Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Vertebrate Histology Exam 2
front 1 Chapter 3: Connective Tissue | back 1 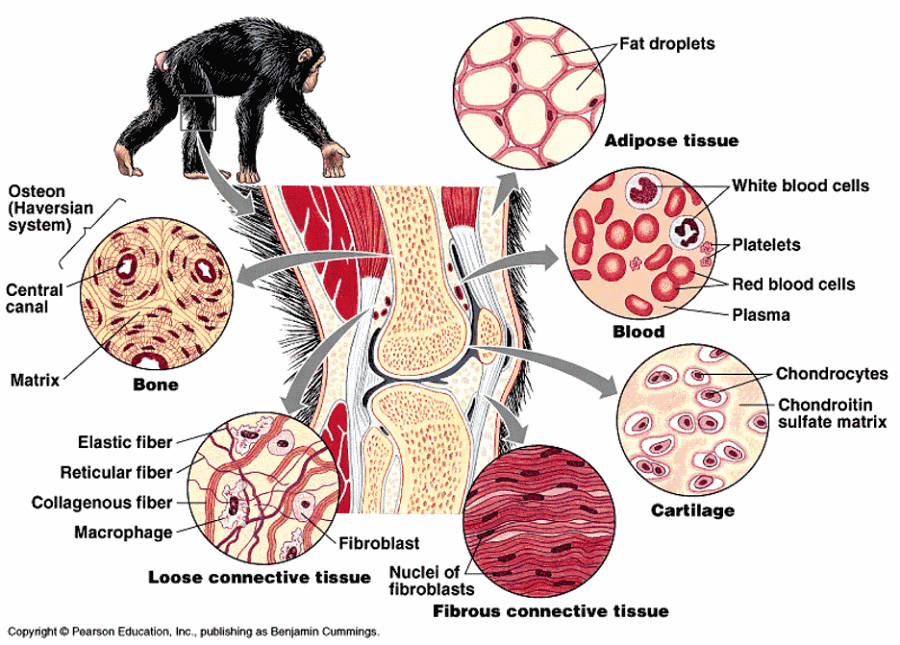 |
front 2 Functions of connective tissue | back 2 Support:
Defense:
Transport:
Storage:
Repair:
|
front 3 Connective tissue | back 3
ECM consists of
|
front 4 Classification of connective tissue | back 4 Based on amount, type, arrangement, and abundance of cells, fibers, and ground substance Loose: loose, irregular arrangement of fibers in matrix and abundant cells Dense: thicker more densely packed fibers with fewer cells and less ground substance
|
front 5 Classification of connective tissue | back 5 Embryonic connective tissue Mesenchyme Mucus connective tissue Connective tissue proper Loose connective tissue Dense connective tissue (regular and irregular) Specialized connective tissue Cartilage Bone Adipose tissue Hematopoietic tissue (blood, bone marrow, lymphatic tissue) |
front 6 Connective Tissue Components | back 6 Cells Extracellular matrix (ECM)
|
front 7 Cells of connective tissue | back 7 Permanent / resident cells Fibroblasts
Adipose cells Cells with pigmented granules Migratory cells
|
front 8 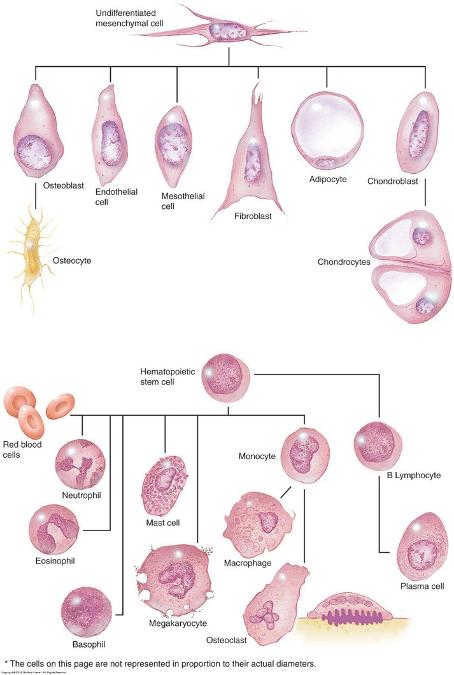 Cells of connective tissue | back 8 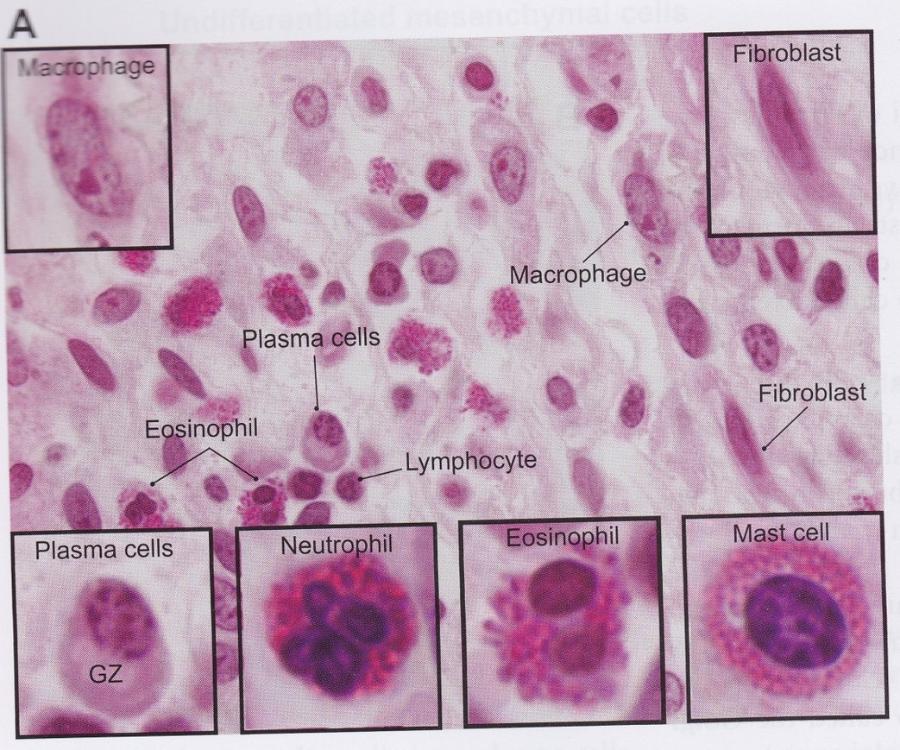 |
front 9 Resident cells: Fibroblasts | back 9 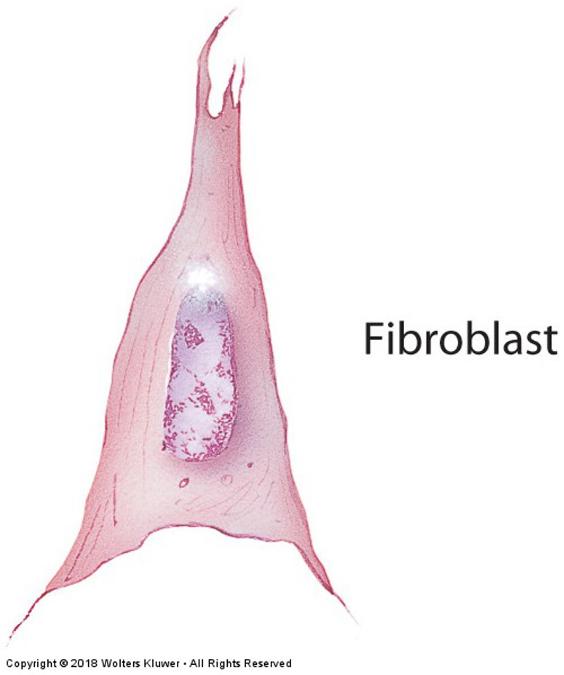 Fibroblasts: fusiform-shaped, synthesize fibers and ground substance (proteins and carbohydrates)
Cartilage = chondroblasts & chondrocytes Bone = osteoblasts & osteocytes |
front 10 Resident cells: Adipose cells | back 10 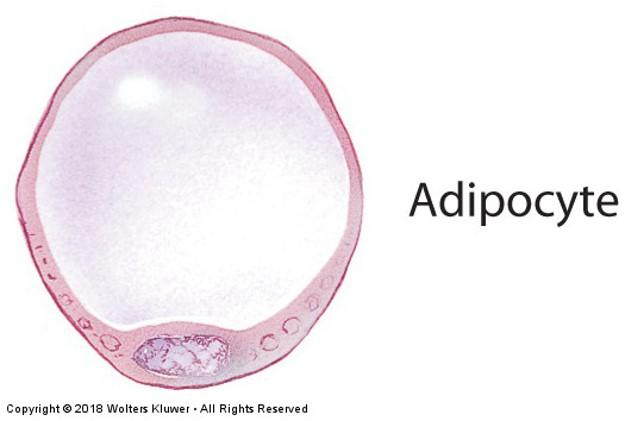
When major cell type, connective tissue is called adipose tissue
|
front 11 Migratory cells: Macrophages | back 11 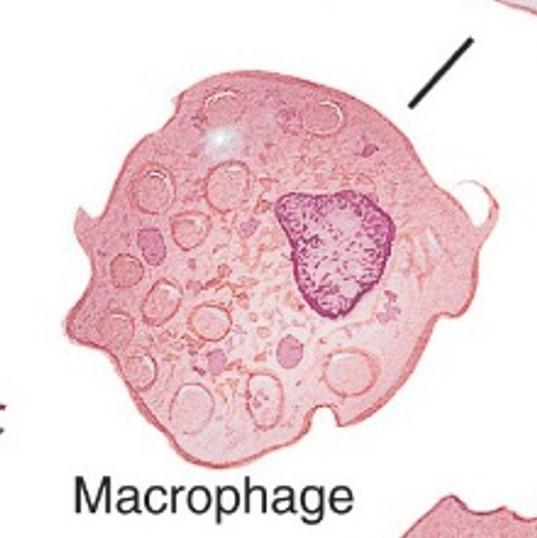
Ingest bacteria, dead cells, cell debris, and foreign material Antigen presentation
|
front 12 Migratory cells: Mast cells | back 12 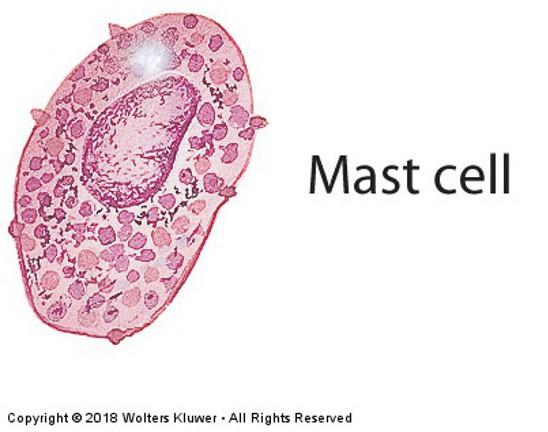
|
front 13 Migratory cells: Plasma cells | back 13 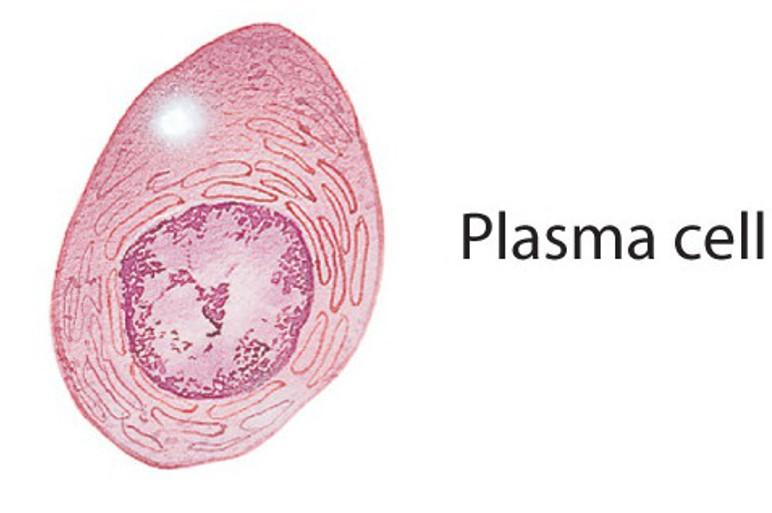
|
front 14 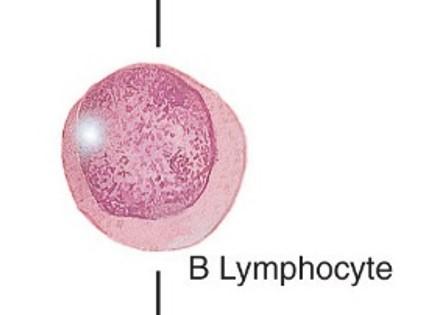 Migratory cells: Other Leukocytes (white blood cells) | back 14 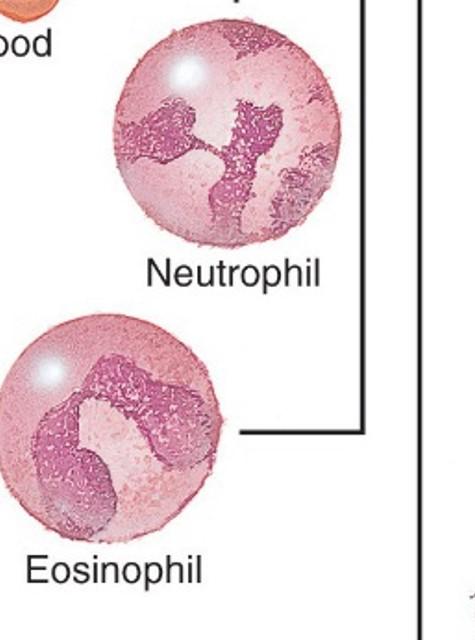
