Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
A&P Ch21
front 1 In which region are the palatine tonsils found? | back 1 oropharynx |
front 2 What type of epithelial tissue forms the walls of the alveoli? | back 2 simple squamous epithelium |
front 3 Which of the following is NOT a physical factor that influences pulmonary ventilation? | back 3 partial pressure of oxygen in the air |
front 4 What is the amount of air that can be exhaled with the greatest possible exhalation after the deepest inhalation called? | back 4 vital capacity |
front 5 During inhalation, | back 5 the diaphragm and rib muscles contract. |
front 6 From which structures do oxygen molecules move from the lungs to the blood? | back 6 Alveoli |
front 7 Which statement is correct? | back 7 In the blood, oxygen is bound to hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells. |
front 8 After blood becomes oxygenated, | back 8 it returns to the heart, and is then pumped to body cells. |
front 9 Hemoglobin | back 9 is a protein that can bind four molecules of oxygen. |
front 10 What is ventilation-perfusion coupling? | back 10 matching the amount of gas reaching the alveoli to the blood flow in pulmonary capillaries |
front 11 Which of the following is the primary factor in oxygen attachment to, or release from, hemoglobin? | back 11 partial pressure of oxygen |
front 12 What is the most powerful respiratory stimulant in a healthy person? | back 12 arterial blood carbon dioxide level |
front 13 Patients with rhinitis often have "watery eyes" because ______. | back 13 the infection has caused inflammation of the nasolacrimal ducts |
front 14 In pneumothorax, the lung collapses because ______. | back 14 intrapleural pressure is higher than intrapulmonary pressure |
front 15 Which of the following processes are unique to the respiratory system? | back 15 pulmonary ventilation and external respiration |
front 16 Which of the following features characterizes the right lung? | back 16 presence of a superior, middle, and inferior lobe |
front 17 Which blood vessels supply oxygenated systemic blood to the lung tissue? | back 17 bronchial arteries |
front 18 The indentation on the medial surface of each lung through which pulmonary and systemic blood vessels, bronchi, lymphatic vessels, and nerves enter and leave is called the ___________. | back 18 hilum |
front 19 Which of the following is NOT a function of the nasal conchae? | back 19 routing air and food into proper channels |
front 20 What part of the larynx covers the laryngeal inlet during swallowing to keep food out of the lower respiratory passages? | back 20 epiglottis |
front 21 During the Valsalva's maneuver, what part of the larynx closes to increase intra-abdominal pressure, such as to help with defecation? | back 21 glottis |
front 22 Which cartilage belonging to the larynx anchors the vocal cords? | back 22 arytenoid cartilages |
front 23 Which of the following is NOT a function of the larynx? | back 23 serving as part of the respiratory zone |
front 24 Since mucus-producing cells and cilia are sparse in the bronchioles and alveoli, how does the body remove microorganisms that make their way into the respiratory zone? | back 24 alveolar macrophages crawl freely along internal alveolar surfaces |
