Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P II FINAL REVIEW
front 1 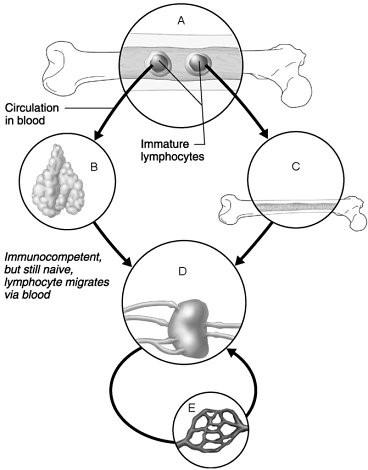 Area seeded by immunocompetent B and T cells. | back 1 D |
front 2 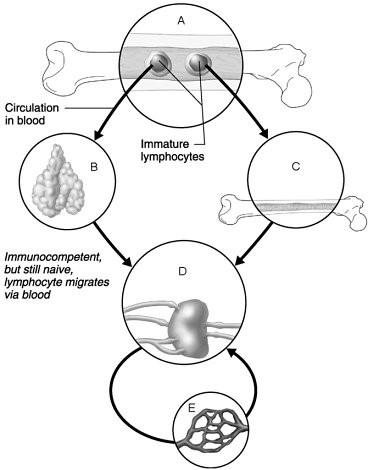 Area where B cells become immunocompetent. | back 2 C |
front 3 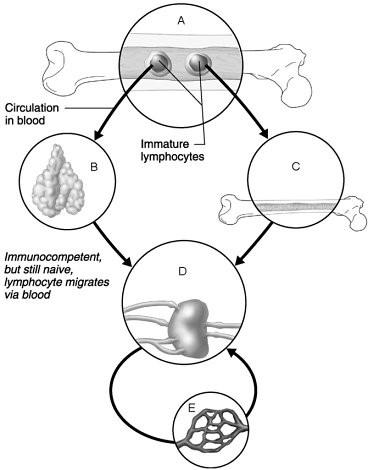 Area where activated immunocompetent B and T cells recirculate | back 3 E |
front 4 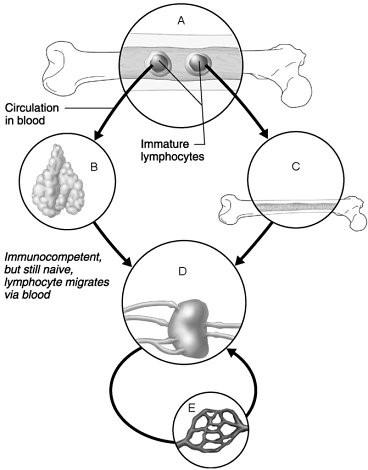 Area where antigen challenge and clonal selection are most likely to occur. | back 4 D |
front 5 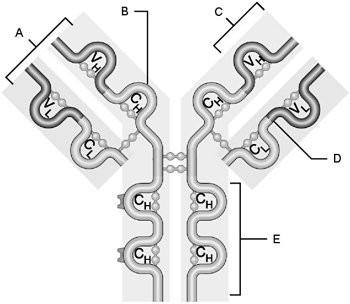 Heavy chain | back 5 B |
front 6 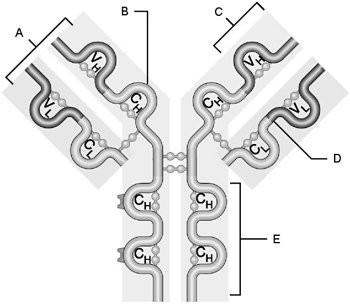 Light chain | back 6 D |
front 7 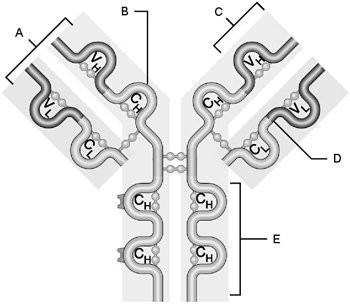 Variable region | back 7 C |
front 8 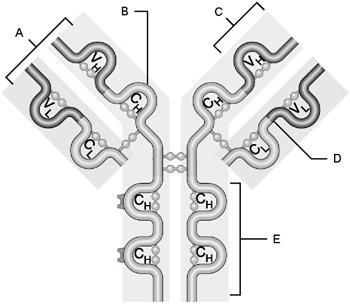 Constant region | back 8 E |
front 9 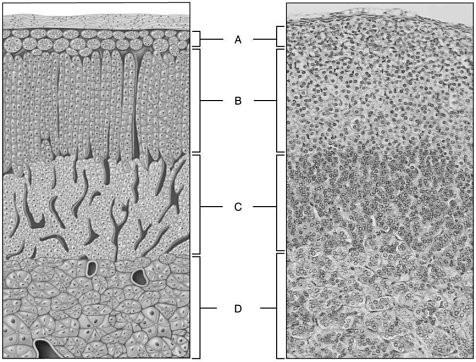 Excess hormone levels from this region result in Cushing's syndrome | back 9 B |
front 10 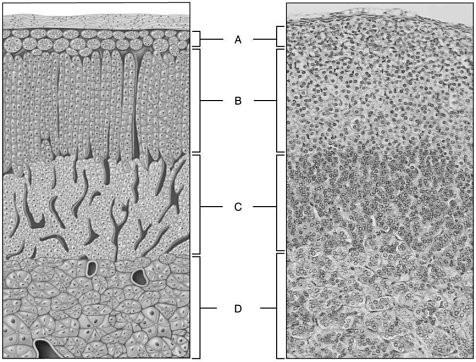 Hormones mimic sympathetic nervous system neurtransmitters | back 10 D |
front 11 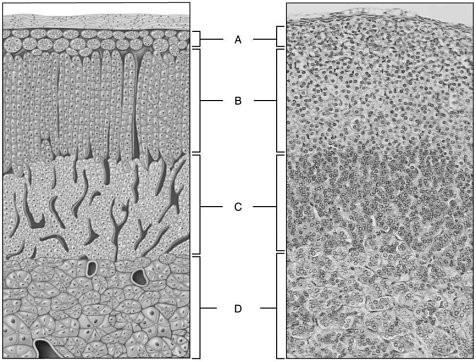 Mainly produces small amounts of gonadocorticoids | back 11 C |
