front 1
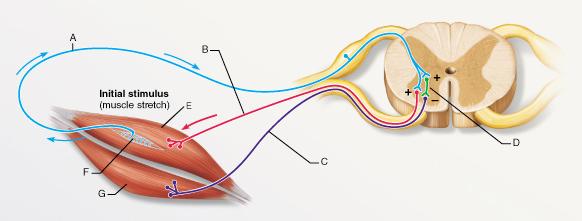
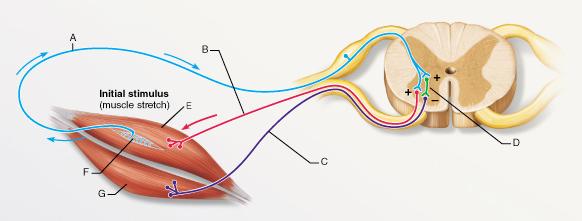
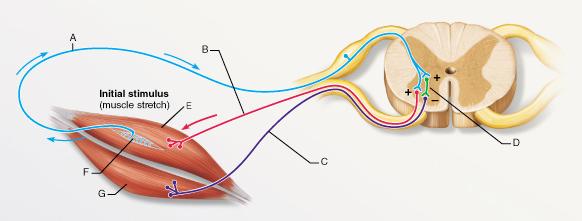
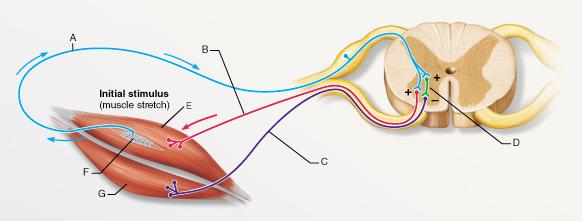
What reaction would occur if the muscle labeled E were suddenly
pulled longer?
- the relaxation of muscle
E
- the relaxation of the both muscles E and G
- the
contraction of muscle E
- the contraction of the both muscles
E and G
| back 1 - the contraction of muscle
E
- A sudden stretch in a muscle leads to the contraction of
the stretched muscle (E) and the relaxation of the antagonistic
muscle (G).
|
front 2
Which cranial nerve transmits information about audition?
- optic
- abducens
- vestibulocochlear
- vagus
| back 2 - vestibulocochlear
- The
vestibular branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve transmits afferent
impulses for the sense of equilibrium. The cochlear branch transmits
afferent impulses for the sense of hearing.
|
front 3
Which cranial nerve innervates most of the visceral organs?
- accessory
- hypoglossal
- vagus
- abducens
| back 3 - vagus
- The vagus nerve
has many targets in the thoracic and abdominal cavities and
innervates many of the visceral organs.
|
front 4
Which of the following carries no sensory information?
- trigeminal nerve
- vestibulocochlear nerve
- hypoglossal nerve
- optic nerve
| back 4 - hypoglossal nerve
- The
hypoglossal nerve carries motor commands to the tongue.
|
| |
front 6
The knee-jerk reflex is an example of a __________.
- tendon reflex
- flexor
reflex
- stretch reflex
- superficial reflex
| back 6 - stretch reflex
- The
most familiar clinical example of a stretch reflex is the knee-jerk
reflex. The overall goal of a stretch reflex is to maintain a
muscle's length and in turn maintain body position. For example, the
knee-jerk reflex, during which the knee extensors contract in
response to being stretched, helps keep your knees from buckling
when you are standing upright.
|
front 7
Which pair below is incorrect?
- cranial nerve VI: eye
movement
- cranial nerve III: oculomotor nerve
- cranial
nerve III: pupillary constriction
- optic nerve: sensory
- cranial Nerve IV: sensory
| back 7 - cranial Nerve IV: sensory
- The trochlear nerve is a motor nerve that innervates the
superior oblique of the eye.
|
front 8
Which reflex has a contralateral component?