front 25 Where does gas exchange occur in the respiratory system? | back 25 alveoli |
front 26 Which of the following represents all of the processes involved in respiration in the correct order? | back 26 pulmonary ventilation; external respiration; transport of respiratory gases; internal respiration; |
front 27 pulmonary ventilation; external respiration; transport of respiratory gases; internal respiration; | back 27 to destroy pathogens entering the nasopharynx |
front 28 Which of the following respiratory structures is more commonly known as the "throat"? | back 28 pharynx |
front 29 Which of the following is NOT a function of the larynx? | back 29 to assist in taste sensation |
front 30 The __________ is also known as the "guardian of the airways." | back 30 epiglottis |
front 31 The smallest subdivisions of the lung visible with the naked eye are the __________, which appear to be connected by black carbon in smokers. | back 31 lobules |
front 32 Systemic venous blood that is to be oxygenated in the lungs is delivered by the __________, and the __________ provide oxygenated systemic blood to lung tissue. | back 32 pulmonary arteries; bronchial arteries |
front 33 __________, the difference between the intrapulmonary and intrapleural pressures, prevents the lungs from collapsing. | back 33 Transpulmonary pressure |
front 34 Quiet inspiration is __________, and quiet expiration is __________. | back 34 an active process; a passive process |
front 35 The adenoids normally destroy pathogens because they contain ______. | back 35 lymphocytes |
front 36 The tissue(s) and/or cells that may be affected during laryngitis ______. | back 36 is epithelial tissue is connective tissue are ciliated cells All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 37 Smoking inhibits cilia by inhibiting the movements of ______. | back 37 dynein molecules |
front 38 Tracheal obstruction by a large piece of food typically involves obstruction of the ______. | back 38 larynx |
front 39 During pleurisy, the inflamed parietal pleura of one lung rubs against the inflamed ______. | back 39 visceral pleura of the same lung |
front 40 Which parts of the respiratory system function as the main sites of gas exchange? | back 40 alveoli |
front 41 Jane had been suffering through a severe cold and was complaining of a frontal headache and a dull, aching pain at the side of her face. What regions are likely to become sites of secondary infection following nasal infection? | back 41 The paranasal sinuses |
front 42 The main site of gas exchange is the ________. | back 42 alveoli |
front 43 The loudness of a person's voice depends on the ________. | back 43 force with which air rushes across the vocal folds |
front 44 The walls of the alveoli are composed of two types of cells, type I and type II. The function of type II is to ________. | back 44 secrete surfactant |
front 45 Select the correct statement about the pharynx. | back 45 The auditory tube drains into the nasopharynx. |
front 46 The larynx contains ________. | back 46 the thyroid cartilage |
