Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
Activity 3: Cranial Nerves and Identifying and Testing Cranial Nerves
front 1 The cranial nerves are part of which nervous system and not the other? | back 1 Part of the PNS and not the CNS |
front 2 How many pairs of cranial nerves are there? | back 2 12 pairs of cranial nerves |
front 3 The 12 pairs of the cranial nerves serve what 2 body parts? | back 3 1. Head 2. Neck |
front 4 What is unique about the vagus nerves (X) in regard to the other nerves? | back 4 It extends into the thoracic and abdominal cavities. |
front 5 What are the only 2 nerves that do not arise from the brain stem and do not pass through the foramina to reach their destination? | back 5 1. Olfactory nerves (I) 2. Optic nerves (II) |
front 6 What does OO, OTTAF-VGVAH stand for? | back 6 On Occasion, Our Trusty Truck Acts Funny-Very Good Vehicle AnyHow |
front 7 On Occasion, Our Trusty Truck Acts Funny-Very Good Vehicle AnyHow List the cranial nerves based on this mnemonic. | back 7 I. Olfactory nerve II. Optic nerve III. Oculomotor nerve IV. Trochlear nerve V. Trigeminal nerve VI. Abducens nerve VII. Facial nerve VIII. Vestibulocochlear nerve IX. Glossopharyngeal nerve X. Vagus nerve XI. Accessory nerve XII. Hypoglossal nerve |
front 8 Most cranial nerves are what kind of nerves? | back 8 Mixed nerves |
front 9 What are mixed nerves? | back 9 Containing both motor and sensory fibers |
front 10 What are 3 pairs of cranial nerves that are primarily or exclusively sensory in function? | back 10 1. Olfactory nerve (I) 2. Optic nerve (II) 3. Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) |
front 11 How come the olfactory nerves (I) are not visible on the brain model? | back 11 They consist of only short axons that run from the nasal mucossa through the cibriform foramina of the ethmoid bone. |
front 12 What from the olfactory nerves (I) is visible on the brain model, and what kind of points do they act as? | back 12 Olfactory bulbs which act as synapse points |
front 13 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Compare the cerebrum, brain stem, and cerebellum. Which of these structures is obviously much larger in the human brain? | back 13 The cerebrum |
front 14 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Axons of olfactory neurons run from the nasal mucosa through the cibriform foramina of the ethmoid bone to synapse with what? | back 14 Olfactory bulbs |
front 15 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain How does the size of the sheep's olfactory bulbs compare with those of humans? | back 15 Sheep=shorter and thicker (larger) |
front 16 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Is the sense of smell more important for protection and foraging in sheep or humans? | back 16 More important for sheeps |
front 17 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain The optic nerve (II) carries sensory impulses from which part of the eye? | back 17 Retina of the eye |
front 18 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Which nerve is involved in the sense of vision? | back 18 Optic nerve (II) |
front 19 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain What 2 structures protrude from the ventral aspect of the hypothalamus? (Hint: posterior to the optic chiasma) | back 19 1. Infundibulum (immediately posterior to the optic chiasma) 2. Mammillary body |
