Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
The Urinary System
front 1 ________ ______________ main function is to keep the body in homeostasis by controlling the composition and volumes of the blood | back 1 Urinary System |
front 2 __________________ means external or posterior to the peritoneum | back 2 Retroperitoneal |
front 3 The Kidneys lie in a ______________ position (between the dorsal body wall and the parietal peritoneum). | back 3 Retroperitoneal |
front 4 Kidneys ...
| back 4
|
front 5 Kidneys...
| back 5
|
front 6
| back 6
|
front 7 The kidneys are _______ -shaped, as they are retroperitoneal; ______ layers of tissue protect and support the kidneys.
| back 7
|
front 8 Kidneys are sectioned in: | back 8
|
front 9 __________ is the indentation where the blood vessels enter and exit from the kidneys , and the ureters ________ from the renal pelvis. | back 9 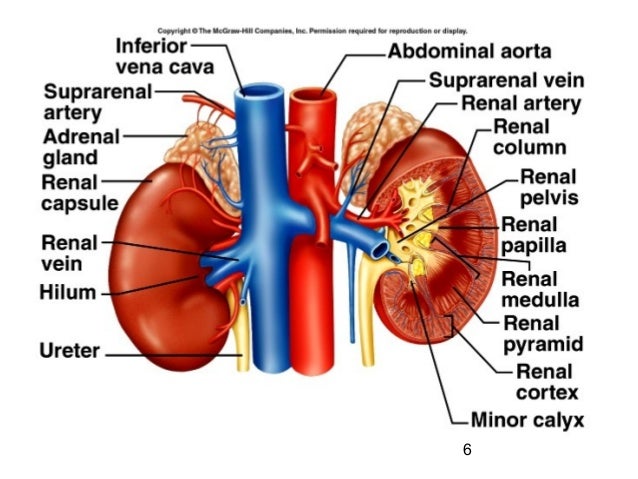
|
front 10 Renal __________ is a cavity in the Kidney in which the renal pelvis can be found. | back 10
|
front 11 ____________ is the area or the kidneys from the base of the renal pyramid to the renal capsule | back 11
|
front 12 ________________ is the area which contains the renal pyramids. | back 12 Medulla |
front 13
| back 13
|
front 14 __________________ are the triangular-shaped structures in the medulla which appear _______ due to the presence of collecting ducts and blood vessels. | back 14
|
front 15 _____ __________ is the tip of the pyramid; the collecting ducts opening is located here. | back 15
|
front 16 _______ __________ are long portions of the cortex between the pyramids, located in the medullar area | back 16
|
front 17 ____________ are cup-like extensions of the renal pelvis which encompass each of the renal papillae. | back 17 Calyxes |
front 18 These last areas or structures form part of the __________________ , and are here listed again:
| back 18 Renal Medulla |
front 19 _______________ are the functional portion of the kidneys which contains the nephrons (cortex and renal pyramids) | back 19 Parenchyma |
front 20 Which is the functional UNIT of the kidney | back 20  The Nephrons |
front 21 A nephron functions are: | back 21
|
front 22 Filtration takes place in the _____________ and processes a cell-free and protein-free __________. | back 22
|
front 23 Reabsorption (reclaims what the body needs to keep) is the process of selectively moving substances from the filtrate back into the _________. It takes place in the renal ___________ and collecting __________. Reclaims almost everything from the Filtrate: | back 23
|
front 24 What happens with what is not reabsorbed: | back 24 Becomes URINE |
front 25 Secretion is the process of selectively moving substances from the ___________ into the ______________. It also takes place in the renal ___________ and collecting __________. | back 25
|
front 26 Nephrons consist of two portions: | back 26
|
front 27 Renal Corpuscle consists of | back 27
|
front 28 Renal Tubule consists of... | back 28
|
front 29 What it the other name for Loop of Henle: | back 29 Loop of Nephron |
front 30
| back 30
|
front 31
| back 31
|
front 32
| back 32
|
front 33 The walls of __________ ____________ tubule are formed by cuboidal epithelial cells with dense microvilli. Just as the intestine, this brush border increases the surface area and capacity for REABSORBING water and solutes from the filtrate and secreting substances into it. | back 33
|
front 34 The U-shape __________ loop, also known as The Loop of ________, has _________ and ___________ limbs. Cells have microvilli also (true or false) | back 34
|
front 35
| back 35 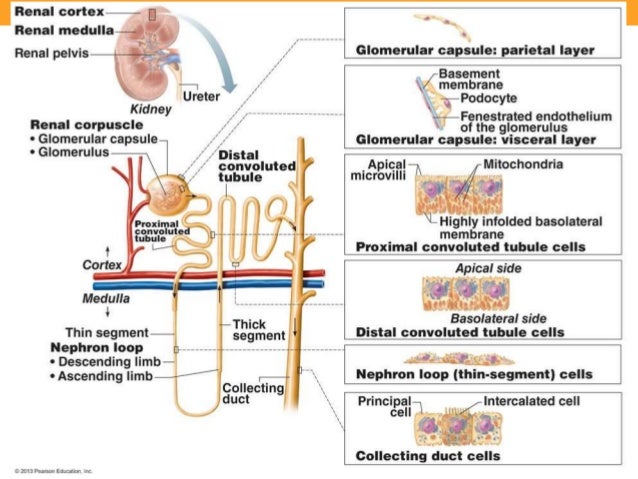
|
front 36 _________ ______________ Tubule is made of ____________ cells, almost entirely lack of microvilli. | back 36
|
front 37 ___________ duct is a duct where many distal convoluted tubules join and deposit their __________ secretion. | back 37
|
front 38 ____________ duct is the end of the collecting duct as it terminates at the end of the renal papilla | back 38
|