- stretch
- crossed-extensor
- tendon
- flexor
| back 8 - crossed-extensor
- The
crossed-extensor reflex activates opposing actions in the opposite
limb.
|
front 9
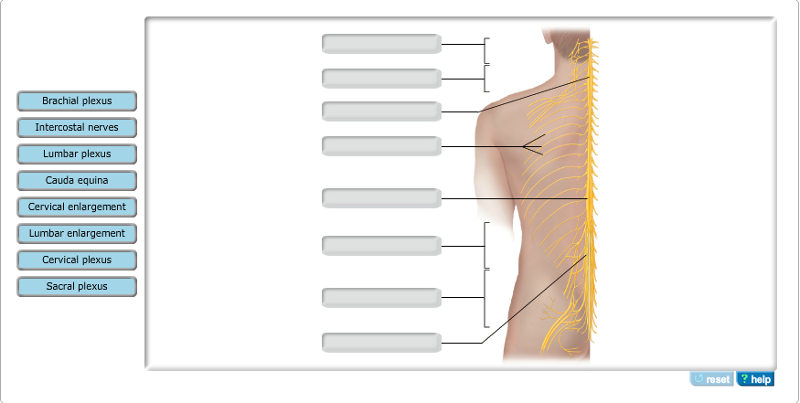
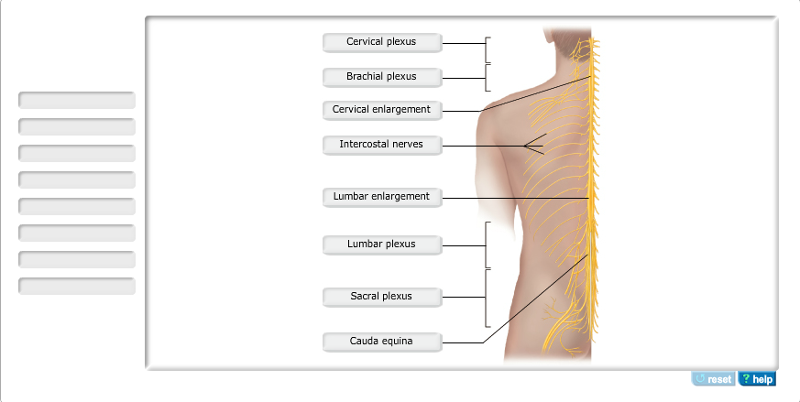
The phrenic nerve is a branch from the __________.
- brachial plexus
- thoracic spinal cord
- vagus nerve
- cervical
plexus
| back 9 - cervical plexus
- The
phrenic nerve, which arises from the cervical plexus, supplies both
motor and sensory fibers to the diaphragm, the main breathing
muscle.
|
front 10
What is the type of reflex represented by the pathway that
includes A, D, and C?
- reciprocal inhibition
- stretch reflex
- cross-extension reflex
- flexor
reflex
| back 10 - reciprocal inhibition
- When a muscle is contracted, its antagonist (“reciprocal”) is
reflexively relaxed.
|
front 11
The sensory division of the PNS is also known as the efferent division.
| back 11 - False
- All of the
sensory information is considered afferent, or flowing toward the
CNS. Efferent means "from the CNS."
|
front 12
__________ are receptors that can respond to painful stimuli.
- Photoreceptors
- Nociceptors
- Mechanoreceptors
- Chemoreceptors
| back 12 - Nociceptors
- Nociceptors respond to potentially damaging stimuli that result
in pain.
|
| |
| |
front 15
What is the specific function of the structure labeled F?
- increasing tension of the
surrounding muscle
- increasing tension of the antagonistic
muscle
- determination of muscle tension
- determination
of muscle length
| back 15 - increasing tension of the
antagonistic muscle
|
front 16
In carpal tunnel syndrome, the __________ is compressed.
