Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Human Anatomy Final
front 1 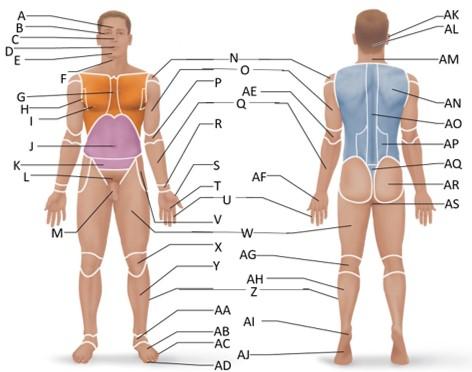 Which letter is the frontal region? | back 1 A |
front 2 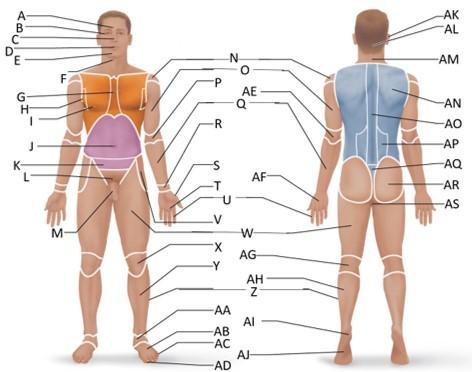 Which letter is the orbital region? | back 2 B |
front 3 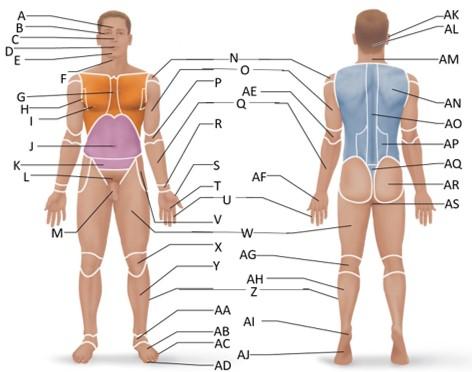 Which letter is the nasal region? | back 3 C |
front 4  Which letter is the oral region? | back 4 D |
front 5 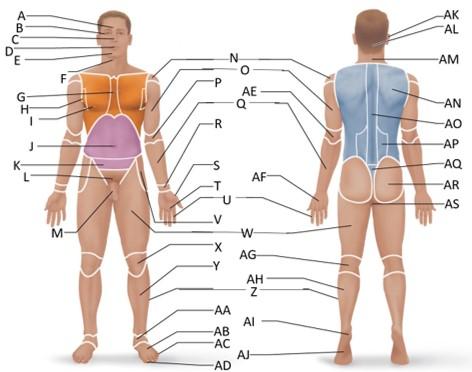 Which letter is the mental region? | back 5 E |
front 6 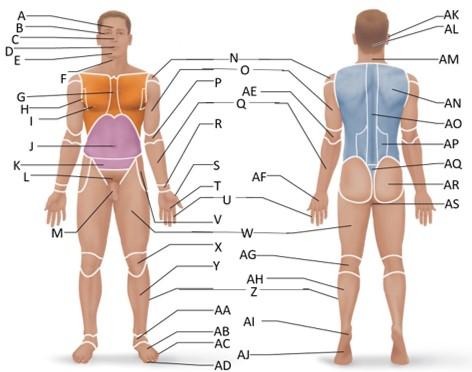 Which letter is the sternal region? | back 6 G |
front 7 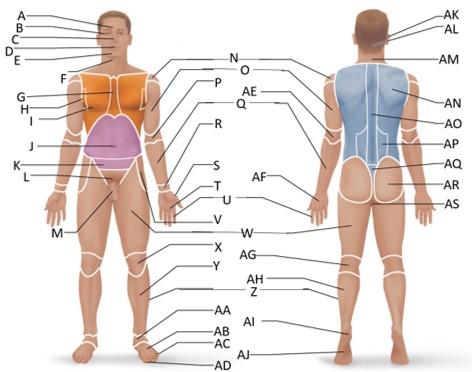 Which letter is the axillary region? | back 7 H |
front 8 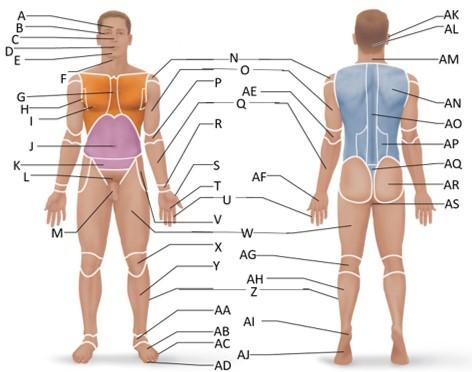 Which letter is the mammary region? | back 8 I |
front 9  Which letter is the umbilical region? | back 9 J |
front 10 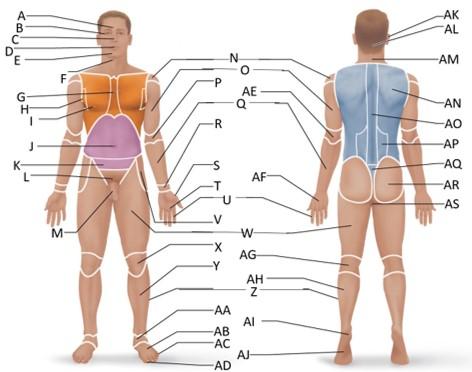 Which letter is the cervical region? | back 10 F |
front 11 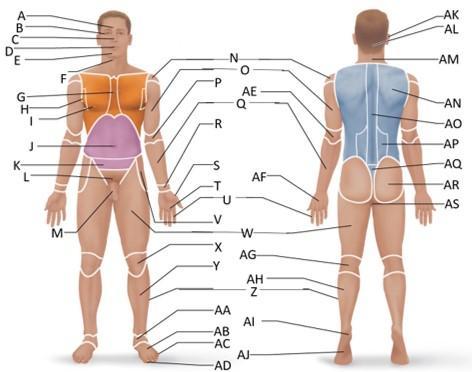 Which letter is the inguinal region? | back 11 J |
front 12 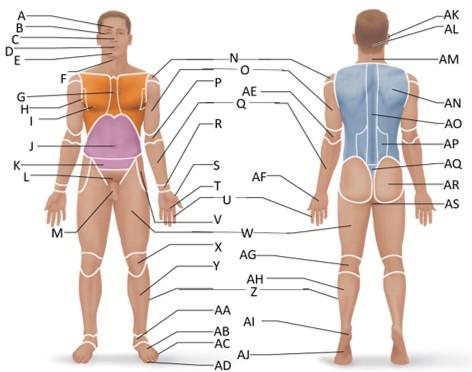 Which letter is the pubic region? | back 12 M |
front 13 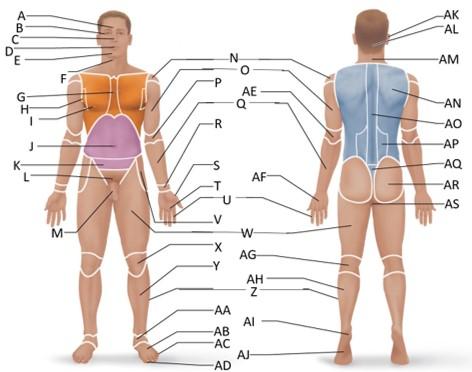 Which letter is the pelvic region? | back 13 K |
front 14 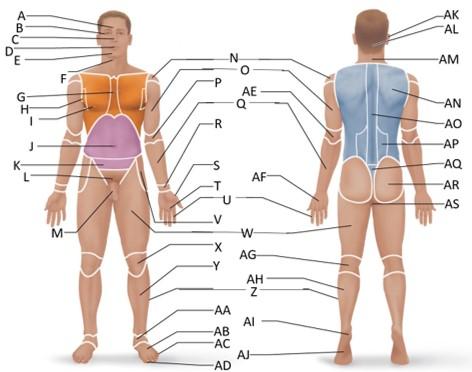 Which letter is the acromial region? | back 14 N |
front 15 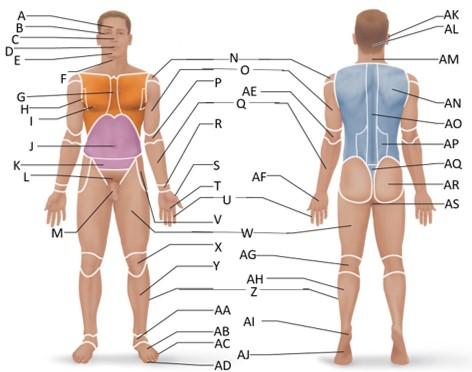 Which letter is the brachial region? | back 15 O |
front 16 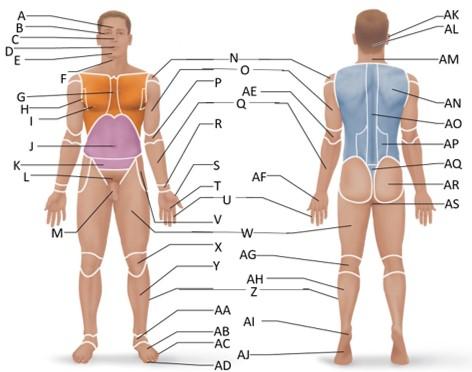 Which letter is the antecubital region? | back 16 P |
front 17  Which letter is the olecranal region? | back 17 AE |
front 18 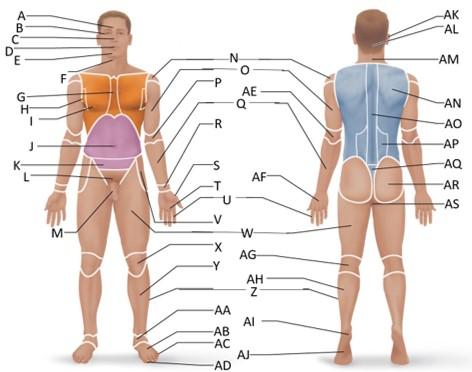 Which letter is the antebrachial region? | back 18 Q |
front 19 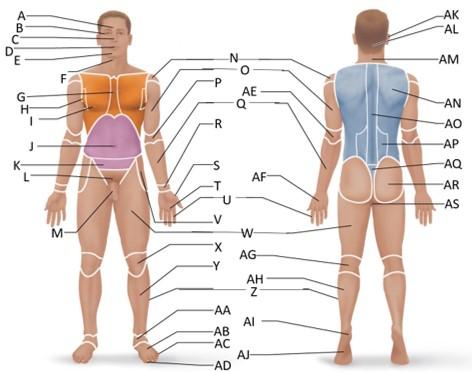 Which letter is the carpal region? | back 19 R |
front 20 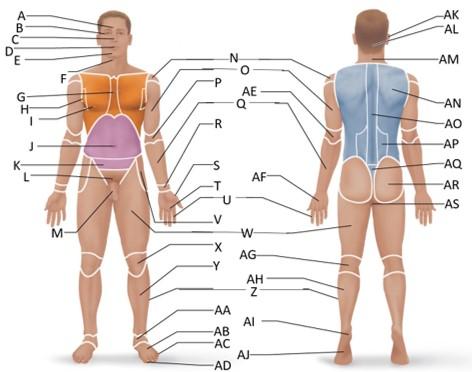 Which letter is the pollex region? | back 20 S |
front 21 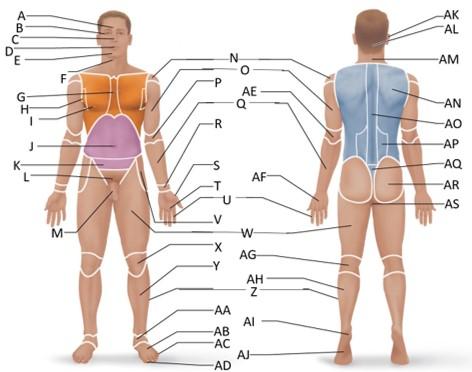 Which letter is the metacarpal region? | back 21 AF |
front 22 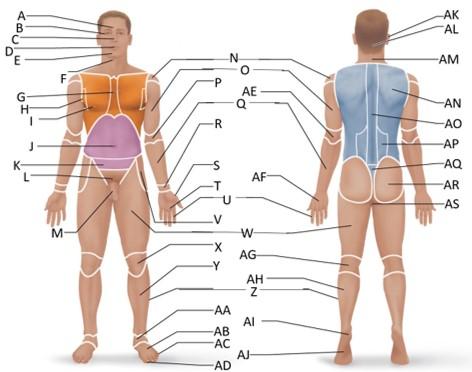 Which letter is the palmar region? | back 22 T |
front 23 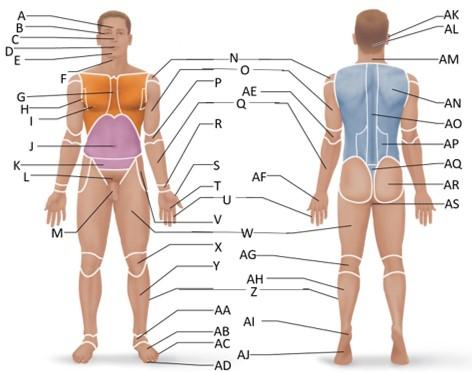 Which letter is the digital (hand) region? | back 23 U |
front 24 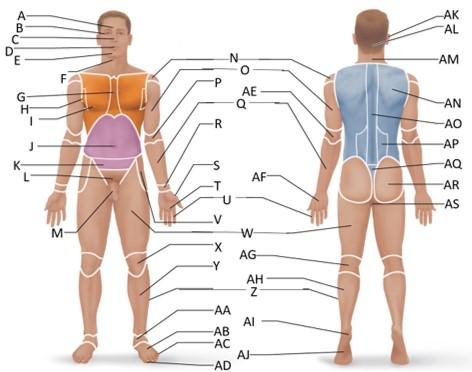 Which letter is the coxal region? | back 24 V |
front 25 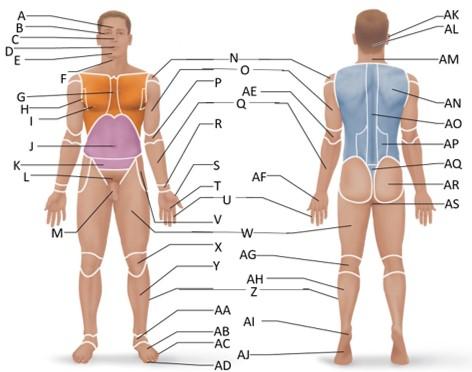 Which letter is the femoral region? | back 25 W |
front 26  Which letter is the patellar region? | back 26 X |
front 27 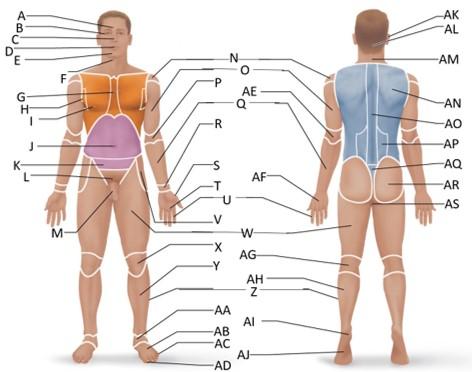 Which letter is the popliteal region? | back 27 AG |
front 28 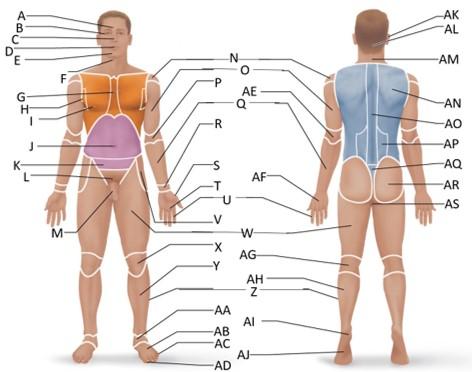 Which letter is the crural region? | back 28 Y |
