbon can form covalent bonds with as many as four other atoms. | back 40 True |
front 41 Organic molecules are those that contain at least | back 41 carbon and hydrogen. |
front 42 (T or F) Waxes consist of a glycerol bonded to three long-chain fatty acids. | back 42 False |
front 43 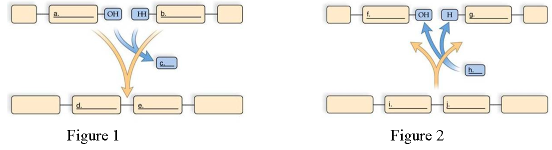 Choose the Figure that depicts polymer synthesis. | back 43 Figure 1 |
front 44 A dehydration reaction can also be called a (an) _________ reaction since it forms water. | back 44 condensation |
front 45 Which carbohydrate is used in the liver for energy storage? | back 45 glycogen |
front 46 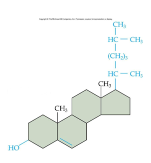 Identify the following molecule: | back 46 cholesterol |
front 47 Which of the following functional groups represents sulfhydryl? | back 47 SH |
front 48 Which one is NOT one of the properties of water? | back 48 the frozen form is more dense than the liquid form |
front 49 Which of the following would NOT be a molecule used for energy storage? | back 49 chitin |
front 50 A peptide bond is found in which type of biological molecule? | back 50 Protein |
front 51 Which of the following gives rise to both lysosomes and vesicles? | back 51 Golgi apparatus |
front 52 DNA is housed within the nucleus, but the mRNA code needs to leave in order to be translated into a protein. How does the mRNA code leave the nucleus if the nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope? | back 52 The nuclear envelope contains pores that allow the mRNA to exit through. |
front 53 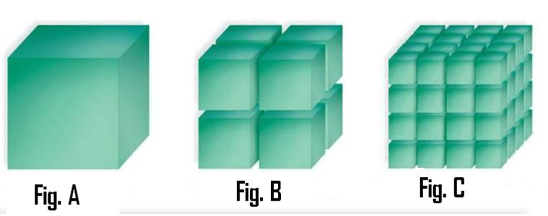 Figures A, B and C to answer Questions 40 - 44. Figure A is an 8-cm. cube. Figure B is eight, 4-cm cubes. Figure C is sixty-four, 2-cm cubes. Diagram What figure has the greatest surface area : volume ratio? | back 53 Figure C |
front 54 Which of the following organelles is found within an autotrophic, eukaryotic cell? | back 54 chloroplast |
front 55 What is the smallest unit of living matter? | back 55 cell |
front 56 The plant cell's central vacuole A. provides the plant cell with support. B. stores nutrients and cellular waste products. C. is a reservoir for water. D. All of the choices are correct. | back 56 All of the choices are correct. |
front 57 Of the following, which is NOT associated with the mitochondria? | back 57 stroma |
front 58 Which organelle is primarily responsible for the breakdown of lipids within the cell? | back 58 peroxisome |
front 59 Which statement is NOT true about bacteria? | back 59 Bacteria contain membrane bound organelles. |
front 60 Which of the following gives rise to both lysosomes and vesicles? | back 60 Golgi apparatus |
front 61 Which cellular organelle is the most prominent? | back 61 nucleus |
front 62 Which of the following features is unique to bacterial cells? | back 62 nucleoid region |
front 63  Use Figures A, B and C to answer Questions 40 - 44. Figure A is an 8-cm. cube. Figure B is eight, 4-cm cubes. Figure C is sixty-four, 2-cm cubes. Diagram What Figure has the greatest volume (height x width x length x number of cubes)? | back 63 All of these have the same volume. |
front 64 Chloroplasts are to ____________ as ___________ are to aerobic respiration. | back 64 photosynthesis, mitochondria |
front 65 Which process is responsible for moving cellular wastes across the cell membrane? | back 65 exocytosis |
front 66 Active transport | back 66 requires an input of ATP. |
front 67 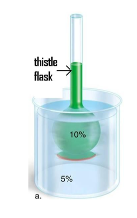 A 10% glucose solution is placed in the thistle tube. The thistle tube is placed in a beaker that contains a 5% glucose solution. Where is the highest concentration of water found? | back 67 In the 5% solution |
front 68 Which type of junctions will create a solid barrier to prevent molecules from moving between the cells? | back 68 tight |
front 69 A major chemical that regulates the fluidity of animal cell membranes by stiffening the membrane at higher temperatures and preventing the membrane from freezing at lower temperature is A. cholesterol B. lipid in nature. C. a steroid. D. All of the choices are correct. | back 69 All of the choices are correct. |
