Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Biology II Test 1
front 1 Which of the following attributes is common to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? a. a membrane-enclosed nucleus b. the use of proteins as information storage molecules c. membrane-enclosed organelles d. generally about the same size e. the use of DNA as the information storage molecule | back 1 e. the use of DNA as the information storage molecule (all cells that have been discovered use DNA to store information) |
front 2 What is the appropriate term for an interacting group of individuals of a single type occupying a defined area? a. species b. community c. ecosystem d. habitat e. population | back 2 e. population (only the organism of a given species that have the opportunity to interact with one another are considered to be within the same population) |
front 3 Which taxonomic domain includes multicellular photosynthetic organisms? a. archaea b. bacteria c. fungi d, plante e. eukarya | back 3 e. eukarya (plants and certain algae are multicellular photosynthetic organisms included in the kingdom plantae of the domain eukarya.) |
front 4 The universal genetic language of DNA is common to virtually all organisms on Earth, however diverse. What is the best explanation for this fact? a. The universal nature of the genetic language of DNA is due to coincidence. b. The universal genetic language is explained by the chemistry of DNA and proteins. c. All living things share a common genetic language of DNA because they share a common ancestry. | back 4 c. All living things share a common genetic language of DNA because they share a common ancestry. (The genetic code is arbitrary, at least to some extent. The fact that all organisms share a single genetic code is due to their common ancestry. Read about the core theme of biology: Evolution accounts for the unity and diversity of life.) |
front 5 In an ecosystem, nutrients _____ and energy _____. a. flow through ... is recycled b. are wasted ... is burned c. cycle ... flows through d. are created ... is lost e. disappear ... cannot be created nor destroyed | back 5 c. cycle ... flows through (Nutrients are always recycled. Energy flows through the system, typically entering as solar energy and leaving as heat.) |
front 6 No amino acid molecule by itself can speed up or catalyze reactions between other molecules; however, when amino acids are joined together to make a protein with catalytic properties, the new structure (enzymatic protein) can speed up the rate of a specific chemical reaction. What does this illustrate? a. emergent properties b. energy flow, processing, and utilization c. polymer duality d. the summation theory e. the complexity/simplicity paradox | back 6 a. emergent properties (A molecule such as a protein has attributes not exhibited by any of its component parts (e.g., amino acids). Therefore, novel properties are emerging that were not present at a simpler level of organization.) |
front 7 How does DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) encode information? a. in the sequence of nucleotides. b. in the different shapes of the DNA molecules. c. The DNA molecule is composed of many amino acids joined together to form a functional protein. d. The genes along the length of DNA molecules encode the information for building all the cell's other molecules. e. in the number of each different nucleotide. | back 7 a. in the sequence of nucleotides |
front 8 Which of the following statements is true about chemical nutrients in an ecosystem? a. They exit the ecosystem in the form of heat. b. They cannot be obtained from decomposition. c. They depend on sunlight as their source. d. They recycle within the ecosystem, being constantly reused. e.They flow through the system, losing some nutrients in the process. | back 8 d. They recycle withing the ecosystem, being constantly reused (Nutrients cycle through the ecosystem by processes such as the decomposition of organic debris.) |
front 9 Which of the following is a correct sequence of levels in life's hierarchy, proceeding downward from an individual animal? a. organism, organ system, tissue, cell, organ b. nervous system, brain, nervous tissue, nerve cell c. organ system, tissue, molecule, cell d. brain, organ system, nerve cell, nervous tissue e. organ system, nervous tissue, brain | back 9 b. nervous system, brain, nervous tissue, nerve cell |
front 10 DNA is composed of building blocks called _____. a. nucleic acids b. Gs c. nucleotides d. adenines e. amino acids | back 10 c. nucleotides (DNA is a composed of nucleotide units.) |
front 11 In eukaryotic cells DNA has the appearance of a _____. a. single strand b. letter U c. double helix d. triple helix e. circle | back 11 c. double helix (Eukaryotic DNA is organized as a double helix.) |
