Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Activity 1: Identifying Organs of the Alimentary Canal and General
front 1 The digestive system provides the body with what 3 general substances? | back 1 1. Nutrients 2. Water 3. Electrolytes |
front 2 The organs of the digestive system does what 4 general functions? | back 2 1. Ingest food 2. Digest food 3. Absorb food 4. Eliminate undigested remains as feces |
front 3 The digestive system extends from and to which body parts? | back 3 Extends from the mouth to the anus |
front 4 How is ingested food made available to body cells? (Hint: describe the 2 ways that must occur in sequential order) | back 4 1. Digestion 2. Absorption |
front 5 Describe digestion. | back 5 Ingested food being broken down into smaller diffusible molecules |
front 6 Describe absorption. | back 6 Digested end products pass through epithelial cells lining the tract into the blood for distribution to the body cells |
front 7 The organs of the digestive system are separated into what 2 major groups? | back 7 1. Alimentary canal aka gastrointestinal (GI) tract 2. Accessory digestive organs |
front 8 The alimentary canal consists of what 6 body features? | back 8 1. Mouth 2. Pharynx 3. Esophagus 4. Stomach 5. Small intestines 6. Large intestines |
front 9 The accessory digestive organs consist of what 5 structures? | back 9 1. Teeth 2. Salivary glands 3. Gallblader 4. Liver 5. Pancreas |
front 10 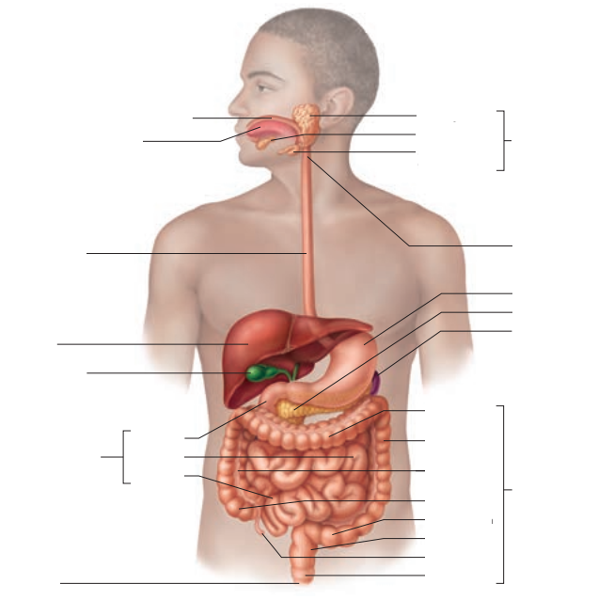 1. Identify the blanks. 2. Also Identify the accessory organs and the alimentary canal organs. 3. Is the spleen an organ of the digestive system? If no, explain which system it belongs to. | back 10 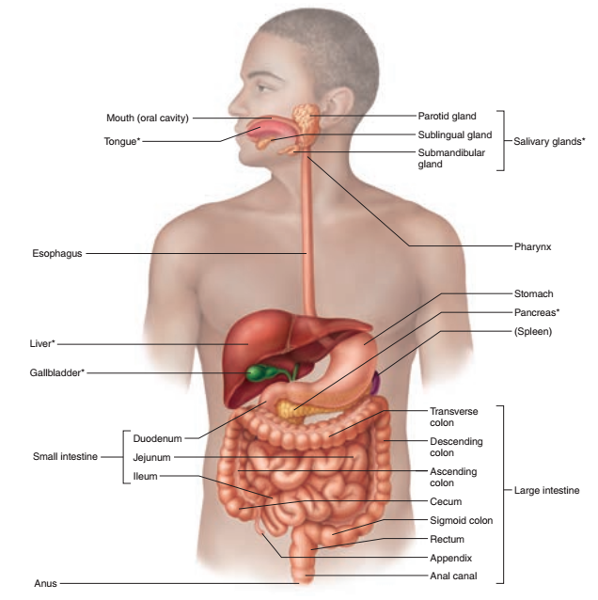 1. Look at the picture. 2. Asterisks are accessory organs. Those without asterisks are alimentary canal organs. 3. No. The spleen belongs to the lymphatic system. |
front 11 What is the genearl function of the teeth? | back 11 Physically break down foods |