front 29 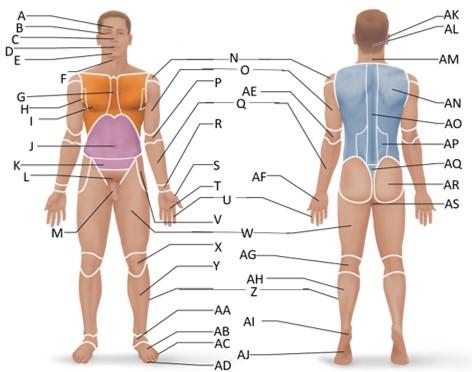 Which letter is the fibular or peroneal region? | back 29 Z |
front 30 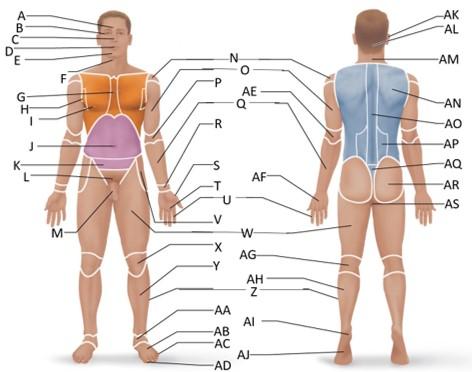 Which letter is the tarsal region? | back 30 AA |
front 31 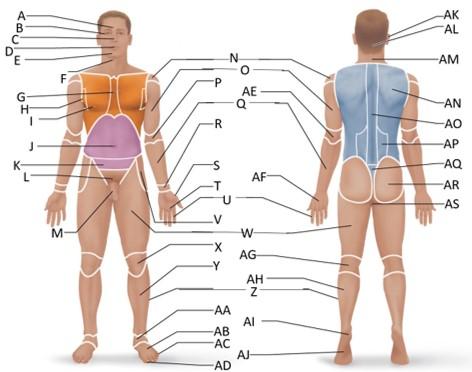 Which letter is the calcaneal region? | back 31 AI |
front 32 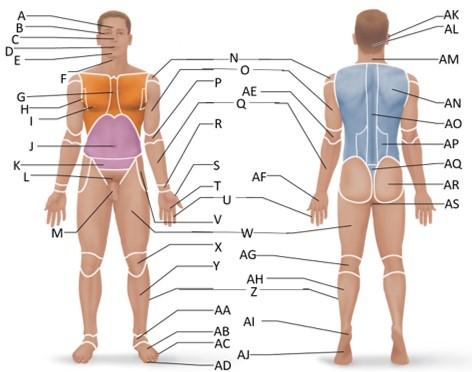 Which letter is the metatarsal region? | back 32 AB |
front 33 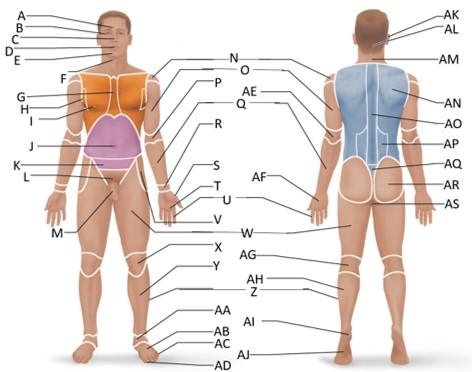 Which letter is the digital (toes) region? | back 33 AC |
front 34 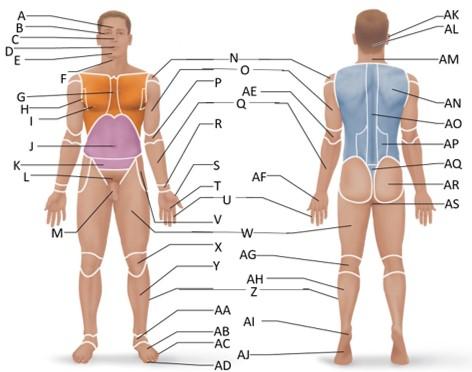 Which letter is the plantar region? | back 34 AJ |
front 35 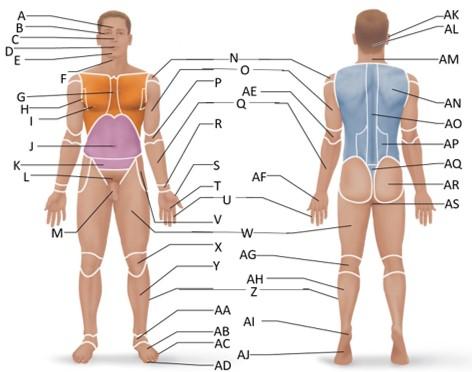 Which letter is the hallux region? | back 35 AD |
front 36 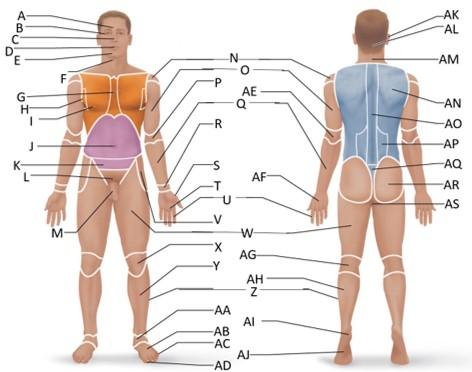 Which letter is the otic region? | back 36 AK |
front 37 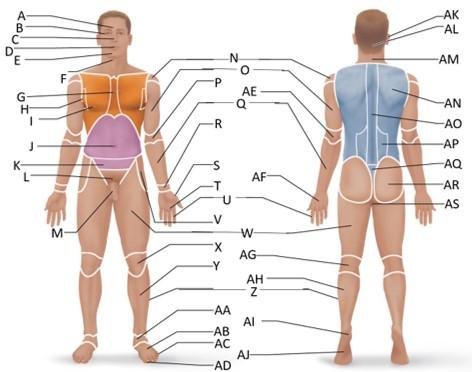 Which letter is the occipital region? | back 37 AL |
front 38 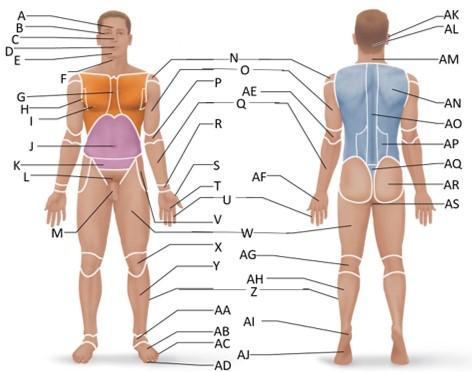 Which letter is the scapular region? | back 38 AN |
front 39 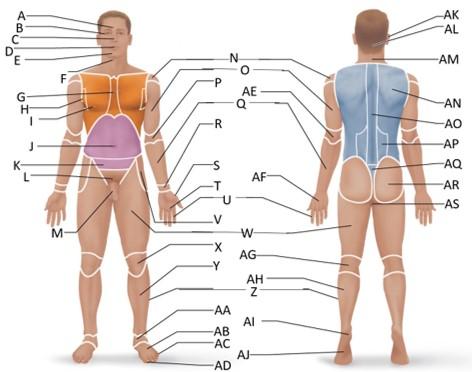 Which letter is the vertebral region? | back 39 AO |
front 40  Which letter is the lumbar region? | back 40 AP |
front 41 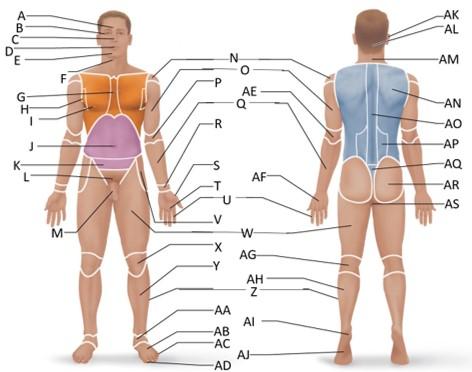 Which letter is the sacral region? | back 41 AQ |
front 42 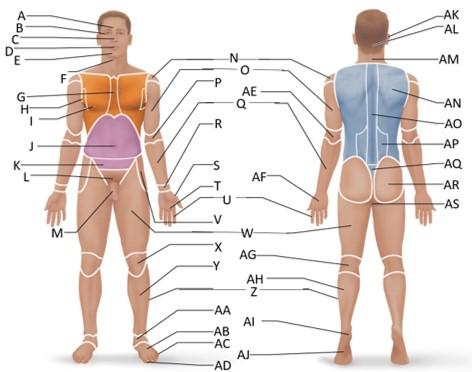 Which letter is the gluteal region? | back 42 AR |
front 43 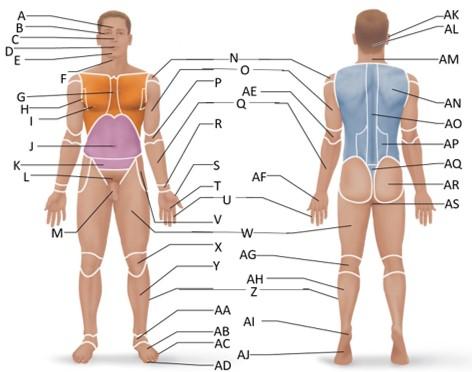 Which letter is the perineal region? | back 43 AS |
front 44 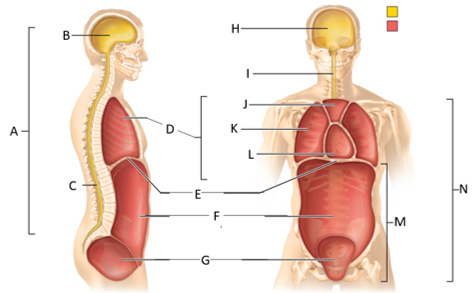 What letter is the dorsal body cavity? | back 44 A |
front 45 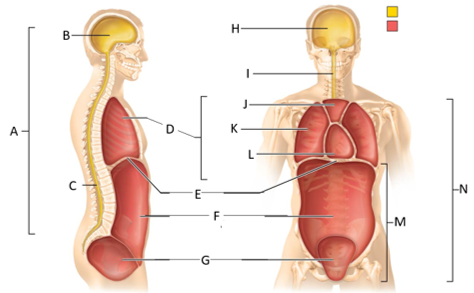 What letter is the cranial cavity (lateral view)? | back 45 B |
front 46 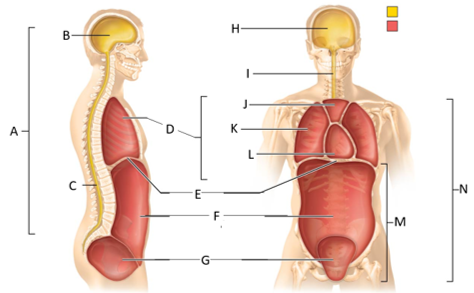 What letter is the vertebral cavity (lateral view)? | back 46 C |
front 47 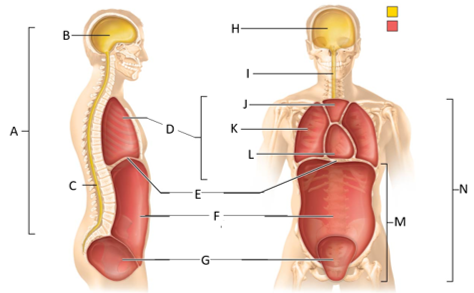 What letter is the thoracic cavity? | back 47 D |
front 48 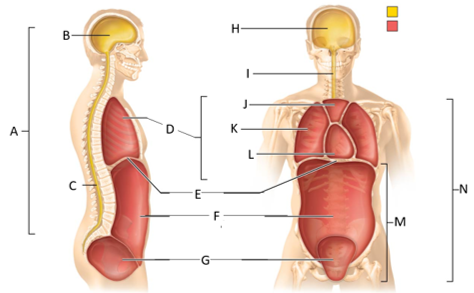 What letter is the diaphragm? | back 48 E |
front 49 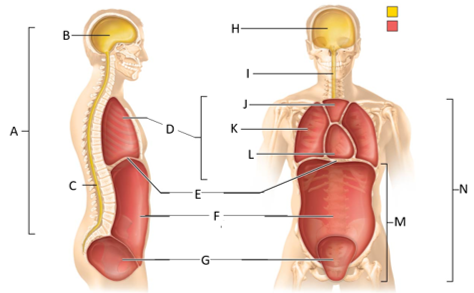 What letter is the pelvic cavity? | back 49 G |
front 50 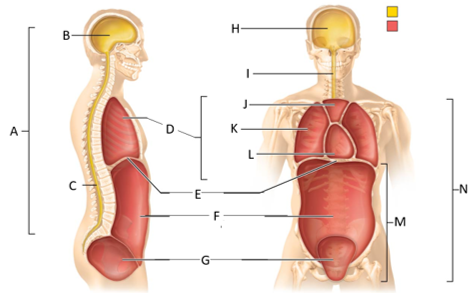 What letter is the abdominal cavity? | back 50 F |
front 51 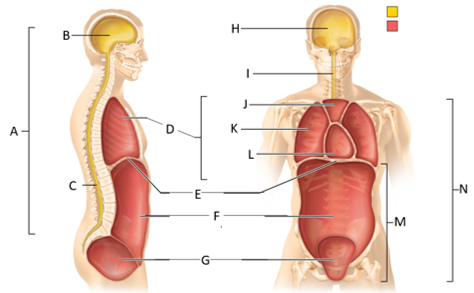 What letter is the cranial cavity (anterior view)? | back 51 H |
front 52 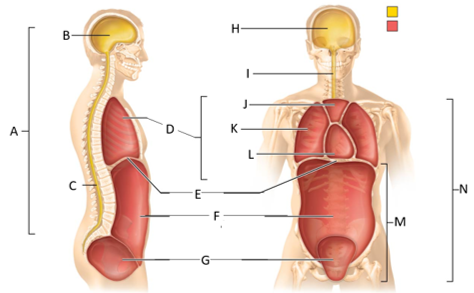 What letter is the vertebral cavity (anterior view)? | back 52 I |
front 53 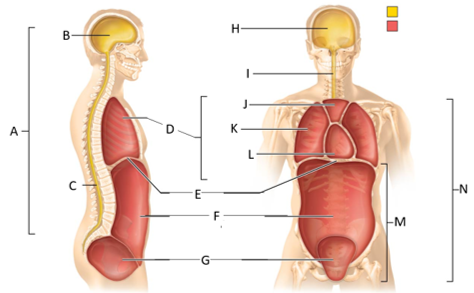 What letter is the superior mediastinum? | back 53 J |
front 54 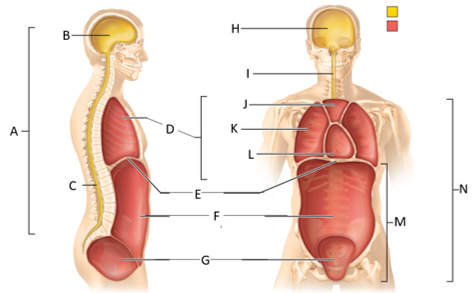 What letter is the pleural cavity? | back 54 K |