front 39 Nephrons are generally divided into 2 major groups, or there are 2 type of Nephrons : | back 39
|
front 40 Cortical Nephron, account _____% of the nephrons. They have their glomerulus in the portion of the _______ and its loop of Henle penetrates into the _________. | back 40
|
front 41 Juxtamedullary Nephrone originate its glomerulus deep in the ________ and its loop of Henle penetrates the ________ almost to the renal __________. | back 41
|
front 42 HISTOLOGY OF THE NEPHRON 1- The endothelial is make of ________ ___________ epithelium which comprises the glomerural ________ ______. This capillary has ___________ or pores ___ or ____ microns in the diameter. These pores are too _______ for blood cells to pass through. | back 42
|
front 43 2- ____________________ is an extracellular fibours glycoprotein matrix which acts as a ______________ membrane. It functions to ________ _____ large molecules from leaving the plasma. | back 43
|
front 44 3- _____________ _________ is formed by the protocytes of the visceral layer of the ____________ ____________.
| back 44
|
front 45
| back 45
|
front 46 Blood Pathway through Kidneys
| back 46
|
front 47 6- The __________ branch off and enter the glomerular capsule to form the ... 7- ________________ where filtration happens 8- The efferent arteriole now leaves the _____________ and branches into a capillary network called the _____________ ____________ | back 47 6-Afferent arteries 7-Glomerulus 8-Glomerulus
|
front 48 9- Peritubular Capillaries and Vasa Recta unite to form the ___________ ___________ vein. 10- then the _____________ veins 11- Interlobal veins 12- Segmental Vens 13- Renal Veins | back 48 9- Cortical Radiate Vein 10- Arcuate veins 11- Interlobal veins 12- segmental veins 13-Renal Veins |
front 49 In the _______________ apparatus the fluid in the DCT are thought to play a role in controlling blood flow through the afferent arterioles (__________) | back 49
|
front 50
| back 50 _of_a_nephron_p_9681318457485220.jpg)
|
front 51
| back 51
|
front 52 Physiology of the Nephrons Nephrons functions are 3: | back 52
|
front 53 The main 3 processes require for Urine Formation are: | back 53
|
front 54
| back 54
|
front 55
| back 55
|
front 56
| back 56
|
front 57 To find the levels of filtration according to hydrostatic pressure, we need to consider these different types of Pressures: | back 57
|
front 58 NFP stands for | back 58 Net (effective) Filtration Pressure |
front 59 NFP tells the ____________ which causes filtrate to be formed (to leave the capillary and enter into the glomerular space). | back 59 Pressure |
front 60 CHP stands for | back 60 Capsular Hydrostatic Pressure |
front 61 CHP is the __________ or ___________ which a fluid under pressure exerts on the walls of a container (capsular wall) | back 61 force or resistance |
front 62 BOP stands for | back 62 Blood Colloidal Osmotic Pressure |
front 63 The pressure which develops from water movement into a contained solution. It walways develops in the solution with the higher concentration of solutes. | back 63 Blood Colloidal Osmotic Pressure |
front 64 Since blood has more proteins than the filtrate. Then, water moves _________ the filtrate and _________ the blood vessels. | back 64
|
front 65 GHP stands for | back 65 Glomerular Hydrostatic Pressure |
front 66 The blood pressure in the glomerulus. This pressure is pushing _________ the walls of the capsule and the filtrate which is already there. | back 66
|
front 67
| back 67
|
front 68 Tm stands for ____________ | back 68 Tubular Max |
front 69
| back 69
|
front 70 Keeping the plasma proteins in the capillaries maintains the________ ___________, which prevents the _______ of all its water to the capsular space. | back 70 Colloid osmotic (oncotic) Pressure. |
front 71 The presence of proteins or ______ _______ cells indicate | back 71
|
front 72 ___________ is only partially resorbed, and is derived from the normal breakdowns of amino acids. | back 72 Urea |
front 73 Water accounts for about ____% of urine volume; the remaining ___% consists of solutes.
