Instructions for Side by Side Printing
- Print the notecards
- Fold each page in half along the solid vertical line
- Cut out the notecards by cutting along each horizontal dotted line
- Optional: Glue, tape or staple the ends of each notecard together
bio 2
front 1 Which one of the following is an adaptation by plants to life on land?
| back 1 C |
front 2 Which of the following was an essential adaptive feature for the evolution of plants from water to the land?
| back 2 A |
front 3 Given that early land plants most likely share a common ancestor with green algae, the earliest land plants were most likely
| back 3 A |
front 4 The architecture and distribution of the root system and production of proteins in plants are directly relevant to the availability ________ in soil.
| back 4 B |
front 5 The symplast is the continuum of cytosol connected by
| back 5 C |
front 6 Which of the following determines the direction of water movement across the membrane?
| back 6 B |
front 7 Plants do not have a circulatory system like that of some animals. If a water molecule did "circulate" (that is, go from one point in a plant to another and back in the same day), it would require the activity of
| back 7 D |
front 8 Plasmodesmata can change in number, and when dilated can provide a passageway for
| back 8 A |
front 9 Typically, on average, what percentage of a plant's fresh biomass is water?
| back 9 C |
front 10 Which of the following would be least likely to affect osmosis in plants?
| back 10 C |
front 11 The movement of water across biological membranes can best be predicted by
| back 11 D |
front 12 An open beaker of pure water has a water potential (Ψ) of
| back 12 D |
front 13 ) If ΨP = 0.3 MPa and ΨS = -0.45 MPa, the resulting Ψ is
| back 13 C |
front 14 The value for Ψ in root tissue was found to be -0.15 MPa. If you take the root tissue and place it in a 0.1 M solution of sucrose (Ψ = -0.23 MPa), the net water flow would
| back 14 A |
front 15 Compared to a cell with few aquaporins in its membrane, a cell containing many aquaporins will
| back 15 A |
front 16 Water flows into the source end of a sieve tube because
| back 16 B |
front 17 What is the role of proton pumps in root hair cells?
| back 17 B |
front 18 One would expect to find the highest density of aquaporins in which of the following?
| back 18 A |
front 19 If isolated plant cells with a water potential averaging -0.5 MPa are placed into a solution with a water potential of -0.3 MPa, which of the following would be the most likely outcome?
| back 19 A |
front 20 Guard cells do which of the following?
| back 20 D |
front 21 Photosynthesis begins to decline when leaves wilt because
| back 21 D |
front 22 The opening of stomata is thought to involve
| back 22 A |
front 23 The following factors may sometimes play a role in the movement of sap through xylem. Which one depends on the direct expenditure of ATP by the plant?
| back 23 D |
front 24 In which plant cell or tissue would the pressure component of water potential most often be negative?
| back 24 B |
front 25 Water potential is generally most negative in which of the following parts of a plant?
| back 25 A |
front 26 Which of the following has the lowest (most negative) water potential?
| back 26 D |
front 27 Active transport would be least important in the normal functioning of which of the following plant tissue types?
| back 27 B |
front 28 Which of the following essential nutrients plays an essential role in the opening and closing of the stomatal aperture?
| back 28 D |
front 29 What is the driving force for the movement of solutes in the phloem of plants?
| back 29 B |
front 30 Which of the following is a correct statement about sugar movement in phloem?
| back 30 B |
front 31 Phloem transport is described as being from source to sink. Which of the following would most accurately complete this statement about phloem transport as applied to most plants in the late spring? Phloem transports ________ from the ________ source to the ________ sink.
| back 31 B |
front 32 Arrange the following five events in an order that explains the mass flow of materials in the phloem.
| back 32 C |
front 33 For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their relationship. (a) The average size of particles that constitute silt (b) The average size of particles that constitute clay
| back 33 A |
front 34 For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their relationship. (a) The amount of molybdenum in a gram of dried plant material (b) The amount of sulfur in a gram of dried plant material
| back 34 B |
front 35 Which of the following would be in the lowest concentration in an actively growing shoot tip?
| back 35 A |
front 36 Atmospheric nitrogen can be fixed by nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Arrange the following forms of nitrogen from the atmospheric N stage to the final form that enters the roots.
| back 36 D |
front 37 If you wanted to increase the cation exchange and water retention capacity of loamy soil, what should you do?
| back 37 B |
front 38 Several properties are characteristic of a soil in which typical plants would grow well. Of the following, which would be the least conducive to plant growth?
| back 38 C |
front 39 Why does overwatering a plant kill it?
| back 39 C |
front 40 Which of the following soil minerals is most likely leached away during a hard rain?
| back 40 D |
front 41 The NPK percentages on a package of fertilizer refer to the
| back 41 D |
front 42 Most of the dry weight of a plant is derived from
| back 42 D |
front 43 In hydroponic culture, what is the purpose of bubbling air into the solute?
| back 43 B |
front 44 which two elements make up more than 90% of the dry weight of plants?
| back 44 D |
front 45 The bulk of a plant's dry weight is derived from
| back 45 B |
front 46 Which of the following elements is required for the stability of cell walls?