front 55 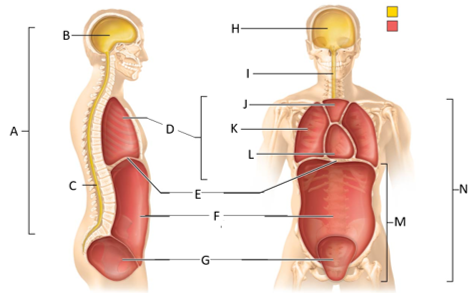 What letter is the pericardial cavity? | back 55 L |
front 56 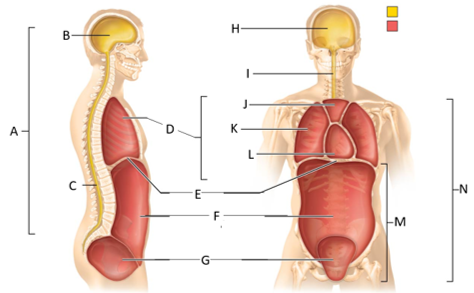 What letter is the abdominopelvic cavity? | back 56 M |
front 57 Which body cavity contains the cranial and vertebral cavities? | back 57 The dorsal body cavity |
front 58 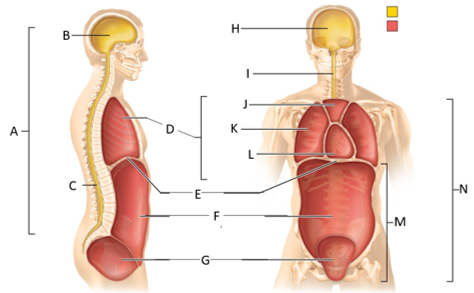 Which letter is the ventral body cavity? | back 58 N |
front 59 Which cavity contains the brain? | back 59 The cranial cavity |
front 60 Which cavity contains the spinal cord? | back 60 The vertebral cavity |
front 61 Which cavity contains the heart and lungs? | back 61 The thoracic cavity |
front 62 Which cavity contains the superior mediastinum, pleural cavity, and pericardial cavity? | back 62 The thoracic cavity |
front 63 Which cavity contains the lungs? | back 63 The pleural cavity |
front 64 Which cavity contains the heart? | back 64 The pericarical cavity |
front 65 Which cavity contains digestive viscera? | back 65 The abdominal cavity |
front 66 Which cavity contains the urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum? | back 66 The pelvic cavity |
front 67 Which body cavity contains the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities? | back 67 The ventral body cavity |
front 68 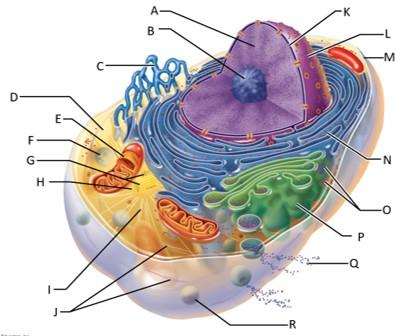 Which letter indicates chromatin? | back 68 A |
front 69  Which letter indicates the nucleolus? | back 69 B |
front 70 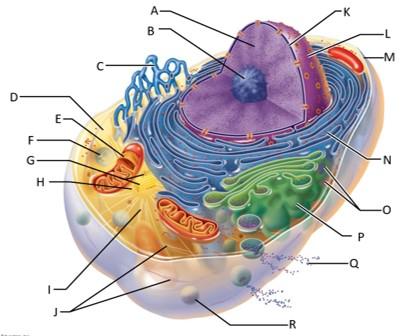 Which letter indicates the smooth endoplasmic reticulum? | back 70 C |
front 71 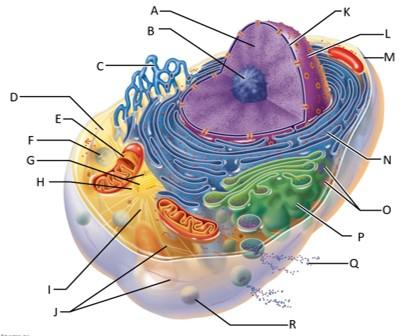 Which letter indicates the cytosol? | back 71 D |
front 72 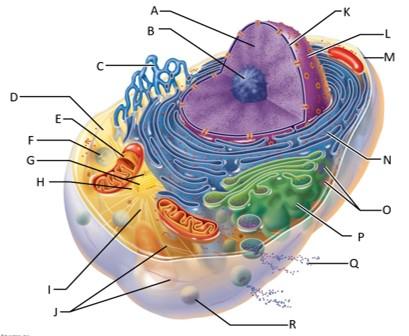 Which letter indicates the lysosome? | back 72 F |
front 73 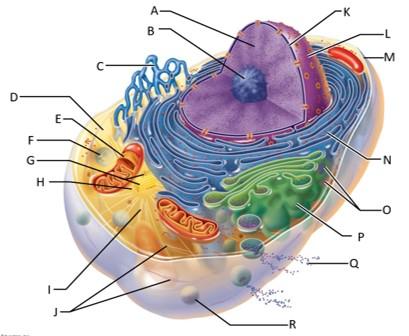 Which letter indicates the mitochondrion? | back 73 E |
front 74 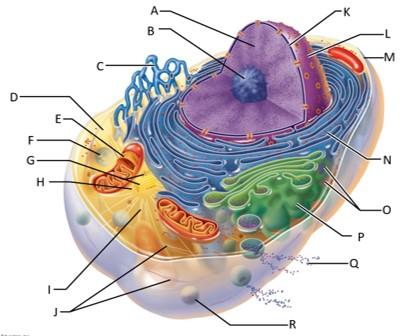 Which letter indicates the centrioles? | back 74 G |
front 75 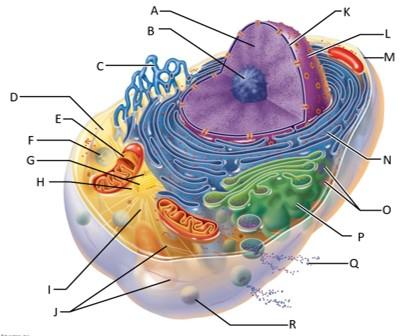 Which letter indicates the centrosome matrix? | back 75 H |
front 76 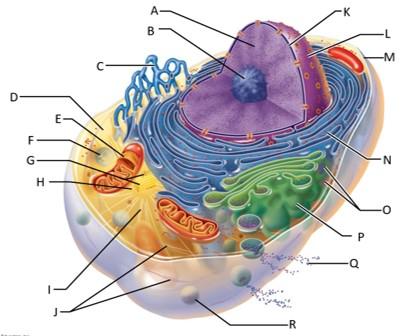 Which letter indicates microtubules? | back 76 I |
front 77 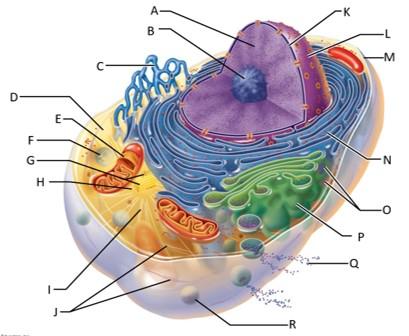 Which letter indicates intermediate filaments? | back 77 J |
front 78 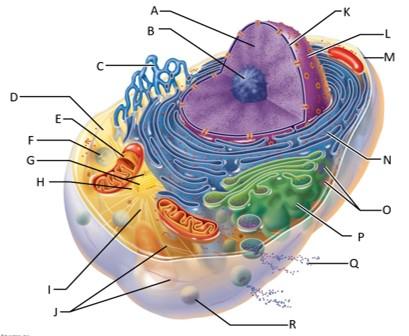 Which letter indicates the nuclear envelope? | back 78 K |
front 79 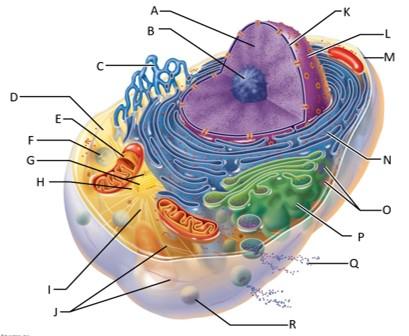 Which letter indicates the nucleus? | back 79 L |
front 80 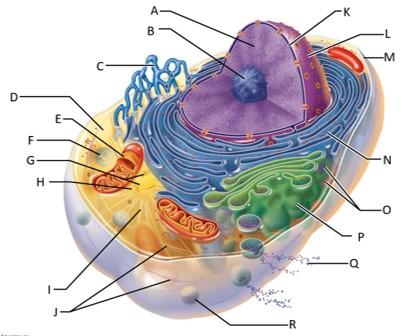 Which letter indicates the plasma membrane? | back 80 M |
