Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 21
front 1 1) Which of the following blood vessels carries blood away from the heart to other organs?
| back 1 a |
front 2 2) Which of the following blood vessels carries blood from the tissues back to the heart?
| back 2 d |
front 3 3) Which layer of the arterial wall is responsible for vasoconstriction?
| back 3 b |
front 4 4) A blockage in the proximal portion of the right subclavian artery will not only affect circulation to the right arm, but also to the
| back 4 d |
front 5 5) The bronchial arteries arise from the
| back 5 e |
front 6 6) A blockage in the external iliac artery will reduce blood flow to the
| back 6 c |
front 7 7) In resting individuals, which vessels serve as a large blood reservoir from which blood can be quickly diverted to other vessels as needed?
| back 7 d |
front 8 8) In order to supply nourishment to liver tissue, which vessel must deliver blood to the organ?
| back 8 a |
front 9 9) If a patient is confined to bed and is unable to walk at all, which of the following will be seriously affected?
| back 9 c |
front 10 10) Capillaries are also referred to as
| back 10 a |
front 11 12) The layer of a blood vessel that is in direct contact with the blood is the
| back 11 c |
front 12 the layer of the vessel that is made up of smooth muscle and elastic fibers is the
| back 12 d |
front 13 13) Which of the following is the most important method of capillary exchange?
| back 13 a |
front 14 14) Which of the following structures is used to control the flow of blood through a capillary bed?
| back 14 b |
front 15 15) Which of the following types of tissues contains continuous capillaries?
| back 15 e |
front 16 16) The alternate route of blood flow to a body part through an anastomosis is called
| back 16 d |
front 17 17) The largest driving force for pulling fluid from the interstitial spaces back into the capillaries is
| back 17 c |
front 18 18) The pressure-driven movement of fluids and solutes from blood into interstitial fluid is called
| back 18 b |
front 19 19) The volume of blood that circulates through the systemic (or pulmonary) blood vessels per minute is called
| back 19 c |
front 20 20) Cardiac output is dependent on both
| back 20 a |
front 21 21) Vascular resistance depends on which of these factors? Select all that apply.
| back 21 a,b,c |
front 22 22) Which of the following would NOT result in an increase in arterial blood pressure?
| back 22 e |
front 23 23) Which of the following would NOT result in an increase in systemic vascular resistance?
| back 23 c |
front 24 24) The right common carotid artery branches directly off the
| back 24 c |
front 25 25) Which of the following is NOT a contribution of the cardiovascular system to other body systems?
| back 25 c |
front 26 26) The cardiovascular center is located
| back 26 d |
front 27 27) The most common disorder affecting the heart and blood vessels is
| back 27 e |
front 28 28) Pericardial arteries supply blood to the
| back 28 d |
front 29 29) Which of the following hormones would NOT stimulate changes that lead to an increase in arterial blood pressure?
| back 29 a |
front 30 30) Blood flow passing through the posterior aspect of the knee is achieved through the
| back 30 b |
front 31 32) The circulatory system aids in the homeostasis of the skeletal system by
| back 31 e |
front 32 33) Nutrients from digested food enter the liver via the
| back 32 a |
front 33 34) Abnormal conditions such as atherosclerosis and patent (open) ductus arteriosus cause a large increase in the
| back 33 c |
front 34 35) The branches from the ascending aorta that supply blood to the cardiac muscle are the
| back 34 b |
front 35 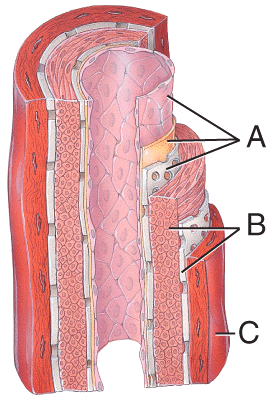 38) Which of the labeled layers in the diagram of the arterial wall consists mainly of elastic fibers and smooth muscle fibers? | back 35 b |
front 36  39) Which of the labeled layers in the diagram of the arterial wall is composed of a simple squamous epithelium, a basement membrane and a layer of elastic tissue? | back 36 a |
front 37 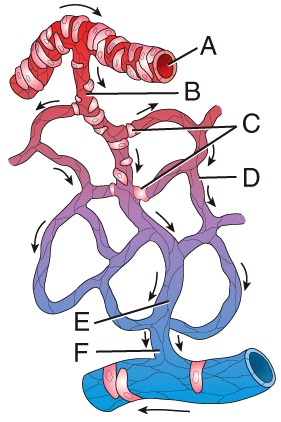 40) Which labeled structure in the figure is a metarteriole? | back 37 b |
front 38 41) A blockage to one or both of the inferior phrenic veins will cause a backup of blood into which structure?