|
front 15 Connective Tissue Components | back 15 Cells Extracellular matrix (ECM)
|
front 16 Extracellular matrix: ECF | back 16 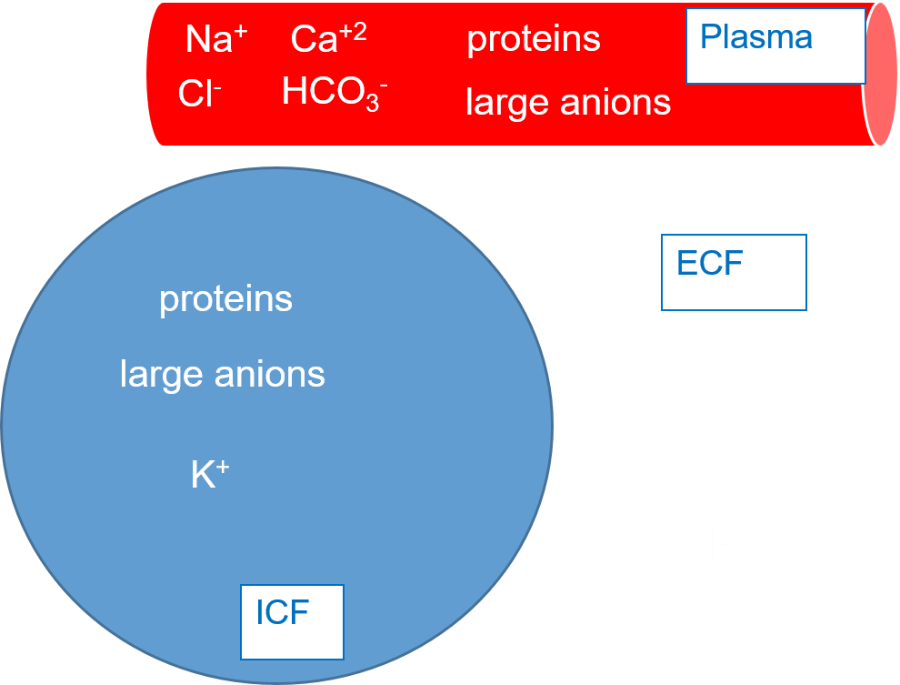 Fluid component that is similar to plasma Circulates throughout the ground substance
Originates from blood in capillaries and returns to blood through capillaries and lymphatic vessels |
front 17 Edema | back 17 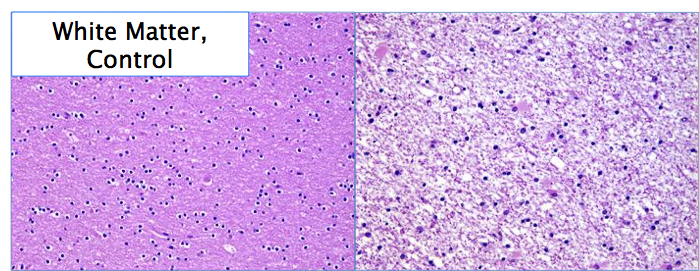 increased ECF and/or cells in any tissue type—common in epithelial & connective tissues |
front 18 Connective Tissue Components | back 18 Cells Extracellular matrix (ECM)
|
front 19 Extracellular matrix: Ground substance | back 19 Amorphous, transparent extracellular matrix Semifluid gel with high water content to allow diffusion of nutrients—due to ECF perfusion
Supports, surrounds, and binds all connective tissue cells and fibers Composed of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, and adhesive glycoproteins (fibronectin, integrins, and laminin) |
front 20 Extracellular matrix: Ground substance | back 20 Gel quality of ground substance slows down flow rate of ECF
|
front 21 Connective Tissue Components | back 21
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
|
front 22 Fibers of connective tissue | back 22 Amount and arrangement of 3 fiber types depend on function of tissues and organs where they are found
All fiber types produced by fibroblasts Proteins with long peptide chains |
front 23 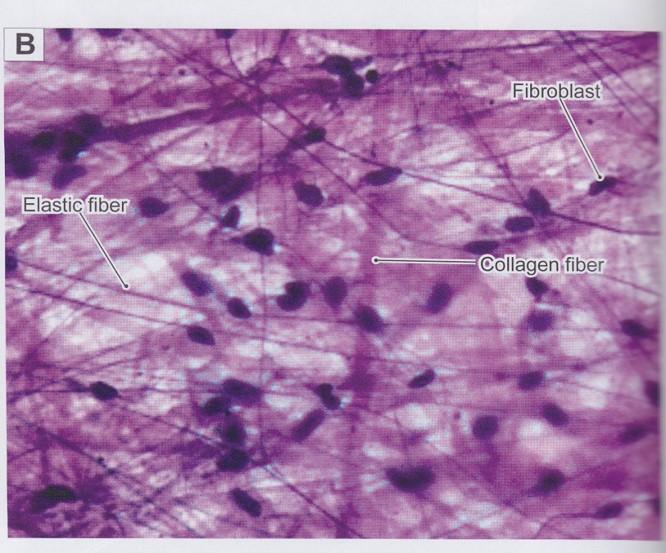 Fibers: Collagen fibers | back 23 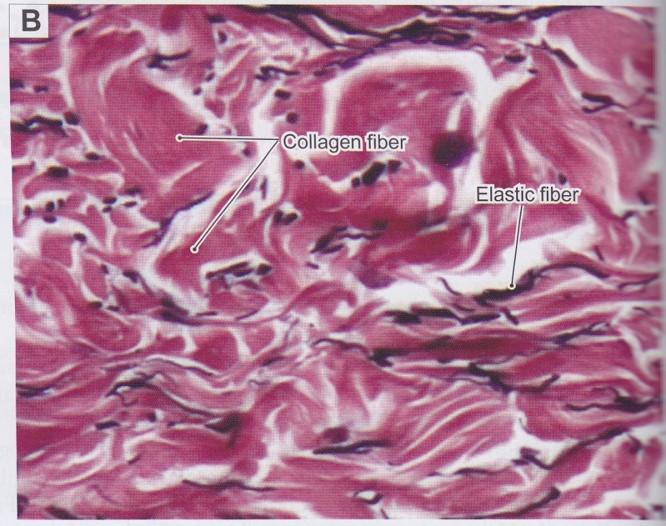
|
front 24 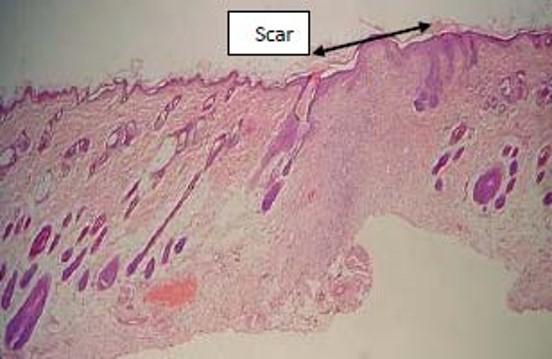 Skin scar (keloid formation): | back 24 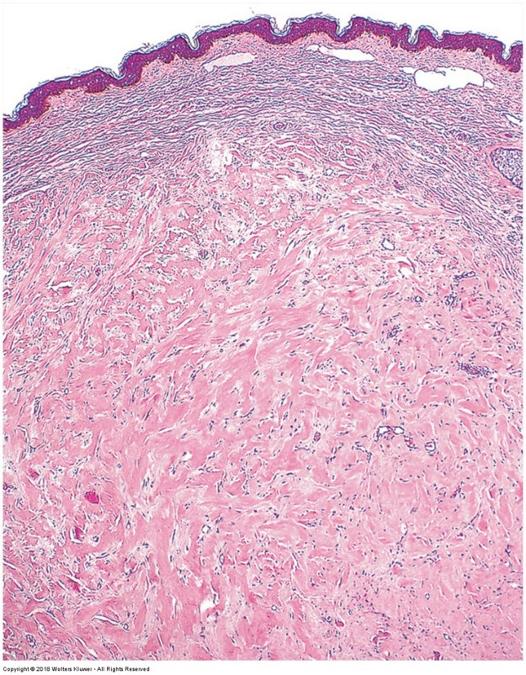 increased abundance of collagen fibers replacing normal tissue structures |
front 25 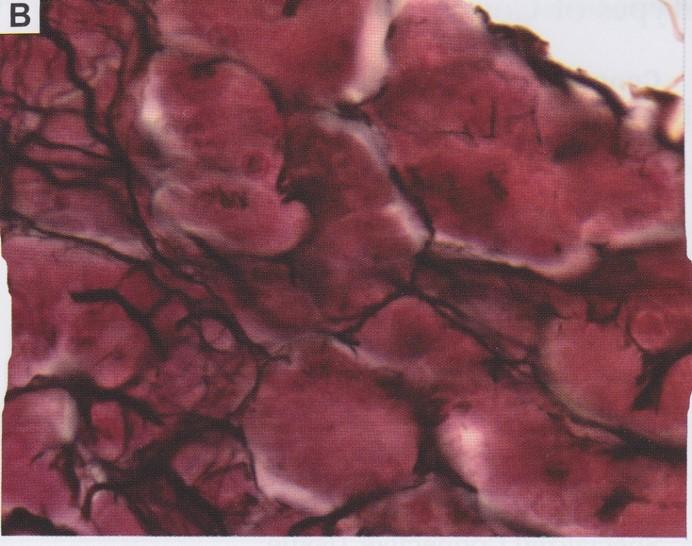 Fibers: Reticular fibers | back 25 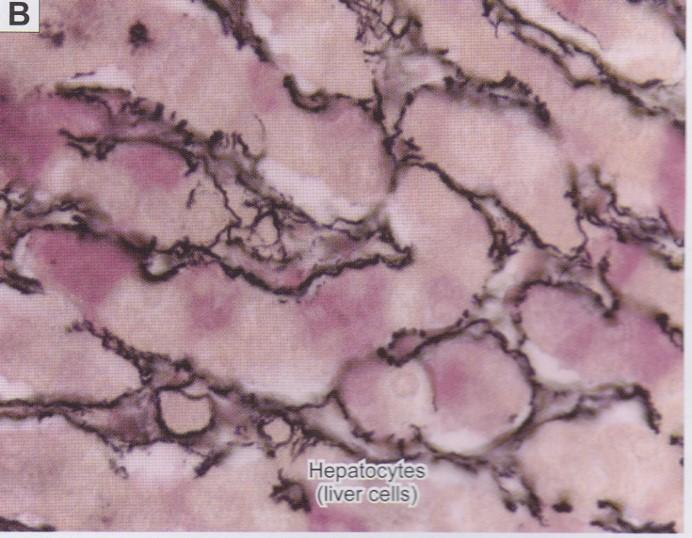
|
front 26 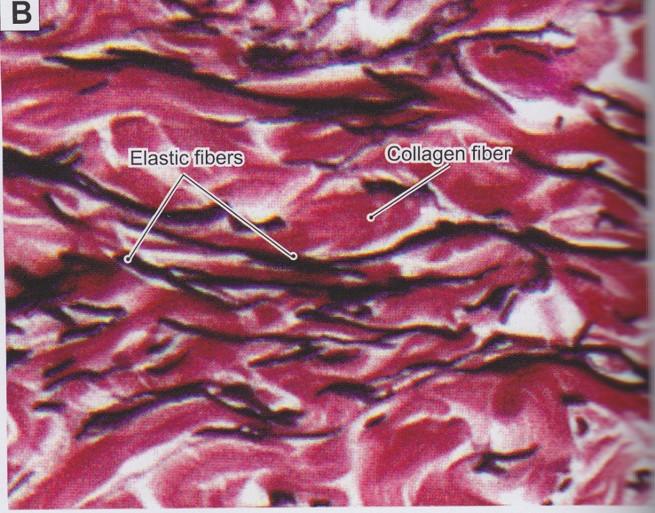 Fibers: Elastic fibers | back 26 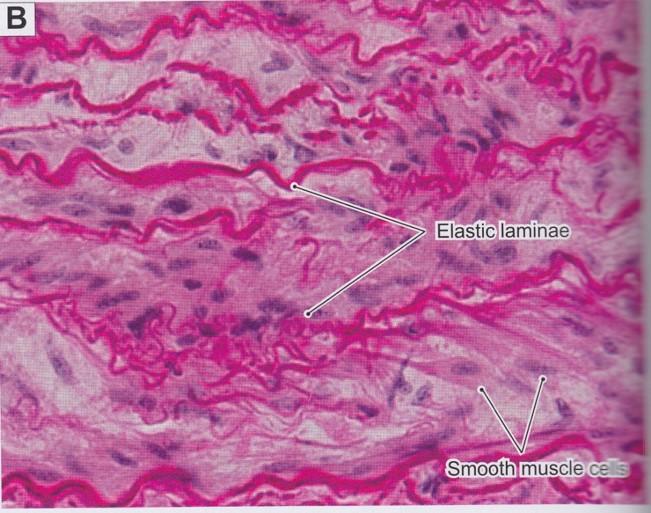
|
front 27 Connective tissue types | back 27 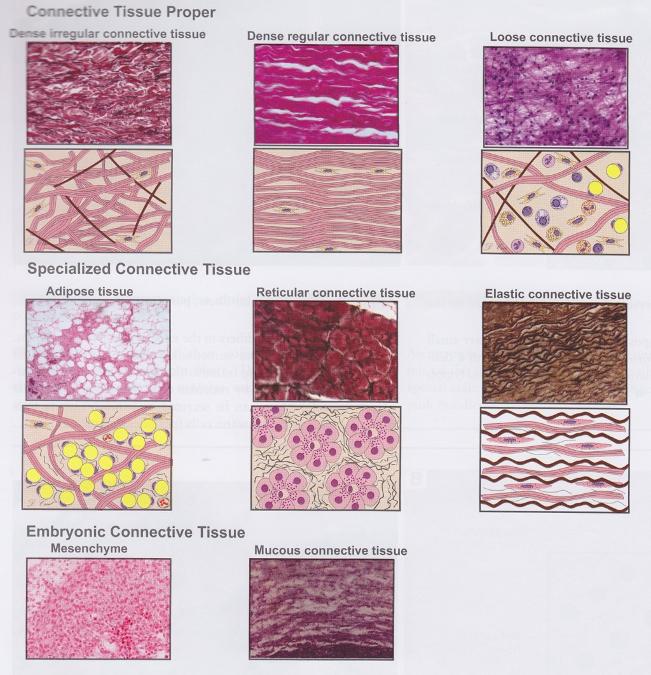 |
front 28 Embryonic connective tissue | back 28
|
front 29 Loose (areolar) connective tissue | back 29 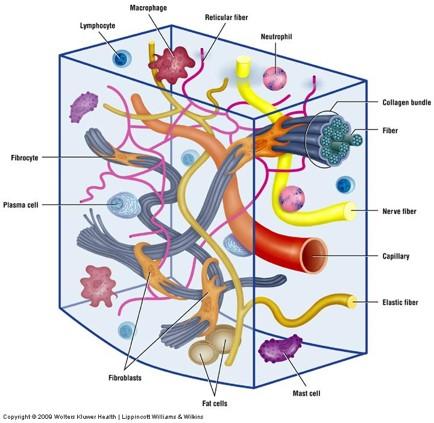
