Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Chapter 2
front 1 1) About twenty-five of the ninety-two natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these twenty-five elements make up approximately 96 percent of living matter? A) carbon, sodium, hydrogen, nitrogen C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, nitrogen | back 1 Answer: D |
front 2 2) Trace elements are those required by an organism in only minute quantities. Which of the following is a trace element that is required by humans and other vertebrates, but not by other organisms such as bacteria or plants? A) calcium B) iodine | back 2 Answer: B |
front 3 3) Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen are the most abundant
elements of living matter. B) Some naturally occurring elements are
toxic to organisms. | back 3 Answer: C |
front 4 4) Which of the following are compounds? A) H2O, O2, and CH4 D) H2O and CH4, but not O2 | back 4 Answer: D |
front 5 5) Knowing the atomic mass of an element allows inferences about which of the following? A) the number of electrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element | back 5 Answer: C |
front 6 6) In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the same? They have the same number of _____. A) protons C) electrons in their valence shells when neutral D) electron shells when neutral | back 6 Answer: C |
front 7 7) Molybdenum has an atomic number of 42. Several common isotopes exist, with mass numbers from 92-100. Therefore, which of the following can be true? A) Molybdenum atoms can have between 50 and 58 neutrons. C) Molybdenum atoms can have between 50 and 58 electrons. D) Isotopes of molybdenum have different numbers of electrons. | back 7 Answer: A |
front 8 8) Carbon-12 is the most common isotope of carbon and has a mass number of 12. However, the average atomic mass of carbon found on a periodic table is slightly more than 12 daltons. Why? A) The atomic mass does not include the mass of electrons. C) Some carbon atoms in nature have more neutrons. | back 8 Answer: C |
front 9  9) Which of the following best describes the relationship between the atoms described below? A) They are isomers. | back 9 Answer: B |
front 10 10) The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. Nitrogen-15 has a greater mass number than nitrogen-14 because the atomic nucleus of nitrogen-15 contains _____. A) 7 neutrons C) 8 protons | back 10 Answer: B |
front 11 11) From its atomic number of 15, it is possible to predict that the phosphorus atom has _____. A) 5 neutrons, 5 protons, and 5 electrons D) 15 protons and 15 electrons | back 11 Answer: D |
front 12 12) Fluorine has an atomic number of 9. Which of the following would you do to a neutral fluorine atom to complete its valence shell? A) add 1 electron C) remove 1 electron | back 12 Answer: A |
front 13 13) Magnesium has an atomic number of 12. What is the most stable charge for a magnesium ion? A) a +1 charge C) a -1 charge | back 13 Answer: B |
front 14 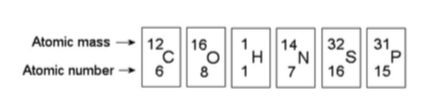 15) How many neutrons are present in the nucleus of a phosphorus-32 (32P) atom (see the figure above)? A) 15 C) 17 | back 14 Answer: C |
front 15 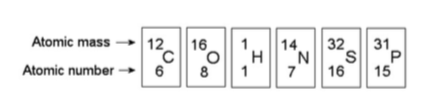 16) How many electrons will a single atom of sulfur with no charge
and no bonds have in its valence shell (see the figure above)? C) 16 | back 15 Answer: A |
front 16 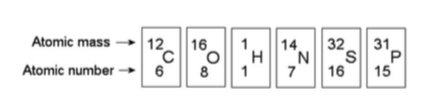 17) Based on electron configuration, which of the elements in the
figure above would exhibit a chemical behavior most like that of
oxygen? C) sulfur | back 16 Answer: C |
front 17  | back 17 Answer: A |
front 18  | back 18 Answer: D |
front 19 20) Oxygen has an atomic number of 8 and most commonly, a mass number
of 16. Thus, what is the atomic mass of an oxygen atom? C) approximately 16 grams | back 19 Answer: D |
front 20 21) If you change the number of neutrons in an atom, you create _____. A) a cation D) a different element | back 20 Answer: C |
front 21 22) Can the atomic mass of an element vary? | back 21 Answer: D |
front 22 23) Which of the following is the best description of an atom's
physical structure? | back 22 Answer: C |
front 23 24) A salamander relies on hydrogen bonding to stick to various
surfaces. Therefore, a salamander would have the greatest difficulty
clinging to a _____. C) surface of mostly carbon-oxygen bonds D) surface of mostly carbon-nitrogen bonds | back 23 Answer: B |
front 24 25) A covalent chemical bond is one in which _____. C) outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill their respective orbitals D) outer-shell electrons of one atom are transferred to fill the inner electron shell of another atom | back 24 Answer: C |
front 25 26) What is the maximum number of covalent bonds that an oxygen atom
with atomic number 8 can make with hydrogen? C) 4 | back 25 Answer: B |
