Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
MICRO CH 25
front 1 1) Which of the following is directly involved in the initiation of dental caries? A) sucrose B) lysozyme C) lactic acid | back 1 C |
front 2 2) Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea is usually preceded by A) eating contaminated food. B) a blood transfusion. C) extended use of antibiotics. | back 2 C |
front 3 3) Which of the following statements about salmonellosis is FALSE? A) It is a bacterial infection. B) Severity of disease depends on number of organisms ingested. C) A healthy carrier state exists. D) The mortality rate is high. | back 3 D |
front 4 4) Disease-causing exotoxins are produced by all of the following organisms EXCEPT A) Clostridium perfringens. B) Vibrio cholerae. C) Shigella dysenteriae. | back 4 C |
front 5 5) Which one of the following diseases of the gastrointestinal system is transmitted by the respiratory route? A) staphylococcal enterotoxicosis B) mumps C) Vibrio gastroenteritis | back 5 B |
front 6 6) The digestive tract is essentially one long tube. The order of the structures, beginning with the mouth, is A) pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine. B) esophagus, pharynx, stomach, small intestine, large intestine. C) pharynx, esophagus, stomach, large intestine, small intestine. | back 6 A |
front 7 7) Which of the following helminthic diseases is a common infestation found in the southeastern United States? A) Enterobius vermicularis B) Ascaris lumbricoides C) Taenia saginata | back 7 B |
front 8 8) Poultry products are a likely source of infection by A) Helicobacter pylori. B) Salmonella enterica. C) Vibrio cholerae. | back 8 B |
front 9 9) All of the following infections can result from drinking contaminated water EXCEPT A) Cyclospora infection. B) giardiasis. C) trichinellosis. | back 9 C |
front 10 10) Which of the following organisms feeds on red blood cells? A) Giardia lamblia B) Escherichia coli C) Taenia spp. D) Vibrio parahaemolyticus E) Entamoeba histolytica | back 10 E |
front 11 11) In humans, beef tapeworm infestations are acquired by ingesting A) the eggs of Taenia saginata. B) segments of Taenia solium tapeworms. C) water contaminated with Diphyllobothrium latum eggs. D) cysticerci of Taenia saginata in undercooked meat. | back 11 D |
front 12 12) Which of the following statements about staphylococcal food poisoning is FALSE? A) It is caused by ingesting an enterotoxin. B) It can be prevented by adequate refrigeration of food. C) It can be prevented by heating foods to 50°C for 15 minutes. | back 12 C |
front 13 13) The most common cause of traveler's diarrhea is A) Shigella spp. B) Salmonella enterica. C) Giardia lamblia. D) Escherichia coli. | back 13 D |
front 14 14) Acute gastroenteritis that occurs after an incubation period of two to three days and commonly affects children is probably caused by A) Giardia. B) rotavirus. C) Salmonella. | back 14 B |
front 15 15) Which of the following is mismatched? A) hydatid disease — humans are the definitive host B) Taenia infestation — humans are the definitive host C) trichinellosis — humans eat larva of parasite | back 15 A |
front 16 16) Thorough cooking of food will prevent all of the following EXCEPT A) trichinellosis. B) beef tapeworm. C) staphylococcal food poisoning. | back 16 C |
front 17 17) Most of the normal microbiota of the digestive system are found in the A) mouth. B) stomach. C) stomach and small intestine. D) small intestine and large intestine. | back 17 D |
front 18 18) Gums bleeding while brushing one's teeth is most commonly associated with A) halitosis. B) cavities. C) gingivitis. | back 18 C |
front 19 19) Typhoid fever differs from salmonellosis in that in typhoid fever A) the microorganisms multiply within macrophages. B) the incubation period is much longer. C) the symptoms are due to infection of the gallbladder. | back 19 B |
front 20 20) Which of the following organisms is likely to be transmitted via contaminated shrimp? A) Trichinella spiralis B) Vibrio parahaemolyticus C) Giardia lamblia | back 20 B |
front 21 21) Which of the following organisms is likely to be transmitted via undercooked pork and horse? A) Salmonella enterica B) Staphylococcus aureus C) Trichinella spiralis | back 21 C |
front 22 22) A vaccine to provide active immunity to HBV is prepared from A) viruses grown in tissue culture. B) genetically modified yeast. C) pooled gamma globulin. | back 22 B |
front 23 23) Aflatoxin is a(n) ________ associated with ingestion of contaminated ________. A) mycotoxin; peanuts B) mycotoxin; rye or other cereal grains C) enterotoxin; peanuts | back 23 A |
front 24 24) Which of the following causes inflammation of the liver? A) Salmonella enterica B) Shigella spp. C) hepatitis A virus | back 24 C |
front 25 25) "Rice water stools" are characteristic of A) salmonellosis. B) cholera. C) bacillary dysentery. | back 25 B |
front 26 26) Epidemics related to bacterial infection of the digestive system are typically caused by A) biological vectors. B) contaminated food and water. C) unpasteurized milk. | back 26 B |
front 27 27) Many bacterial infections of the lower digestive tract are treated with A) antitoxin. B) penicillin. C) water and electrolytes. | back 27 C |
front 28 28) Dental plaque is an example of A) a pellicle. B) a biofilm. C) gingivitis. | back 28 B |
front 29 29) Which of the following is mismatched? A) ergot — gangrene B) Salmonella endotoxin — lyses red blood cells C) Vibrio enterotoxin — secretion of Cl-, K+, and H2O | back 29 B |