front 81 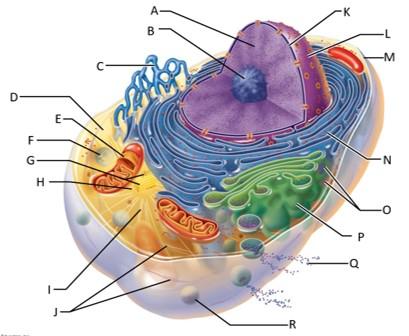 Which letter indicates the rough endoplasmic reticulum? | back 81 N |
front 82 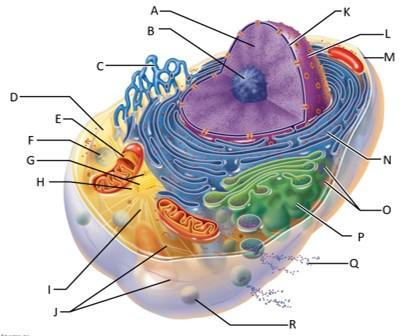 Which letter indicates ribosomes? | back 82 O |
front 83 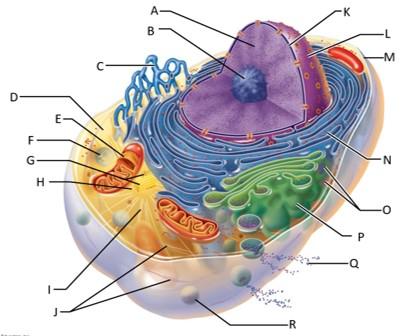 Which letter indicates the golgi apparatus? | back 83 P |
front 84 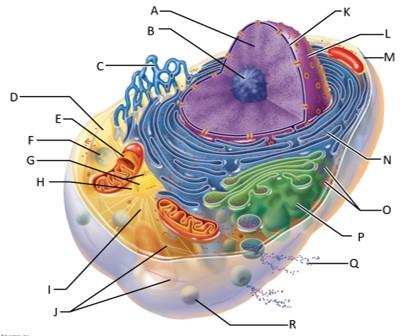 Which letter indicates a secretion being released from the cell by exocytosis? | back 84 Q |
front 85 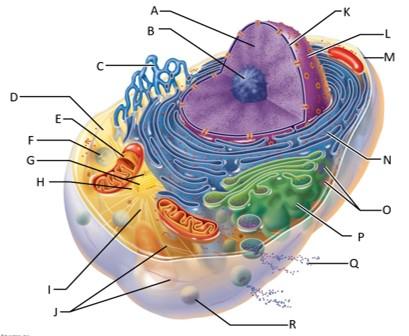 Which letter indicates a peroxisome? | back 85 R |
front 86 What serves as an external cell barrier and acts in the transport of substances into or out of the cell? | back 86 The plasma membrane? |
front 87 What is the granular, threadlike material that is composed of DNA and histone proteins? | back 87 Chromatin |
front 88 What is the site of ribosome subunit manufacture? | back 88 The nucleolus |
front 89 What is the site of lipid and steriod hormone synthesis, lipid metabolism, and drug detoxification? | back 89 The smooth ER |
front 90 What is the fluid containing dissolved solutes in the cytoplasm? | back 90 Cytosol |
front 91 What is the site of ATP synthesis? | back 91 Mitochondria |
front 92 What are the sites of intracellular digestion? | back 92 Lysosomes |
front 93 What organize a microtubule network during mitosis to form the spindle and asters? | back 93 Centrioles |
front 94 What support the cell and give it shape, are involved in intracellular movements, and form centrioles? | back 94 Microtubules? |
front 95 What are the stable cytoskeletal elements that resist tension forces acting on the cell? | back 95 Intermediate filaments |
front 96 What separates the nucleoplasm from the cytoplasm and regulates passage of substances to and from the nucleus? | back 96 The nuclear envelope |
front 97 What is the control center of the cell that is responsible for transmitting genetic information and providing the instructions for protein synthesis? | back 97 The nucleus |
front 98 What makes proteins that are secreted from the cell? | back 98 The rough ER |
front 99 What are the sites of protein synthesis? | back 99 Ribosomes |
front 100 What packages, modifies, and segregates proteins for secretion from the cell? | back 100 The golgi apparatus |
front 101 What are the enzymes that detoxify a number of toxic substances including hydrogen peroxide? | back 101 Peroxisomes |
front 102 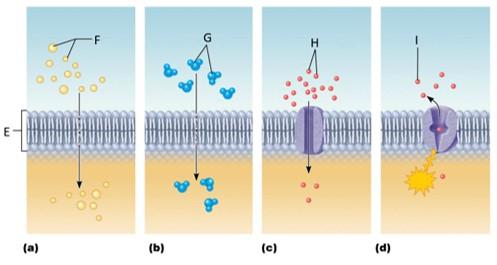 Which letter signifies simple diffusion? | back 102 A |
front 103 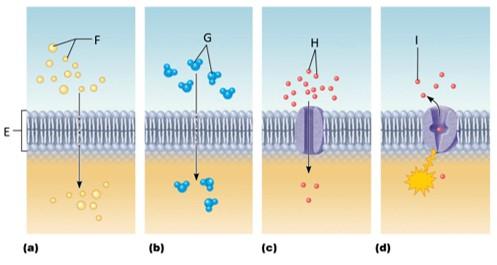 Which letter signifies osmosis? | back 103 B |