front 12 The salivary glands, gallbladder, liver, and pancreas secrete their products into where? | back 12 Into the alimentary canal |
front 13 Describe the basic structure of the alimentary canal from the esophagus to the anal canal. | back 13 Similar |
front 14 The alimentary canal wall has how many layers aka tunics? | back 14 4 |
front 15 What are the 4 layers of the alimentary canal from the lumen outward? | back 15 1. Mucosa 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis externa 4. Serosa (*adventitia in the esophagus since it is located outside of the peritoneal cavity) |
front 16 The mucosa layer of the alimentary canal has how many subdivisions? | back 16 3 |
front 17 What are the 3 subdivisions of the mucosa layer of the alimentary canal from innermost to outermost? | back 17 1. Epithelium 2. Lamina propria 3. Muscularis mucosae |
front 18 What are the 2 tissue types in the epithelium of the alimentary canal? (Hint: mouth+esophagus+anus and the remainder of the canal) | back 18 1. Mouth+esophagus+anus=stratified squamous epithelium 2. Remainder of the canal=simple columnar epithelium |
front 19 What is the tissue type of the lamina propria, and what vessels and follicles does that tissue type contain? | back 19 Areolar connective tissue containing blood vessels and lymphoid follicles |
front 20 What are the 3 functions of the mucosa? (Hint: One function has 3 secretions) | back 20 1. Secretion of mucus, digestive enzymes, and hormones 2. Absorption of end products into the blood 3. Protection against infectious diseases |
front 21 The submucosa layer of the alimentary canal has how many subdivisions? | back 21 0 |
front 22 The submucosa layer of the alimentary canal is made up of what 2 tissues that contain which 2 vessels and what type of fibers? | back 22 Areolar and dense irregular connective tissue containing blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerve fibers |
front 23 Which tunic is the submucosal nerve plexus located? | back 23 In the submucosa |