| back 73
|
front 74
| back 74
|
front 75
| back 75
|
front 76
| back 76
|
front 77
| back 77
|
front 78 ________ follows since the Proximal C.T. are always permeable to it. | back 78 H2O |
front 79
| back 79
|
front 80
| back 80
|
front 81
| back 81
|
front 82 About _____ - ______ ml (volume) are eliminated per day and is influenced by: | back 82
|
front 83
| back 83 K+, H+, ammonium ions, urea, creatinine, penicillin, etc. Selectively |
front 84 Tubular secretion functions to ______ the body of certain materials as well as help to control the ____________ | back 84
|
front 85 The body tries to maintain a pH of ___________ | back 85 7.35 to 7.45 |
front 86 Normal urine has a pH of | back 86 6 pH |
front 87 To raise the blood in renal tubules secrete _____ ions and _____________ into the filtrate. | back 87
|
front 88 Which is the main site of secretion: | back 88 PCT |
front 89 Urine eventually excreted contain both __________ and _____________ substances. With one major exception. | back 89
|
front 90 ____________ ________________ is a process which allows the kidneys to secrete hypertonic urine or hypotonic urine. | back 90 Countercurrent Multiplier Mechanism |
front 91 ____________ deliver urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. | back 91 Ureters |
front 92
| back 92
|
front 93 In a cross-sectional view of ureters we find different layers of: | back 93
|
front 94 Mucosa in the ureter is formed of: | back 94
|
front 95 Muscularis is formed of | back 95
|
front 96 Fibrous | back 96 which holds tu ureters with Adventitia |
front 97 ______________ is a hollow muscular organ held in place by the peritoneum. | back 97 Urinary bladder |
front 98 Urinary bladder consists of 4 coats | back 98
|
front 99 1- Mucosa is composed of ___________ ______________, contains folds called ______________ which allow the urinary bladder to _____________ as it fills with urine. | back 99
|
front 100 2- Submucosa is a ____ layer which holds the _______ layer to the ______ coat. | back 100
|
front 101 3- Muscularis or _________ ________ consists of __ layers of ________:
| back 101
|
front 102 4- Peritoneum is the external ___________ covering | back 102 Serous |
front 103 ________________ is the expulsion of urine from the urinary bladder; urination; voiding. | back 103 Micturition |
front 104 The average urinary bladder capacity is _______ | back 104 400 to 800 ml |
front 105 _______________ a smooth mucosal layer; the ureters drain into the urinary bladder at the base corners of this layer (at top) | back 105 Trigone |
front 106 ________________ is a tube extending from the urinary bladder to the external urethral orifice through which urine is expelled. | back 106 Urethra |
front 107 _____________ is only partially resorbed, and is derived from the normal breakdowns of amino acids. | back 107 Urea |
front 108 _________ occurs when toxic levels of urea in the blood due to the kidneys not functioning correctly | back 108 Uremia |
front 109 ____________ is an infection in renal pelvis and calyxes | back 109 Pyelitis |
front 110 _____________ is an infection or inflammation the entire kidney | back 110 Pyelonephritis |
front 111 ______ ________ when rapid weight loss removes fat causing the kidney to fall to a lower position | back 111 Renal Ptosis |
front 112 ________________ is the back up of urine from ureter obstruction. | back 112 Hydronephrosis |