Main constituents:
|
front 30 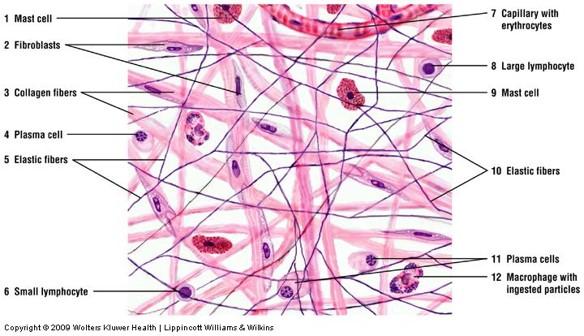 Loose connective tissue | back 30 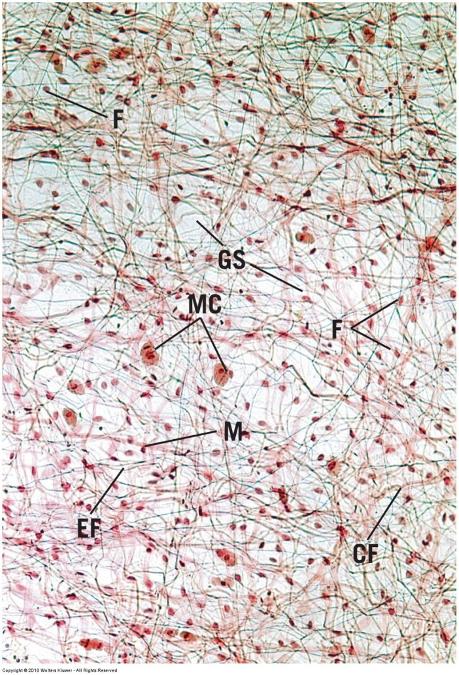 |
front 31 Loose connective tissue | back 31 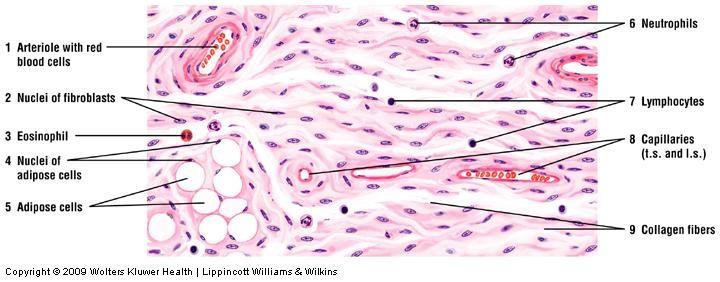 |
front 32 Dense connective tissue | back 32
|
front 33 Dense irregular connective tissue | back 33
|
front 34 Dense irregular connective tissue | back 34 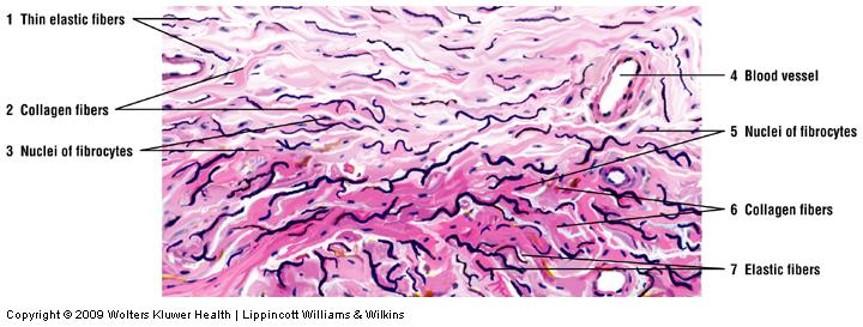 |
front 35 Dense irregular connective tissue | back 35 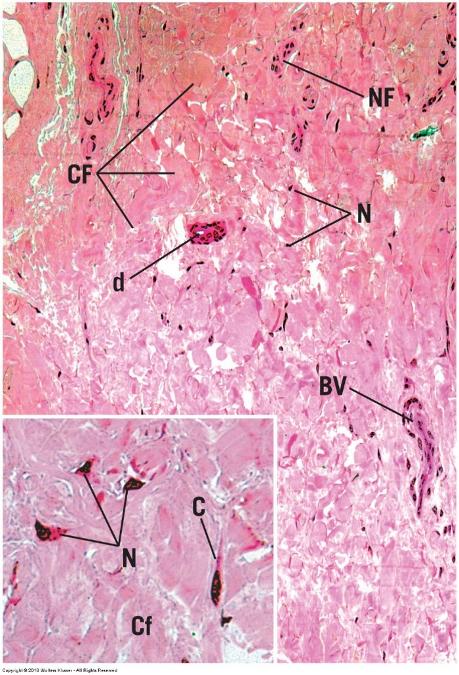 |
front 36 Dense irregular connective tissue | back 36 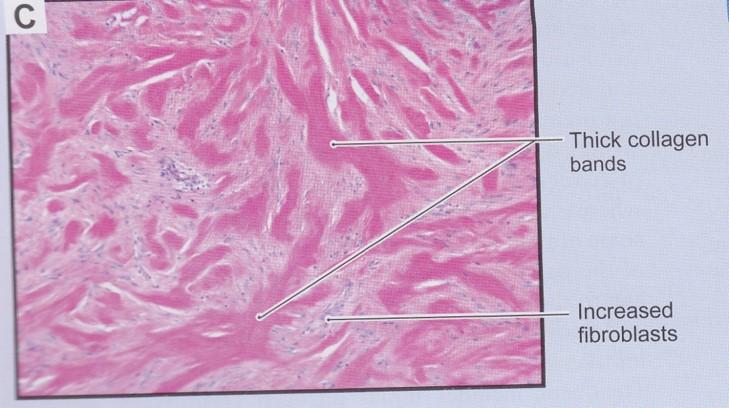 Hypertrophic scars and keloids |
front 37 Dense regular connective tissue | back 37
|
front 38 Dense regular connective tissue: longitudinal section | back 38 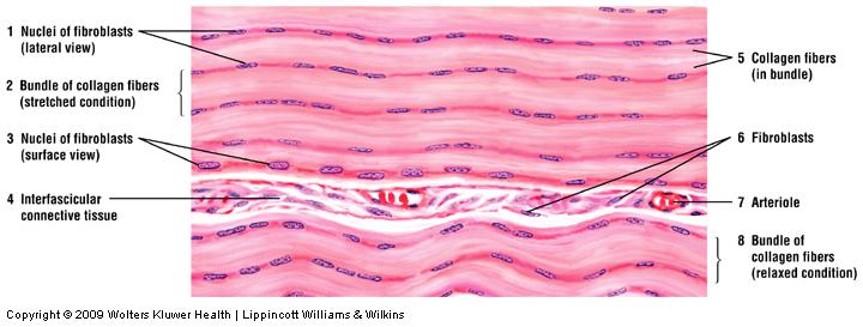 |
front 39 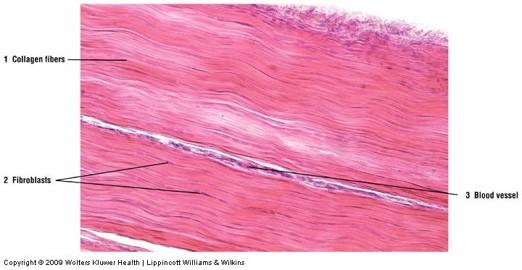 Dense regular connective tissue: longitudinal section | back 39 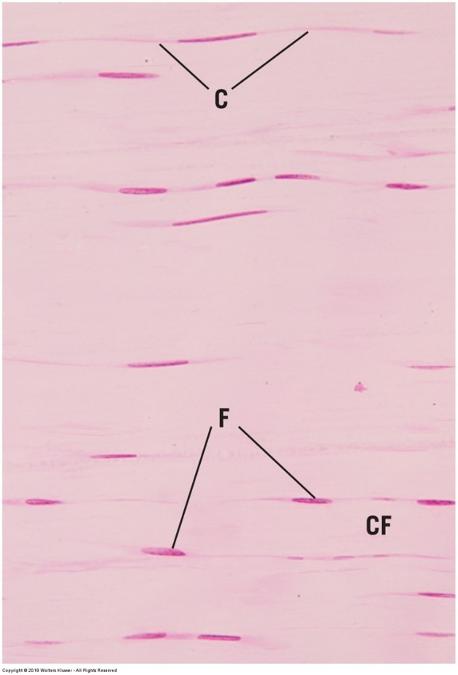 |
front 40 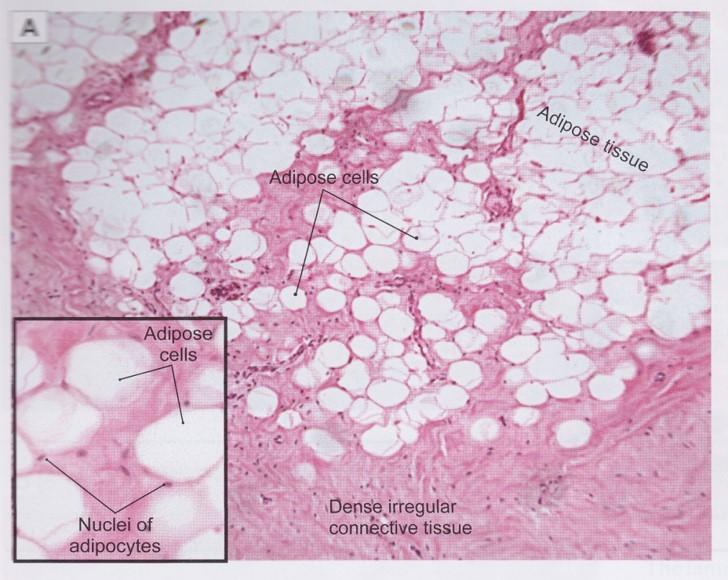 White adipose (unilocular) tissue | back 40 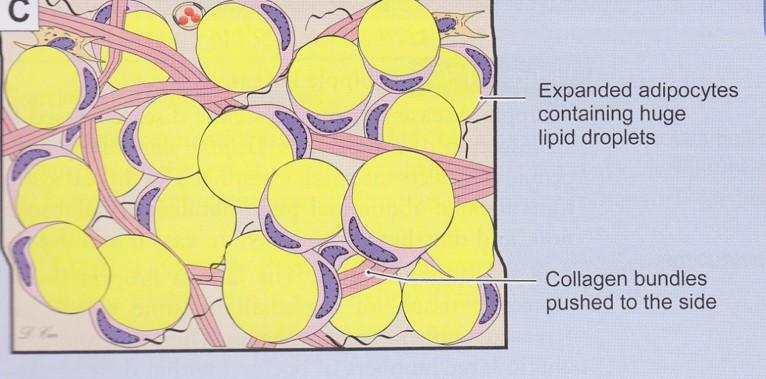
|
front 41 White adipose (unilocular) tissue | back 41 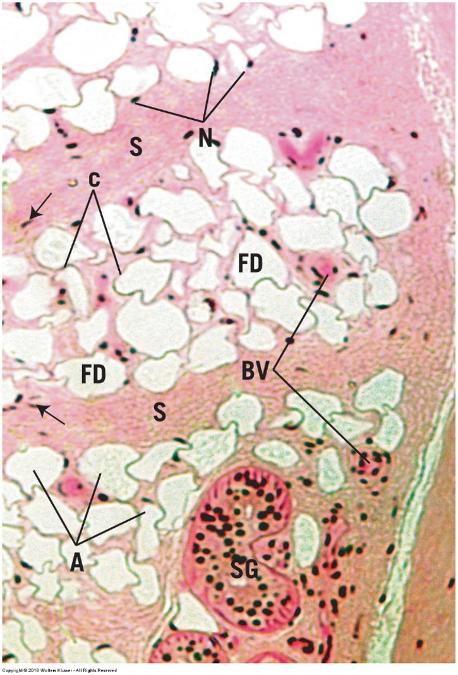 |
front 42 Brown adipose (multilocular) tissue | back 42 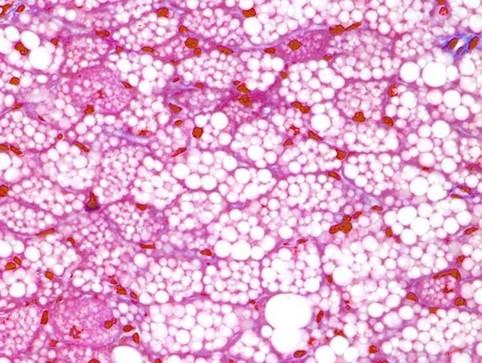
|
front 43 Cartilage | back 43 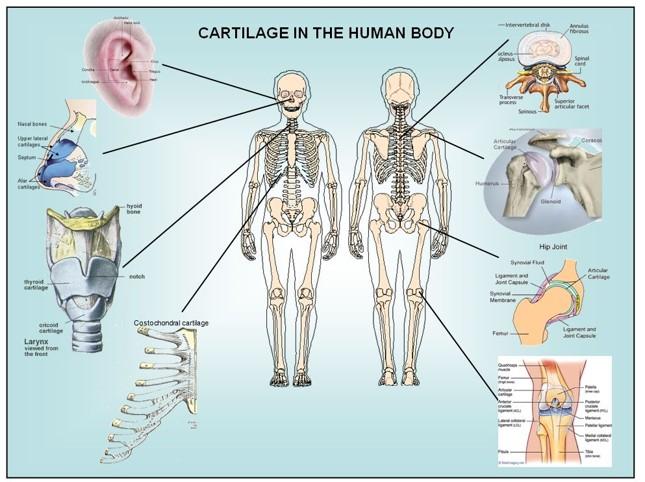
|
front 44 Cartilage has typical connective tissue components | back 44 Cells Extracellular matrix
Collagen often obscured by viscosity of ground substance |
front 45 Cartilage | back 45 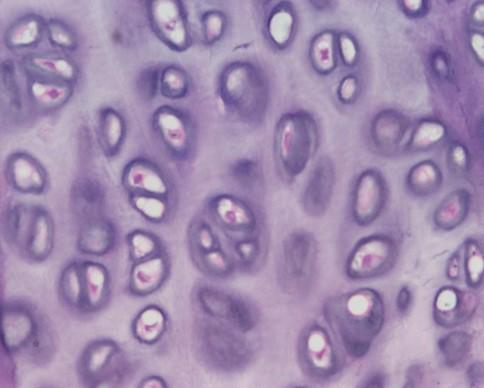 Cells
Extracellular matrix (ECM) (>95% tissue volume)
Nonvascular: nutrients must diffuse through ECM |
front 46 Cartilage cells | back 46 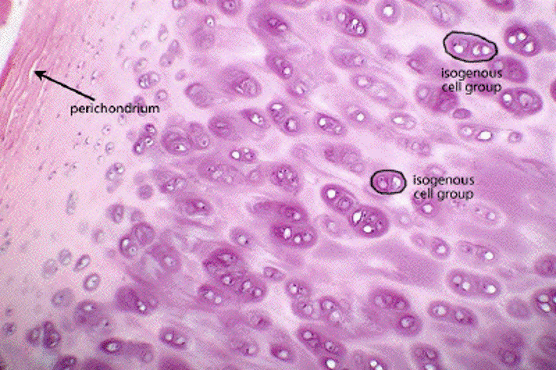 Mesenchyme cells (during development)
Chondroblasts
Chondrocytes
|
front 47 Perichondrium | back 47  Found surrounding hyaline and elastic cartilages only Peripheral layer of vascularized dense irregular connective tissue
|
front 48 Cartilage matrix | back 48  Produced and maintained by chondrocytes and chondroblasts
Collagen fibers provide firmness and resilience
Ground substance associated with fibers