front 24 What are the 2 functions of the submucosa layer of the alimentary canal? (Hint: Functions of blood vessels and elastic fibers) | back 24 1. Blood vessels absorb and transport nutrients 2. Elastic fibers help maintain the shape of each organ |
front 25 The muscularis externa layer of the alimentary canal has how many subdivisions? | back 25 2 |
front 26 What are the 2 subdivisions of the muscularis externa layer of the alimentary canal (from innermost to outermost)? | back 26 1. Circular layer 2. Longitudinal layer |
front 27 What are the 2 functions of the muscularis externa layer of the alimentary canal? | back 27 1. Segmentation of digested food along the tract 2. Peristalsis of digested food along the tract |
front 28 Segmentation and peristalsis by the muscularis externa layer of the alimentary canal are controlled by what nerve plexus? | back 28 Myenteric nerve plexus |
front 29 1. Which tunic is the myenteric nerve plexus located? 2. Which subdivision of the aforementioned tunic is the meyenteric nerve plexus located? | back 29 1. The muscularis externa 2. The circular layer |
front 30 The serosa of the alimentary canal is composed of how many subdivisions? | back 30 2 |
front 31 What are the 2 subdivisions of the serosa from innermost to outermost? (Hint: One is a tissue type) | back 31 1. Connective tissue 2. Epithelium |
front 32 What are the tissue type and epithelium that make up the serosa of the alimentary canal? | back 32 1. Areolar connective tissue 2. Simple squamous epithelium |
front 33 What is the function of the serosa of the alimentary canal? | back 33 Reduces friction as the digestive system organs slide across one another |
front 34 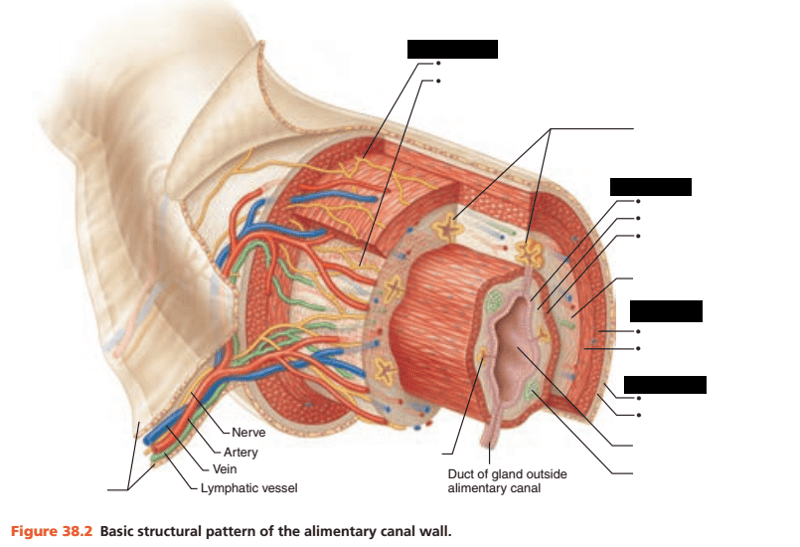 Identify the blanks | back 34 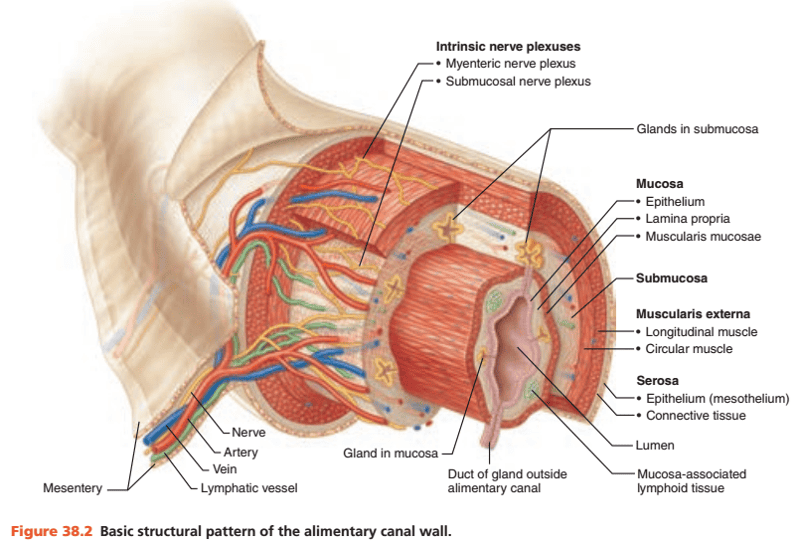 |
front 35 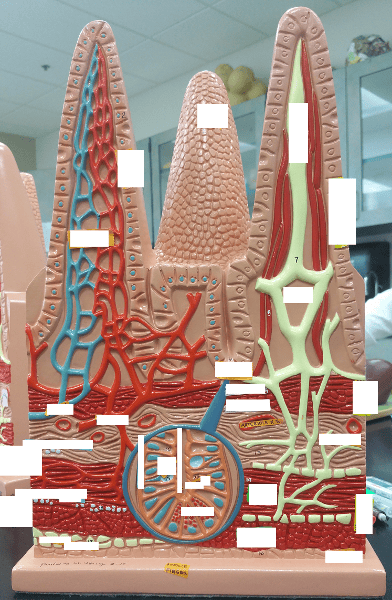 Identify the blanks | back 35 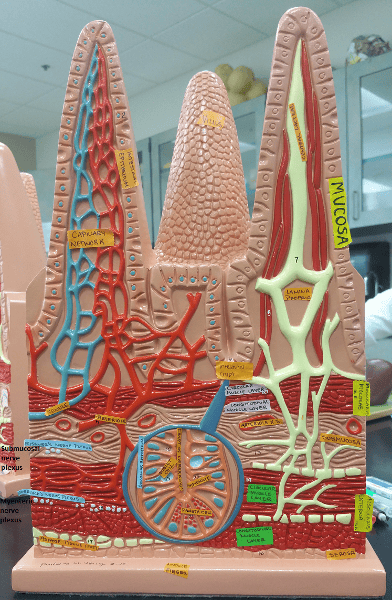 |
front 36 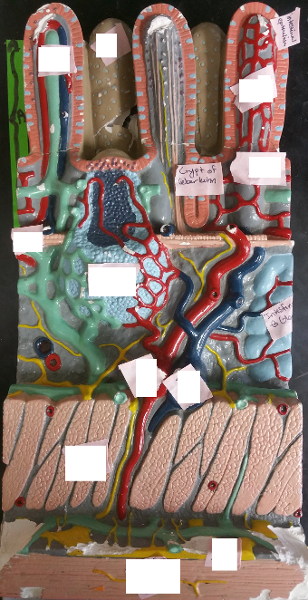 Identify the blanks. | back 36 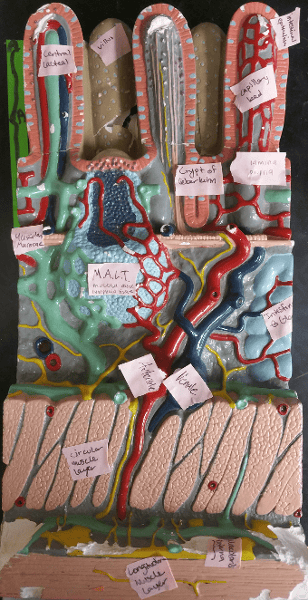 |