front 70 Proteins in a membrane are: A. peripheral if they are on the inside surface held in place by the cytoskeleton. B. integral if they are embedded in the membrane and protrude from both surfaces of the bilayer. C. integral if they protrude from only one surface of the bilayer. D. All of the choices are correct. | back 70 All of the choices are correct. |
front 71 If a living plant were moved from a freshwater aquarium to a saltwater aquarium, which of the following would occur? | back 71 The plant's cells would lose water and plasmolysis would occur. |
front 72 Which statement is true about the plasma membrane? | back 72 The movement of proteins and phospholipids can occur sideways within the plane of the membrane. |
front 73 Whether a molecule can cross the plasma membrane depends upon A. the size of the molecule. B. the shape of the molecule. C. the chemical properties of the molecule. D. the charge of the molecule. E. All of the choices are correct. | back 73 All of the choices are correct. |
front 74  In the cell pictured, there is no net movement of water. The amount leaving the cell and entering the cell is the same. In what type of environment is this cell found? | back 74 isotonic |
front 75 Which cell junction will allow the movement of molecules between two plant cells? | back 75 plasmodesmata |
front 76 Which of the following is NOT associated with animal cells? | back 76 plasmodesmata |
front 77 (T or F) In the sodium-potassium pump, sodium is transported out of the cell and potassium is transported into the cell as ATP is broken by a membrane protein. | back 77 True |
front 78 Which is the best definition of osmosis? | back 78 The movement of water across a semi permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration. |
front 79 Which of the following situations is most likely to produce a heart attack? | back 79 The gap junctions have collapsed and they do not allow the correct flow of ions from one cell to the next. |
front 80 Photosynthetic pigments capture _____ of the solar energy that reaches the earth. | back 80 less than 2% |
front 81 Which correctly describes the light-independent reactions? | back 81 CO2 is reduced. |
front 82 CO2 fixation occurs when CO2 combines with _____. | back 82 ribulose bisphosphate |
front 83 In photosynthesis: | back 83 carbon dioxide is reduced to sugar. |
front 84 The endproducts of photosynthesis are: | back 84 Glucose and O2 |
front 85 _______ plant pigments absorb light in the violet-blue-green range and therefore appear as shades of yellow and orange. | back 85 Carotenoid |
front 86 About 20-50% of the protein content in chloroplasts is _____, which speeds up CO2 fixation. | back 86 RuBP carboxylase |
front 87 C4 plants fix CO2 to _____. | back 87 PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate) |
front 88 The energy and electrons needed for carbohydrate synthesis during the Calvin Benson Cycle are supplied by: | back 88 NADPH and ATP |
front 89 The oxygen given off by photosynthesis comes from ___________. | back 89 H2O |
front 90 This product of fermentation is lethal to the cells that produce it: | back 90 Alcohol |
front 91 Which of the following statements correctly describes glycolysis? | back 91 Glycolysis produces two molecules of pyruvate. |
front 92 All of the following statements about catabolism are true EXCEPT: A. Catabolism breaks down larger molecules into smaller molecules. B. Catabolic pathways tend to be exergonic. C. Photosynthesis is catabolic. D. Catabolism drives anabolism. | back 92 Photosynthesis is catabolic. |
front 93 If oxygen is not available the pyruvates produced by glycolysis are fed into: | back 93 fermentation. |
front 94 There is/are _____ pyruvate molecule(s) produced per glucose molecule during glycolysis. | back 94 two |
front 95 During fermentation, _____ is regenerated and returns to glycolysis to pick up more electrons. | back 95 NAD+ |
front 96 Which of the following citric acid cycle byproducts is disposed of by our respiratory system when we exhale? | back 96 CO2 |
front 97 Plants are able to synthesize all of the amino acids they need. Humans are only capable of synthesizing 11 amino acids with the others termed _________. | back 97 essential amino acids |