front 12 A localized group of organisms that belong to the same species is called a a. population. b. biosystem. c. ecosystem. d. family. e. community. | back 12 a. population |
front 13 The main source of energy for producers in an ecosystem is a. chemical energy. b. kinetic energy. c. thermal energy. d. ATP. e. light energy. | back 13 e. light energy |
front 14 Which of the following types of cells utilize deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) as their genetic material but do not have their DNA encased within a nuclear envelope? a. plant b. protists c. archaea d. fungi e. animal | back 14 c. archaea |
front 15 To understand the chemical basis of inheritance, we must understand the molecular structure of DNA. This is an example of the application of which concept to the study of biology? a. feedback regulation b. reductionism c. evolution d. the cell theory e. emergent properties | back 15 b. reductionism |
front 16 Once labor begins in childbirth, contractions increase in intensity and frequency until delivery. The increasing labor contractions of childbirth are an example of which type of regulation? a. positive feedback b. a bioinformatic system c. enzymatic catalysis d. feedback inhibition e. negative feedback | back 16 a. positive feedback |
front 17 When the body's blood glucose level rises, the pancreas secretes insulin and, as a result, the blood glucose level declines. When the blood glucose level is low, the pancreas secretes glucagon and, as a result, the blood glucose level rises. Such regulation of the blood glucose level is the result of a. positive feedback. b. catalytic feedback. c. protein-protein interactions. d. negative feedback. e. bioinformatic regulation. | back 17 d. negative feedback |
front 18 Global warming, as demonstrated by observations such as the rise in average ambient temperatures and the melting of glaciers, has already had many effects on living organisms. Which of the following might best offer a solution to this problem? a. Increase the abilities of animals to migrate to more suitable habitats. b. Recycle as much as possible. c. Do nothing; nature will attain its own balance. d. Limit the burning of fossil fuels and regulate our loss of forested areas. e. Continue to measure these and other parameters of the problem. | back 18 d. Limit the burning of fossil fuels and regulate our loss of forested areas. |
front 19 Which branch of biology is concerned with the naming and classifying of organisms? a. schematic biology b. taxonomy c. informatics d. genomics e. evolution | back 19 b. taxonomy |
front 20 Prokaryotes are classified as belonging to two different domains. What are the domains? a. Bacteria and Protista b. Eukarya and Monera c. Bacteria and Eukarya d. Bacteria and Archaea e. Archaea and Monera | back 20 d. Bacteria and Archaea |
front 21 A water sample from a hot thermal vent contained a single-celled organism that had a cell wall but lacked a nucleus. What is its most likely classification? a. Protista b. Archaea c. Fungi d. Eukarya e. Animalia | back 21 b. Archaea |
front 22 The nucleus of a nitrogen atom contains 7 neutrons and 7 protons. Which of the following is a correct statement concerning nitrogen? a. The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 7 and an atomic number of 14. b. The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 14 and an atomic number of 14. c. The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 7 and an atomic number of 21. d. The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 14 and an atomic number of 21 e. The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 14 and an atomic number of 7. | back 22 e. The nitrogen atom has a mass number of approximately 14 and an atomic number of 7. |
front 23 One difference between carbon-12 is that carbon-14 has a. two more protons than carbon-12. b. two more neutrons than carbon-12. c. two more protons and two more neutrons than carbon-12. d. two more electrons than carbon-12. e. two more electrons and two more neutrons than carbon-12. | back 23 b. two more neutrons than carbon-12 |
front 24 How many electrons does an atom of sulfur have in its valence shell? a. 4 b. 6 c. 16 d. 8 e. 32 | back 24 b. 6 |
front 25 A covalent chemical bond is one in which a. an electron occupies a hybrid orbital located between the nuclei of two atoms. b. outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner electron shell of another atom. c. protons and neutrons are shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both atoms. d. electrons are removed from one atom and transferred to another atom so that the two atoms become oppositely charged. e. outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill the outer electron shells of both atoms. | back 25 e. outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill the outer electron shells of both atoms. |