front 37 Food enters the mouth through which cavity? | back 37 Oral cavity |
front 38 The oral cavity is commonly called what? | back 38 Mouth |
front 39 The oral cavity is filled with what? | back 39 Mucous |
front 40 The oral cavity is lined with what 4 digestive accessory structures? | back 40 1. Gums 2. Teeth 3. Tongue 4. Openings of the ducts of the salivary glands |
front 41 What protects the opening of the oral cavity anteriorly? | back 41 Lips |
front 42 What forms the lateral walls of the oral cavity? | back 42 Cheeks |
front 43 What forms the roof of the oral cavity? | back 43 Palate |
front 44 The anterior portion of the palate is referred to as what? | back 44 Hard palate |
front 45 Why is the hard palate referred to by that name? (Hint: 2 bones underlie it) | back 45 The palatine processes of the maxillae and the palatine bones underlie it |
front 46 What is the posterior portion of the palate? | back 46 Soft palate |
front 47 1. The soft palate is what type of structure? 2. Is the soft palate supported by bone? | back 47 1. Fibromuscular structure 2. No |
front 48 The floor of the oral cavity is occupied by what organ? | back 48 Tongue |
front 49 The tongue is supported by what specific muscle? | back 49 Mylohyoid muscle |
front 50 What secures the inferior midline of the tongue to the floor of the mouth? | back 50 Lingual frenulum |
front 51 The space between the lips and cheeks and the teeth and the gums is called what? | back 51 Oral vestibule |
front 52 What is the area that lies within the teeth and gums? | back 52 Oral cavity proper |
front 53 On each side of the mouth at its posterior end are masses of lymphoid tissue called what? | back 53 Palatine tonsils |
front 54 The palatine tonsils are bounded anteriorly and posteriorly by what 2 membranes? (Hint: think arches) | back 54 1. Anteriorly: Palatoglossal arch 2. Posteriorly: Palatopharyngeal arch |
front 55 The mass of lymphoid tissue that covers the base of the tongue is called what? | back 55 Lingual tonsil |