front 47 Which of the choices below is not a role of the pleura? | back 47 aids in blood flow to and from the heart because the heart sits between the lungs |
front 48 Which of the following provide the greatest surface area for gas exchange? | back 48 alveoli |
front 49 The respiratory membrane is a combination of ________. | back 49 alveolar and capillary walls and their fused basement membranes |
front 50 The nose serves all the following functions except ________. | back 50 as the direct initiator of the cough reflex |
front 51 The factors responsible for holding the lungs to the thorax wall are ________. | back 51 surface tension from pleural fluid and negative pressure in the pleural cavity |
front 52 Most inspired particles such as dust fail to reach the lungs because of the ________. | back 52 ciliated mucous lining in the nose |
front 53 Which of the following maintains the patency (openness) of the trachea? | back 53 C-shaped cartilage rings |
front 54 Which of the following descriptions accurately describes Boyle’s law? | back 54 The pressure of gas in your lungs is inversely proportional to the volume in your lungs. |
front 55 Which muscles, when contracted, would increase the volume of air in the thoracic cavity? | back 55 diaphragm and external intercostals |
front 56 Which pressure is the result of the natural tendency of the lungs to decrease their size (because of elasticity) and the opposing tendency of the thoracic wall to pull outward and enlarge the lungs? | back 56 intrapleural pressure |
front 57 During an allergic reaction, which of the following would aid respiration? | back 57 epinephrine |
front 58 If the transpulmonary pressure equals zero, what will happen to the lung? | back 58 lungs will collapse |
front 59 Which of the following pressures rises and falls with the phases of breathing, but eventually equalizes with the atmospheric pressure? | back 59 intrapulmonary pressure |
front 60 Which of the following pressures must remain negative to prevent lung collapse? | back 60 intrapleural pressure |
front 61 Calculate the transpulmonary pressure if atmospheric pressure is 755 mm Hg. | back 61 4 mm Hg |
front 62 Which of the following gives the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas? | back 62 Boyle's law |
front 63 Which of the following pressure relationships best illustrates when inspiration will occur? | back 63 Ppul < Patm |
front 64 Which muscles are activated during normal quiet inspiration? | back 64 diaphragm and external intercostal muscles |
front 65 What is the volume of the total amount of exchangeable air for a healthy, young adult male? | back 65 4800 ml |
front 66 Which volumes are combined to provide the inspiratory capacity? | back 66 tidal volume (TV) + inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) |
front 67 What is the tidal volume of an average adult male? | back 67 500 ml |
front 68 Which form of hypoxia reflects poor O2 delivery resulting from too few RBCs or from RBCs that contain abnormal or too little hemoglobin? | back 68 anemic hypoxia |
front 69 Which form of CO2 transport accounts for the least amount of CO2 transported in blood? | back 69 dissolved in plasma |
front 70 If the compliance of the thoracic wall is decreased, ______. | back 70 the intrapleural pressure would not decrease normally during inhalation |