front 104 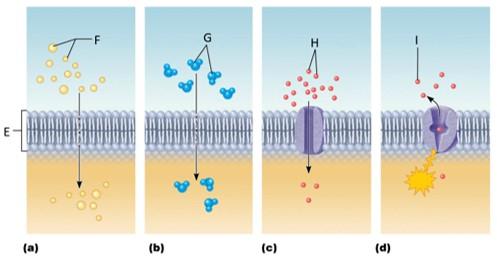 Which letter signifies facilitated diffusion? | back 104 C |
front 105 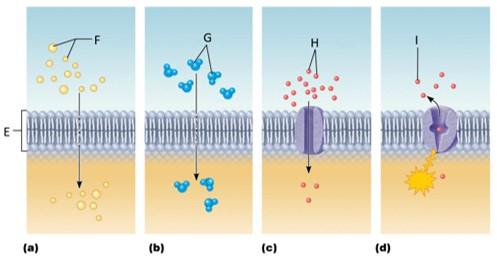 Which letter signifies active transport? | back 105 D |
front 106 What is simple diffusion? | back 106 The tendency of molecules to move down their concentration gradient |
front 107 What is osmosis? | back 107 The diffusion of water molecules across a membrane |
front 108 What is facilitated diffusion? | back 108 The movement of molecules down their concentration gradient through an integral protein |
front 109 What is active transport? | back 109 Intergral proteins moving molecules across the plasma membrane against their concentration gradient |
front 110 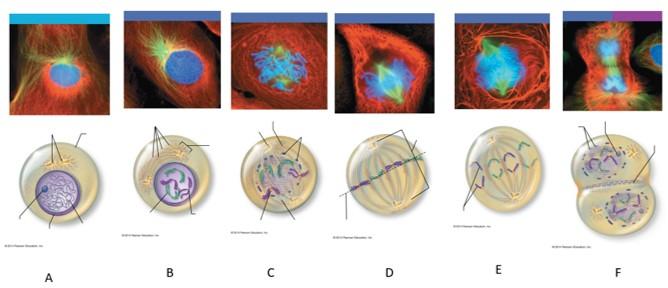 Which letter shows interphase? | back 110 A |
front 111 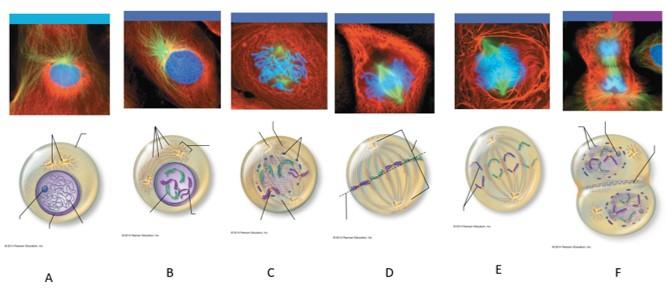 Which letter shows early prophase? | back 111 B |
front 112 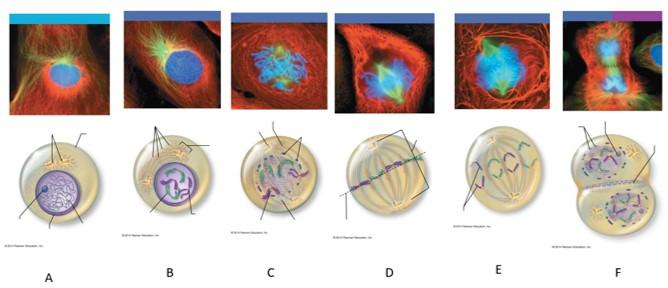 Which letter shows late prophase? | back 112 C |
front 113  Which letter shows metaphase? | back 113 D |
front 114 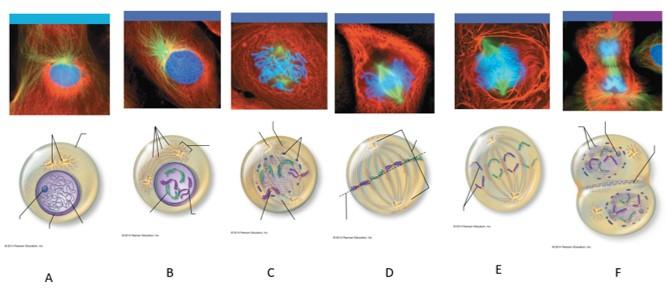 Which letter shows anaphase? | back 114 E |
front 115 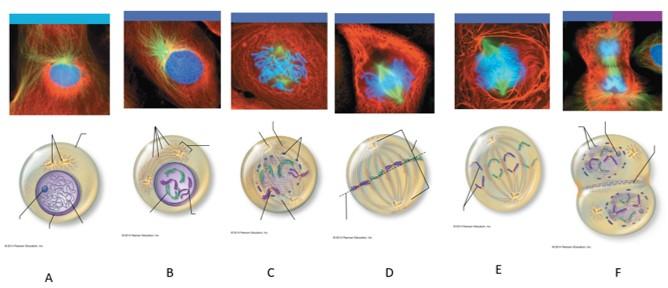 Which letter shows telophase and cytokenesis? | back 115 F |
front 116 What is interphase? | back 116 The period of a cell's life when it carries out its normal metabolic activities and grows. |
front 117 What happens during interphase? | back 117 The DNA-containing material is in the form of chromatin, and the nuclear envelope and one or more nucleoli are intact and visible. |
front 118 What happens during early prophase? | back 118 The chromatin coils and condenses, forming bar-like chromosomes. As the chromosomes appear, the nucleoli disappear, and the two centrosomes separate from one another. Microtubles lengthen and propel the centrosomes toward opposite poles of the cell. Asters extend from the centrosome matrix. |
front 119 What happens during late prophase? | back 119 The nuclear envelope breaks up, allowing the spindle to interact with the chromosomes. Microtubules draw the chromosomes to the center of the cell. |
front 120 What happens during metaphase? | back 120 The two centromeres are at opposite poles of the cell. The chromosomes align at the midline of the cell. |
front 121 What happens during anaphase? | back 121 The centromeres split, and each chromatid becomes its own chromosome. The microtubules pull each chromosome toward a pole as the poles are pushed apart. |
front 122 What happens during telophase? | back 122 The identical sets of chromosomes at the opposite poles of the cell begin to uncoil and resume their threadlike chromatin form. A new nuclear envelope forms around each chromatin mass, nucleoli reappear within the nuclei, and the spindle breaks down and disappears. |