front 56 The tonsils are part of which body system? | back 56 The body's defense system |
front 57 What is tonsillitis? | back 57 Inflammation of the palatine tonsils |
front 58 Inflammation causes what to happen to the palatine tonsils? | back 58 Enlargement |
front 59 Tonsilitis blocks entrance to what specific region? | back 59 Blocks entrance to the pharynx posteriorly |
front 60 Describe tonsilitis's effect on swallowing? | back 60 Makes it difficult and paintful |
front 61 How many salivary glands are there? (Hint: think pairs) | back 61 3 pairs of salivary glands |
front 62 The salivary glands secrete what specific substance? | back 62 Saliva |
front 63 Saliva is duct by the salivary glands into which cavity? | back 63 Oral cavity |
front 64 Describe the function of salivary amylase, one component of saliva. | back 64 Begins the digestion of starchy foods within the oral cavity |
front 65 What 2 things happen to food as it enters the mouth? | back 65 1. Mixed with saliva 2. Masticated aka chewed |
front 66 What is the function of the cheeks and lips in regards to food that is in the mouth? | back 66 Hold the food between the teeth during mastication |
front 67 What are the 2 functions of the tongue in regards to food that is in the mouth? | back 67 1. Manipulates the food 2. Initiates swallowing |
front 68 What 2 breakdowns of food begins in the oral cavity? | back 68 1. Mechanical breakdown 2. Chemical breakdown |
front 69 The Pharynx | back 69 The Pharynx |
front 70 When the tongue initiates swallowing, the food passes posteriorly into which oral cavity feature? | back 70 Pharynx |
front 71 The pharynx is divided into what 3 parts? | back 71 1. Nasopharynx 2. Oropharynx 3. Laryngopharynx |
front 72 The nasopharynx is located behind which cavity? | back 72 Nasal cavity |
front 73 1. The oropharynx is located behind which cavity? 2. The oropharynx extends from what to what? (Hint: palate to what feature) | back 73 1. Oral cavity 2. Soft palate to the epiglottis |
front 74 The laryngopharynx extends from what to what? | back 74 From the epiglottis to the larynx |