front 71 Which of the following would NOT be involved in causing bronchiolar constriction during an asthma attack? | back 71 adrenal medulla |
front 72 In babies born prematurely, pulmonary surfactant may not be present in adequate amounts ______. | back 72 due to insufficient exocytosis in the type II alveolar cells |
front 73 What is the most immediate driving force behind pulmonary ventilation? | back 73 intrapulmonary pressure change |
front 74 Surfactant helps to prevent the alveoli from collapsing by ________. | back 74 interfering with the cohesiveness of water molecules, thereby reducing the surface tension of alveolar fluid |
front 75 Which of the choices below describes the forces that act to pull the lungs away from the thorax wall and thus collapse the lungs? | back 75 the natural tendency for the lungs to recoil and the surface tension of the alveolar fluid |
front 76 The major nonelastic source of resistance to air flow in the respiratory passageways is ________. | back 76 friction |
front 77 Which of the following determines lung compliance? | back 77 alveolar surface tension |
front 78 Tidal volume is air ________. | back 78 exchanged during normal breathing |
front 79 The lung volume that represents the total volume of exchangeable air is the ________. | back 79 vital capacity |
front 80 The amount of air that can be inspired above the tidal volume is called ________. | back 80 inspiratory reserve |
front 81 Which respiratory-associated muscles would contract if you were to blow up a balloon? | back 81 internal intercostals and abdominal muscles would contract |
front 82 Complete the following statement using the choices below. Air moves out of the lungs when the pressure inside the lungs is | back 82 greater than the pressure in the atmosphere. |
front 83 Inspiratory capacity is ________. | back 83 the total amount of air that can be inspired after a tidal expiration |
front 84 Unlike inspiration, expiration is a passive act because no muscular contractions are involved. Expiration, however, depends on two factors. Which of the choices below lists those two factors? | back 84 the recoil of elastic fibers that were stretched during inspiration and the inward pull of surface tension due to the film of alveolar fluid |
front 85 Which of the following is not possible? | back 85 Pressure gradient equals gas flow over resistance. |
front 86 Select the correct statement about the physical factors influencing pulmonary ventilation. | back 86 As alveolar surface tension increases, additional muscle action will be required. |
front 87 Intrapulmonary pressure is the ________. | back 87 pressure within the alveoli of the lungs |
front 88 The relationship between gas pressure and gas volume is described by ________. | back 88 Boyle's law |
front 89 Which of the following arterial blood levels is the most powerful respiratory stimulant? | back 89 rising CO2 levels |
front 90 Which of the following structures would be the LEAST vulnerable to damage caused by oxygen toxicity? | back 90 costal cartilages |