| back 46 C |
front 47 Synthesis of which of the following compounds in a mature leaf would be least impacted by a temporary soil nitrogen deficiency?
| back 47 D |
front 48 What is a major function of magnesium in plants?
| back 48 C |
front 49 Copper plays a critical role in ________ of plant cells.
| back 49 B |
front 50 Reddish-purple coloring of leaves, especially along the margins of young leaves, is a typical symptom of deficiency of which element?
| back 50 D |
front 51 A corn (Zea mays) mutant is developed that is impaired in magnesium uptake. The most likely phenotypic expression would be
| back 51 A |
front 52 If an African violet has chlorosis, which of the following elements might be a useful addition to the soil?
| back 52 D |
front 53 Iron deficiency is often indicated by yellowing in newly formed leaves. This suggests that iron
| back 53 A |
front 54 Which of the following, if used as a fertilizer, would be most immediately available for plant uptake?
| back 54 D |
front 55 The enzyme complex nitrogenase catalyzes the reaction that reduces atmospheric nitrogen to
| back 55 B |
front 56 In a root nodule, the gene coding for nitrogenase
| back 56 D |
front 57 The most efficient way to increase essential amino acids in crop plants for human consumption would be to
| back 57 A |
front 58 If a plant is infected with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, what is the most probable effect on the plant?
| back 58 D |
front 59 You are weeding your garden when you accidentally expose some roots of your pea plants. You notice swellings (root nodules) on the roots and there is a reddish tinge to the ones you accidentally damaged. Most likely your pea plants
D) contain developing insect pupa | back 59 B |
front 60 Which of the following statements about nitrogen fixation in root nodules is true?
| back 60 C |
front 61 Upregulation of leghemoglobin biosynthesis in a leguminous species would most likely indicate
| back 61 B |
front 62 An example of a mutualistic association between a plant and a fungus would be
| back 62 C |
front 63 Hyphae form a covering over roots. These hyphae create a large surface area that helps to do which of the following?
| back 63 A |
front 64 Which of the following is a primary difference between ectomycorrhizae and endomycorrhizae?
| back 64 C |
front 65 The earliest vascular plants on land had underground stems (rhizomes) but no roots. Water and mineral nutrients were most likely obtained by
D) diffusion across the cuticle of the rhizome | back 65 B |
front 66 A rootless, green plant is found growing on the branches and trunks of rain forest trees, but lacks any apparent adaptation for collecting rainwater. This plant is most likely
| back 66 D |
front 67 What are epiphytes?
| back 67 D |
front 68 Carnivorous plants have evolved mechanisms that trap and digest small animals. The products of this digestion are used to supplement the plant's supply of
| back 68 C |
front 69 Rhizobia, actinomycetes, and cyanobacteria all share the common feature that they can
| back 69 D |
front 70 Why is nitrogen fixation an essential process?
| back 70 B |
front 71 In what way do nitrogen compounds differ from other minerals needed by plants?
| back 71 B |
front 72 Nitrogen fixation is a process that
| back 72 D |
front 73 Which of the following would be the most effective strategy to remove toxic heavy metals from a soil?
| back 73 C |
front 74 Which of the following plant structures shares the most common features and functions with a fungal hyphae?
| back 74 D |
front 75 A plant developed a mineral deficiency after being treated with a fungicide. What is the most probable cause of the deficiency?
| back 75 B |
front 76 Pine seedlings grown in sterile potting soil grow much slower than seedlings grown in soil from the area where the seeds were collected. This is most likely because
| back 76 D |
front 77 Some botanists argue that the entire plant should be considered as a single unit rather than a composite of many individual cells. Which of the following cellular structures best supports this view?
| back 77 D |
front 78 Root hairs are most important to a plant because they
| back 78 C |
front 79 A water molecule could move all the way through a plant from soil to root to leaf to air and pass through a living cell only once. This living cell would be a part of which structure?
| back 79 D |
front 80 The Casparian strip in plant roots is correctly described by which of the following?
| back 80 D |
front 81 What drives the flow of water through the xylem?
| back 81 C |
front 82 What is the main force by which most of the water within xylem vessels moves toward the top of a tree?
| back 82 C |
front 83 Most of the water taken up by a plant is
| back 83 C |
front 84 Which cells in a root form a protective barrier to the vascular system where all materials must move through the symplast?
| back 84 D |
front 85 The water lost during transpiration is a side effect of the plant's exchange of gases. However, the plant derives some benefit from this water loss in the form of
| back 85 D |
front 86 Ignoring all other factors, what kind of day would result in the fastest delivery of water and minerals to the leaves of a tree?
| back 86 B |
front 87 Which of the following experimental procedures would most likely reduce transpiration while allowing the normal growth of a plant?
| back 87 B |
front 88 As a biologist, it is your job to look for plants that have evolved structures with a selective advantage in dry, hot conditions. Which of the following adaptations would be least likely to meet your objective?
| back 88 D |
front 89 Most of the dry weight of a plant is the result of uptake of
| back 89 C |
front 90 Which of the following elemental ions plays a critical role in opening and closing of stomata?