front 20 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain What is different with the sheep's mammillary body versus that of a human's? | back 20 The sheep's mammillary body is a single rounded eminence, whereas in humans, it is a double structure. |
front 21 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain What are cerebral peduncles? | back 21 Fiber tracts |
front 22 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Cerebral peduncles connect what 2 brain parts? | back 22 1. Cerebrum 2. Medulla oblongata |
front 23 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain The large oculomotor nerves (III) and trochlear nerves (IV) provide motor fibers to what muscles of what body part? | back 23 To extrinsic muscles of the eyeball. |
front 24 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain The pons and the medulla oblongata are composed primarily of what? | back 24 Ascending and descending fiber tracts. |
front 25 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain What are the 2 functions of trigeminal nerves (V)? | back 25 1. Involved in chewing 2. Involved in sensations of the head and face |
front 26 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Abducens nerves (VI) do what to the eye? | back 26 Abduct the eye |
front 27 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Facial nerves (VII) are involved in what 3 functions? | back 27 1. Taste sensation 2. Gland function (i.e. salivary and lacrimal glands) 3. Facial expression |
front 28 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Vestibulocochlear nerves (VIII) are involved in what 2 functions? | back 28 1. Hearing 2. equilibrium |
front 29 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Vestibulocochlear nerves (VIII) are mostly what type of nerves? | back 29 Sensory nerves |
front 30 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Glossopharyngeal nerves (IX) contain ____ fibers that innervate throat structures and sensory fibers that transmit ____ stimuli. | back 30 Motor fibers that innervate throat structures and sensory fibers that transmit taste stimuli. |
front 31 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Vagus nerves (X) serve what 3 body parts? | back 31 1. head 2. thorax 3. abdominal cavity |
front 32 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Accesssory nerves (XI) serve muscles of what 3 body parts? | back 32 1. Neck 2. Larynx 3. Shoulders |
front 33 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Hypoglossal nerves (XII) stimulate muscles of what 2 body parts? | back 33 1. tongue muscles 2. neck muscles |
front 34 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain How does the depth of the fissures in the sheep's cerebral hemispheres compare to that in the human brain? | back 34 Sheep brain has less deep fissures. |
front 35 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain How does the cerebellum of the sheep and human differ? | back 35 The sheep's cerebellum is not divided longitudinally. |
front 36 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain What dural fold is missing in the sheep brain that is present in humans? | back 36 The falx cerebelli is missing in sheep brains, because in humans, this structure separates the cerebellar hemispheres. |