front 26 27) Nitrogen (N) is more electronegative than hydrogen (H). Which of
the following is a correct statement about the atoms in ammonia
(NH3)? B) Ammonia has an overall positive charge. | back 26 Answer: A |
front 27 28) Bonds between two atoms that are equally electronegative are _____. A) hydrogen bonds D) ionic bonds | back 27 Answer: C |
front 28 29) What results from an unequal sharing of electrons between atoms? A) a nonpolar covalent bond D) a hydrophobic interaction | back 28 Answer: B |
front 29 30) A covalent bond is likely to be polar when _____. | back 29 Answer: A |
front 30 31) What is the difference between covalent bonds and ionic
bonds? | back 30 Answer: B |
front 31 32) The atomic number of chlorine is 17. The atomic number of
magnesium is 12. What is the formula for magnesium chloride? C) Mg2Cl D) MgCl3 | back 31 Answer: B |
front 32 33) How many electron pairs are shared between carbon atoms in a molecule that has the formula C2H4? A) 1 | back 32 Answer: B |
front 33 34) Which bond or interaction would be difficult to disrupt when compounds are put into water? A) covalent bonds between carbon atoms D) ionic and hydrogen bonds | back 33 Answer: A |
front 34 35) Water molecules are attracted to one another by _____. A) nonpolar covalent bonds D) hydrophobic interactions | back 34 Answer: C |
front 35 36) Van der Waals interactions may result when _____. B) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water | back 35 Answer: A |
front 36 37) What is the maximum number of hydrogen atoms that can be
covalently bonded in a molecule containing two carbon atoms? C) 6 | back 36 Answer: C |
front 37 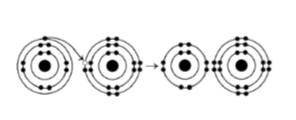 38) What results from the chemical reaction illustrated above? The reactants have no charge. A) a cation with a net charge of +1 and an anion with a net charge
of +1 D) a cation with a net charge of +1 and an anion with a net charge of -1 | back 37 Answer: D |
front 38 39) What is the atomic number of the cation formed in the reaction illustrated above? A) 8 D) 16 | back 38 Answer: C |
front 39 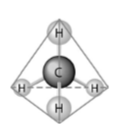 40) What causes the shape of the molecule shown above? A) the shape of the 2 p orbitals in the carbon atom C) the shape of the sp3 hybrid orbitals of the electrons shared
between the carbon and hydrogen atoms | back 39 Answer: C |
front 40 41) How many electrons are involved in a single covalent bond? A) one D) four | back 40 Answer: B |
front 41 42) How many electrons are involved in a double covalent bond? A) one D) four | back 41 Answer: D |
front 42 43) If an atom has a charge of +1, which of the following must be true? A) It has two more protons than neutrons. D) It has one more proton than it does electrons. | back 42 Answer: D |
front 43 44) Elements found on the left side of the periodic table contain
outer shells that are _____; these elements tend to form _____ in
solution. C) almost full; cations | back 43 Answer: A |
front 44 45) An atom has four electrons in its valence shell. What types of
covalent bonds is it capable of forming? C) single bonds only | back 44 Answer: A |
front 45 46) When are atoms most stable? C) when all of the electron orbitals in the valence shell are filled D) when all electrons are paired | back 45 Answer: C |
front 46 47) When the atoms involved in a covalent bond have the same
electronegativity, what type of bond results? C) a nonpolar covalent bond | back 46 Answer: C |
front 47 48) Nitrogen (N) normally forms three covalent bonds with a valence
of 5. However, ammonium has four covalent bonds, each to a different
hydrogen (H) atom (H has a valence of 1). What do you predict to be
the charge on ammonium? B) -1 | back 47 Answer: A |
front 48 49) You need to write down information about a molecule, but need to
indicate only the type and number of atoms it contains. Which
representation would work best? C) ball-and-stick model | back 48 Answer: A |
front 49 50) You need to represent a molecule to best illustrate the relative
sizes of the atoms involved and their interrelationships. Which
representation would work best? C) ball-and-stick model | back 49 Answer: D |
front 50 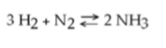 51) Which of the following is true for this reaction? A) The reaction is nonreversible. C) Ammonia is being formed and decomposed simultaneously. | back 50 Answer: C |
front 51 52) Which of the following correctly describes all chemical
equilibrium? | back 51 Answer: A |
front 52 53) Which of the following correctly describes a reaction that has reached chemical equilibrium? A) The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the
reverse reaction. D) Both the forward and the reverse reactions have stopped, with no net effect on the concentration of the reactants and the products. | back 52 Answer: A |