front 98 Iron-containing proteins that are part of electron transport chains are: | back 98 cytochromes |
front 99 When NADH produced during the preparatory reaction and citric acid cycle delivers electrons to the electron transport system, _____ ATP is/are produced. | back 99 3 |
front 100 Which statement below lists the correct steps for binary fission? | back 100
|
front 101 Interphase A. occupies the majority of the cell cycle B. includes G1, S and G2 stages C. results in an increase in cell size D. all of the above E. none of the above | back 101 All of the above |
front 102 Apoptosis A. is programmed cell death. B. is a process that acts to decrease the number of somatic cells. C. frees the fingers and toes of the human embryo from their ‘webbed' structure to independent structures. D. All of the choices are correct. | back 102 All of the choices are correct. |
front 103 (T or F) Viruses and chemical exposure can cause mutations in proto-oncogenes which can lead to cancer. | back 103 True |
front 104 If a parent cell has 48 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have after mitosis and cytokinesis occurs? | back 104 48 chromosomes |
front 105 What is the result of a cell not meeting the criteria to pass the G1checkpoint? A. The cell cycle halts. B. The cell may enter the G0 stage. C. The cell may undergo apoptosis. D. All of the above. E. None of the above. | back 105 All of the above. |
front 106 The critical checkpoints that control the cell cycle are the: | back 106 G1 to S stage and G2 to M stage. |
front 107 (T or F) Contact inhibition stops normal cells from dividing when they come in contact with neighboring cells, but this is not functional in cancer cells. | back 107 True |
front 108 Which represents the correct sequence of stages in the cell cycle? | back 108 G1, S, G2, M |
front 109 The region that contains the genetic information in a bacterial cell is called the | back 109 nucleoid |
front 110 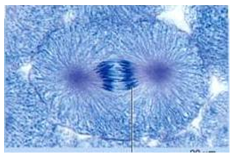 What phase of mitosis is pictured? | back 110 anaphase |
front 111 Which is NOT correctly associated with cancer? | back 111 The disorganized mass of cells is encapsulated and does not invade adjacent tissue. |
front 112 (T or F) The enzymes that bring about apoptosis are: | back 112 True |
front 113 Which of the following is NOT true about cancer cells? | back 113 They exhibit contact inhibition. |
front 114 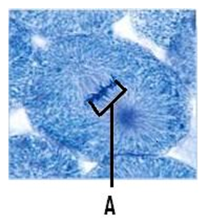 What is (are) the structures designated by the letter ‘A'. | back 114 chromosomes |
front 115 The function of mitosis is: A. growth of the organism and tissue repair. B. to ensure that each new cell receives a complete set of genetic information. C. asexual reproduction in some species. D. All of the choices are correct. | back 115 All of the choices are correct. |
front 116 The haploid (n) number of chromosomes for a human being is | back 116 23 |
front 117 The diploid (2n) number of chromosomes for a human being is | back 117 46 |
front 118 Cancer cells require many nutrients, which are supplied by blood vessels. The growth of new blood vessels to cancerous tissue is called: | back 118 angiogenesis |
front 119 Apoptosis refers to cell death and | back 119 can be programmed and is essential to normal development. |
front 120 What occurs in anaphase? | back 120 Chromosomes move to opposite poles. |
front 121 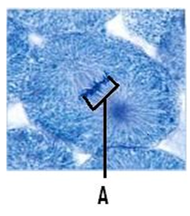 What phase of mitosis is pictured? | back 121 metaphase |
front 122 Although cancer may originate in many regions of the body, many patients die from cancerous growth in the lungs, lymph glands, or liver. This is most readily explained as | back 122 metastasis occurring more commonly in organs that have a filter effect. |
front 123 Which of the following is NOT true concerning mitosis? | back 123 Animal cells form a cell plate during cytokinesis while plant cells do not. |
front 124 Cytokinesis in plant cells differs from this process in animal cells because | back 124 the Golgi apparatus produces vesicles that migrate along microtubules and fuse to become a cell plate. |