front 91 During pneumonia, the lungs become "waterlogged"; this means that within the alveoli there is an abnormal accumulation of ______. | back 91 interstitial fluid |
front 92 Emphysema can result in an ______. | back 92 increased level of carbaminohemoglobin increased level of deoxyhemoglobin increased likelihood of the skin of Caucasians developing a slightly blue coloration All of the listed responses are correct. |
front 93 For gas exchange to be efficient, the respiratory membrane must be ________. | back 93 0.5 to 1 micrometer thick |
front 94 The local matching of blood flow with ventilation is ________. | back 94 ventilation-perfusion coupling |
front 95 Which of the following is not an event necessary to supply the body with O2 and dispose of CO2? | back 95 blood pH adjustment |
front 96 Which of the choices below determines the direction of respiratory gas movement? | back 96 partial pressure gradient |
front 97 Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in the lungs and through all cell membranes by ________. | back 97 diffusion |
front 98 The statement, "in a mixture of gases, the total pressure is the sum of the individual partial pressures of gases in the mixture" paraphrases ________. | back 98 Dalton's law |
front 99 Oxygen is unloaded where it is most needed when blood pH drops, this is a phenomenon known as ___________. | back 99 the Bohr effect |
front 100 What is the most common method of carbon dioxide transport? | back 100 as bicarbonate ions in the plasma |
front 101 Which of the following qualifies as a fully saturated hemoglobin molecule? | back 101 hemoglobin is transporting four oxygen molecules |
front 102 Hypoxia can be caused by ______. | back 102 hyposecretion of erythropoietin |
front 103 What is the primary form in which carbon dioxide is carried in blood? | back 103 as a bicarbonate ion in plasma |
front 104 With the Bohr effect, more oxygen is released because a(n) ________. | back 104 decrease in pH (acidosis) weakens the hemoglobin-oxygen bond |
front 105 In the plasma, the quantity of oxygen in solution is ________. | back 105 only about 1.5% of the oxygen carried in blood |
front 106 Which of the following counteracts the movement of bicarbonate ions from the RBC? | back 106 chloride shifting |
front 107 Possible causes of hypoxia include ________. | back 107 too little oxygen in the atmosphere |
front 108 Which statement about CO2 is incorrect? | back 108 More CO2 dissolves in the blood plasma than is carried in the RBCs. |
front 109 How is the bulk of carbon dioxide carried in blood? | back 109 as the bicarbonate ion in the plasma after first entering the red blood cells |
front 110 Which of the following incorrectly describes mechanisms of CO2 transport? | back 110 attached to the heme part of hemoglobin |
front 111 Which of the choices below is not a factor that promotes oxygen binding to and dissociation from hemoglobin? | back 111 number of red blood cells |
front 112 Select the correct statement about oxygen transport in blood: | back 112 A 50% oxygen saturation level of blood returning to the lungs might indicate an activity level higher than normal. |
front 113 Which of the following does not influence hemoglobin saturation? | back 113 nitric oxide |