front 37 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain In the sheep brain, what connects the cerebellum to the medulla? | back 37 The inferior cerebellar peduncles. |
front 38 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain In the sheep brain, what connects the cerebellum to the pons? | back 38 The middle cerebellar peduncles. |
front 39 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain In the sheep brain, what connects the cerebellum to the midbrain? | back 39 The superior cerebellar peduncles. |
front 40 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain What is the function of the corpora quadrigemina? | back 40 Act as reflex centers for vision and hearing. |
front 41 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain In both brains, what is the thin nervous tissue membrane that is ventral to the corpus callosum and separates the lateral ventricles? | back 41 Septum pellucidum |
front 42 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain How does the size of the fornix in the sheep brain compare with the human fornix? | back 42 The sheep fornix is larger. |
front 43 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain Why is the sheep fornix larger than the human fornix? | back 43 The fornix in sheeps is involved in the memory of smell, a sense that is more important in sheeps. |
front 44 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain In both brains, what forms the floor of the third ventricle? | back 44 The hypothalamus |
front 45 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain In both brains, what forms the anterior walls of the fourth ventricle? | back 45 Cerebral peduncles |
front 46 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain T/F. In both brains, the medulla oblongata continues into the spinal cord without any obvious anatomical change. | back 46 True. |
front 47 Sheep Brain vs Human Brain In both brains, when does the spinal cord begin? | back 47 When the fourth ventricle narrows to a small canal. |
front 48 What is the origin of the olfactory nerve (I) | back 48 Olfactory epithelium |
front 49 The olfactory nerve (I) is purely what type of nerve? | back 49 Purely sensory nerve |
front 50 What is the function of the olfactory nerve (I)? | back 50 Carries afferent impulses associated with smell |
front 51 What is the origin of the optic nerve (II)? | back 51 Retina of eye |
front 52 What type of nerve is the optic nerve (II)? | back 52 Purely sensory nerve |
front 53 What is the function of the optic nerve (II)? | back 53 Carries afferent impulses associated with vision. |
front 54 What is the origin of the oculomotor nerve (III)? | back 54 Midbrain |
front 55 What type of nerve is the oculomotor nerve (III)? | back 55 Primarily motor nerve |
front 56 What is the function of the oculomotor nerve (III)? | back 56 Carries somatic motor fibers to inferior oblique and superior, inferior, and medial rectus muscles to direct eyeball. |
front 57 What is the origin of the trochlear nerve (IV)? | back 57 Midbrain |
front 58 What type of nerve is the trochlear nerve (IV)? | back 58 Primarily motor |
front 59 What is the function of the trochlear nerve (IV)? | back 59 Provides somatic fibers to superior oblique muscle that moves the eyeball. |
front 60 What is the origin of the trigeminal nerve (V)? | back 60 From the face |