|
front 49 Cartilage matrix staining regions | back 49 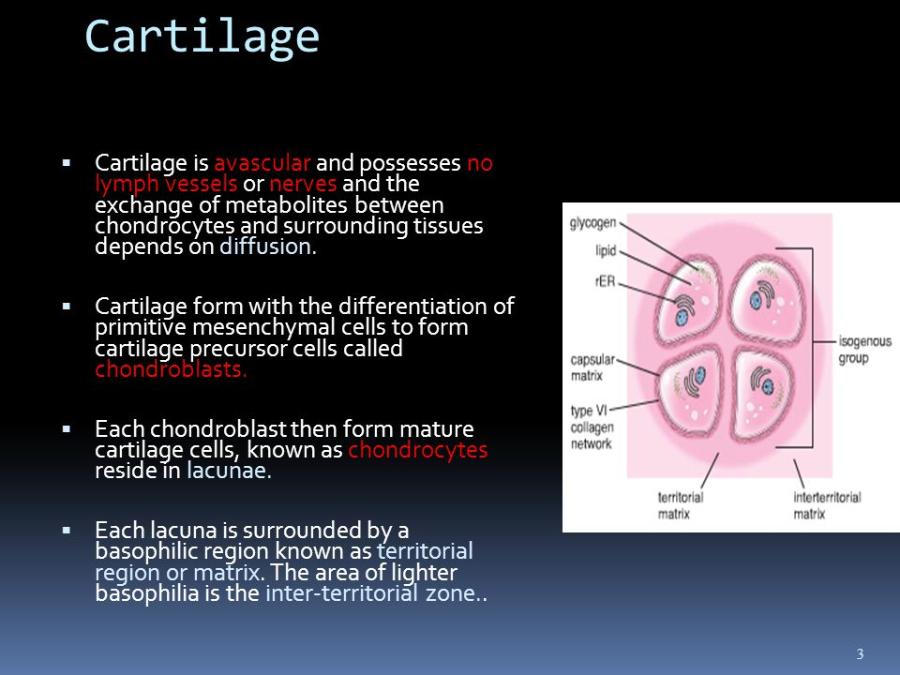
|
front 50 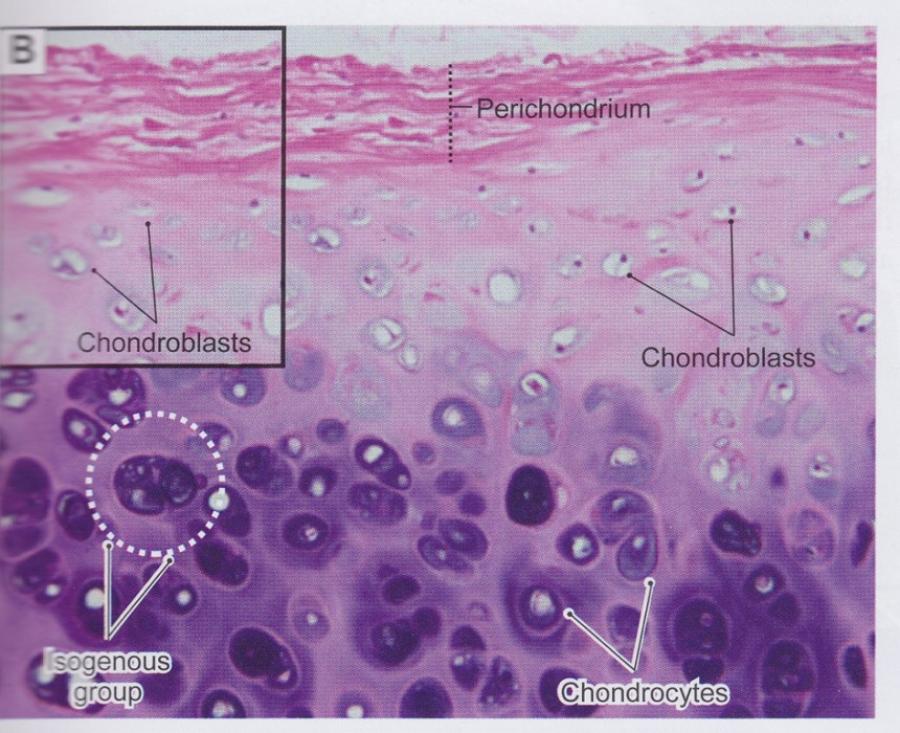 Cartilage matrix, cells, and perichondrium | back 50 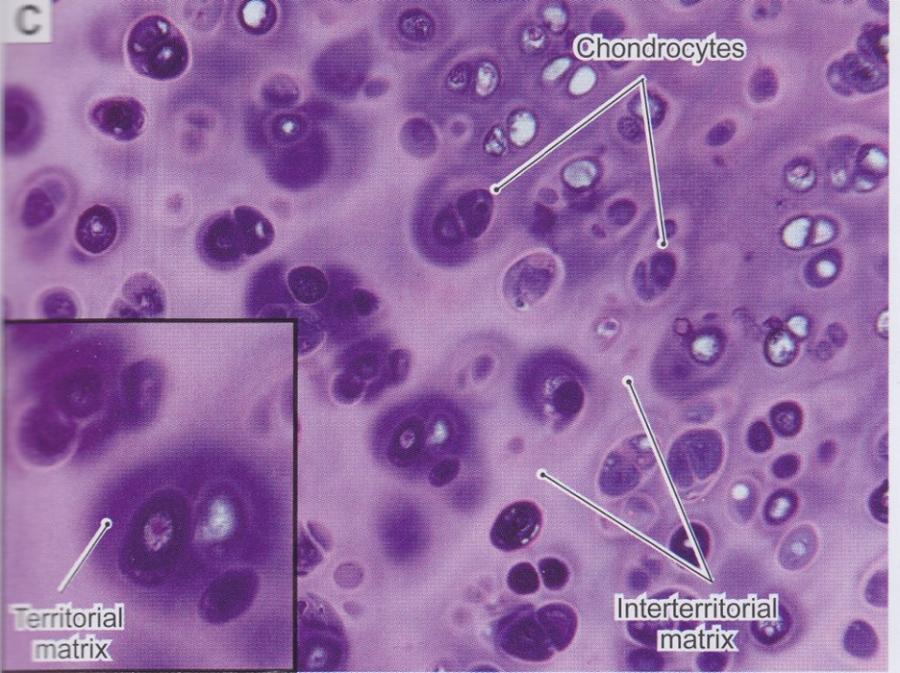 |
front 51 Types of cartilage are distinguished based on amount and types of fibers | back 51 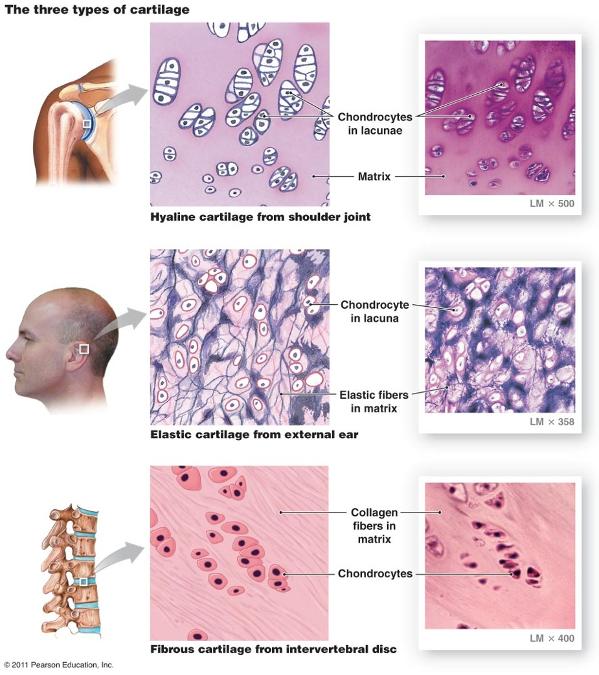 |
front 52 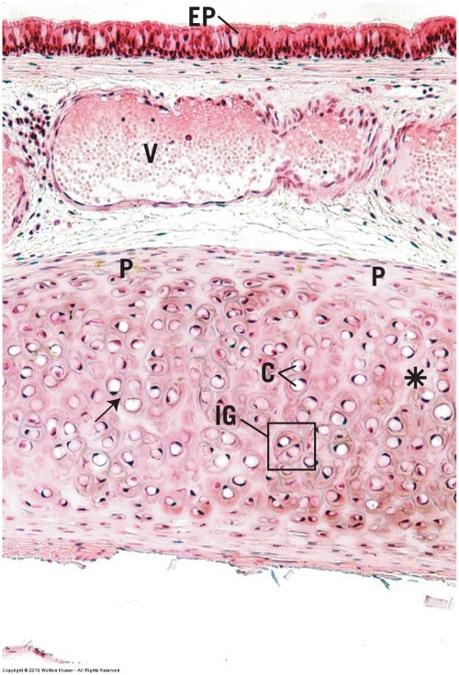 Hyaline cartilage | back 52 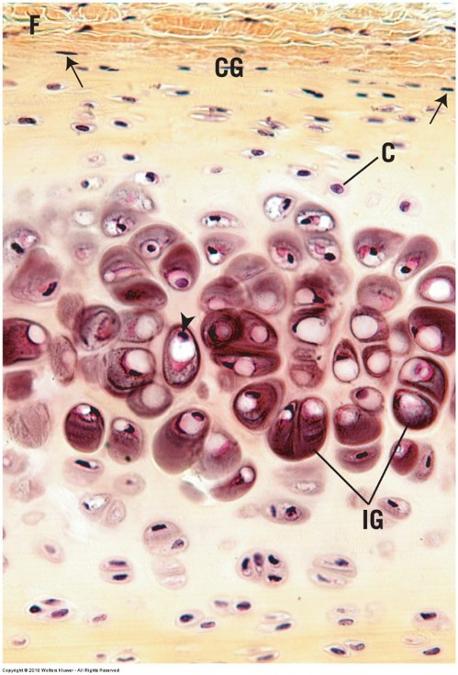 Most common with glassy ECM Embryos
Adults
Firm structural and flexible support |
front 53 Hyaline cartilage and perichondrium: trachea | back 53 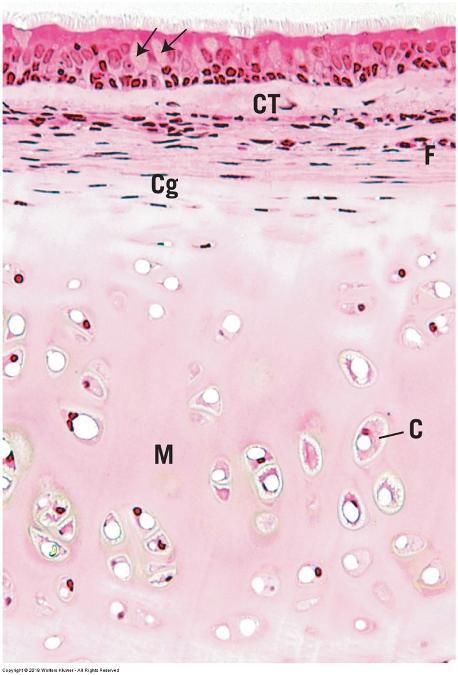 |
front 54 Osteoarthritis: Erosion of Joint Hyaline Cartilage | back 54 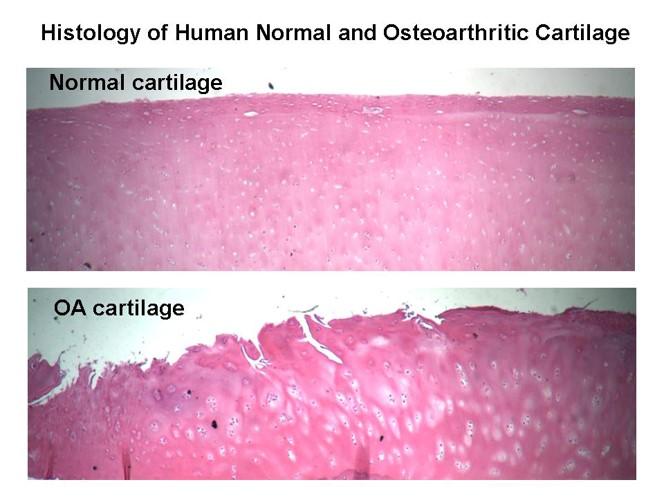 |
front 55 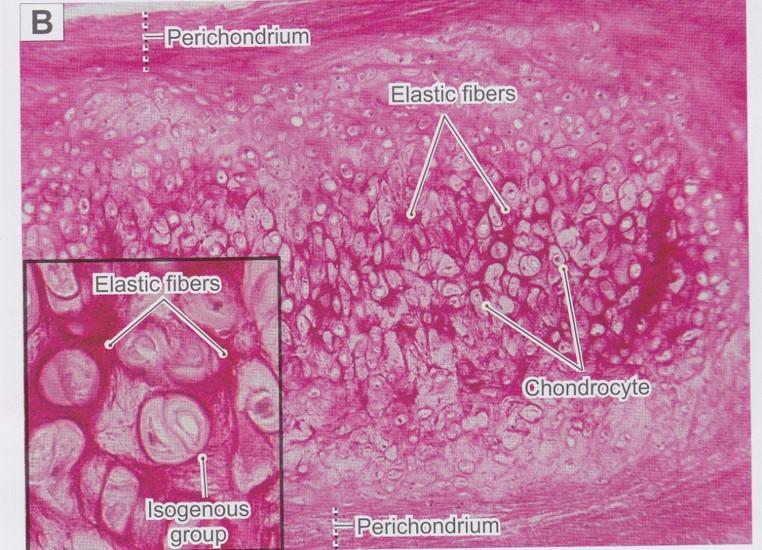 Elastic cartilage | back 55 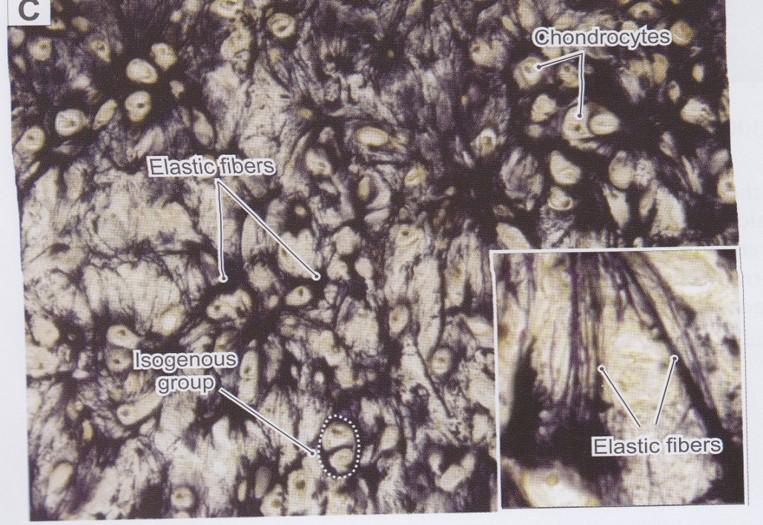 Similar in appearance to hyaline cartilage Matrix has numerous branching elastic fibers in matrix in addition to hyaline cartilage components
External ear, walls of auditory tube, epiglottis, and larynx |
front 56 Elastic cartilage (epiglottis) | back 56 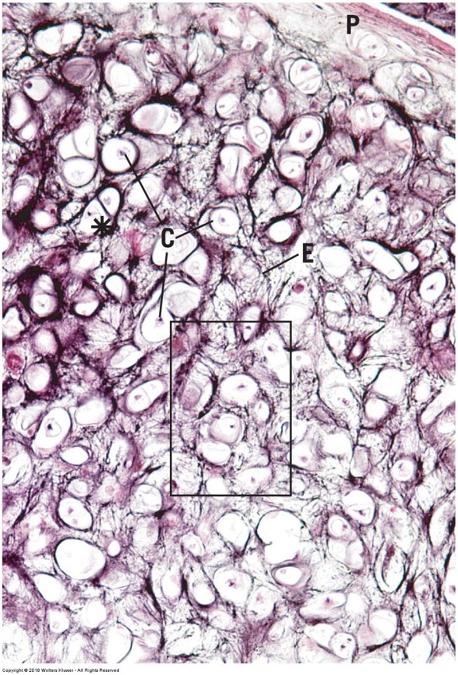 |
front 57 Fibrocartilage | back 57 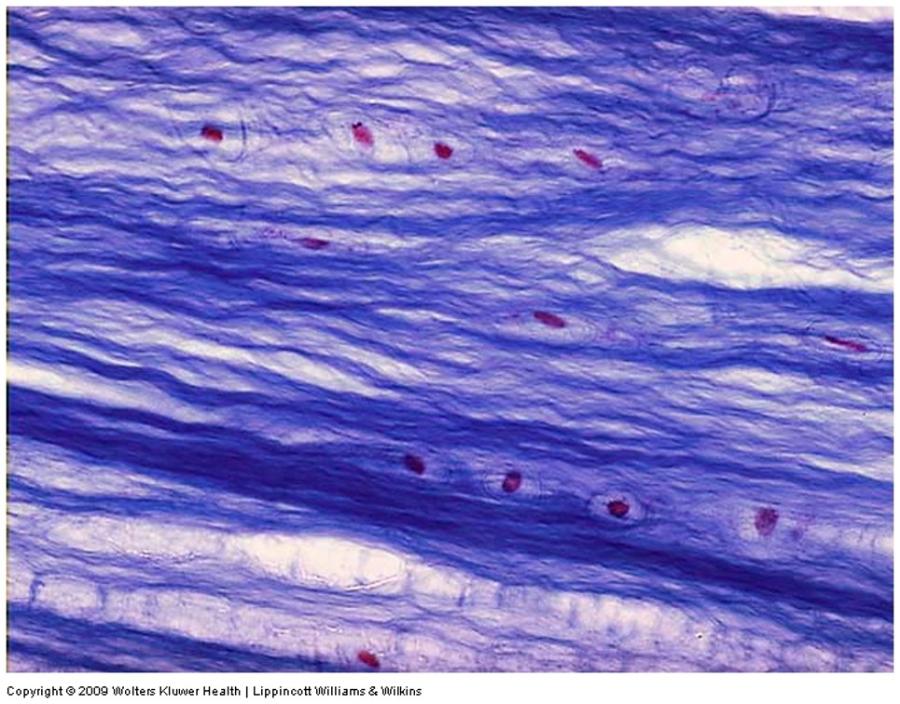 Large amounts of dense irregular bundles of coarse collagen in ECM
Fibers oriented in direction of stress Intervertebral disks, symphysis pubis, and certain joints
No perichondrium |
front 58 Fibrocartilage (intervertebral disk) | back 58 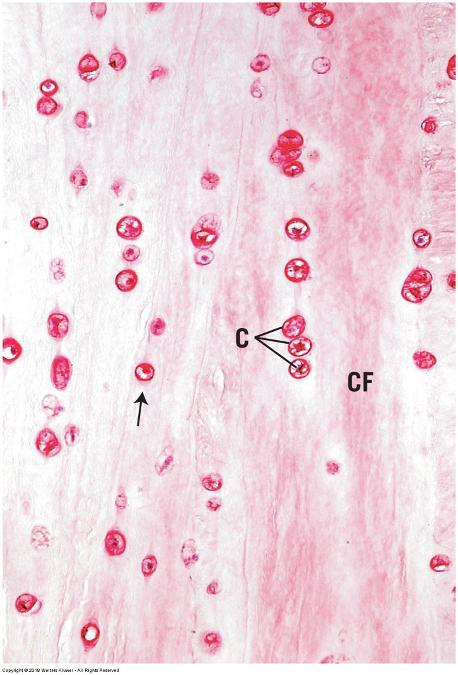 |
front 59 Chondrogenesis | back 59 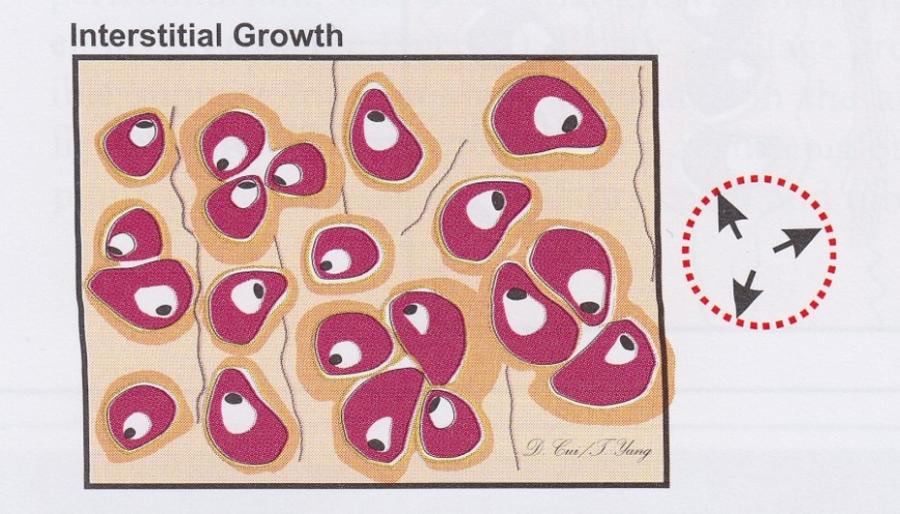 Interstitial growth
|
front 60 Chondrogenesis | back 60 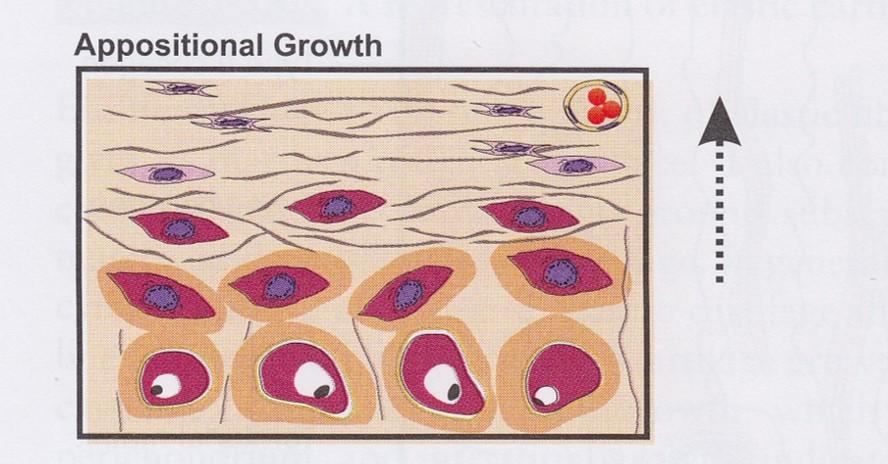 Appositional growth
|
front 61 Bone | back 61 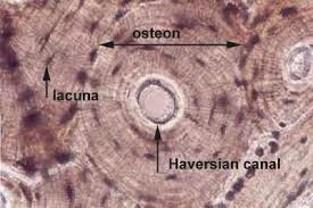 Calcified due to mineral deposition in matrix
Can bear more weight than cartilage
Hemopoeisis (blood cell formation) Storage of calcium, phosphate, and other minerals |
front 62 Bone | back 62 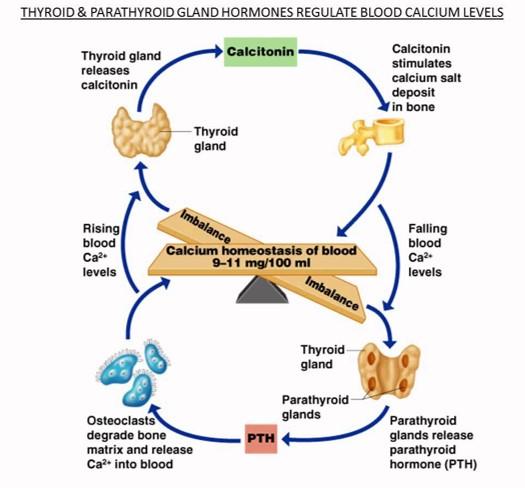 ECM continually renewed or remodeled
Blood calcium regulation
|
front 63 Bone formation (ossification) | back 63 Endochondral ossification