front 75 The walls of the pharynx consist of how many layers of what muscle type? | back 75 2 layers of skeletal muscles |
front 76 Describe the makeup of the 2 layers of the pharynx. | back 76 1. Inner layer of longitudinal muscle 2. Outer layer of circular constrictor muscles |
front 77 The outer layer of circular constrictor muscles in the pharynx has what function? | back 77 Initiate wavelike contractions that propel food inferiorly into the esophagus Aka as peristalsis |
front 78 Does the pharynx have a mucosa? | back 78 Yes |
front 79 The mucosa of the pharynx is composed of what epithelium? | back 79 Stratified squamous epithelium |
front 80 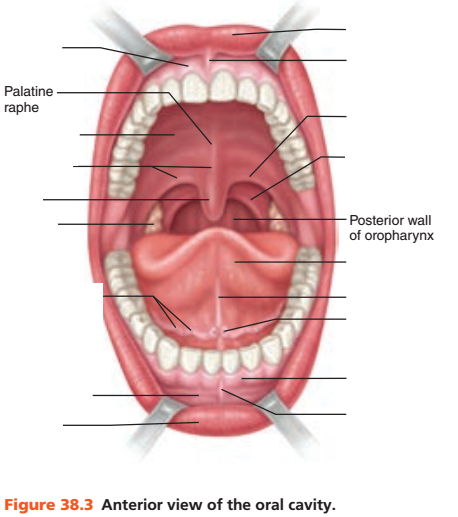 Identify the blanks. | back 80 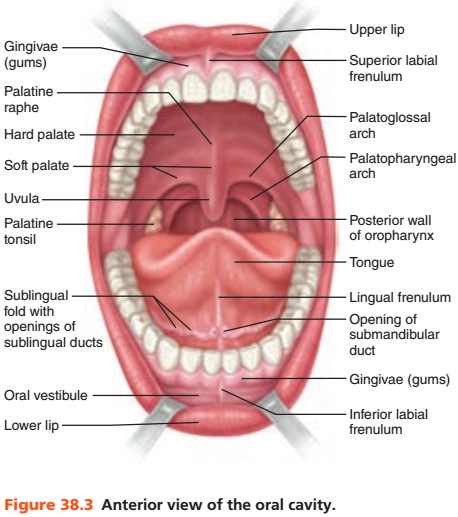 |
front 81 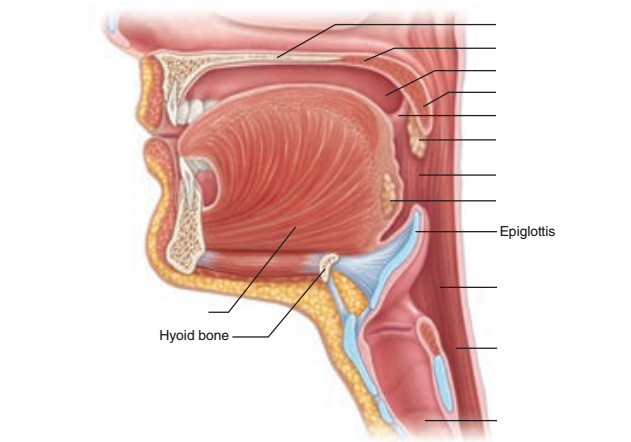 Identify the blanks. | back 81 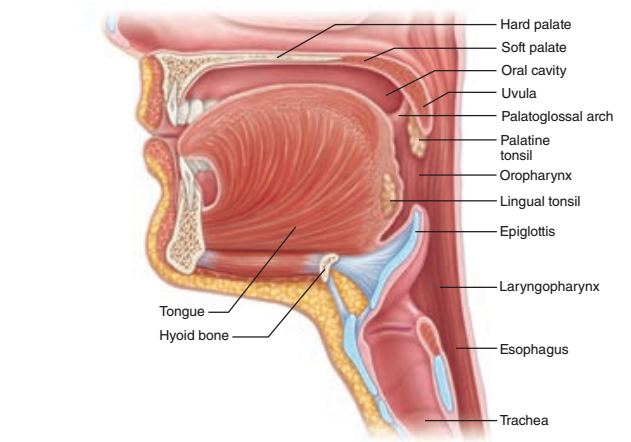 |
front 82 The Esophagus | back 82 The Esophagus |
front 83 Any organ that is part of the alimentary canal has the 4 common tunics or layers, mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa (from innermost to outermost). Since the esophagus is outside the peritoneal cavity, its serosa is replaced by what? | back 83 Adventitia |
front 84 The adventitia of the esophagus is made up of what type of tissue? | back 84 Areolar connective tissue |
front 85 What is the function of the adventitia of the esophagus? | back 85 Binds the esophagus to the surrounding tissues |
front 86 The esophagus extends from where, passes through which organ, and stops at which structure? (Hint: ends at a specific sphincter) | back 86 Extends from the pharynx through the diaphragm to the gastroesophageal sphincter |
front 87 The esophagus conducts food to the stomach in what type of motion? | back 87 Peristaltic wavelike motion |
front 88 The esophagus is devoid of what 2 functions? | back 88 1. Digestion 2. Absorption |
front 89 The walls at the superior end of the esophagus contains what type of muscle? | back 89 Skeletal muscle |