front 114 What area in the brain sets the respiratory rhythm? | back 114 ventral respiratory group (VRG) |
front 115 Inspiratory neurons send information to the diaphragm via what nerve? | back 115 phrenic nerve |
front 116 What directly stimulates the central chemoreceptors, thus increasing respiration? | back 116 H+ (hydrogen ions) |
front 117 As a result of hyperventilation, what will happen to the partial pressures of CO2 (pCO2) and pH? | back 117 decreased pCO2 and increased pH |
front 118 Which receptors inhibit inspiration during hyperinflation of the lungs? | back 118 pulmonary stretch receptors |
front 119 What stimulates increased respiration at the beginning of exercise? | back 119 sensory input from receptors in joints, neural input from the motor cortex, and other factors |
front 120 A homeostatic control mechanism controls respiration. What acts as the effector(s) in this system? | back 120 respiratory muscles |
front 121 Which of the following initiates inspiration? | back 121 ventral respiratory group (VRG) |
front 122 Which of the following respiratory rates illustrates eupnea for an average, healthy adult at rest?` | back 122 15 breaths per minute |
front 123 Which of the following modifies and smoothes the respiratory pattern? | back 123 pontine respiratory centers |
front 124 Which of the following stimuli is the most powerful respiratory stimulant to increase respiration? | back 124 rising carbon dioxide levels |
front 125 Which of the following inhibits the respiration rate? | back 125 stimulation of stretch receptors in the lungs |
front 126 Which of the following conditions or scenarios increases the respiratory rate? | back 126 acidosis |
front 127 Hypocapnia causes ______. | back 127 hypoxia |
front 128 What determines the respiratory rhythm in the body? | back 128 medullary respiratory centers |
front 129 A patient was admitted to the hospital with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. His PO2 was 55 and PCO2 was 65. A new resident orders 54% oxygen via the venturi mask. One hour later, after the oxygen was placed, the nurse finds the patient with no respiration or pulse. She calls for a Code Blue and begins cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Why did the patient stop breathing? | back 129 Oxygen dilates pulmonary arterioles, increasing perfusion and worsening an already poor ventilation-perfusion mismatch. In addition, oxygen drives more CO2 off of hemoglobin, dumping it into alveoli from which it cannot be removed. |
front 130 How will the lungs compensate for an acute rise in the partial pressure of CO2 in arterial blood? | back 130 Respiratory rate will increase. |
front 131 The most powerful respiratory stimulus for breathing in a healthy person is ________. | back 131 increase of carbon dioxide |
front 132 Which of the following is not a stimulus for breathing? | back 132 rising blood pressure |
front 133 Respiratory control centers are located in the ________. | back 133 medulla and pons |
front 134 Factors that influence the rate and depth of breathing include ________. | back 134 voluntary cortical control |
front 135 Gas emboli may occur because a ________. | back 135 diver holds his breath upon ascent |