front 123 What happens during cytokenesis? | back 123 A contractile ring of actin microfilaments forms a cleavage furrow around the cell and pinches it apart. |
front 124 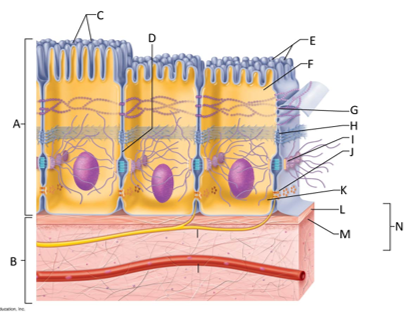 What letter is the epithelium? | back 124 A |
front 125  What letter is connective tissue? | back 125 B |
front 126 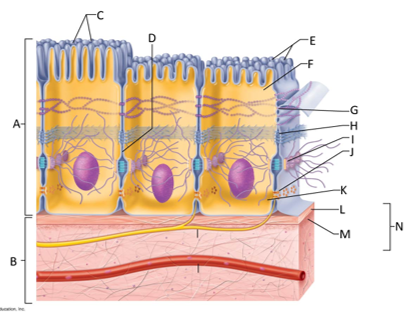 What letter is cilia? | back 126 C |
front 127 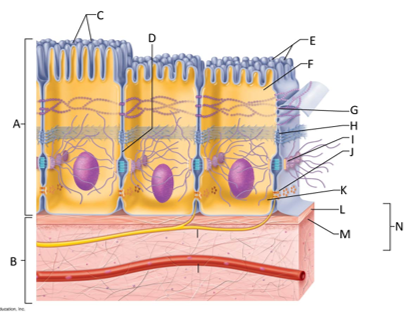 What letter is showing the narrow extracellular space? | back 127 D |
front 128 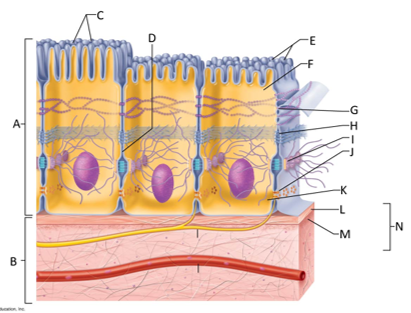 What letter is the microvilli? | back 128 E |
front 129  What letter is the apical region of an epithelial cell? | back 129 F |
front 130 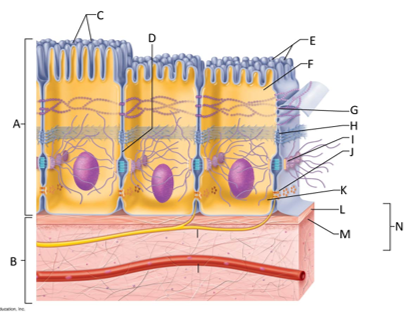 What letter is showing a tight junction? | back 130 G |
front 131 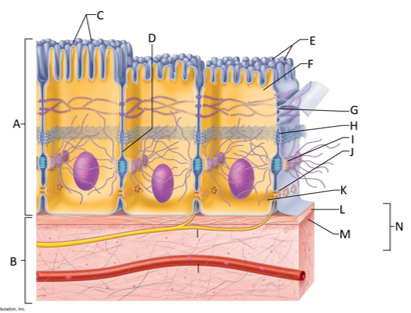 What letter is the adhesive belt? | back 131 H |
front 132 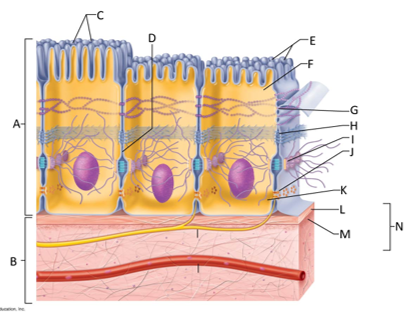 What letter is the desmosome? | back 132 I |
front 133 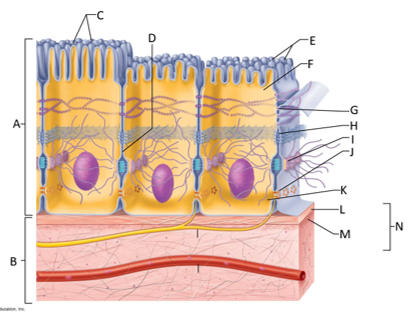 What letter is showing a gap junction? | back 133 J |
front 134 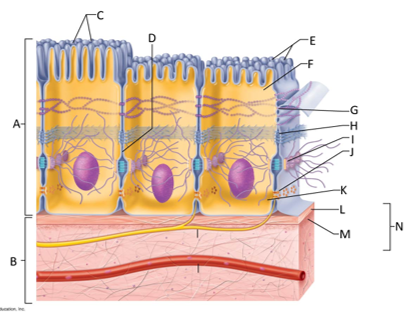 What letter is the basal region? | back 134 K |
front 135 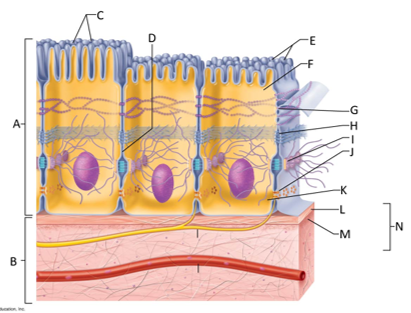 What letter is the basal lamina? | back 135 L |
front 136 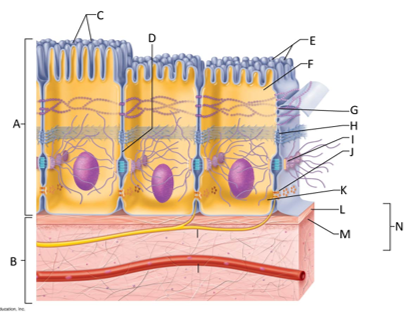 What letter is showing the reticular fibers? | back 136 M |
front 137 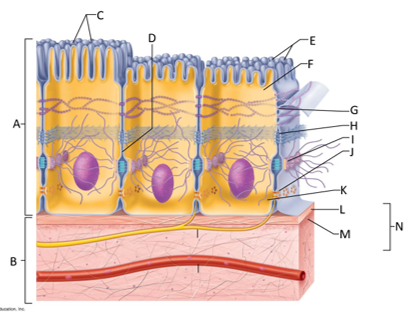 What letter is the basement membrane? | back 137 N |
front 138 What is an epithelium? | back 138 A sheet of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity. |
front 139 What is connective tissue? | back 139 Tissue that connects the tissues and organs of the body together, forms the basis of the skeleton, stores and carries nutrients, surrounds blood vessels and nerves, and leads the body's fight against infection. Support all epithelia. |
front 140 What is the purpose of cilia? | back 140 To push mucus and other substances over the epithelial surface |
front 141 What is the purpose of microvilli? | back 141 To maximize the surface area across which small molecules enter or leave cells and help anchor mucus sheets to the epithelial surface. |
front 142 What are desmosomes? | back 142 The main junctions for binding cells together. |
front 143 What is the function of gap junctions? | back 143 They allow small molecules to move directly between neighboring cells. |
front 144 What is the function of the apical surface of epithelium? | back 144 To abut the open space of a cavity, tubule, gland, or hollow organ. |