front 30 30) Bacterial intoxications differ from bacterial infections of the digestive system in that intoxications A) are transmitted via contaminated water. B) are more severe. C) have shorter incubation times. | back 30 C |
front 31 31) The most common mode of HAV transmission is A) contamination of food during preparation. B) contamination of food before it reaches a food service establishment. C) blood transfusion. | back 31 A |
front 32 32) Which of the following correctly lists the stages of tooth decay? A) plaque accumulation, destruction of enamel, advancement of decay through enamel, decay in dentin, decay in tooth pulp B) decay in dentin, plaque accumulation, destruction of enamel, advancement of decay through enamel, decay in tooth pulp C) plaque accumulation, destruction of enamel, decay in tooth pulp, advancement of decay through enamel, decay in dentin | back 32 A |
front 33 33) A 38-year-old man had onset of fever, chills, nausea, and myalgia while vacationing on the Gulf of Mexico. On April 29, he had eaten raw oysters and gone wading in the warm coastal waters. On May 2, he was admitted to a hospital because of a fever of 39°C and two circular necrotic lesions on the left leg. He had a history of alcoholic liver disease. He was transferred to the ICU; therapy with antibiotics was initiated. On May 4, he died. Which of the following is the most likely cause? A) Bacillus cereus B) Cyclospora cayetanensis C) Salmonella typhi D) Vibrio vulnificus | back 33 D |
front 34 34) Which of the following is included in GALT? A) thymus B) Peyer's patches C) tonsils | back 34 B |
front 35 35) Microscopic examination of a patient's fecal culture shows spiral bacteria. The bacteria probably belong to the genus A) Campylobacter jejuni. B) Escherichia coli. C) Salmonella typhi. | back 35 A |
front 36 36) Which of the following pertains to typhoid fever? A) It is acquired via ingestion of contaminated meat. B) Enterotoxin spreads via the blood. C) It is caused by several different species of Salmonella. D) Causative microorganism multiplies in patient phagocytes. | back 36 D |
front 37 37) All of the following are gram-negative rods that cause gastroenteritis EXCEPT A) Clostridium perfringens. B) Escherichia coli. C) Salmonella typhi. | back 37 A |
front 38 38) Helicobacter pylori can grow in the stomach because it A) hides in macrophages. B) makes a capsule. C) possesses an enzyme that neutralizes HCl. | back 38 C |
front 39 39) All of the following are eukaryotic organisms that cause diarrheal disease EXCEPT A) Cryptosporidium. B) Cyclospora. C) Entamoeba. D) Giardia. E) Campylobacter. | back 39 E |
front 40 40) All of the following pertain to pinworm infections EXCEPT A) transmission is typically by contact with fomites or inhalation of eggs. B) diagnosis is by detecting eggs on transparent tape pressed to the perianal area. C) all family members living with the patient must also be treated. D) it is most commonly transmitted by cysts in water. | back 40 D |
front 41 41) What is a Dane particle? A) the chlorine-resistant virus that causes HAV B) the infectious virion that causes HBV C) the spherical particles found in serum of patients with HBV | back 41 B |
front 42 42) Which of the following is mismatched? A) beef — E. coli O157:H7 B) custard and cream pies — Staphylococcus aureus C) eggs — Trichinella spiralis | back 42 C |
front 43 Following a county fair, 160 persons complained of gastrointestinal symptoms. Symptoms included diarrhea (84 percent), abdominal cramps (96 percent), nausea (84 percent), vomiting (82 percent), body aches (50 percent), fever (60 percent; median body temperature = 38.3°C); median duration of illness 6 days (range 10 hr to 13 days). 43) In Situation 25.1, fecal samples should be cultured for all of the following EXCEPT A) Salmonella enterica. B) Shigella spp. C) Campylobacter jejuni. D) enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. E) Giardia lamblia. | back 43 E |
front 44 44) In Situation 25.1, fecal samples were found to be negative when cultured. The next step in diagnosing the cause of illness would be A) to begin antibiotic therapy. B) blood cultures. C) microscopic examination of feces for oocysts. | back 44 C |
front 45 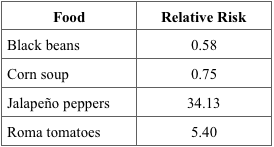 45) The relative risks shown in Table 25.1 were calculated for foods suspected of transmitting Salmonella. Which food is the most likely source of infection? A) black beans B) corn soup C) jalapeño peppers | back 45 C |
front 46 1) Campylobacter gastroenteritis is the leading cause of foodborne illness in the United States. | back 46 TRUE |
front 47 2) Dental caries can also be referred to as periodontal disease. | back 47 FALSE |
front 48 3) Bacterial infections, but not intoxications, can cause diarrhea. | back 48 FALSE |
front 49 4) An outbreak of viral gastroenteritis occurs in a pediatrics ward. Rotavirus is the most likely causative agent. | back 49 TRUE |
front 50 5) Aflatoxin poisoning is associated with liver cancer. | back 50 TRUE |
front 51 6) Approximately 30 percent of the body's immune system is located in the intestinal tract. | back 51 FALSE |
front 52 7) Lactic acid, an end product of fructose fermentation, causes breakdown of tooth enamel and, eventually, cavities. | back 52 TRUE |
front 53 8) Gastroenteritis due to ingestion of food contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus is due to intoxication by enterotoxins. | back 53 TRUE |
front 54 9) EHEC is a major cause of diarrhea in developing countries and may result in the death of small children. | back 54 FALSE |
front 55 10) H. pylori is able to survive the acidic environment of the stomach as a result of adaptations that allow it to increase the pH of the immediate environment. | back 55 TRUE |