Intramembranous ossification
|
front 64  Endochondral ossification | back 64 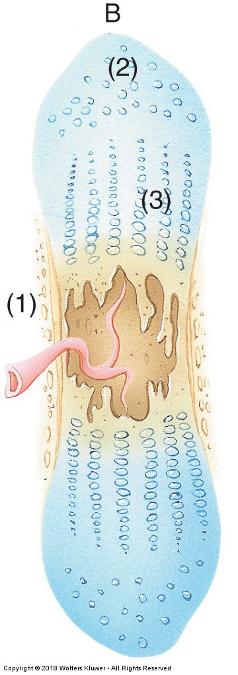 Way most bones develop Temporary hyaline cartilage model precedes bone formation As cartilage model grows and development progresses
|
front 65 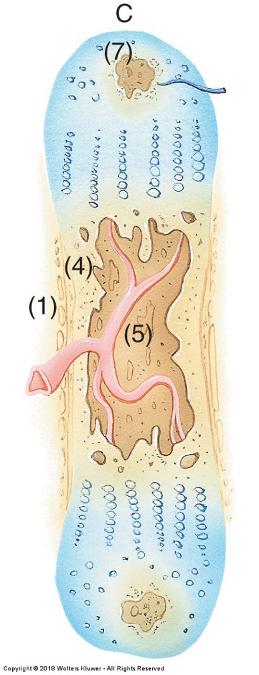 Endochondral ossification | back 65 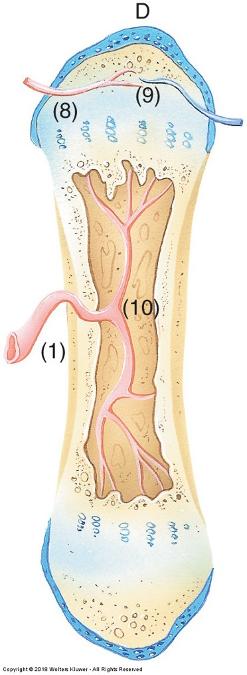 Inner perichondrial cells form thin collar of bone around middle of bone shaft
Osteoblasts secrete osteoid matrix that later calcifies
|
front 66 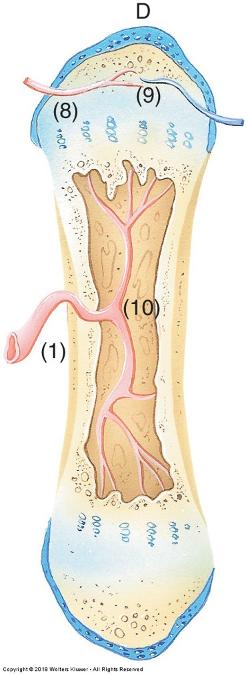 Endochondral ossification | back 66 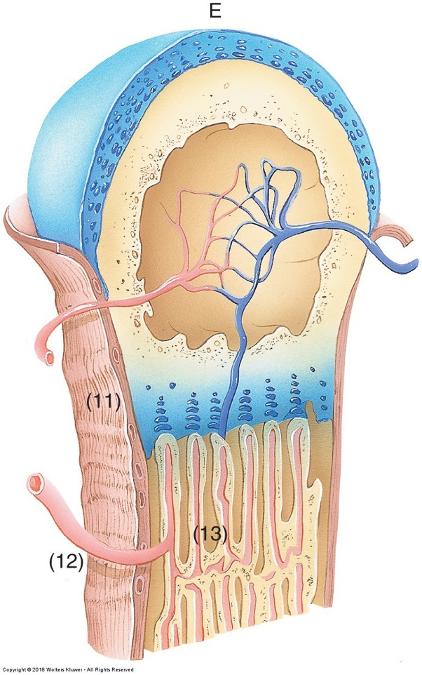 Osteocytes form cell-cell connections through channels called canaliculi
Osteoprogenitor cells are also found on inner bone surface (endosteum) Bone gradually replaces cartilage |
front 67 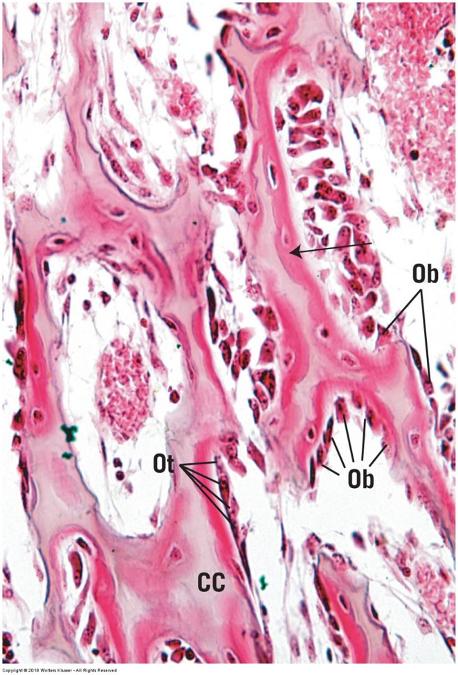 Endochondral ossification | back 67 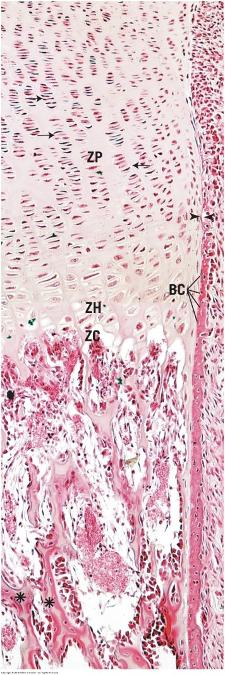 |
front 68 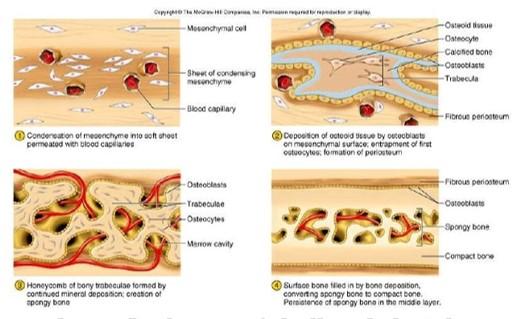 Intramembranous ossification | back 68 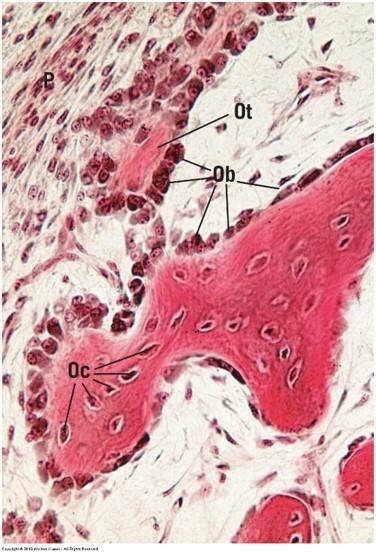
|
front 69 Bone cells | back 69 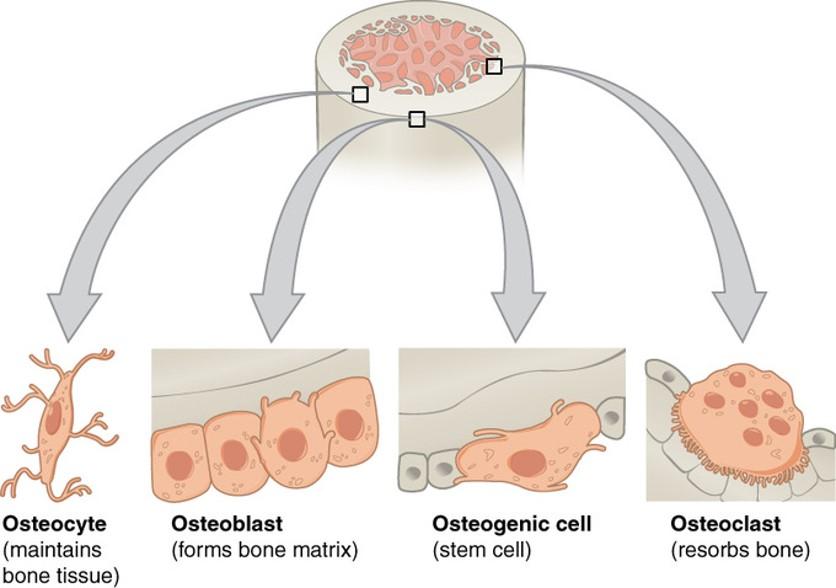
|
front 70 Osteoprogenitor (osteogenic) cells | back 70 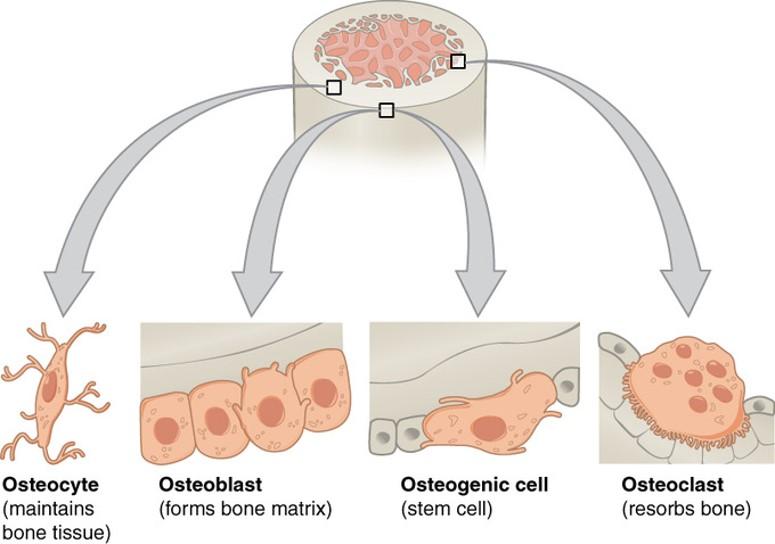
|
front 71 Osteoblasts | back 71 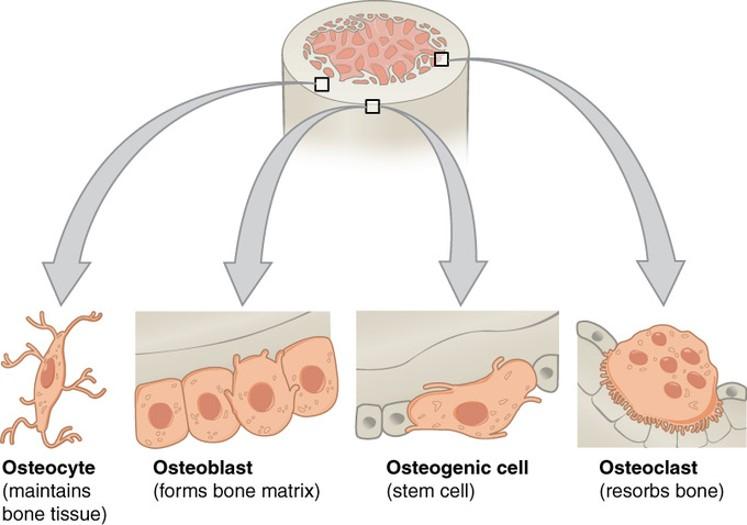
|
front 72 Osteocytes | back 72 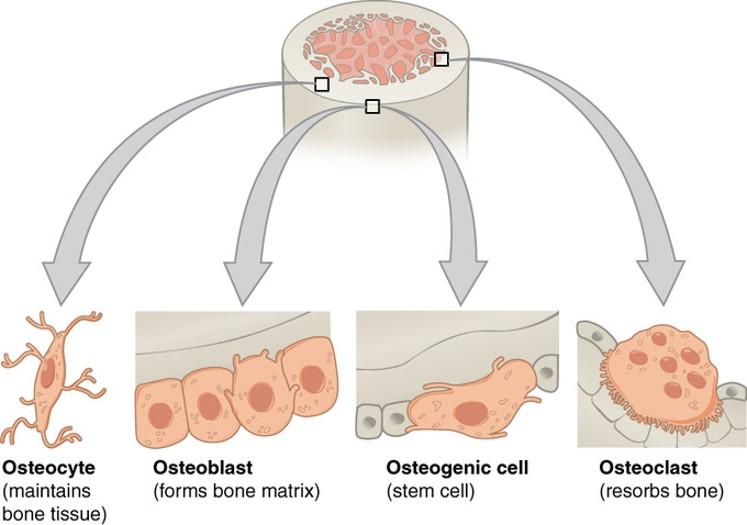
|
front 73 Osteoclasts | back 73 
|
front 74 Bone matrix | back 74 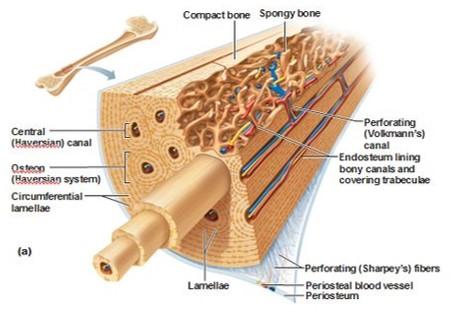 Hard, no diffusion of nutrients
Resists tension and compression Mostly collagen fibers Other components
|
front 75 Bone types | back 75 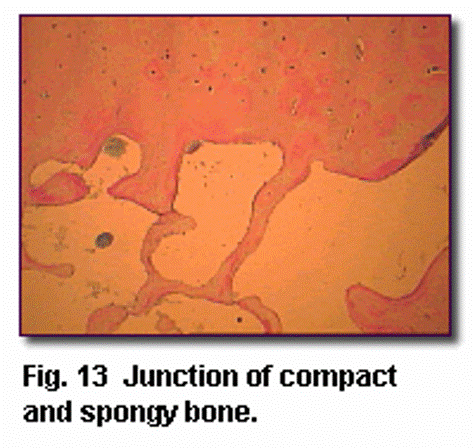
|
front 76 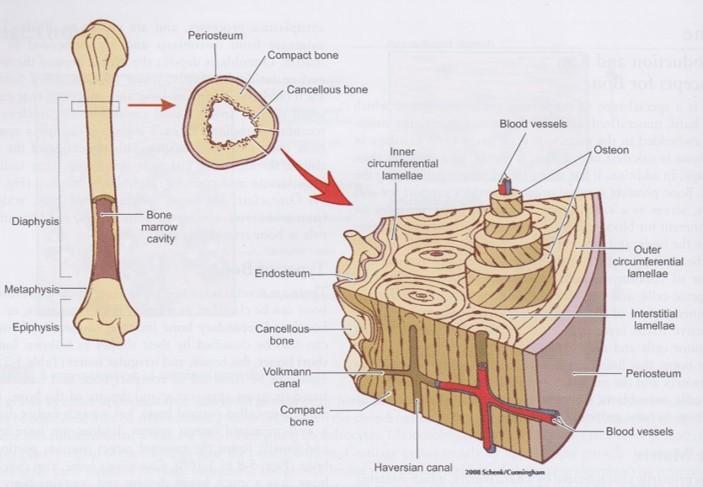 Compact bone | back 76  Collagen fibers arrange in thin layers of bone called lamellae
Outer circumferential lamellae
Inner circumferential lamellae
Concentric lamellae
|
front 77 Compact bone | back 77 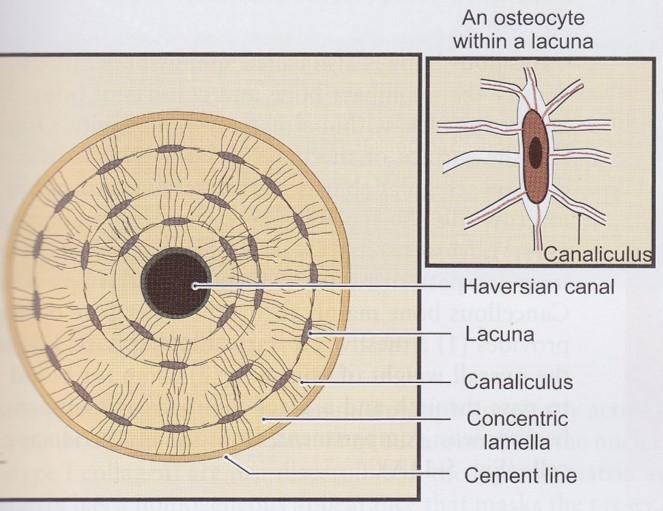
|
front 78 Compact bone | back 78  |
front 79 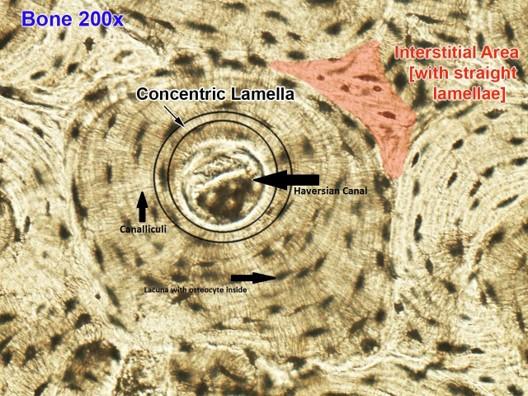 Compact bone | back 79 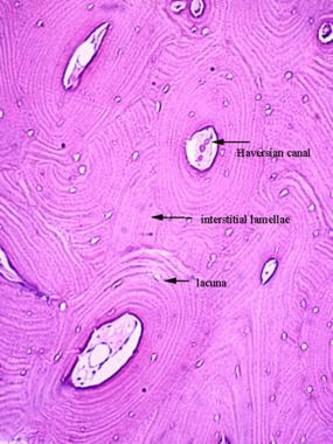 |
front 80  Cancellous (spongy) bone | back 80 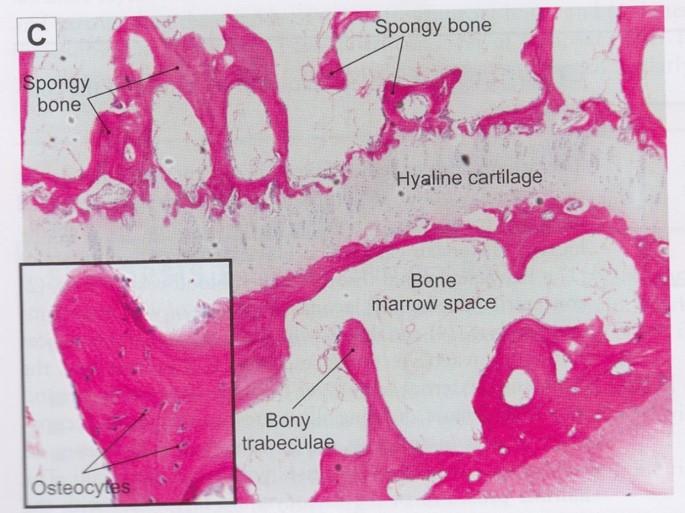
|