front 26 What results from an unequal sharing of electrons between atoms? a. a polar covalent bond b. a hydrogen bond c. a hydrophobic interaction d. a nonpolar covalent bond e. an ionic bond | back 26 a. a polar covalent bond |
front 27 Fluorine has an atomic number of 9 and a mass number of 19. How many electrons are needed to complete the valence shell of a fluorine atom? a. 9 b. 1 c. 0 d. 3 e. 7 | back 27 b. 1 |
front 28 What bonding or interaction is most likely to occur among a broad array of molecules of various types (polar, nonpolar, hydrophilic, hydrophobic)? a. hydrogen bonding b. ionic bonding c. van der Waals interactions d. covalent bonding e. polar covalent bonding | back 28 c. van der Waals interactions |
front 29 Which of the following is not considered to be a weak molecular interaction? a. a covalent bond b. an ionic bond in the presence of water c. a hydrogen bond d. both a hydrogen bond and a covalent bond e. a van der Waals interaction | back 29 a. a covalent bond |
front 30 Which of the following takes place as an ice cube cools a drink? a. Evaporation of the water in the drink increases. b. Kinetic energy in the drink decreases. c. A calorie of heat energy is transferred from the ice to the water of the drink. d. Molecular collisions in the drink increase. e. The specific heat of the water in the drink decreases. | back 30 b. Kinetic energy in the drink decreases. |
front 31 Liquid water's high specific heat is mainly a consequence of the a. absorption and release of heat when hydrogen bonds break and form. b. high specific heat of oxygen and hydrogen atoms. c. higher density of liquid water than solid water (ice). d. small size of the water molecules. e. fact that water is a poor heat conductor. | back 31 a. absorption and release of heat when hydrogen bonds break and form. |
front 32 Which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize? a. ionic bonds b. hydrogen bond c. both hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds d. polar covalent bonds e. both polar covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds | back 32 b. hydrogen bond |
front 33 If the pH of a solution is increased from pH 5 to pH 7, it means that the a. concentration of OH- O H − is one-hundredth (0.01X) what it was at pH 5. b. concentration of OH- O H − is 100 times greater than what it was at pH 5. c. concentration of H+ H +H+H+ is one-half (1/2) what it was at pH 5. d. concentration of H+ H +H+H+ is twice (2X) what it was at pH 5. e. concentration of H + H+ is 100 times greater and the concentration of OH- is one-hundredth what they were at pH 5 | back 33 b. concentration of OH- O H − is 100 times greater than what it was at pH 5. |
front 34 If the cytoplasm of a cell is at pH 7, and the mitochondrial matrix is at pH 8, this means that a. the concentration of H+ H + ions in the cytoplasm is 7/8 the concentration in the mitochondrial matrix. b. the concentration of H+ H + ions is tenfold higher in the cytoplasm than in the mitochondrial matrix. c. the concentration of H+ H + ions is tenfold higher in the mitochondrial matrix than in the cytoplasm. d. the mitochondrial matrix is more acidic than the cytoplasm. e. the concentration of H+ H +H+ ions in the cytoplasm is 8/7 the concentration in the mitochondrial matrix. | back 34 b. the concentration of H+ H + ions is tenfold higher in the cytoplasm than in the mitochondrial matrix. |
front 35 A strong acid like HCl HCl a. ionizes completely in an aqueous solution. b. increases the pH when added to an aqueous solution. c. reacts with strong bases to create a buffered solution. d. both ionizes completely in aqueous solutions and is a strong buffer at low pH. e. is a strong buffer at low pH. | back 35 a. ionizes completely in an aqueous solution. |
front 36 Why does ice float in liquid water? a. The high surface tension of liquid water keeps the ice on top. b. Hydrogen bonds stabilize and keep the molecules of ice farther apart than the water molecules of liquid water. c. Ice always has air bubbles that keep it afloat. d. The crystalline lattice of ice causes it to be denser than liquid water. e. The ionic bonds between the molecules in ice prevent the ice from sinking. | back 36 b. Hydrogen bonds stabilize and keep the molecules of ice farther apart than the water molecules of |
front 37 Why does evaporation of water from a surface cause cooling of the surface? a. The breaking of bonds between water molecules absorbs heat. b. The expansion of water vapor extracts heat from the surface. c. Water molecules absorb heat from the surface in order to acquire enough energy to evaporate. d. The water molecules with the most heat energy evaporate more readily. e. The solute molecules left behind absorb heat. | back 37 d. The water molecules with the most heat energy evaporate more readily. |