| back 38 d |
front 39  42) Which labeled structure in the figure is precapillary sphincter? | back 39 c |
front 40 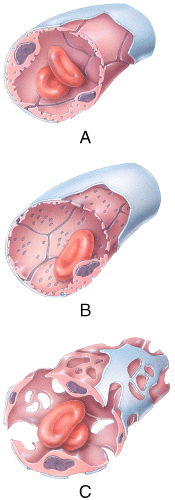 43) Which of the capillaries shown in the figure has an incomplete or absent basement membrane? | back 40 c |
front 41  44) Which of the types of capillaries shown in the figure is commonly found in the kidneys, villi of the small intestine, choroid plexuses, and some endocrine glands? | back 41 b |
front 42 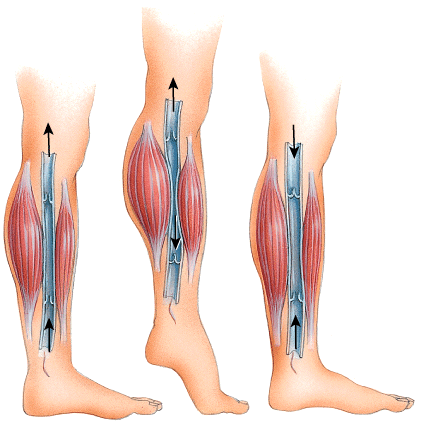 45) What physiological process is depicted in this figure?
| back 42 b |
front 43 47) Which of the following would NOT occur in response to hypovolemic shock?
| back 43 d |
front 44 48) All the veins of the systemic circulation eventually drain into the
e) superior and inferior vena cava and coronary sinus | back 44 e |
front 45 49) The pulmonary trunk divides into
| back 45 d |
front 46 50) If the foramen ovale doesn’t close at birth, the result will be
| back 46 d |
front 47 52) Which of the following vessels supplies blood to the intestines?
| back 47 c |
front 48 54) Which of the following vessels drains blood from the lower leg?
| back 48 c |
front 49 55) Which of the following vessels drains blood from the head and neck?
| back 49 e |
front 50 56) Which of the following vessels carries the venous blood from the lower body into the right atrium?
| back 50 a |
front 51 57) When the umbilical cord is tied after birth, the umbilical arteries close by filling in with
| back 51 c |
front 52 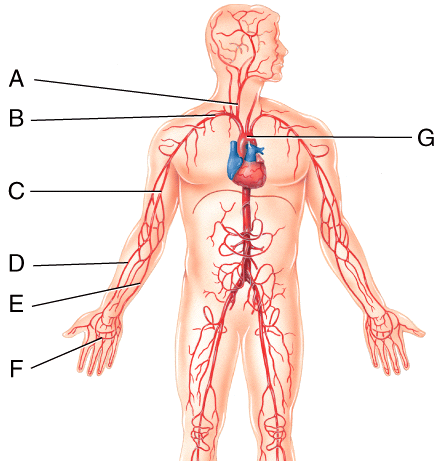 63) Which vessel in the figure is labeled “B”?