front 81 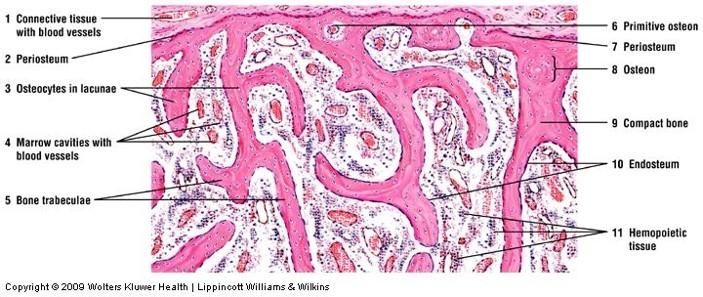 Cancellous (spongy) bone | back 81 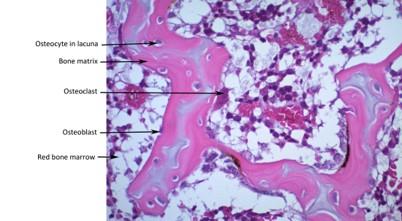 |
front 82 Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI) | back 82 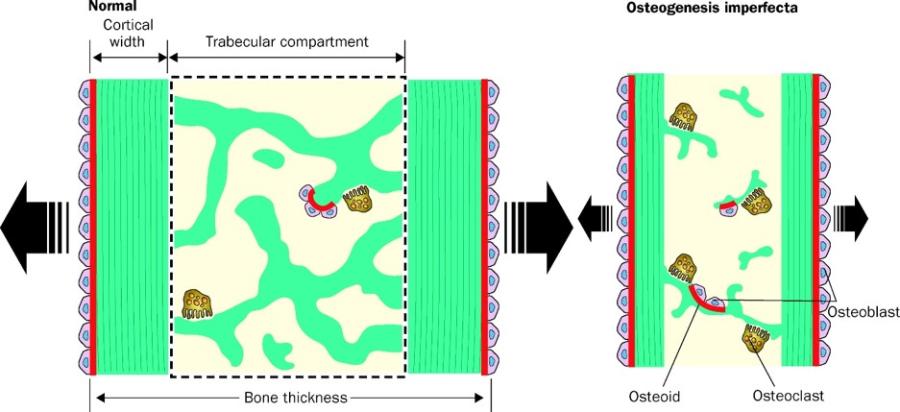 Genetically inherited mutation of Collagen Type I genes
OI decreases bone thickness due to slow bone formation, reduced # trabeculae, thinner trabeculae, & increased bone resorption |
front 83 Overview of Blood | back 83 Fluid connective tissue (ECM = ECF + Ground Substance) Functions
|
front 84 Components of blood | back 84 Cells (45% volume)—formed elements
Plasma (55% volume)
|
front 85 Blood Cell Types: Appearance | back 85 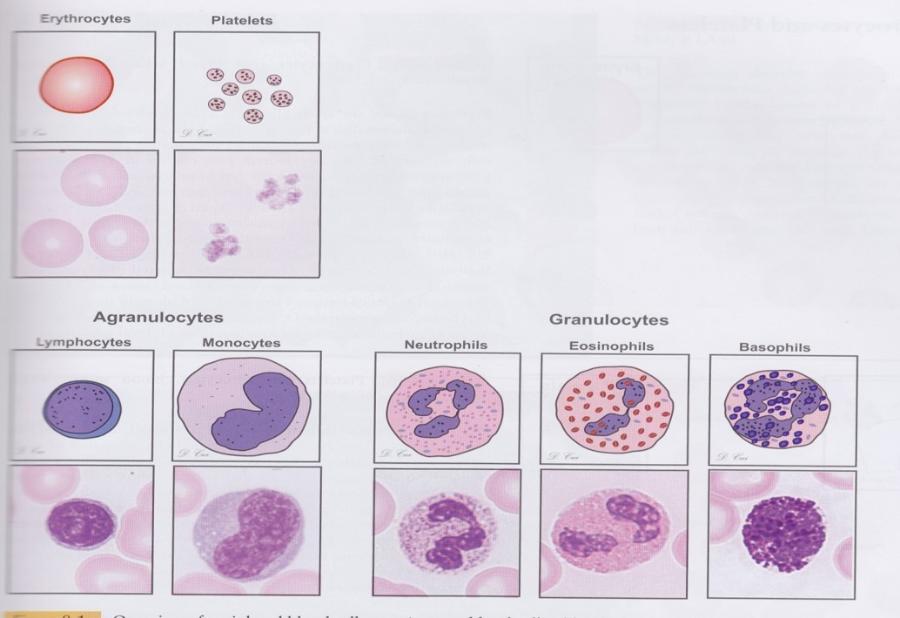 |
front 86 Blood Cell Types: General Features | back 86 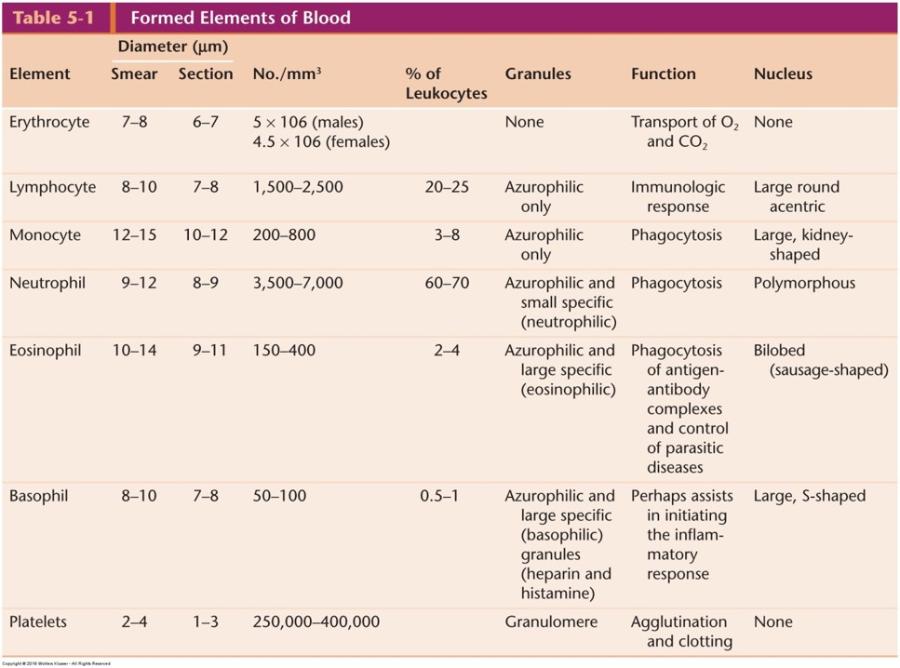 |
front 87 Erythrocytes | back 87
|
front 88 Erythrocytes and platelets | back 88 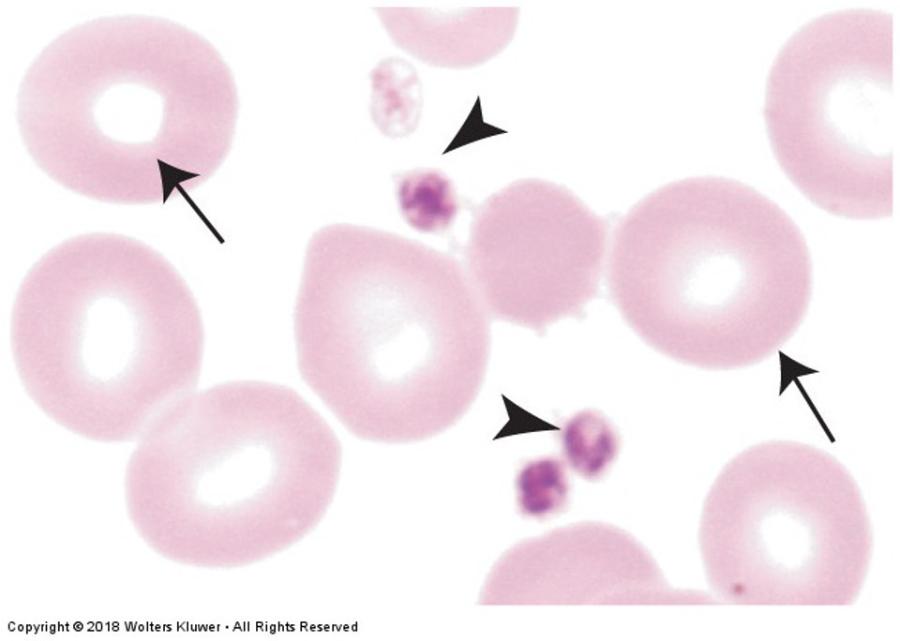 |
front 89 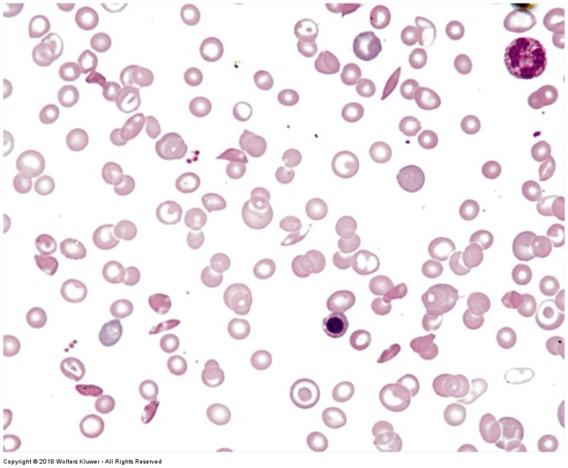 Erythrocytes: sickle cell anemia | back 89 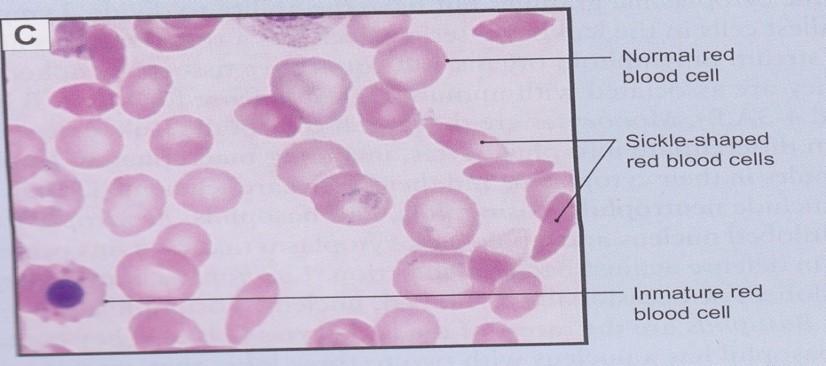 |
front 90 Leukocytes | back 90 Granulocytes: cells containing specific granules
Agranulocytes: cells without specific granules
Function outside of blood vessels (defense) |
front 91 Neutrophils | back 91 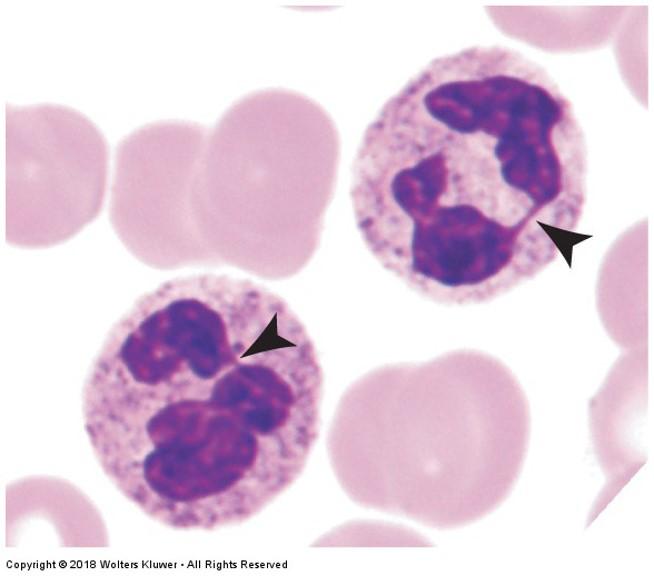
|
front 92 Eosinophils | back 92 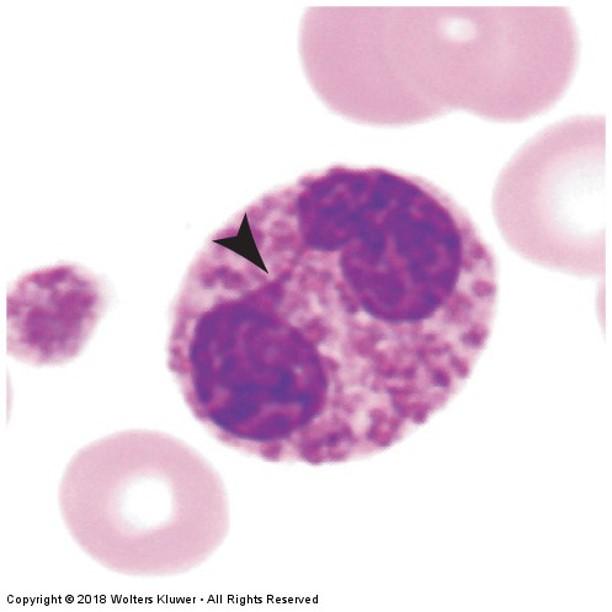
|
front 93 Eosinophillia in epithelial tissue during parasitic infections or allergic reactions | back 93 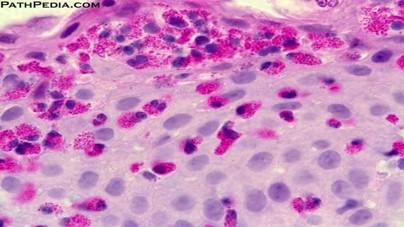 |
front 94 Basophils | back 94 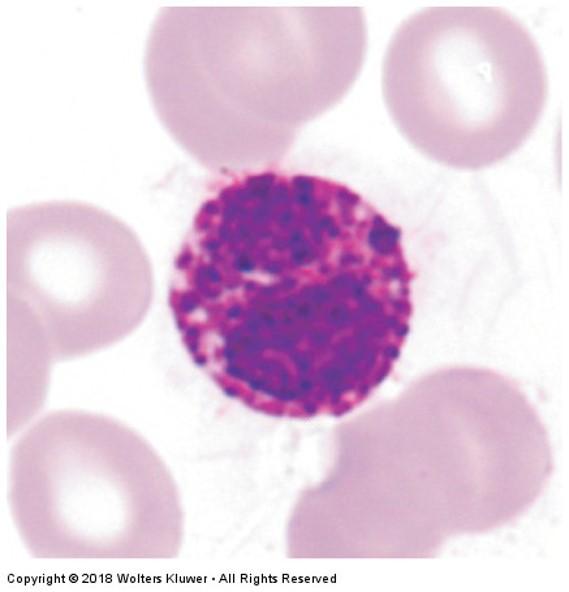
|
front 95 Lymphocytes | back 95 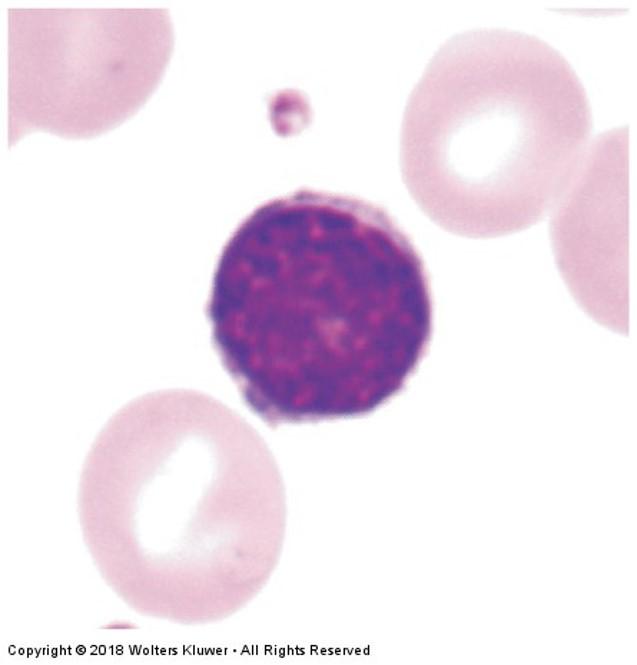
|
front 96 Lymphocytes: Leukemia | back 96 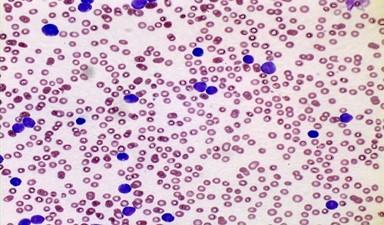 |
front 97 Monocytes | back 97 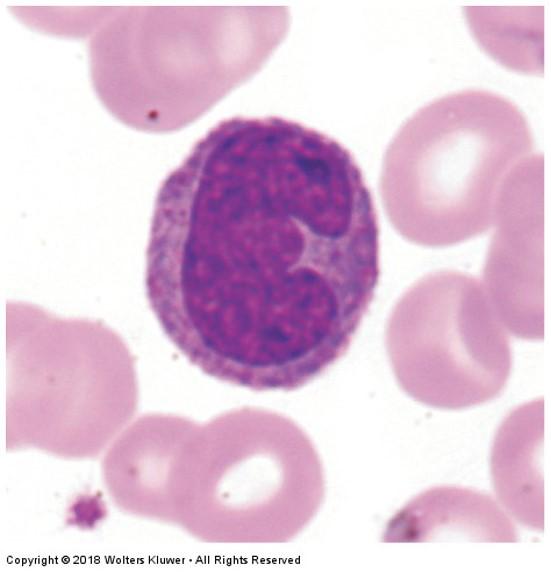
|
front 98 Thrombocytes: | back 98 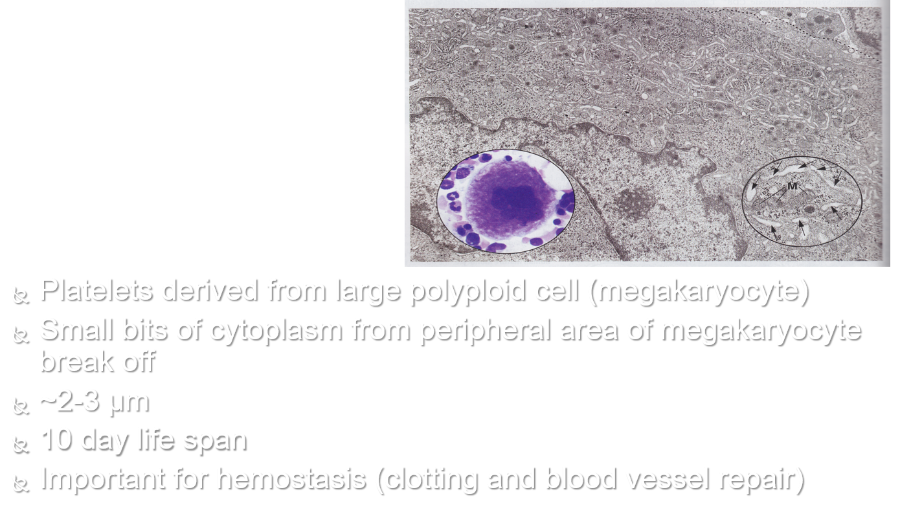
|
front 99 Human blood smear | back 99 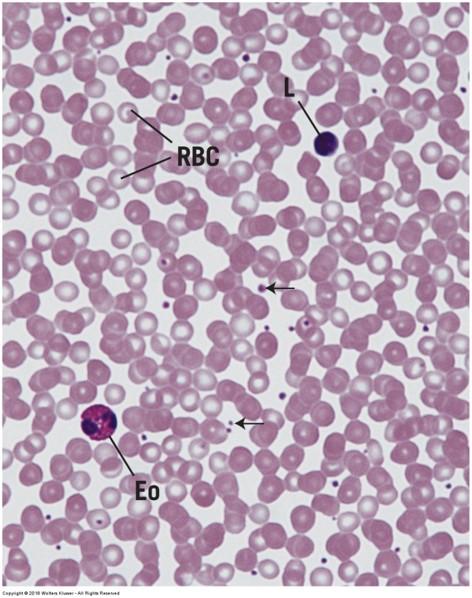 |
front 100 Formation of blood cells | back 100 Hemopoiesis (hematopoiesis) includes erythropoiesis, leukopoiesis, and thrombopoiesis Blood cells are continuously produced and destroyed Formed in red bone marrow and lymphatic tissue of adults