- axillary nerve
- median nerve
- musculocutaneous nerve
- radial
nerve
| back 16 - median nerve
- The
median nerve descends through the arm and forearm before passing
through the wrist. Compression of this nerve in the anterior wrist
causes carpal tunnel syndrome.
|
front 17
The synapse between which of the following two neurons is a part
of a monosynaptic reflex arc?
- A and D
- A and B
- B and C
- A and C
| back 17 - A and B
- A
monosynaptic reflex arc includes a synapse between sensory and motor
neurons without the involvement of an interneuron.
|
front 18
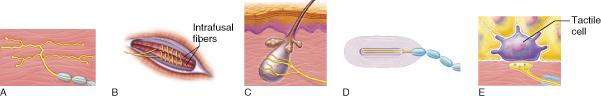
Which of the receptor types pictured functions exclusively as a proprioceptor?
- B
- C
- D
- All of the listed responses are correct.
| back 18 - B
- Proprioceptors are
sensitive to stimuli associated with body movements. The muscle
spindle shown in B is responsive to muscle stretch.
|
front 19
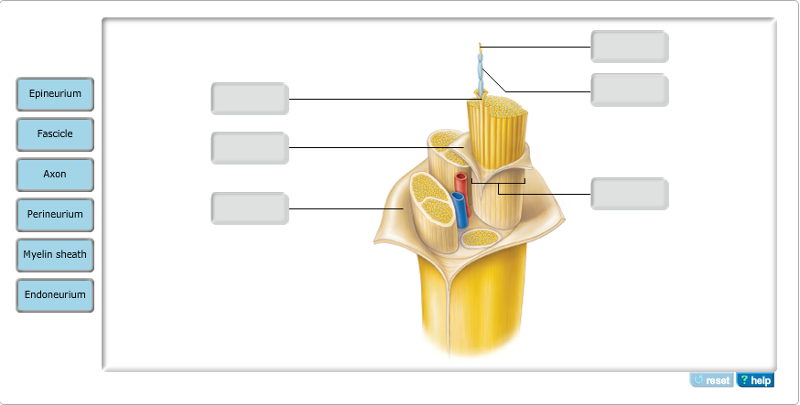
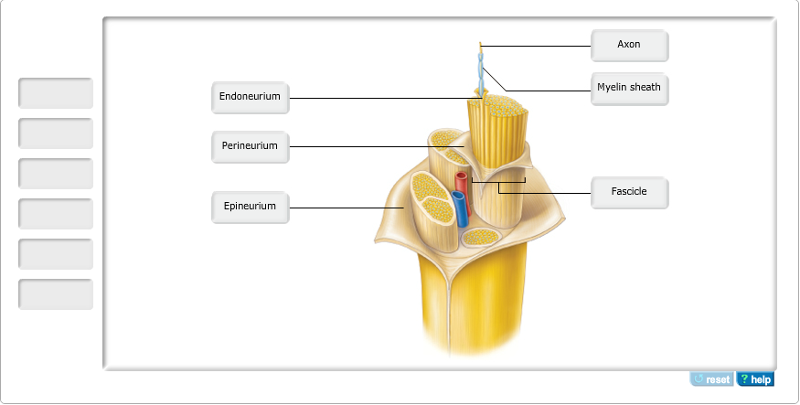
Which of the following is NOT correct concerning nerves?
- Nerves do not contain cell
bodies.
- Nerves are analogous to tracts in the CNS.
- Nerves are covered by an outer sheath called the
epineurium.
- Nerves are collection of axons of either sensory
or motor neurons but not both.
| back 19 - Nerves are collection of axons
of either sensory or motor neurons but not both.
- Nerves can
be mixed collections of both sensory and motor axons.
|
front 20
Which of the following cranial nerves carries only motor information?
- optic
- trigeminal
- olfactory
- abducens
| back 20 - abducens
- The abducens
carries efferent (motor) signals to the extrinsic eye muscle that
abducts the eye (turns it laterally).
|