front 61 What type of nerve is the trigeminal nerve (V)? | back 61 Mixed nerve |
front 62 What are the 2 functions (sensory and motor) of the trigeminal nerve (V)? | back 62 1. Sensory fibers conduct sensory impulses from skin of face 2. Motor fibers innervate muscles of mastication |
front 63 What is the origin of the abducens nerve (VI)? | back 63 Pons |
front 64 What type of nerve is the abducens nerve (VI)? | back 64 Primarily motor nerve |
front 65 What is the function of the abducens nerve (VI)? | back 65 Carries somatic motor fibers to lateral rectus muscle that abducts the eyeball |
front 66 What is the origin of the facial nerve (VII)? | back 66 Pons |
front 67 What type of nerve is the facial nerve (VII)? | back 67 Mixed nerve |
front 68 What are the 2 functions (motor and sensory) of the facial nerve (VII)? | back 68 1. Supplies motor fibers to muscles of facial expression 2. Carries sensory fibers from taste receptors to tongue |
front 69 What is the origin of the vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)? | back 69 Inner ear equilibrium and hearing apparatus |
front 70 What type of nerve is the vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)? | back 70 Mostly sensory nerve |
front 71 What is the 2 functions (vestibular and cochlear branches) of the vestibulochochlear nerve (VIII)? | back 71 1. Vestibular branch transmits impulses associated with sense of equilibrium 2. Cochlear branch transmits impulses associated with hearing |
front 72 What is the origin of the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)? | back 72 Medulla oblongata |
front 73 What type of nerve is the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)? | back 73 Mixed nerve |
front 74 What are the 2 functions (motor and sensory) of the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)? | back 74 1. Somatic fibers serve pharyngeal muscles 2. Sensory fibers carry impulses from pharynx |
front 75 What is the origin of the vagus nerve (X)? | back 75 Medulla oblongata |
front 76 What type of nerve is the vagus nerve (X)? | back 76 Mixed nerve |
front 77 What are the 2 functions (motor and sensory) of the vagus nerve (X)? | back 77 1. Somatic motor fibers carry impulses to pharynx and larynx 2. Transmits sensory impulses from viscera |
front 78 What is the origin of the accessory nerve (XI)? | back 78 Medulla oblongata |
front 79 What type of nerve is the accessory nerve (XI) but what is it primarily in function? | back 79 Mixed nerve but primarily motor in function |
front 80 What are the function of the accessory nerve (XI)? | back 80 Provides somatic motor fibers to sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. |
front 81 What is the origin of the hypoglossal nerve (XII)? | back 81 Medulla oblongata |
front 82 What type of nerve is the hypoglossal nerve (XII) but what is it primarily in function? | back 82 Mixed nerve but primarily motor in function |
front 83 What is the function of the hypoglossal nerve (XII)? | back 83 Carries somatic motor fibers to tongue muscles |
front 84 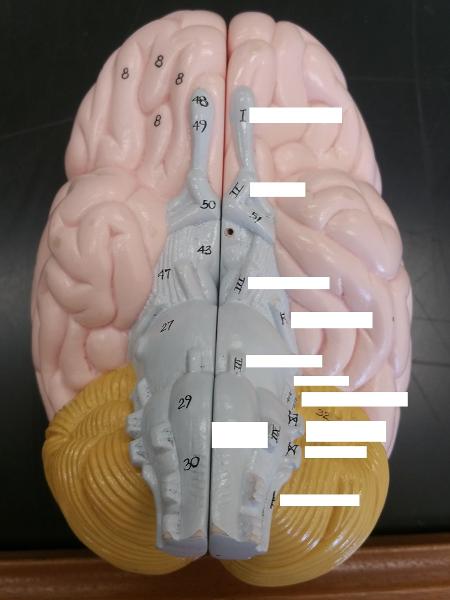 Identify the blanks. | back 84 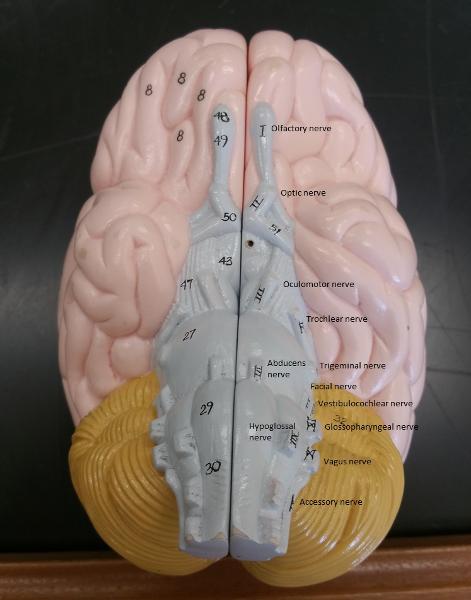 |
front 85 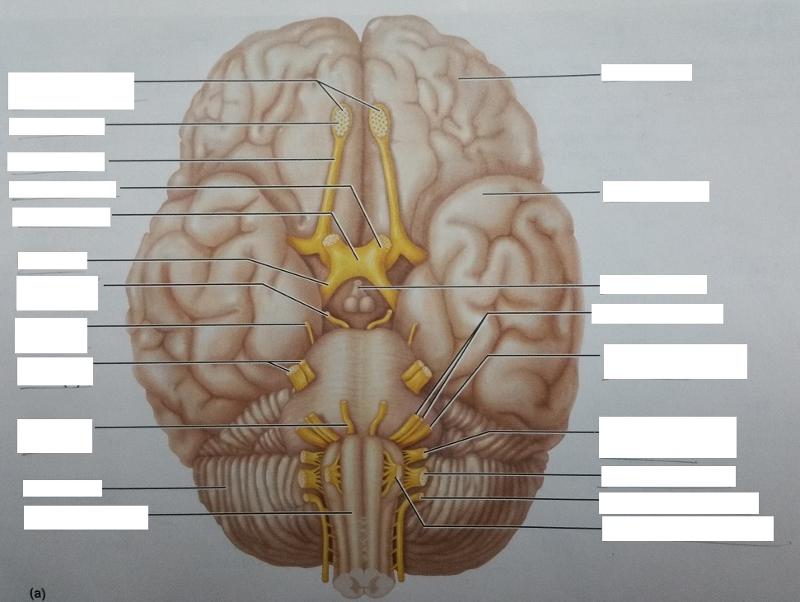 Identify the blanks. | back 85 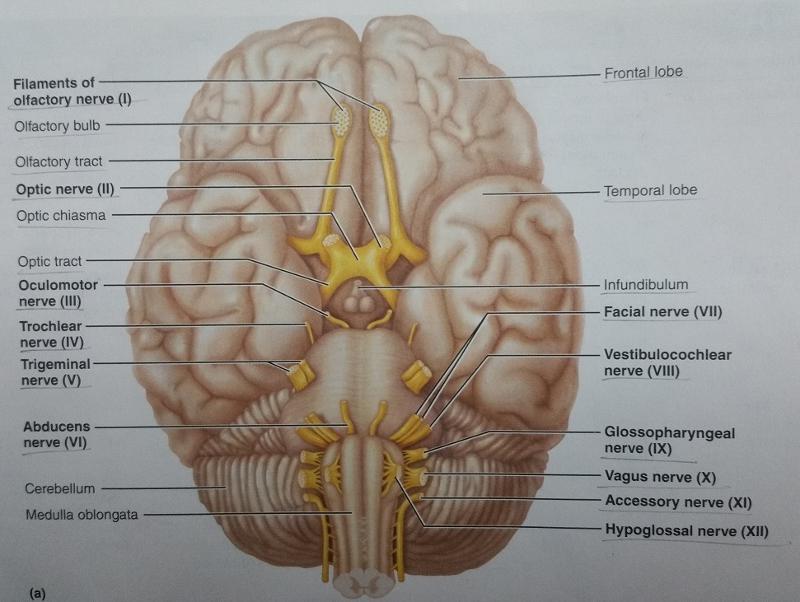 |