Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Lab quiz # 5
front 1 During which part of the cell cycle does dna replication occur ? | back 1 Interphase (s phase) |
front 2 During what stages of mitosis are chromosomes composed of two chromatids ? | back 2 (S phase) of interphase, prophase, anaphase |
front 3 During what stages of mitosis are chromosomes single structures composed of one chromatid? | back 3 Anaphase and telophase |
front 4 How does cytokinesis differ in plant and animal cells? | back 4 Plant- cell plate animal - cleavage |
front 5 Most cells spend the longest amount of time in ? | back 5 Interphase |
front 6 Mitosis | back 6 Series of events result in equal distribution of the chromosomes that carry the genetic information to the two new cells |
front 7 Mitosis | back 7 Cloning |
front 8 meiosis | back 8 Only make eggs |
front 9 mitosis has | back 9 46 parent cells 46 daughter cells -----&--- 46 daughter cells |
front 10 meiosis has | back 10 46 parent cells Meiosis I -46 & 46 Meiosis II- 23,23 & 23, 23 |
front 11 describe the main event happening in any cell undergoing metaphase? | back 11 Spindle is binding to chromosomes, aligning them in cell equator. |
front 12 why is meiosis necessary in sexually reproducing organisms? | back 12 meiosis cuts the chromosomes numbers in half; 23 chromosomes |
front 13 Synapis occurs ? | back 13 meiosis I (prophase I) |
front 14 Crossing over occurs? | back 14 Prophase I |
front 15 Reduction from diploid and haploid occurs ? | back 15 Anaphase II |
front 16 Separation of chromosomes occurs? | back 16 Anaphase II |
front 17 stages of the cell cycle in Mitosis ? | back 17 Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase |
front 18 Cytokinesis occurs ? | back 18 telophase |
front 19 Majority of the life of a cell is spent in a non dividing condition known as? | back 19 interphase |
front 20 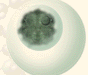 interphase | back 20 The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly discerned in the nucleus, although a dark spot called the nucleolus may be visible. |
front 21 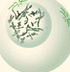 prophase | back 21 Chromatin in the nucleus begins to condense and becomes visible in the light microscope as chromosomes. |
front 22 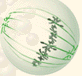 Metaphase | back 22 Spindle fibers align the chromosomes along the middle of the cell nucleus. This line is referred to as the metaphase plate. This organization helps to ensure that in the next phase, when the chromosomes are separated, each new nucleus will receive one copy of each chromosome. |
front 23 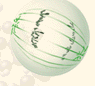 Anaphase | back 23 The paired chromosomes separate at the kinetochores and move to opposite sides of the cell. Motion results from a combination of kinetochore movement along the spindle microtubules and through the physical interaction of polar microtubules. |
front 24  telophase | back 24 New membranes form around the daughter nuclei while the chromosomes disperse and are no longer visible under the light microscope. Cytokinesis or the partitioning of the cell may also begin during this stage. |