front 38 Temperature usually increases when water condenses. Which behavior of water is most directly responsible for this phenomenon? a. the release of heat by the breaking of hydrogen bonds b. the release of heat by the formation of hydrogen bonds c. the change in density when it condenses to form a liquid or solid d. the high surface tension of water e. reactions with other atmospheric compounds | back 38 b. the release of heat by the formation of hydrogen bonds |
front 39 Which of the following effects is produced by the high surface tension of water? a. Lakes don't freeze solid in winter, despite low temperatures. b. Water flows upward from the roots to the leaves in plants. c. Evaporation of sweat from the skin helps to keep people from overheating. d. Organisms resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reactions. e. A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond. | back 39 e. A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond. |
front 40 The element present in all organic molecules is a. hydrogen. b. phosphorus. c. carbon. d. nitrogen. e. oxygen. | back 40 c. carbon |
front 41 no data | back 41 Carbonyl |
front 42 no data | back 42 Carboxyl |
front 43 no data | back 43 Methyl |
front 44 no data | back 44 Amino |
front 45 no data | back 45 Phosphate |
front 46 no data | back 46 Hydroxyl |
front 47 What is a ketone? | back 47 no data |
front 48 What is an aldehyde? | back 48 no data |
front 49 no data | back 49 Sulfhydryl |
front 50 Molecules with which functional groups may form polymers via dehydration reactions? a. hydroxyl groups b. carboxyl groups c. either carbonyl or carboxyl groups d. either hydroxyl or carboxyl groups e. carbonyl groups | back 50 d. either hydroxyl or carboxyl groups |
front 51 Which of these classes of biological molecules consist of both monomers and polymers? a. lipids b. lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids all consist of only macromolecular polymers c. carbohydrates d. proteins e. nucleic acids | back 51 c. carbohydrates |
front 52 How many molecules of water are needed to completely hydrolyze a polymer that is 11 monomers long? a. 12 b. 11 c. 10 d. 9 e. 8 | back 52 c. 10 |
front 53 Which of the following best summarizes the relationship between dehydration reactions and hydrolysis? a. Hydrolysis creates monomers, and dehydration reactions break down polymers. b. Dehydration reactions assemble polymers, and hydrolysis reactions break down polymers. c. Dehydration reactions eliminate water from lipid membranes, and hydrolysis makes lipid membranes water permeable. d. Dehydration reactions ionize water molecules and add hydroxyl groups to polymers; hydrolysis reactions release hydroxyl groups from polymers. e. Dehydration reactions can occur only after hydrolysis. | back 53 b. Dehydration reactions assemble polymers, and hydrolysis reactions break down polymers. |
front 54 Polysaccharides, triacylglycerides, and proteins are similar in that they a. are decomposed into their monomers by dehydration reactions. b. are synthesized from monomers by the process of hydrolysis. c. are synthesized as a result of peptide bond formation between monomers. d. are synthesized from monomers by dehydration reactions. e. all contain nitrogen in their monomer building blocks. | back 54 d. are synthesized from monomers by dehydration reactions. |
front 55 The molecular formula for glucose is C6H1206. C 6 H 12 OC What would be the molecular formula for a molecule made by linking three glucose molecules together by dehydration reactions? | back 55 C18H32O16 |
front 56 The enzyme amylase can break glycosidic linkages between glucose monomers only if the monomers are the α form. Which of the following could amylase break down? a. chitin b. starch and chitin only c. starch d. starch, cellulose, and chitin e. cellulose | back 56 c. starch |
front 57 On food packages, to what does the term insoluble fiber refer? a. starch b. cellulose c. polypeptides d. chitin e. amylopectin | back 57 b. cellulose |
front 58 A molecule with the chemical formula C 6 H 12 O 6 is probably a a. carbohydrate. b. lipid. c. monosaccharide d. carbohydrate and lipid only. e. carbohydrate and monosaccharide only. | back 58 e. carbohydrate and monosaccharide only. |
front 59 All of the following are polysaccharides except a. chitin. b. glycogen. c. cellulose. d. lactose. e. amylopectin. | back 59 d. lactose. |
front 60 Which of the following is true of cellulose? a. It is a polymer composed of enantiomers of glucose. b. It is a storage polysaccharide for energy in plant cells. c. It is digestible by bacteria in the human gut. d. It is a major structural component of plant cell walls. e. It is a polymer composed of enantiomers of glucose, it is a storage polysaccharide for energy in plant cells, it is digestible by bacteria in the human gut, and it is a major structural component of plant cell walls. | back 60 d. It is a major structural component of plant cell walls. |