front 136 Which center is located in the pons? | back 136 pontine respirator group (PRG) |
front 137 Select the correct statement about the neural mechanisms of respiratory control. | back 137 The pons is thought to be instrumental in the smooth transition from inspiration to expiration. |
front 138 The erythrocyte count increases after a while when an individual goes from a low to a high altitude because the ________. | back 138 concentration of oxygen and/or total atmospheric pressure is lower at high altitudes |
front 139 Why is a patient with tuberculosis often noncompliant with treatment? | back 139 Due to the time length of treatment, the patient may stop taking the medication when they start to feel better. |
front 140 Which of the following is not a form of lung cancer? | back 140 Kaposi's sarcoma |
front 141 Which of the disorders below is characterized by destruction of the walls of the alveoli producing abnormally large air spaces that remain filled with air during exhalation? | back 141 emphysema |
front 142 The paired lungs occupy all of the thoracic cavity. | back 142 F |
front 143 Smoking diminishes ciliary action and eventually destroys the cilia. | back 143 T |
front 144 Tracheal obstruction is life threatening. | back 144 T |
front 145 The parietal pleura lines the thoracic wall. | back 145 T |
front 146 The olfactory mucosal lining of the nasal cavity contains the receptors for the sense of smell. | back 146 T |
front 147 Nasal conchae mainly work on inhalation to warm and moisten air. They serve minor functions for exhalation. | back 147 F |
front 148 The functions of the nasal conchae are to enhance the air turbulence in the cavity and to increase the mucosal surface area exposed to the air. | back 148 T |
front 149 The lungs are perfused by two circulations: the pulmonary and the bronchial. The pulmonary circulation is for oxygenation of blood. The bronchial circulation supplies blood to the lung structures (tissue). | back 149 T |
front 150 Valsalva's maneuver involves closing off the glottis (preventing expiration) while contracting the muscles of expiration, causing an increase in intra-abdominal pressure. | back 150 T |
front 151 The average individual has 500 ml of residual volume in his lungs. | back 151 F |
front 152 Atelectasis (lung collapse) renders the lung useless for ventilation. | back 152 T |
front 153 Under certain conditions, the vocal folds act as a sphincter that prevents air passage. | back 153 T |
front 154 Intrapleural pressure is normally about 4 mm Hg less than the pressure in the alveoli. | back 154 T |
front 155 During normal quiet breathing, approximately 750 ml of air moves into and out of the lungs with each breath. | back 155 F |
front 156 The alveolar ventilation rate is the best index of effective ventilation. | back 156 T |
front 157 The structures within the respiratory system's conducting zone include the trachea and the paranasal sinuses. | back 157 T |
front 158 Ventilation perfusion coupling means that more blood flows past functional alveoli than past nonfunctional alveoli. | back 158 T |
front 159 Dalton's law states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is the sum of the pressures exerted independently by each gas in the mixture. | back 159 T |