front 12 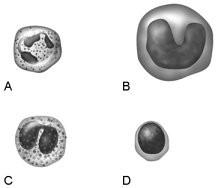 A granulocyte, phagocyte, and the most common white blood cell found in whole blood. | back 12 A |
front 13 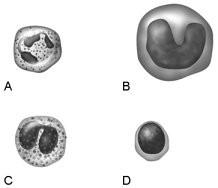 Main bacteria killer during acute infections | back 13 A |
front 14 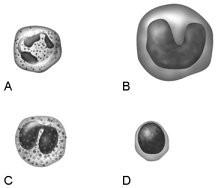 Mounts a humoral immune response by producing antibodies | back 14 D |
front 15 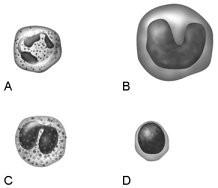 Releases granules that kill parasitic worms | back 15 C |
front 16 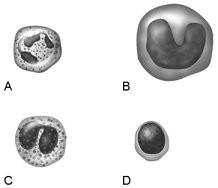 When activated becomes a macrophage that fights infection. | back 16 B |
front 17 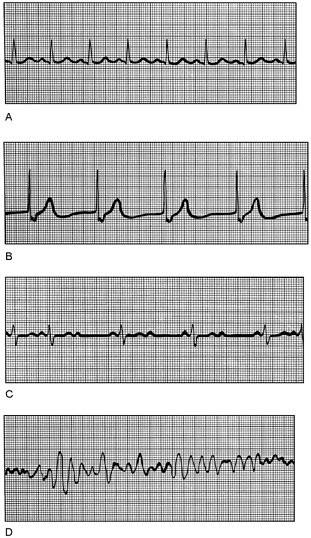 Ventricular fibrillation | back 17 D |
front 18 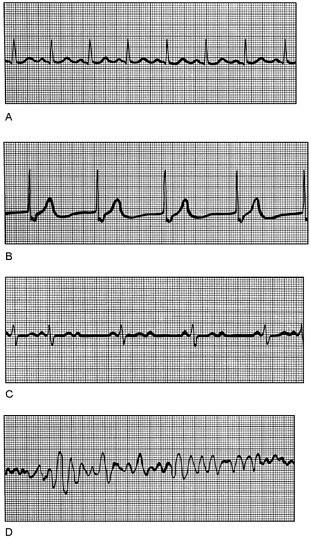 Second degree heart block | back 18 C |
front 19 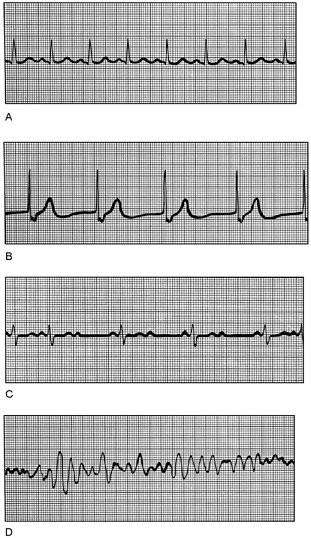 Junctional rhythm | back 19 B |
front 20 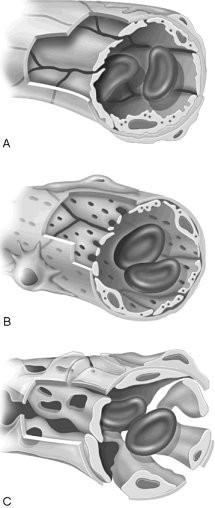 Capillary with intercellular clefts found in the skin and muscles. | back 20 A |
front 21  Capillary found where active capillary absorption of filtrate occurs. | back 21 B |
front 22  Capillary found in endocrine organs that allows hormones to gain rapid entry into the blood | back 22 B |