| back 52 b |
front 53  64) Which vessel in the figure is labeled “A”?
| back 53 c |
front 54 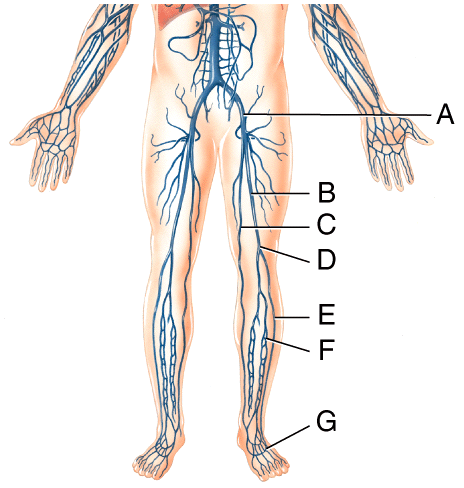 65) Which vessel in the figure is labeled “B”?
e) left fibular vein | back 54 a |
front 55  66) Which vessel in the figure is labeled “C”?
| back 55 b |
front 56  67) Which vessel in the figure is labeled “F”?
| back 56 d |
front 57 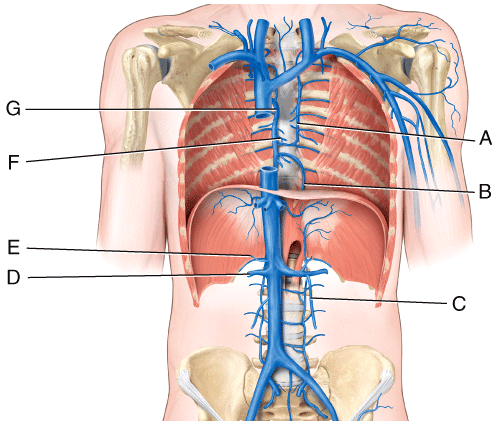 68) Which vessel in the figure is labeled “C”?
| back 57 c |
front 58  69) Which vessel in the figure is labeled “D”?
| back 58 c |
front 59  70) Which vessel in the figure is labeled “G”?
| back 59 e |
front 60 71) In the fetal heart, several structures allow blood from the left and right sides to mix. When the newborn takes its first breath, these structures must close to ensure that oxygenated blood from the left side does not mix with deoxygenated blood from the right side. Which of the following closed structures prevent this mixing between the systemic and pulmonary circulation after the umbilical cord is cut? Select all that apply.
| back 60 a,b |
front 61 73) During embryonic development, blood vessels are formed by
| back 61 c |
front 62 74) During embryonic development, blood cells are formed from
| back 62 b |
front 63 76) Normal blood pressure for a young adult male is less than
| back 63 a |
front 64 77) Which of the following types of blood vessels have high, pulsing blood pressure?
| back 64 a |
front 65 78) What would the mean arterial pressure be for an individual with a blood pressure of 120/80?
| back 65 b |
front 66 79) Which of the following effectors would NOT be activated as described below in response to hypovolemic shock?
| back 66 d |
front 67 80) The pulmonary circulatory route carries blood from the
| back 67 b |
front 68 81) Emphysema is a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) that causes progressive destruction of alveoli (air sacs) in the lungs leading to a decreased ability to exhale. How does this disease affect carbon dioxide levels in the blood?
| back 68 b |
front 69 82) Into which of the following categories would an individual with a blood pressure of 145/95 be placed?
| back 69 d |
front 70 83) Which of the following categories of hypertension drugs lower blood pressure by blocking formation of angiotensin II, which results in vasodilation and decreased aldosterone secretion?
| back 70 b |
front 71 84) Which of the following veins drains the muscles, bones and skin of the hand of the forearm? Select all that apply.
| back 71 b,c |
front 72 85) The chemical histamine causes capillary walls to become more permeable. Excess histamine secretion, as might be seen in allergic responses, might lead to
| back 72 b |