front 160 The alveoli are also known as alveolar sacs. | back 160 F |
front 161 Dalton's law of partial pressures states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is the sum of the pressures exerted independently by each gas in the mixture. | back 161 T |
front 162 The largest amount of carbon dioxide is transported in the bloodstream in the form of carbonic anhydrase. | back 162 F |
front 163 Increased temperature results in decreased O2 unloading from hemoglobin. | back 163 F |
front 164 As carbon dioxide enters systemic blood, it causes more oxygen to dissociate from hemoglobin (the Haldane effect), which in turn allows more CO2 to combine with hemoglobin and more bicarbonate ion to be generated (the Bohr effect). | back 164 F |
front 165 Oxygenated hemoglobin releases oxygen more readily when the pH is more basic. | back 165 F |
front 166 Changes in arterial pH can modify respiration rate and rhythm even when carbon dioxide and oxygen levels are normal. | back 166 T |
front 167 Dalton's law of partial pressures states that when a gas is in contact with a liquid, that gas will dissolve in the liquid in proportion to its partial pressure. | back 167 F |
front 168 The Hering-Breuer reflex is a potentially dangerous response that may cause overinflation of the lung. | back 168 F |
front 169 Strong emotions and pain acting through the limbic system activate sympathetic centers in the hypothalamus, thus modulating respiratory rate and depth by sending signals to the respiratory centers. | back 169 T |
front 170 Emphysema is distinguished by permanent shrinkage of the alveoli. | back 170 F |
front 171 Although lung cancer is difficult to cure, it is highly preventable. | back 171 T |
front 172 Labored breathing is termed dyspnea. | back 172 T |
front 173 In chronic bronchitis, mucus production is decreased and this leads to the inflammation and fibrosis of the mucosal lining of the bronchial tree. | back 173 F |
front 174 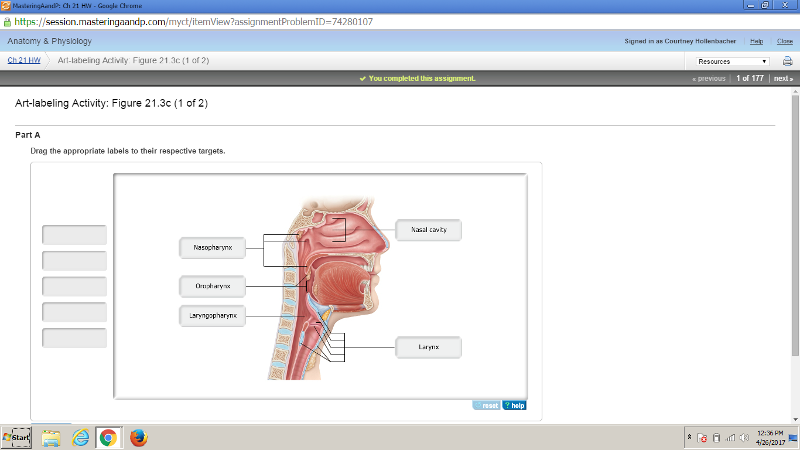 | back 174 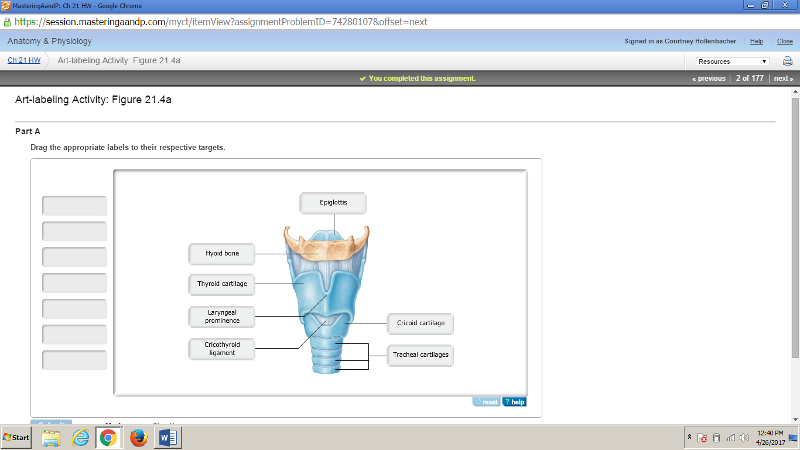 |
front 175 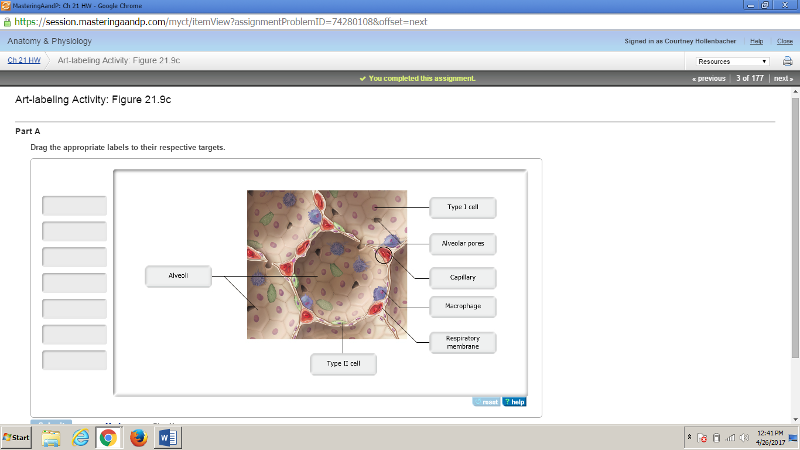 | back 175 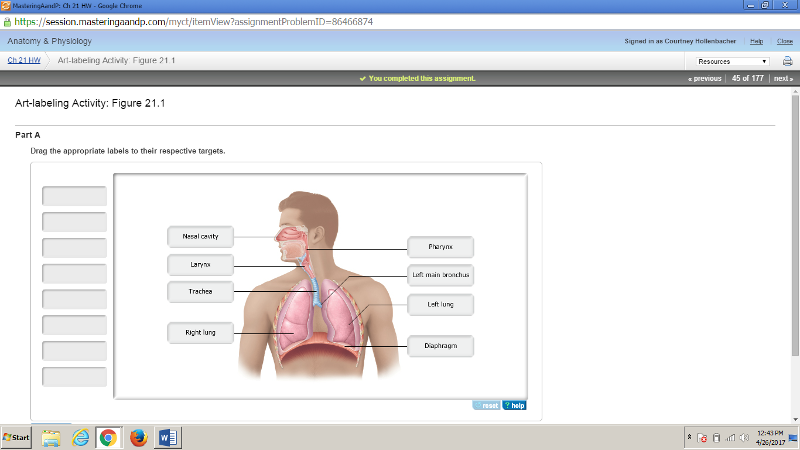 |
front 176 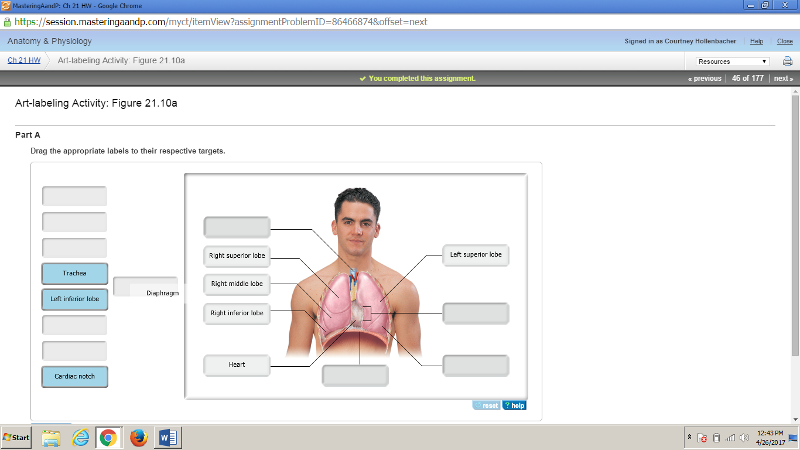 | back 176 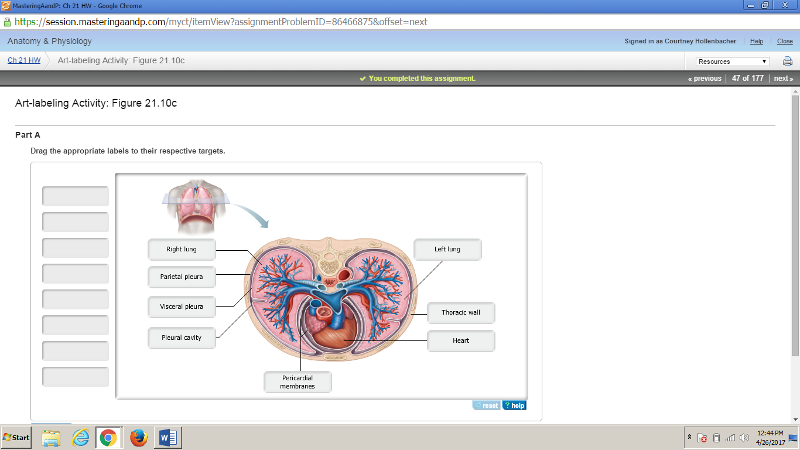 |
front 177 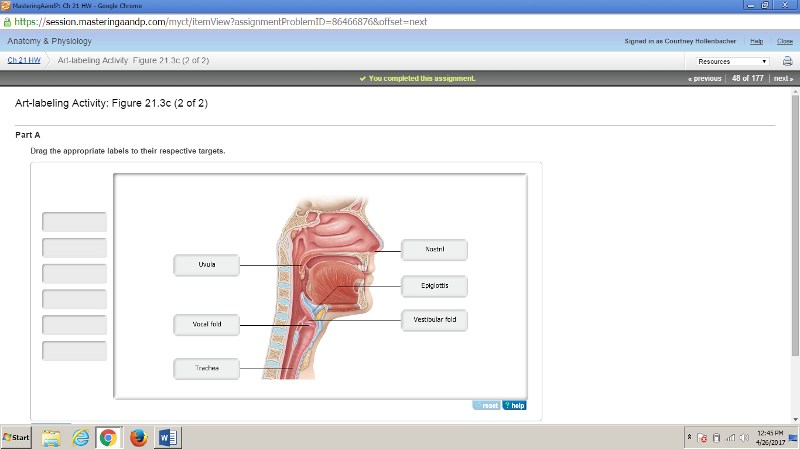 | back 177 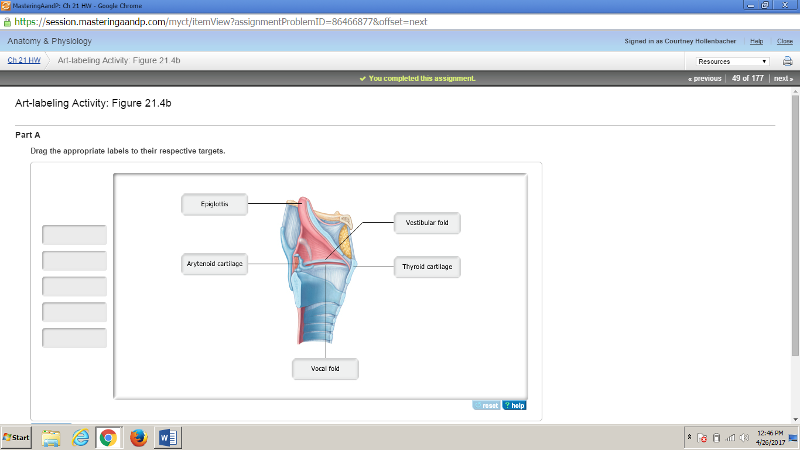 |
front 178 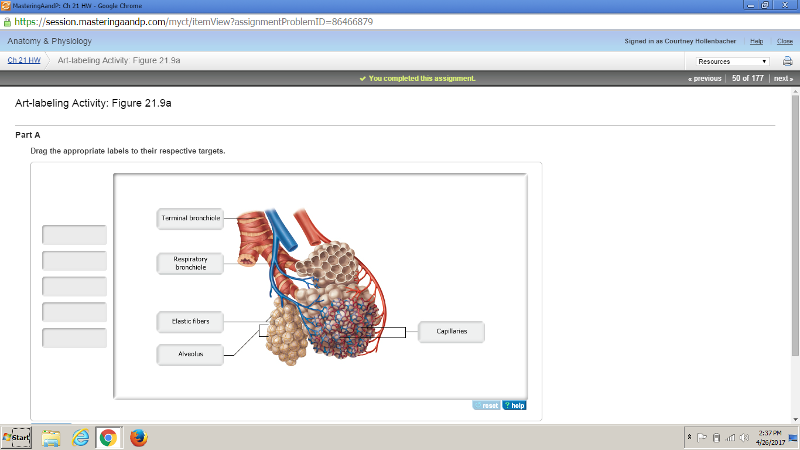 | back 178 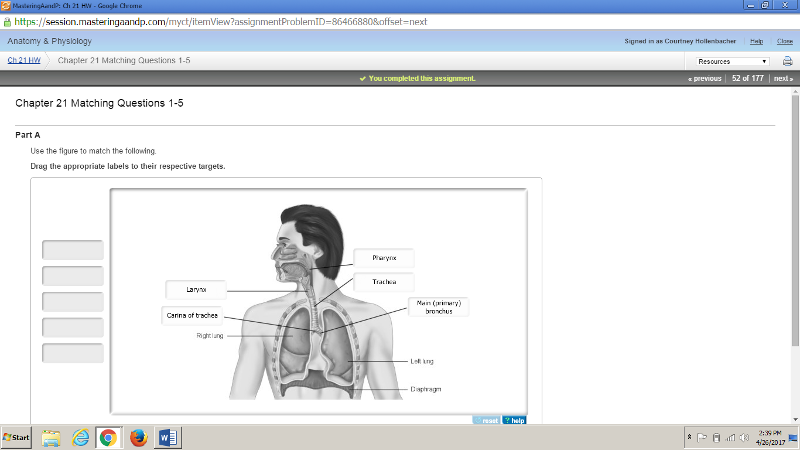 |
front 179 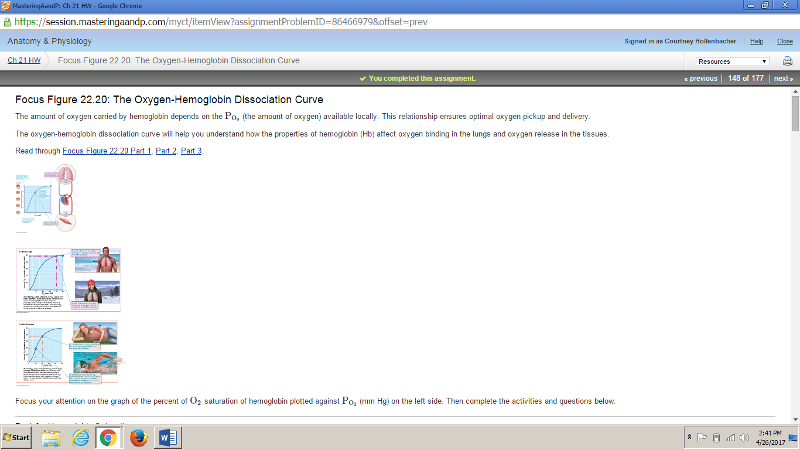 | back 179 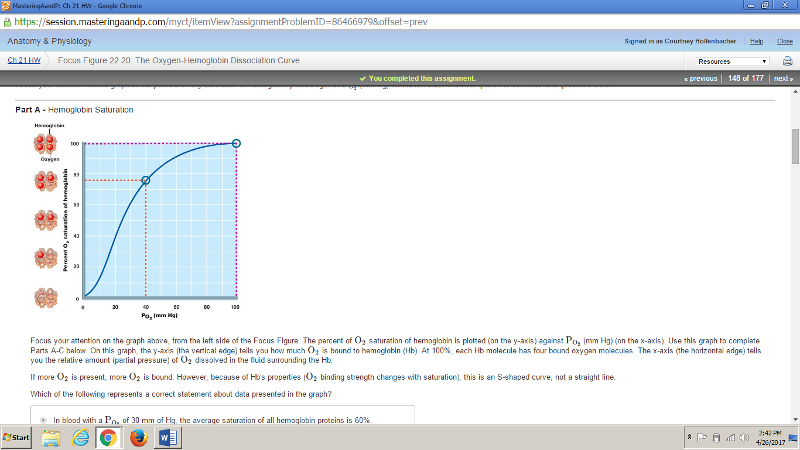 |
front 180 Using the same graph as in Part A above, what is the average number of oxygens bound to hemoglobin at a saturation of 50%? | back 180 2 |
front 181 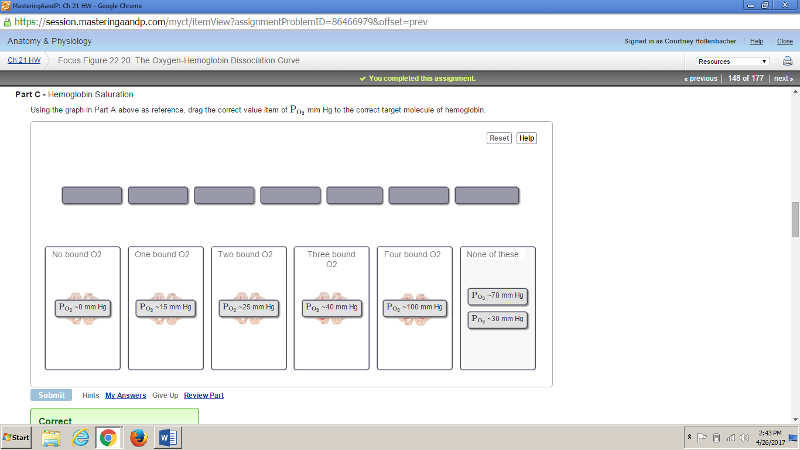 | back 181 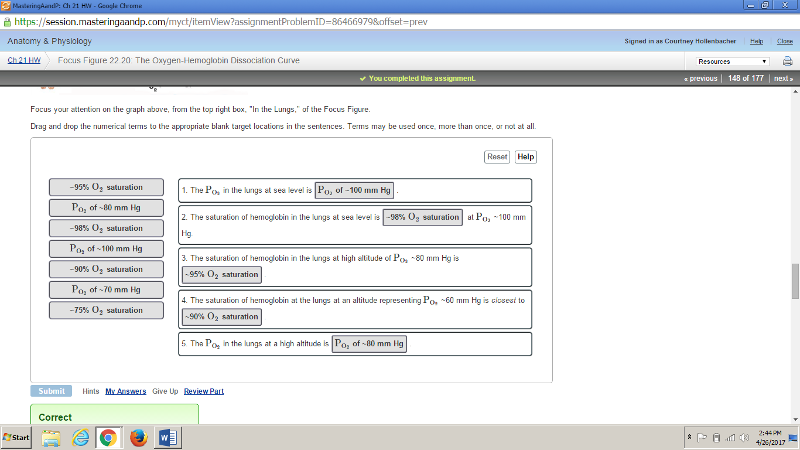 |
front 182 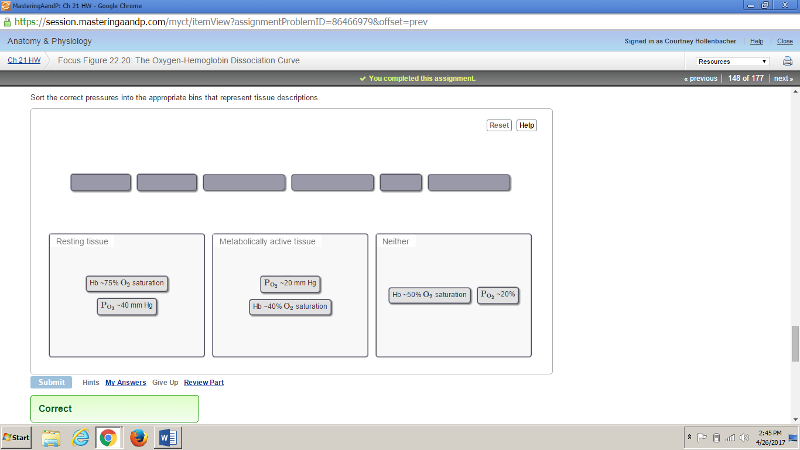 | back 182 no data |
front 183 A fireman breathes in air normally as he enters a building following an explosion and fire. He has a meter that predicts the | back 183 The fireman's hemoglobin saturation will be about one oxygen per hemoglobin, and he will require an external air tank. |