front 145 What is the function of the basement membrane of epithelia? | back 145 To provide support |
front 146 What is the function of the basal lamina? | back 146 It consists of proteins secreted by epithelial cells and acts as a selective filter and scaffolding. |
front 147 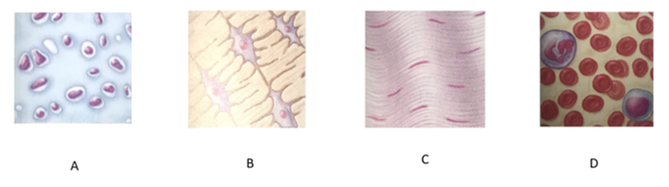 Which letter indicates connective tissue proper? | back 147 A |
front 148 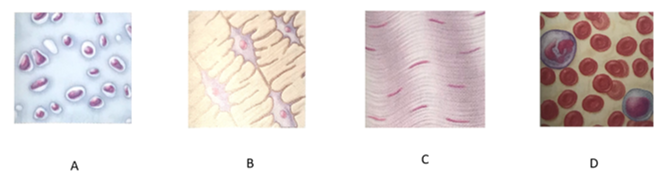 Which letter indicates cartilage? | back 148 B |
front 149 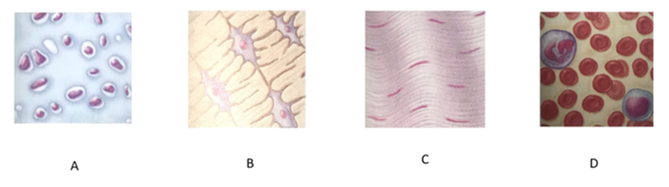 Which letter indicates bone tissue? | back 149 C |
front 150 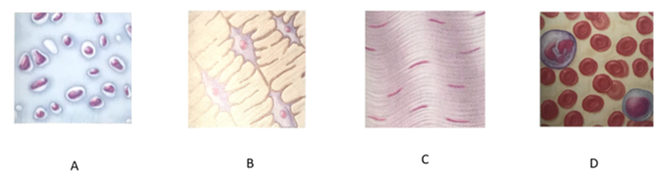 Which letter indicates blood? | back 150 D |
front 151 What is the function of connective tissue proper? | back 151 It functions as a binding tissue that resists mechanical stress, particularly tension. |
front 152 What is the function of cartilage? | back 152 It resists compression and functions to cushion and support body structures. |
front 153 What is the function of bone tissue? | back 153 It is a hard tissue that functions in support and resists both compression and tension |
front 154 What is the function of blood? | back 154 Carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes, and other substances throughout the body |
front 155 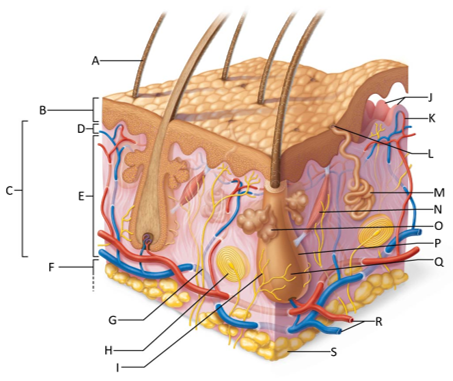 Which letter shows the hair shaft? | back 155 A |
front 156 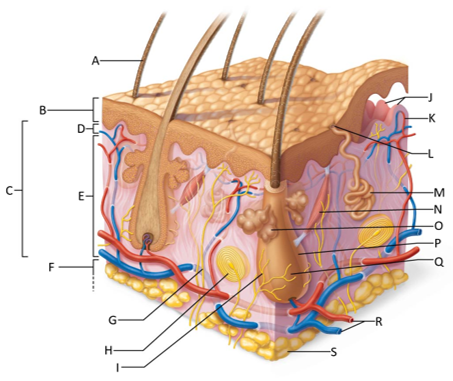 Which letter is pointing to the epidermis? | back 156 B |
front 157 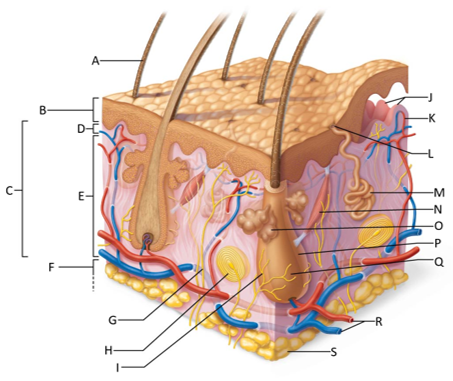 Which letter is pointing to the dermis? | back 157 C |
front 158 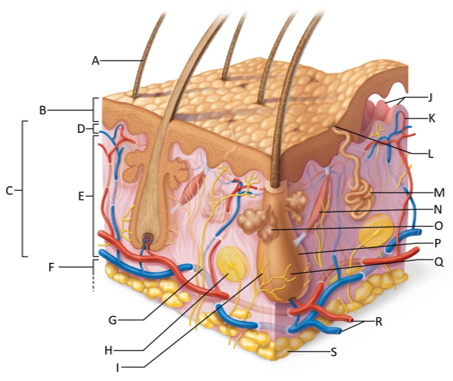 Which letter is pointing to the papillary dermis? | back 158 D |
front 159 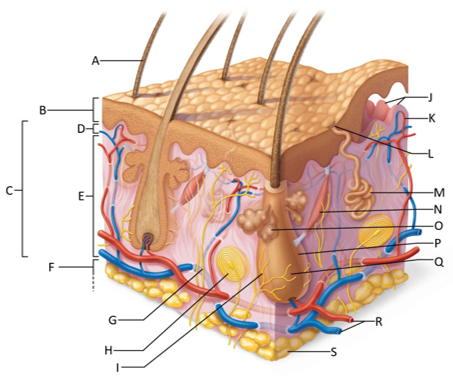 Which letter is pointing to the reticular dermis? | back 159 E |
front 160 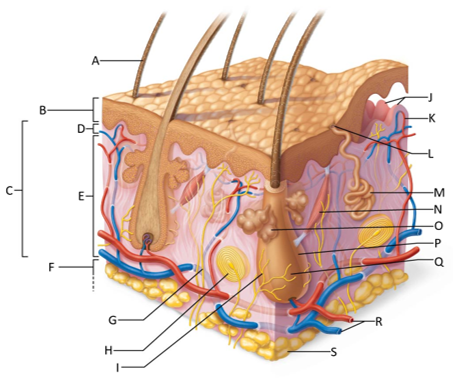 Which letter is pointing to the hypoderma? | back 160 F |
front 161 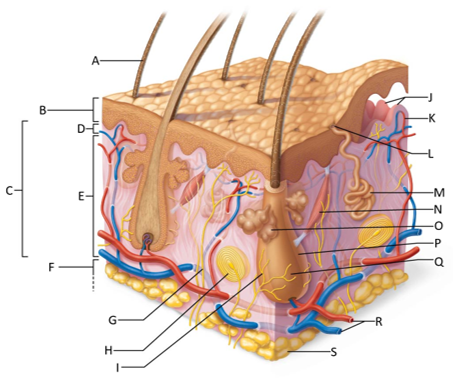 Which letter is pointing to the sensory nerve fiber? | back 161 G |
front 162 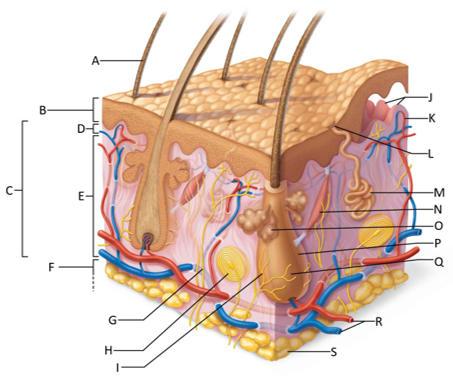 Which letter is pointing to the lamellar corpuscle? | back 162 H |
front 163 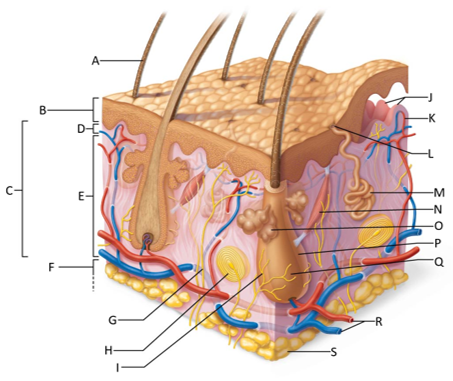 Which letter is pointing to the hair follicle receptor? | back 163 I |
front 164 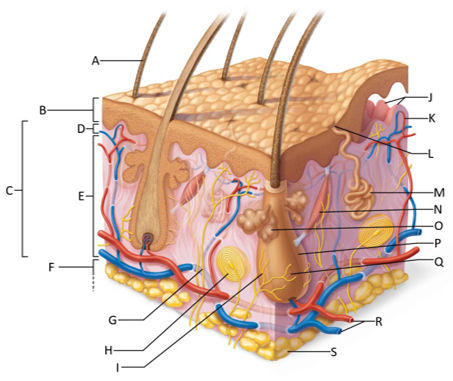 Which letter is pointing to the dermal papillae? | back 164 J |
front 165 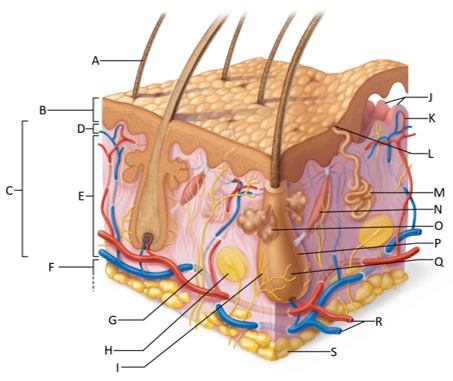 Which letter is pointing to the subpapillary vascular plexus? | back 165 K |
front 166 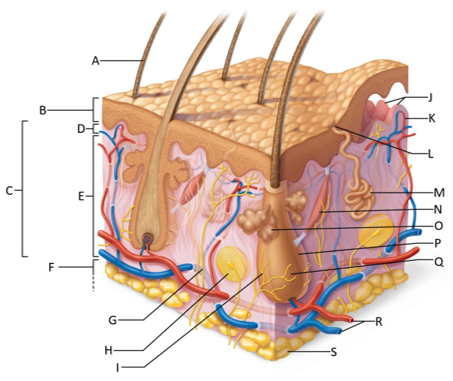 Which letter is pointing to the sweat pore? | back 166 L |