Monophyletic theory of hemopoiesis: blood cells derived from a common stem cell |
front 101 Formation of blood cells | back 101 Cell #1: Pluripotential hemopoietic stem cell in red bone marrow is common stem cell Cell #2 (one of the following):
Erythrocytes, granulocytes, monocytes, megakaryocytes
Lymphocytes Stem cells undergo numerous divisions and differentiations before mature blood cells are formed |
front 102 Formation of blood cells | back 102 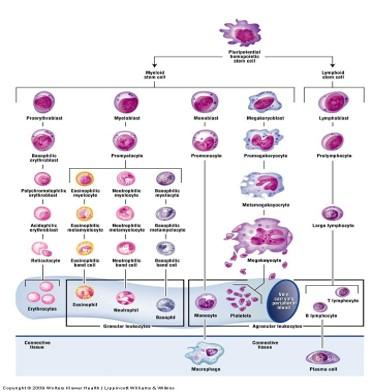 |
front 103 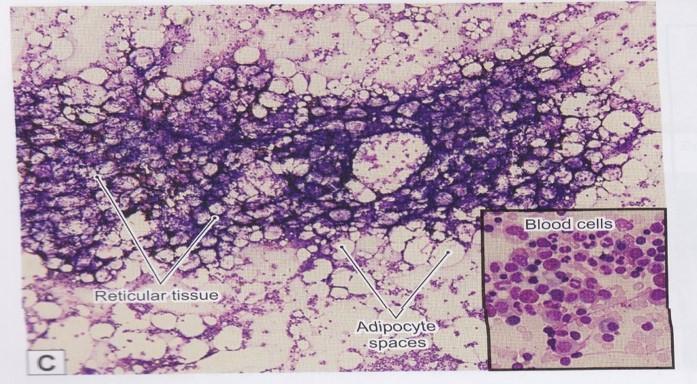 Red bone marrow: reticular connective tissue | back 103 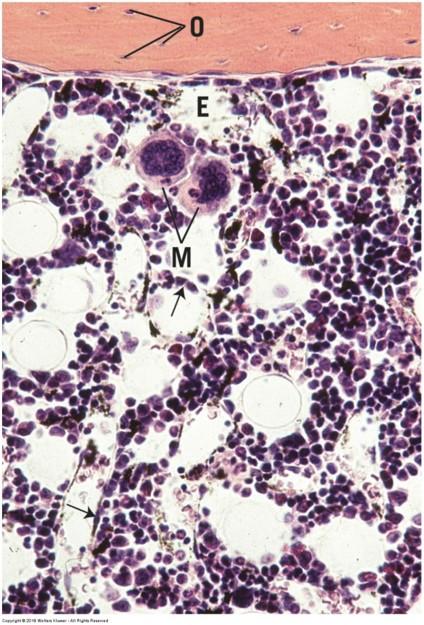 |
front 104 Erythropoiesis | back 104 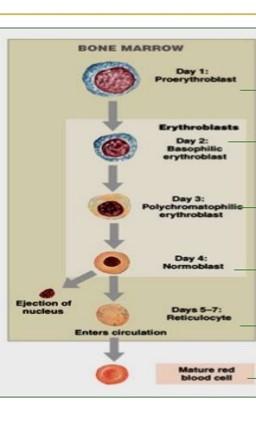 1.Pluripotential hemopoietic stem cell 2.Pluripotential myeloid stem cell 3.Proerythroblast 4.Basophilic erythroblast 5.Polychromatophilic erythroblast 6.Normoblast 7.Reticulocyte 8.Mature erythrocyte |
front 105 Development of granulocytes: part of leukopoiesis | back 105 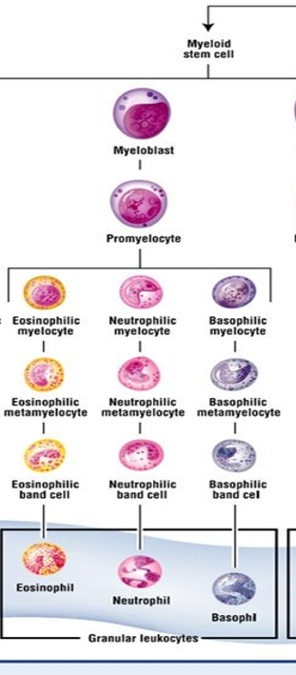 1.Pluripotential hemopoietic stem cell 2.Pluripotential myeloid stem cell 3.Myeloblast 4.Promyelocyte 5.Myelocyte (one of the following):
|
front 106 Development of monocytes: part of leukopoiesis | back 106 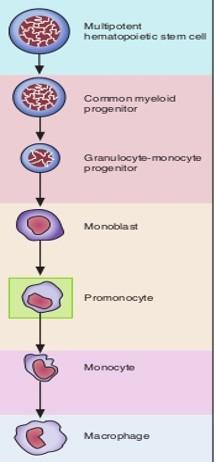 1.Pluripotential hemopoietic stem cell 2.Pluripotential myeloid stem cell 3.Monoblast 4.Promonocyte 5.Monocyte leaves blood à Macrophage in connective tissue |
front 107 Development of lymphocytes: part of leukopoiesis | back 107 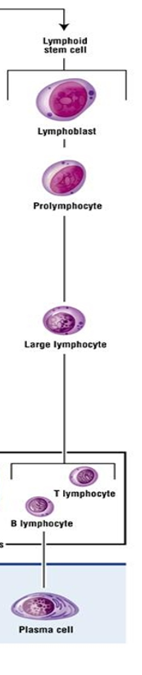 1.Pluripotential hemopoietic stem cell 2.Pluripotential lymphoid stem cell 3.Lymphoblast 4.Prolymphocyte 5.Large lymphocyte
|
front 108 Thrombopoiesis | back 108 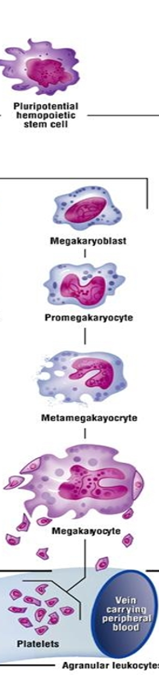 1.Pluripotential hemopoietic stem cell 2.Pluripotential myeloid stem cell 3.Megakaryoblasts 4.Megakaryocytes 5.Platelets |
front 109 Muscle | back 109 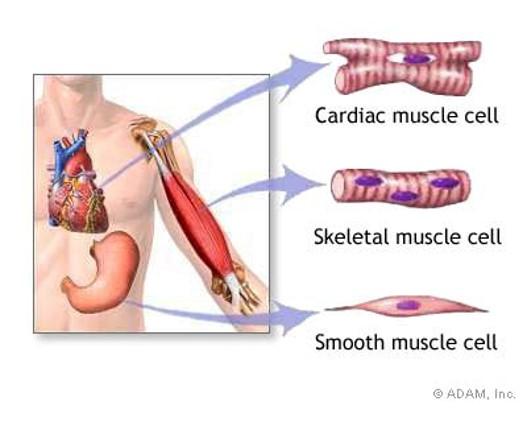 |
front 110 Muscle types | back 110 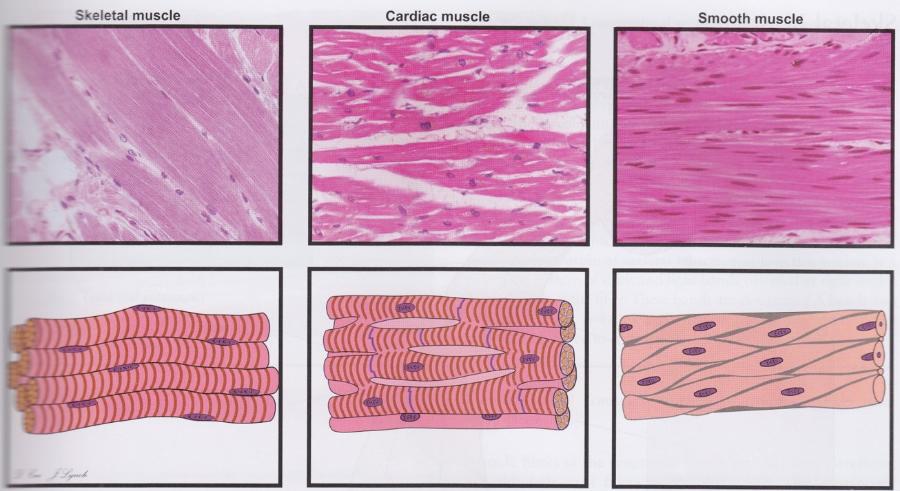 Cells are oriented differently in three muscle types. |
front 111 Functions of muscle tissue | back 111 Movement of body and parts of the body
Change size and shape of internal organs
|