front 90 As the esophagus approaches the stomach, the skeletal muscle in its walls are replaced by what muscle type? | back 90 Smooth muscle |
front 91 The gastroesophageal sphincter is made up of what muscle type? | back 91 Smooth muscle |
front 92 Where is the gastroesophageal sphincter located? (Hint: junction) | back 92 At the esophagus-stomach junction |
front 93 What is the function of the gastroesophageal sphincter? | back 93 Controls passage of food into the stomach |
front 94 The Stomach | back 94 The Stomach |
front 95 The stomach is located on what side of the abdominal cavity and hidden by what 2 organs? | back 95 Located on the left side of the abdominal cavity and is hidden by the liver and diaphragm |
front 96 The stomach is broken up into what 4 important regions? | back 96 1. Cardial part 2. Fundus 3. Body 4. Pyloric part |
front 97 What enters the cardial part of the stomach? | back 97 Food |
front 98 What is the largest region of the stomach? | back 98 The body |
front 99 What region forms the distal stomach? | back 99 The pyloric part |
front 100 The pyloric part is broken up into what 4 parts? | back 100 1. Pyloric antrum 2. Pyloric canal 3. Pylorus 4. Pyloric sphincter |
front 101 The pylorus is continuous with what organ? | back 101 The small intestine |
front 102 What is the function of the pyloric sphincter? | back 102 Controls the emptying of the stomach |
front 103 The pyloric sphincter empties into what organ? | back 103 The small intestine |
front 104 What is the mesentery? | back 104 Double layer of the peritoneum that extends from the digestive organs to the body wall |
front 105 What are the 2 mesenteries? | back 105 1. Greater omentum 2. Lesser omentum |
front 106 The 2 mesenteries connect to what organ? | back 106 Stomach |
front 107 The lesser omentum extends from what organ to what feature of the stomach? | back 107 Extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach |
front 108 The greater omentum extends from what feature of the stomach and covers how many organs? | back 108 Extends from the greater curvature of the stomach and covers most of the abdominal organs |
front 109 How long does the stomach store food? | back 109 Temporarily |
front 110 The stomach is the site for what 2 breakdowns of food? | back 110 1. Chemical breakdown 2. Mechanical breakdown |
front 111 What is the innermost muscularis externa layer of the stomach? | back 111 Oblique smooth muscle |
front 112 What are the 3 functions of the oblique layer of the stomach's muscularis externa? | back 112 1. Churn food 2. Mix food 3. Pummel food |
front 113 Gastric glands of the stomach mucosa secrete what 2 secretions? | back 113 1. Hydrochloric acid 2. Hydrolytic enzymes |
front 114 The mucosal glands of the stomach secrete what and what is it's function? | back 114 Secrete a mucus that prevents the stomach itself from being digested by the proteolytic enzymes |
front 115 Most digestive activity occurs in what part of the stomach? | back 115 Pyloric part of the stomach |
front 116 After the food is processed in the stomach, what is it called? | back 116 Chyme |
front 117 How does chyme enter the small intestine? (Hint: through which sphincter?) | back 117 Enters the small intestine through the pyloric sphincter |
front 118 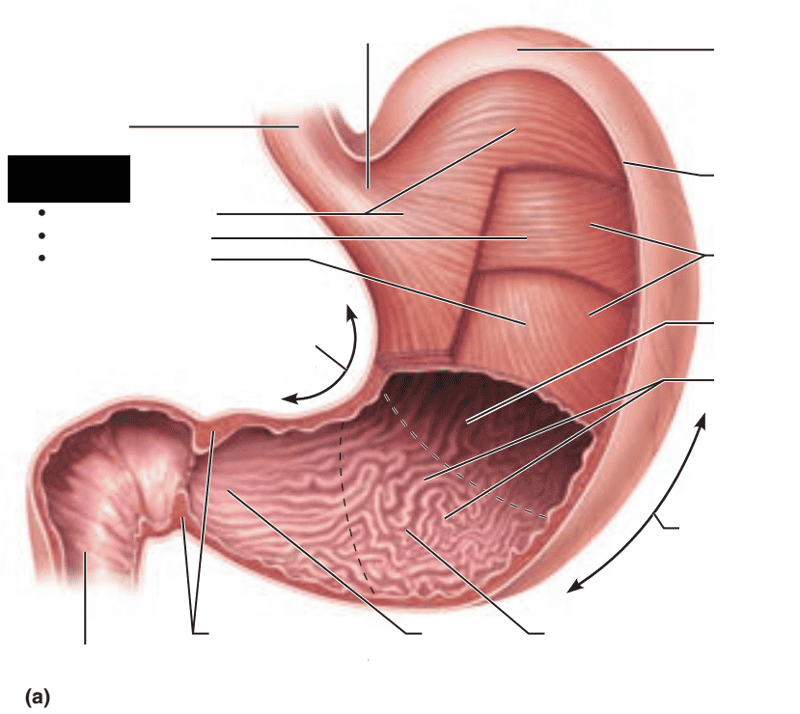 Identify the blanks. | back 118 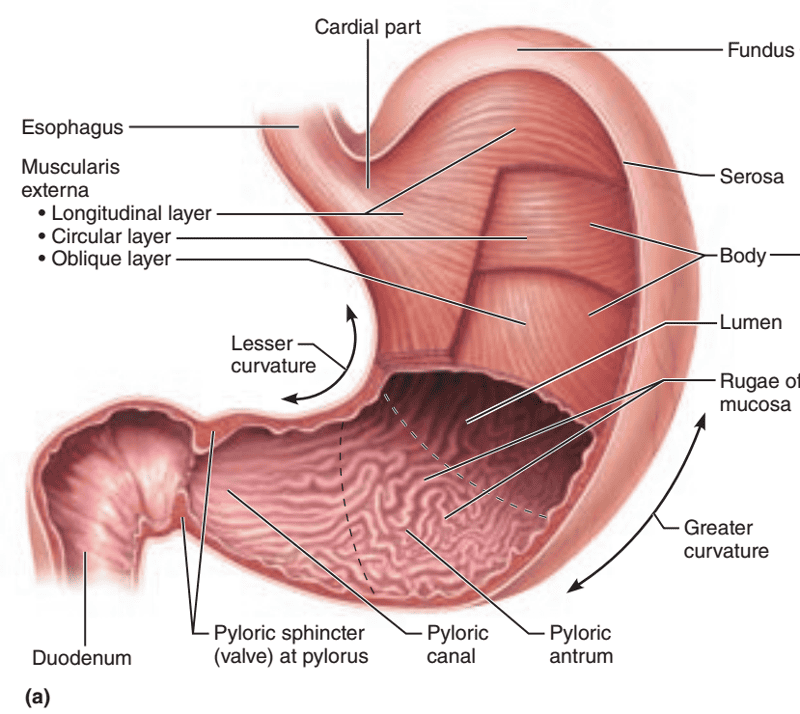 |
front 119 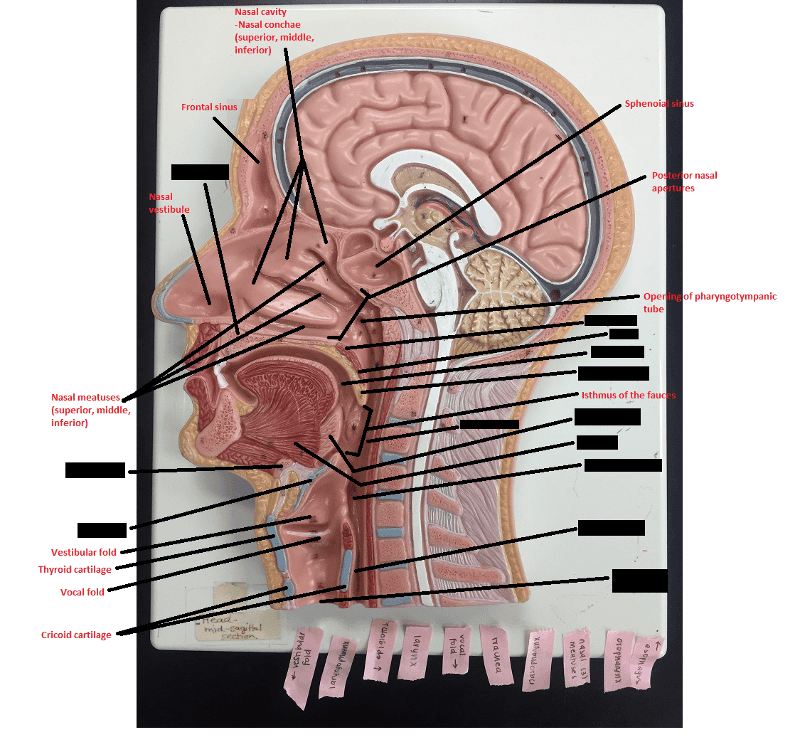 Identify the blanks. | back 119 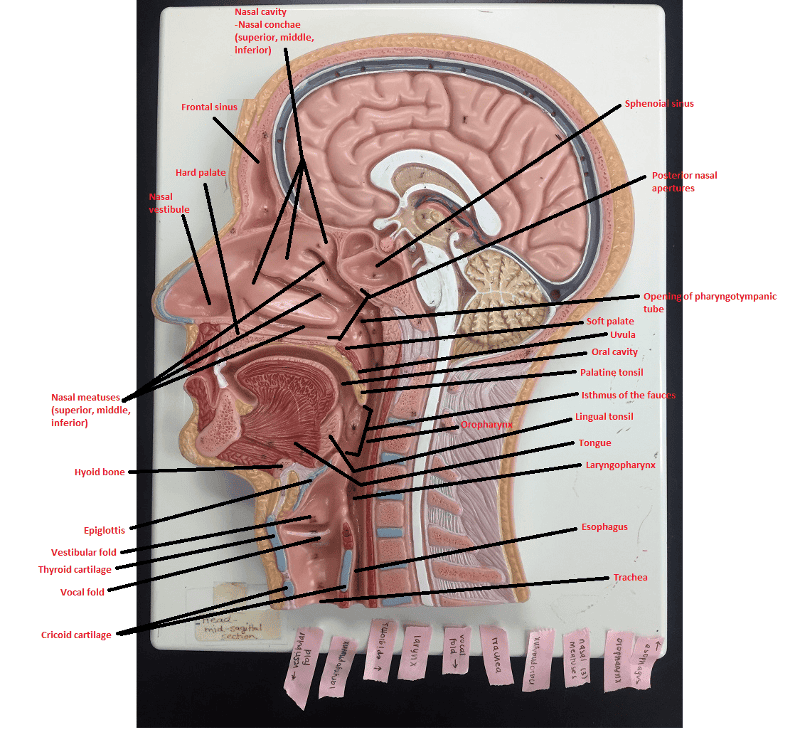 |
front 120 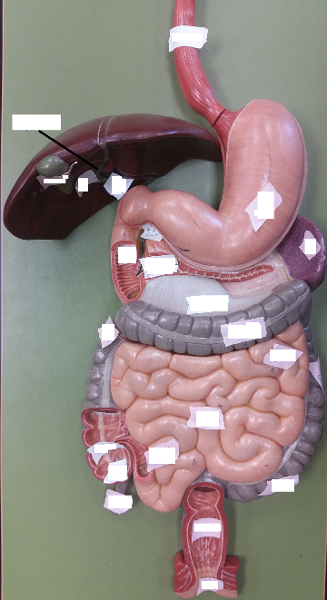 Identify the blanks. | back 120 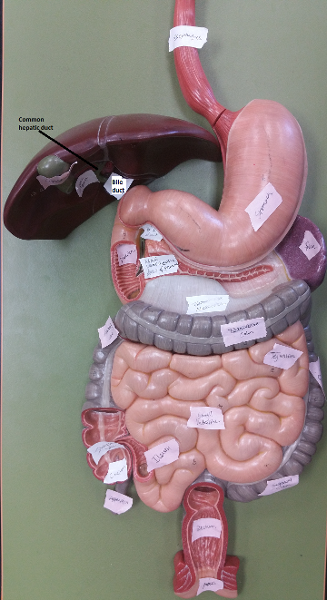 |
front 121 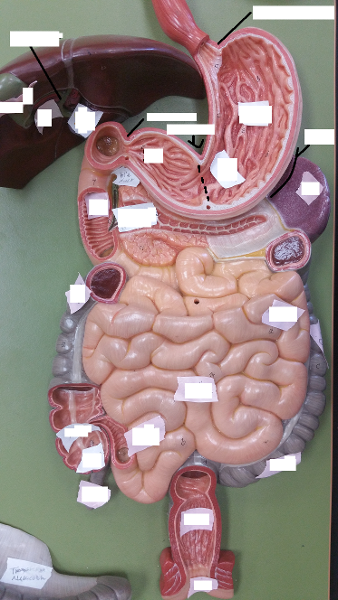 Identify the blanks. | back 121 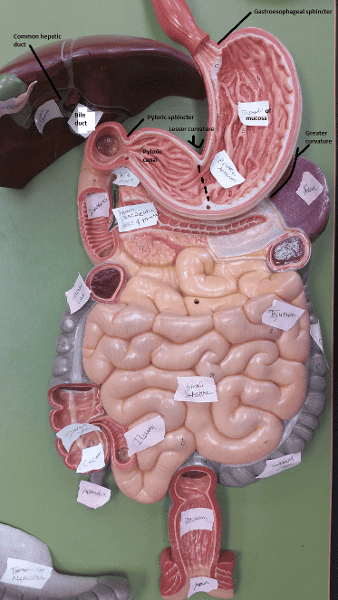 |
front 122 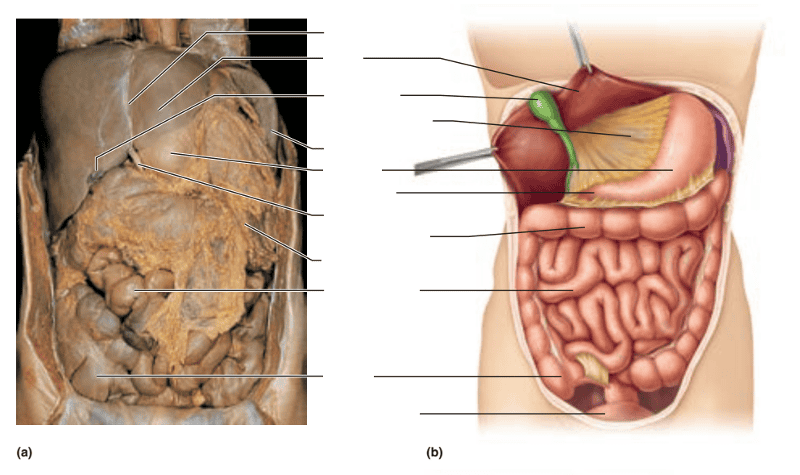 Identify the blanks. | back 122 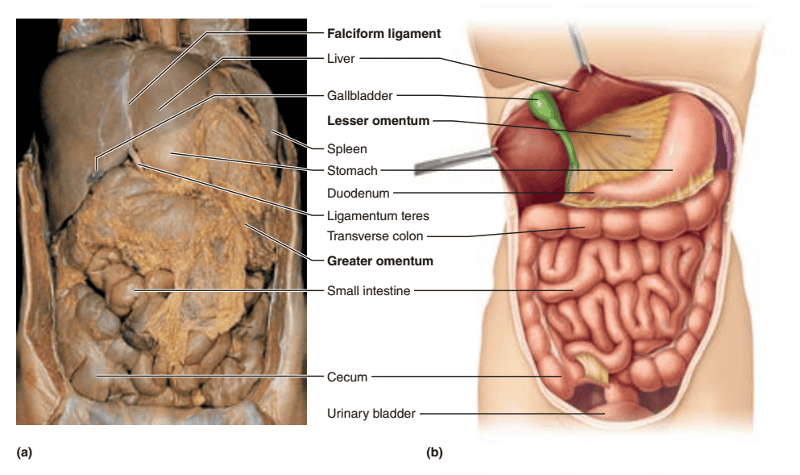 |
front 123 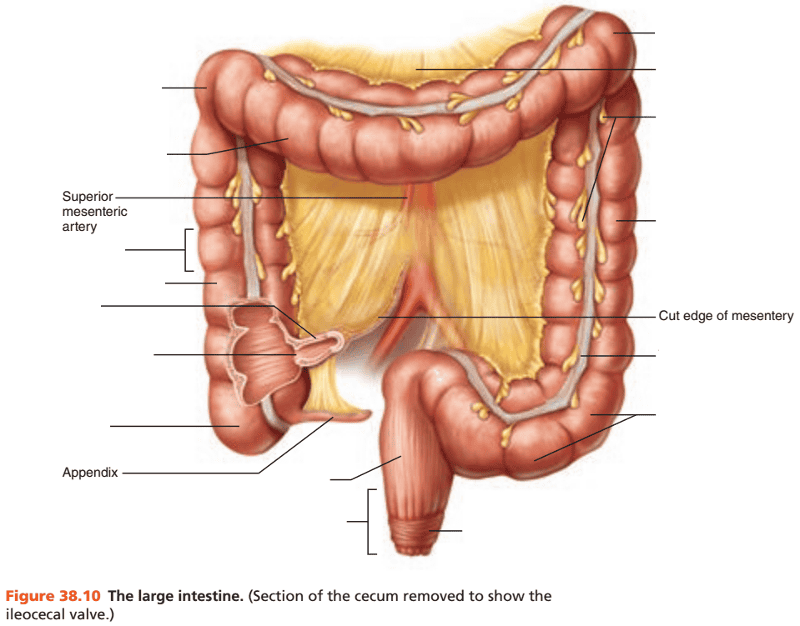 Identify the blanks. | back 123 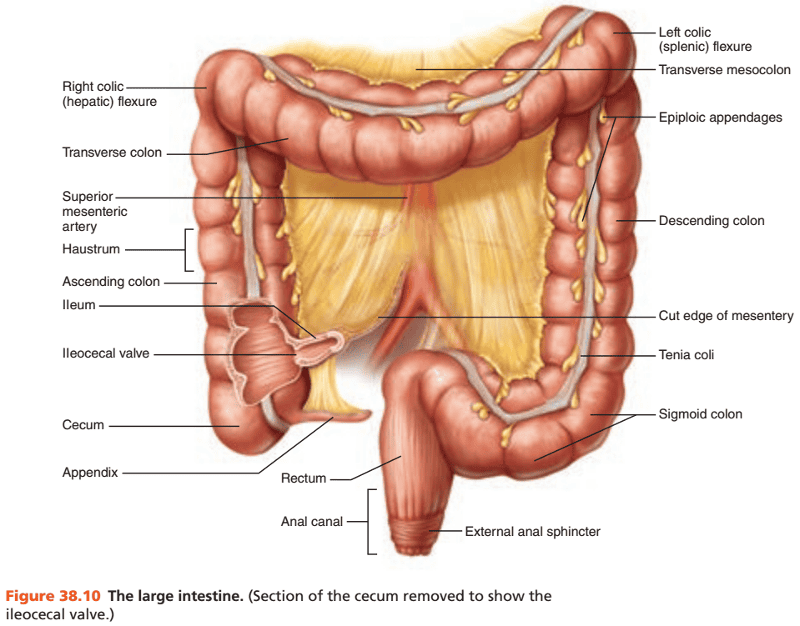 |