| back 90 B |
front 91 According to the pressure flow hypothesis of phloem transport,
D) the formation of starch from sugar in the sink increases the osmotic concentration | back 91 A |
front 92 If you were to prune the shoot tips of a plant, what would be the effect on the plant and the leaf area index?
| back 92 D |
front 93 One is most likely to see guttation in small plants when the
| back 93 B |
front 94 A young farmer purchases some land in a relatively arid area and is interested in earning a reasonable profit for many years. Which of the following strategies would best allow the farmer to achieve such a goal?
| back 94 D |
front 95 Which of the following is of least concern to a researcher in a mineral nutrition experiment?
| back 95 C |
front 96 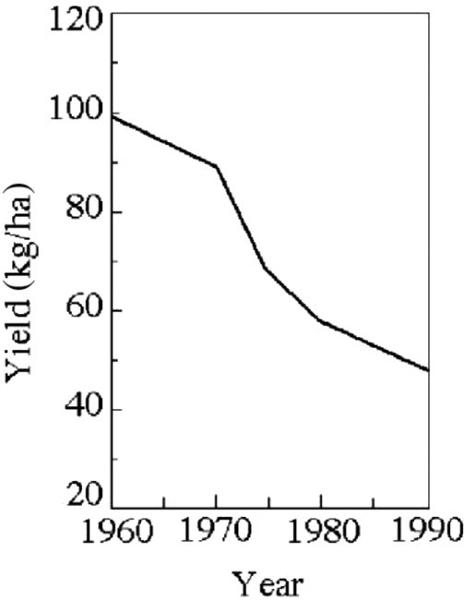 Based on the information provided in Figure 29.1, what is the most likely cause of the decline in productivity?
| back 96 D |
front 97 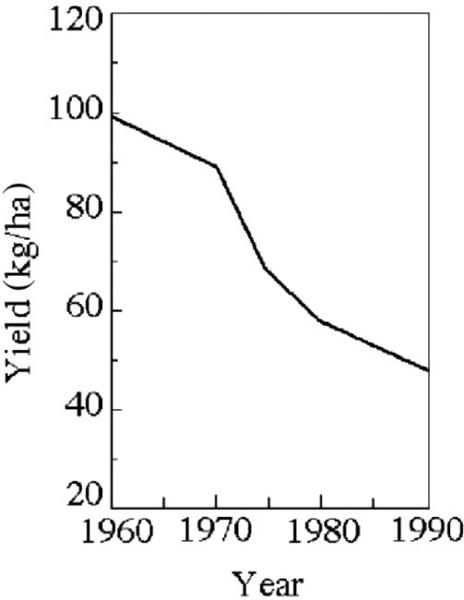 If you were the county agriculture agent, what would be the best advice you could give the farmer who owns the field under study in Figure 29.1?
| back 97 A |
front 98 You are conducting an experiment on plant growth. You take a plant fresh from the soil that weighs 5 kg. Then you dry the plant overnight and determine the dry weight to be 1 kg. Of this dry weight, how much would you expect to be made up of organic molecules?
| back 98 D |
front 99 Ten tomato plants are germinated and maintained in a large tray with no drainage. After several weeks they all begin to wilt and die despite repeated watering and fertilization. The most likely cause of this die-off is
| back 99 B |
front 100 A greenhouse experiment to test growth rates in tomato cultivars was conducted using sterile soil mix and watering with sterile solutions of water and fertilizer. Following germination, half of the plants in each group were transplanted into soil that was obtained from a nearby agricultural field (nonsterile) and the other half into sterile soil. After several weeks the plants that were transplanted into nonsterile soil exhibited a much higher growth rate compared to the plants transplanted into sterile soil. The most likely explanation for this result is
| back 100 A |
front 101 Several tomato plants are growing in a small garden plot. If soil water potential were to drop significantly on a hot summer afternoon, which of the following would most likely occur?
| back 101 A |
front 102 A fellow student brought in a leaf to be examined. The leaf was dark green and thin, had stoma on the lower surface only, and had a total surface area of 10 square meters. What is the most likely environment where this leaf was growing?
| back 102 C |
front 103 Plants produce storage products in the form of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Which one of the following is the backbone element in all these stored products?
| back 103 D |
front 104 Which structure or compartment is part of the symplast?
| back 104 B |
front 105 Which of the following is an adaptation that enhances the uptake of water and minerals by roots?
| back 105 A |
front 106 Movement of xylem sap from roots to leaves
| back 106 B |
front 107 What would enhance water uptake by a plant cell?
| back 107 B |
front 108 A plant cell with a ΨS of -0.65 MPa maintains a constant volume when bathed in a solution that has a ΨS of -0.30 MPa and is in an open container. The cell has a
| back 108 C |
front 109 Compared with a cell with few aquaporin proteins in its membrane, a cell containing many aquaporin proteins will have a
| back 109 A |
front 110 Two groups of tomatoes were grown in the laboratory, one with humus added to the soil and the other a control without humus. The leaves of the plants grown without humus were yellowish (less green) compared with those of the plants grown in humus-enriched soil. The best explanation for this difference is that
| back 110 C |