front 61 Which of the following statements concerning saturated fats is not true? a. They contain more hydrogen than unsaturated fats having the same number of carbon atoms. b. They have multiple double bonds in the carbon chains of their fatty acids. c. They are one of several factors that contribute to atherosclerosis. d. They are more common in animals than in plants. e. They generally solidify at room temperature. | back 61 b. They have multiple double bonds in the carbon chains of their fatty acids. |
front 62 Which of the following is true regarding saturated fatty acids? a. They have double bonds between carbon atoms of the fatty acids. b. They are the principal molecules in lard and butter. c. They are the predominant fatty acid in corn oil. d. They are usually produced by plants. e. They are usually liquid at room temperature. | back 62 b. They are the principal molecules in lard and butter. |
front 63 What is the term used for a protein molecule that assists in the proper folding of other proteins? a. renaturing protein b. enzyme protein c. denaturing protein d. tertiary protein e. chaperonin | back 63 e. chaperonin |
front 64 In animal metabolism, most of the monomers released by digestion of food macromolecules are metabolized to provide energy. Only a small portion of these monomers are used for synthesis of new macromolecules. The net result is that a. the water consumed is exactly balanced by the water generated, to maintain homeostasis. b. water is generated by animal metabolism. c. water is consumed during homeostasis, but water is generated during periods of growth. d. water is generated during homeostasis, but water is consumed during periods of growth. e.water is consumed by animal metabolism. | back 64 e.water is consumed by animal metabolism. |
front 65 Large organic molecules are usually assembled by polymerization of a few kinds of simple subunits. Which of the following is an exception to this statement? a. an enzyme b. a steroid c. cellulose d. a contractile protein e. DNA | back 65 b. a steroid |
front 66 Some regions of the plasma membrane, called lipid rafts, have a higher concentration of cholesterol molecules. At high temperatures, these regions a. have higher rates of lateral diffusion of lipids and proteins into and out of these regions. b. are able to flip from inside to outside. c. detach from the plasma membrane and clog arteries. d. are more fluid than the surrounding membrane. e. are less fluid than the surrounding membrane. | back 66 e. are less fluid than the surrounding membrane. |
front 67 Which of the following types of molecules are the major structural components of the cell membrane? a. nucleic acids and proteins b. phospholipids and cellulose c. glycoproteins and cholesterol d. phospholipids and proteins e. proteins and cellulose | back 67 d. phospholipids and proteins |
front 68 The presence of cholesterol in the plasma membranes of some animals a. enables the animal to add hydrogen atoms to unsaturated phospholipids. b. enables the animal to remove hydrogen atoms from saturated phospholipids. c. makes the animal more susceptible to circulatory disorders. d. enables the membrane to stay fluid more easily when cell temperature drops. e. makes the membrane less flexible, allowing it to sustain greater pressure from within the cell. | back 68 d. enables the membrane to stay fluid more easily when cell temperature drops. |
front 69 Which of the following is one of the ways that the membranes of winter wheat are able to remain fluid when it is extremely cold? a. by cotransport of glucose and hydrogen b. by increasing the percentage of cholesterol molecules in the membrane c. by increasing the percentage of unsaturated phospholipids in the membrane d. by using active transport e. by decreasing the number of hydrophobic proteins in the membrane | back 69 c. by increasing the percentage of unsaturated phospholipids in the membrane |
front 70 Which of the following is true of integral membrane proteins? a. They are not mobile within the bilayer. b. They serve only a structural role in membranes. c. They lack tertiary structure. d. They are loosely bound to the surface of the bilayer. e. They are usually transmembrane proteins. | back 70 e. They are usually transmembrane proteins. |
front 71 The cell membranes of Antarctic ice fish might have which of the following adaptations? a. a higher percentage of trans-fatty acids b. very long chain fatty acids c. branched isoprenoid lipids d. a high percentage of polyunsaturated fatty acids e. no cholesterol | back 71 d. a high percentage of polyunsaturated fatty acids |