front 112 Features of all muscle tissue | back 112 Aggregates of specialized, elongated cells arranged for mechanical work Myofilaments are the contractile proteins (clustered into myofibrils)
Special terms for cellular structures
|
front 113 Striated vs. smooth muscle | back 113 Striated have stripes that are visible under the light microscope due to the arrangement of myofilaments (sarcomere)
Smooth has no stripes because myofilaments are not arranged into sarcomeres |
front 114 Skeletal muscle | back 114 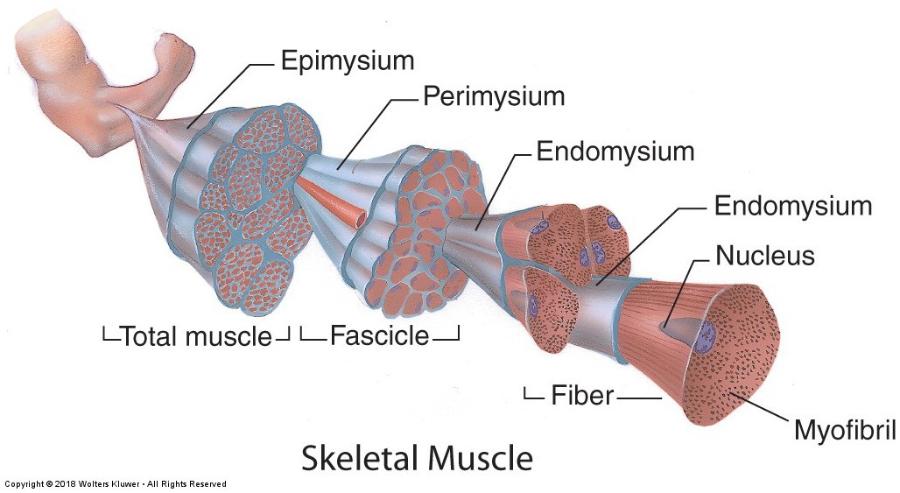
|
front 115 Skeletal muscle- longitudinal section | back 115 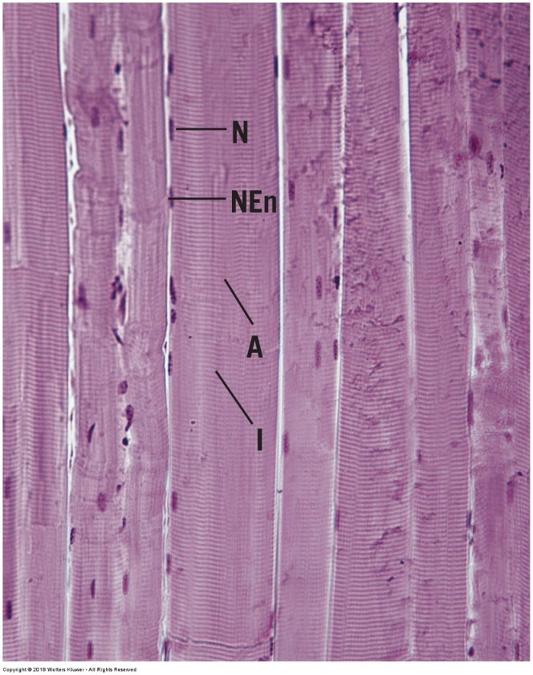 |
front 116 skeletal muscle-cross section | back 116 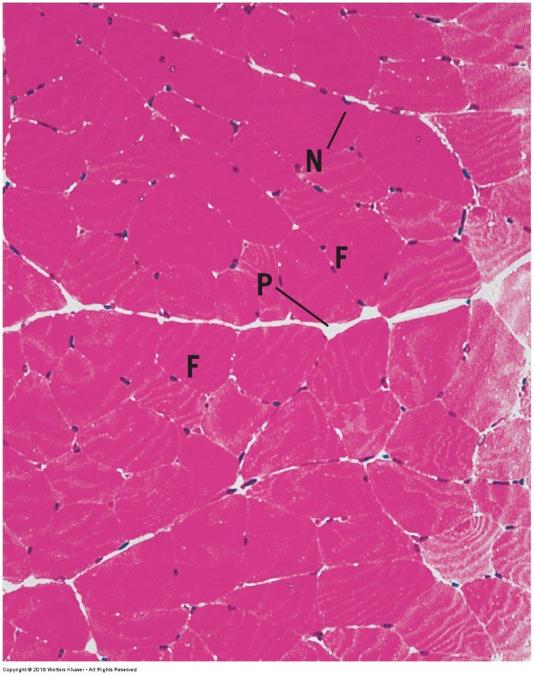 |
front 117 Skeletal muscle | back 117 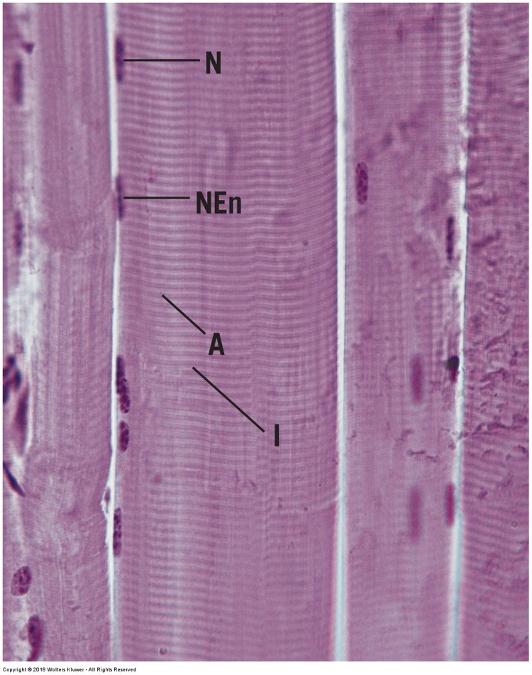 |
front 118 Skeletal muscle organization: connective tissue sheaths | back 118 
|
front 119 Skeletal muscle: myofilaments & sarcomere | back 119 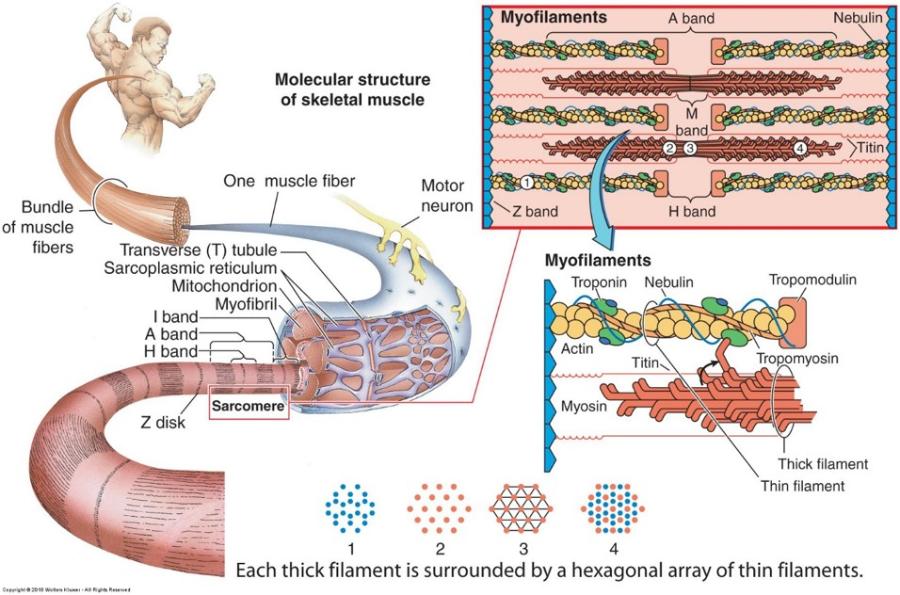 Each muscle cell is filled longitudinally with repeating arrays of myofilaments called myofibrils Striations
Sarcomere = Z disc to Z disc |
front 120 Duchenne’s Muscular Dystrophy | back 120 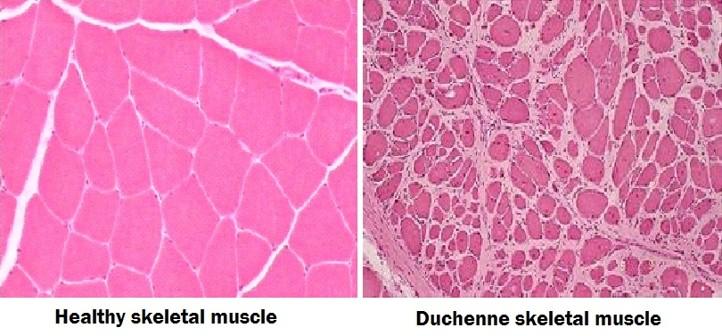
|
front 121 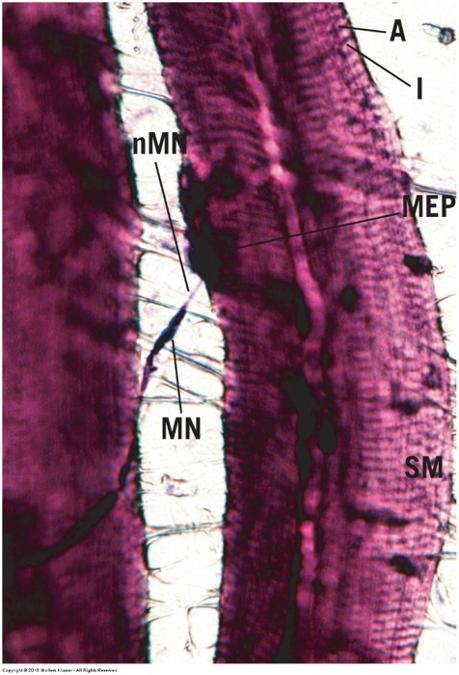 Skeletal muscle: motor innervation | back 121 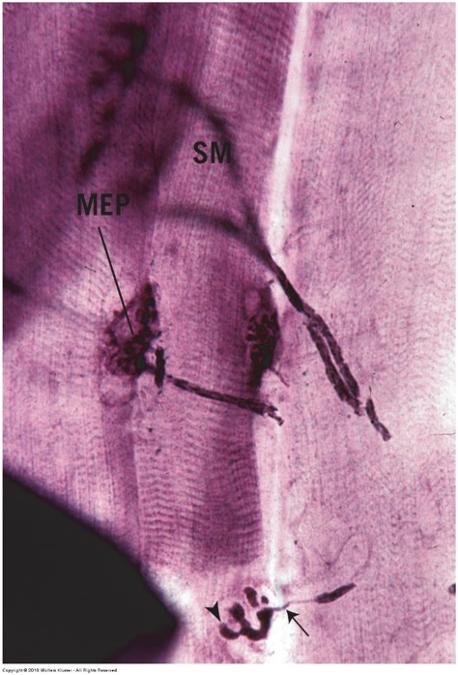
|
front 122 Cardiac muscle | back 122 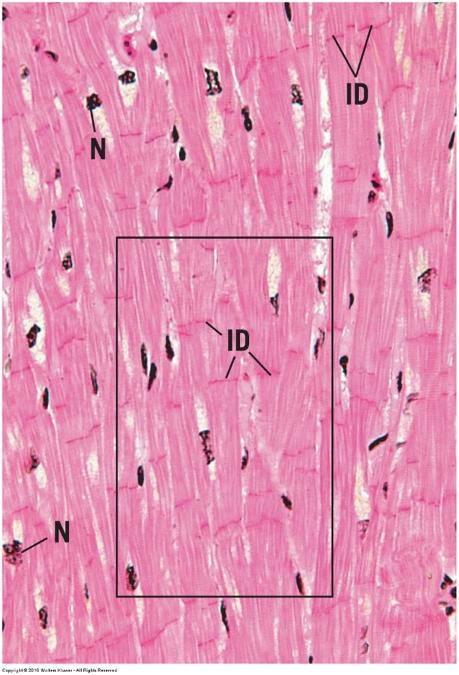
|
front 123 Cardiac muscle | back 123 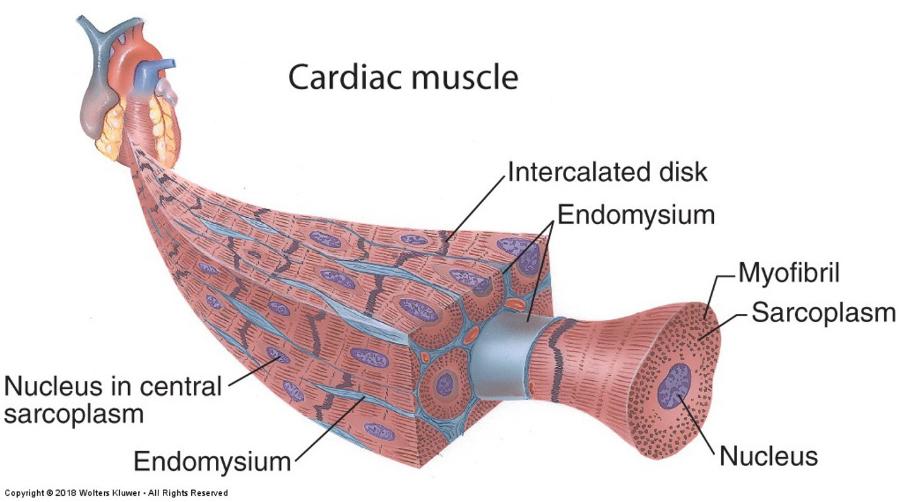 |
front 124 Cardiac muscle | back 124 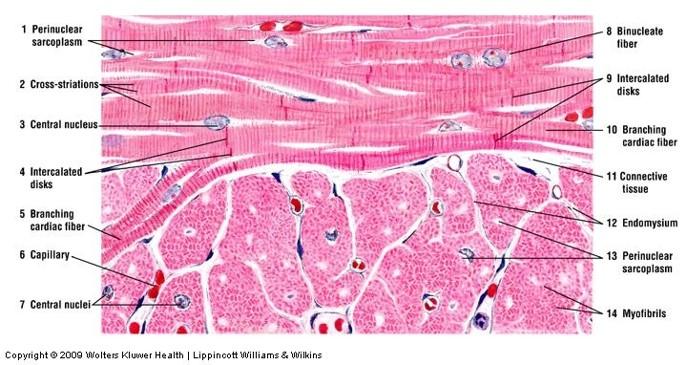 |
front 125 Cardiac muscle- longitudinal section | back 125 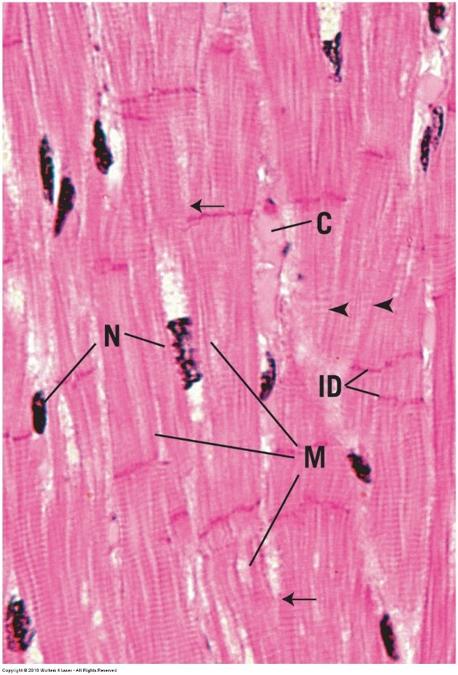 |
front 126 cardiac muscle- cross section | back 126 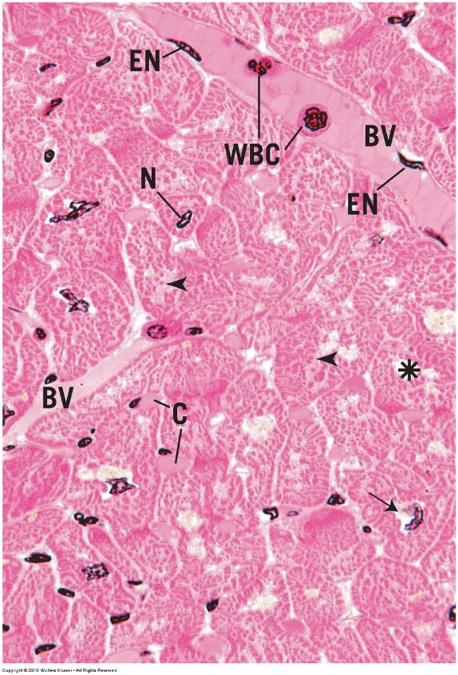 |
front 127 Myocardial Infarction: Heart Attack | back 127 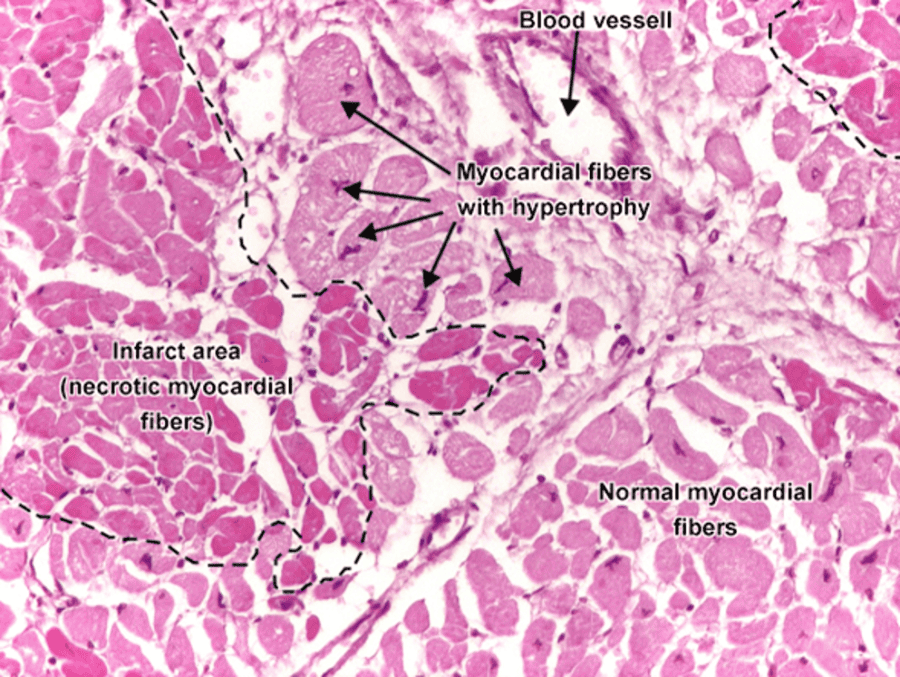 |
front 128 smooth muscle | back 128 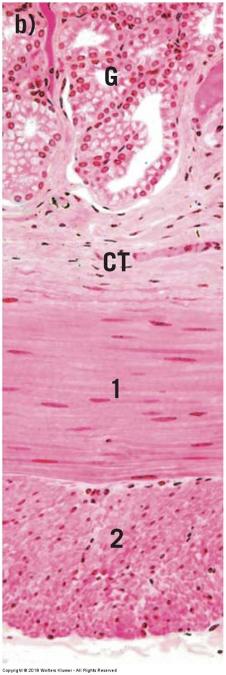
|
front 129 Smooth muscle | back 129 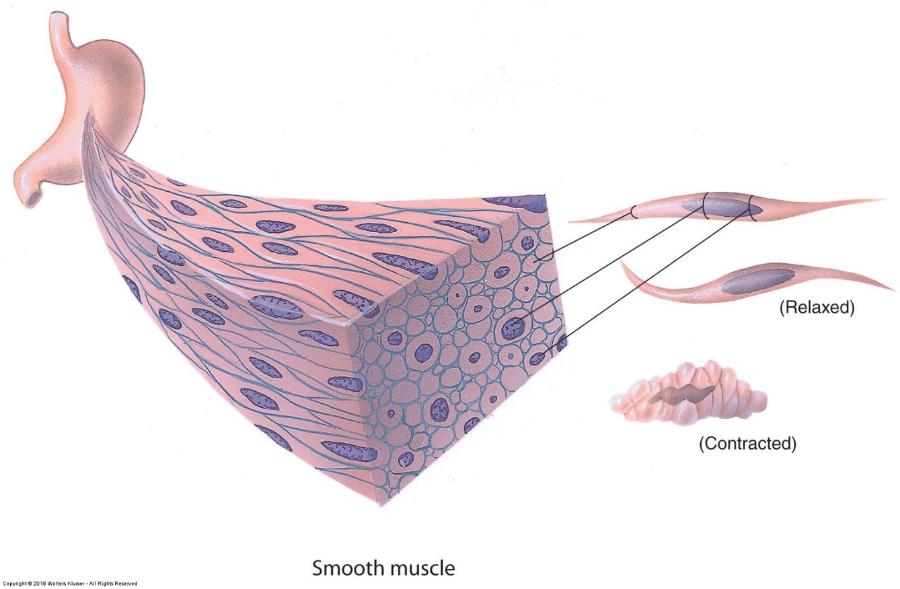 |
front 130 Smooth muscle- longitudinal section | back 130 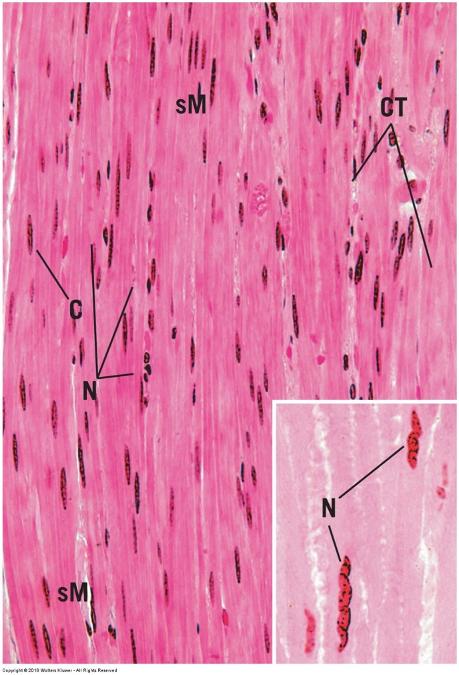 |
front 131 smooth muscle- cross section | back 131  |