front 167 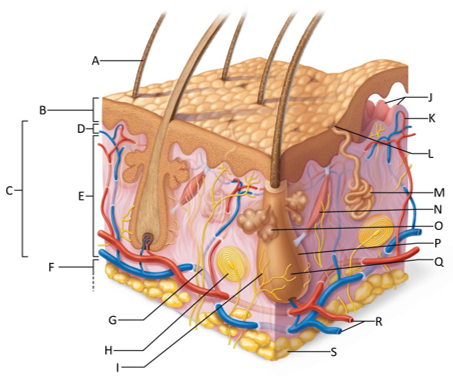 Which letter is pointing to the eccrine sweat gland? | back 167 M |
front 168 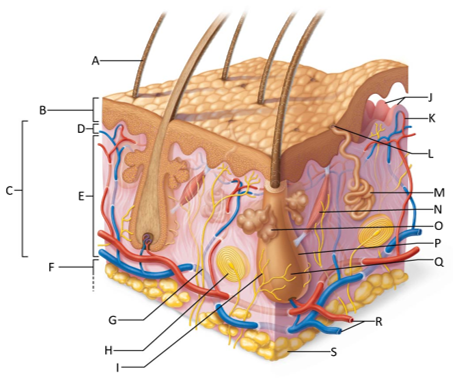 Which letter is pointing to the arrector pilli muscle? | back 168 N |
front 169 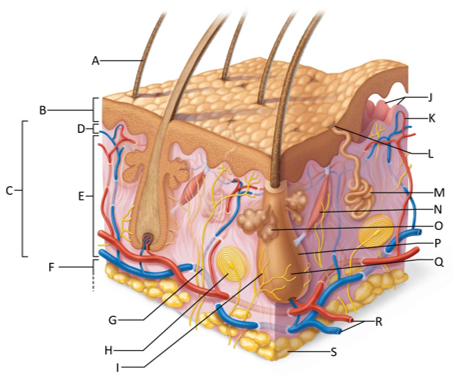 Which letter is pointing to the sebaceous gland? | back 169 O |
front 170 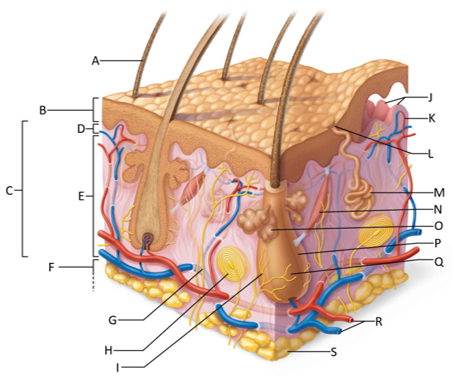 Which letter is pointing to the hair follicle? | back 170 P |
front 171 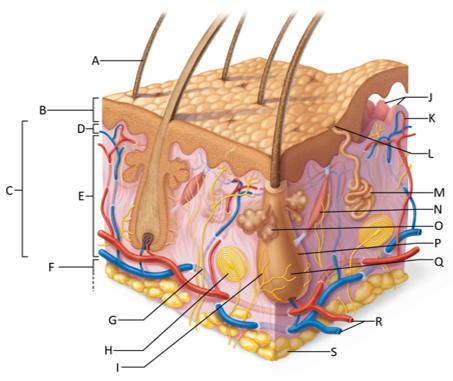 Which letter is pointing to the hair root? | back 171 Q |
front 172 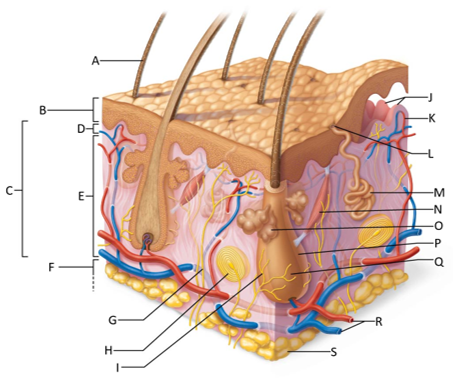 Which letter is pointing to the adipose tissue? | back 172 S |
front 173 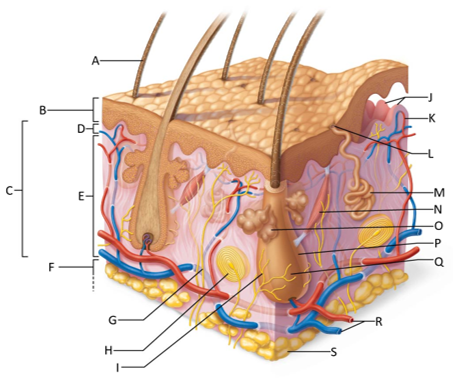 Which letter is pointing to the dermal vascular plexus? | back 173 R |
front 174 What is the epidermis? | back 174 A keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that contains four distinct types of cells: keratinocytes, melanocytes, tactile epithelial cells, and dendritic cells. |
front 175 What is the dermis? | back 175 The second layer of the skin that is a strong, flexible, connective tissue. |
front 176 What is the papillary dermis? | back 176 The superficial 20% of the dermis which is areolar connective tissue that contains very thin collagen fibers. |
front 177 What is the reticular dermis? | back 177 The lower 80% of the dermis which is dense irregular connective tissue with thick bundles of interlacing collagen and elastic fibers that run in many different planes. |
front 178 What is the hypodermis? | back 178 Fatty layer under the skin consisting of areolar and adipose tissues that anchors the skin to the underlying structures and insulates our body |
front 179 What is the function of the hair follicle receptor? | back 179 To stimulate nerve endings when the hair shaft bends, making the hair a touch receptor |
front 180 What is the function of dermal papillae? | back 180 To increase the surface area of the dermis for the exchange of gasses, nutrients, and waste products. |
front 181 Where is hyaline cartilage found in the body? | back 181 It makes up the articular cartilage that covers the ends of adjoining bones in movable joints. It also forms the cartilaginous attachments of the ribs to the sternum, accounts for most of the cartilage found in respiratory structures, and forms the embryonic skeleton |
front 182 Where is elastic cartilage found in the body? | back 182 The epiglottis and the outer ear. |
front 183 Where is fibrocartilage found in the body? | back 183 Discs between vertebrae and the meniscus of the knee |