front 125 To what does the term chiasma refer? | back 125 a structure that holds together homologues during crossing-over |
front 126 Which is NOT true about daughter cells of mitosis or meiosis? | back 126 In meiosis, the daughter cells are genetically identical. |
front 127 Which of the following statements is true about the life cycle of animals? | back 127 The gametes are the haploid phase of the animals life cycle. |
front 128 If the diploid number of chromosomes for an organism is 52, what will the haploid number of chromosomes be? | back 128 The gametes are the haploid phase of the animals life cycle. |
front 129 If the diploid number of chromosomes for an organism is 52, what will the haploid number of chromosomes be? | back 129 26 |
front 130 Where in the human male does spermatogenesis occur? | back 130 testes |
front 131 Why do polar bodies form?. | back 131 They allow a reduction in chromosomes while preserving most of the cytoplasm for one egg. |
front 132 Species X reproduces asexually by fission and species Y reproduces sexually. Consider that all other relevant characteristics are similar between these species. When the environment changes, then | back 132 species Y should have a better chance of surviving than species X. |
front 133 (T or F) Jacobs Syndrome, XYY, results from nondisjunction during spermatogenesis. | back 133 True |
front 134 All of the following are true concerning Down Syndrome EXCEPT | back 134 chances of a woman having a child with Down Syndrome decreases with her age |
front 135 During which stage of meiosis does the homologue separation occur? | back 135 anaphase I |
front 136 Sources of genetic variation in a sexually reproducing population include(s) which of the following? A. crossing over in Prophase I of meiosis B. independent assortment in Metaphase I of meiosis C. fertilization D. All of the choices are sources of genetic variation. E. None of the choices are sources of genetic variation. | back 136 All of the choices are sources of genetic variation. |
front 137 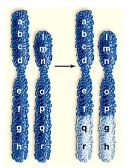 The following picture depicts which of the following changes in chromosome structure. | back 137 translocation |
front 138 Which of the following events occurs during prophase I but does not occur during prophase of mitosis? | back 138 crossing over |
front 139 Meiosis occurs during all of the following EXCEPT | back 139 pangenesis. |
front 140 Which of the following steps would NOT lead to variation of genetic material? | back 140 crossing over of sister chromatids |
front 141 It could be said that males are able to provide gametes with more genetic diversity than females for reproduction. One main reason would be: | back 141 Spermatogenesis in males results in four functional sperm while oogenesis in females results in only one egg and three structures that contain genetic information that is lost when they disintegrate. |
front 142 Which of the following statements is correct about the chromosomal position during mitosis and meiosis? | back 142 During metaphase of mitosis the duplicated chromosomes are at the metaphase plate while during metaphase I of meiosis the bivalents are present at the metaphase plate |
front 143 Characterize the following statements about changes in chromosome
number and structure as True or False. | back 143 True |
front 144 If a sperm cell contains 8 chromosomes, it comes from an animal that has ______ chromosomes. | back 144 16 |
front 145 During which stage of meiosis does crossing-over occur? | back 145 prophase I of meiosis I |
front 146 During which stage of meiosis are the bivalents arranged along the equator? | back 146 metaphase I |
front 147  The following picture depicts which of the following changes in chromosome structure. | back 147 duplication |
front 148 The cell formed through fertilization of an egg by a sperm is called a/an | back 148 zygote |
front 149 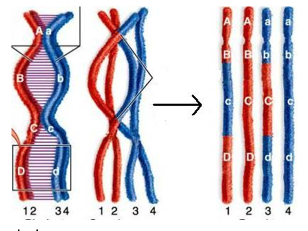 Study the diagram to answer the following questions. Diagram What process is occurring in this diagram? | back 149 crossing over |
front 150 The polar body is | back 150 a nonfunctional cell rudiment formed at the same time as an egg cell. |