front 72 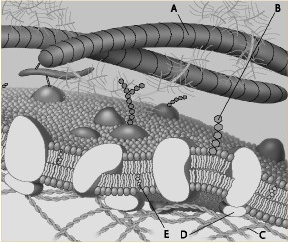 Which component is the peripheral protein? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E | back 72 d. D |
front 73 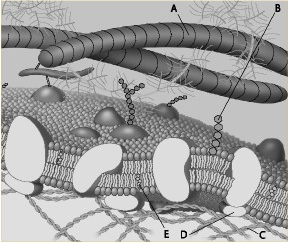 Which component is the fiber of the extracellular matrix? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E | back 73 a. A |
front 74 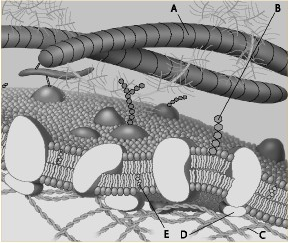 Which component is a microfilament of the cytoskeleton? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E | back 74 c. C |
front 75 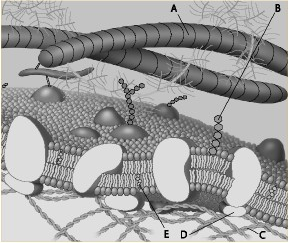 Which component is a glycolipid? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E | back 75 b. B |
front 76 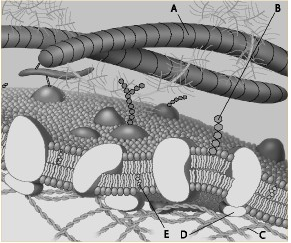 Which component is a microfilament of the cytoskeleton? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E | back 76 c. C |
front 77 Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease in humans in which the CFTR protein, which functions as a chloride ion channel, is missing or nonfunctional in cell membranes. The CFTR protein belongs to what category of membrane proteins? a. electrogenic ion pumps b. gap junctions c. hydrophilic channels d. aquaporins e. cotransporters | back 77 a. electrogenic ion pumps |
front 78 In facilitated diffusion, what is the role of the transport protein? a. Transport proteins organize the phospholipids to allow the solute to cross the membrane. b. Transport proteins provide a low-resistance channel for water molecules to cross the membrane. c. Transport proteins provide the energy for diffusion of the solute. d. Transport proteins provide a hydrophilic route for the solute to cross the membrane. e. Transport proteins provide a protein site for ATP hydrolysis, which facilitates the movement of a solute across a membrane. | back 78 d. Transport proteins provide a hydrophilic route for the solute to cross the membrane. |
front 79 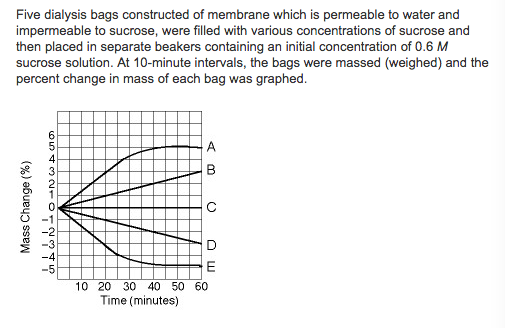 Which line in the graph represents the bag that contained a solution isotonic to the 0.6 M solution at the beginning of the experiment? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E | back 79 c. C |
front 80 The sodium-potassium pump is called an electrogenic pump because it a. contributes to the membrane potential. b. is used to drive the transport of other molecules against a concentration gradient. c. ionizes sodium and potassium atoms. d. pumps equal quantities of Na+ and K+ across the membrane. e. pumps hydrogen ions out of the cell. | back 80 a. contributes to the membrane potential. |
front 81 The sodium-potassium pump in animal cells requires cytoplasmic ATP to pump ions across the plasma membrane. When the proteins of the pump are first synthesized in the rough ER, what side of the ER membrane will the ATP binding site be on? a. It doesn't matter, because the pump is not active in the ER. b. It could be facing in either direction because proteins are properly reoriented in the Golgi apparatus. c. It will be on the cytoplasmic side of the ER. d. It will be on the side facing the interior of the ER. | back 81 c. It will be on the cytoplasmic side of the ER. |
front 82 Which of the following membrane activities requires energy from ATP hydrolysis? a. facilitated diffusion of chloride ions across the membrane through a chloride channel b. movement of water into a cell c. movement of Na+ N a +N ions from a lower concentration in a mammalian cell to a higher concentration in the extracellular fluid d. movement of glucose molecules into a bacterial cell from a medium containing a higher concentration of glucose than inside the cell e. movement of carbon dioxide out of a paramecium | back 82 c. movement of Na+ N a +N ions from a lower concentration in a mammalian cell to a higher concentration in the extracellular fluid |
front 83 The sodium-potassium pump in animal cells requires cytoplasmic ATP to pump ions across the plasma membrane. When the proteins of the pump are first synthesized in the rough ER, what side of the ER membrane will the ATP binding site be on? a. It could be facing in either direction because proteins are properly reoriented in the Golgi apparatus. b. It doesn't matter, because the pump is not active in the ER. c. It will be on the cytoplasmic side of the ER. d. It will be on the side facing the interior of the ER. | back 83 c. It will be on the cytoplasmic side of the ER. |
front 84 What is the voltage across a membrane called? a. membrane potential b. osmotic potential c. water potential d. electrochemical gradient e. chemical gradient | back 84 a. membrane potential |
front 85 Which of the following would increase the electrochemical potential across a membrane? a. a chloride channel b. a sucrose-proton cotransporter c. a potassium channel d. a proton pump e. both a proton pump and a potassium channel | back 85 d. a proton pump |